Hormones play a dominant role in the mechanism of egg fertilization, pregnancy and childbirth. If nature had not endowed us with these biologically active substances, humanity would not have had a single chance of reproducing its own kind. Let's find out what hormones are released during pregnancy and what normal indicators should be used to guide such a study.
To produce hormones, the body uses endocrine glands, and blood delivers specific substances to organs and systems. When talking about the quantitative indicators of certain hormones that change during different periods of a woman’s life (menstruation, pregnancy, menopause), the definition “hormonal background” is used. Taking hormone tests during pregnancy is a reliable way to prevent various abnormalities in fetal development.
Functions of hormones
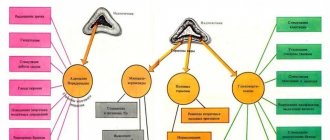
Hormones are involved in metabolism, they ensure vital processes and growth of the body. These substances are produced by glands that make up the human endocrine system. Endocrine glands are located in different parts of the body and influence different processes.
Main glands:
- The pituitary gland is located in the brain, it exercises control over other glands, pituitary hormones determine the size of a person and the intensity of growth processes;
- the thyroid gland is located in the cervical region, its hormones are involved in metabolism;
- The parathyroid glands are located near the thyroid gland, they help regulate the synthesis of calcium and phosphorus;
- The thymus or thymus gland is located in the upper part of the chest, produces thymosin, which helps in creating the immune system;
- the pancreas secretes juice to digest food, as well as insulin, which regulates carbohydrate metabolism;
- the adrenal glands produce substances that participate in metabolism and support the functionality of the nervous system; the gland also produces sex hormones;
- the pineal gland or pineal gland is located in the brain, produces melatonin, which regulates the daily routine;
- the sex glands are responsible for reproduction, their hormones develop secondary sexual characteristics (in girls, the shape of the skeleton and pelvis changes, the mammary glands enlarge, the figure is outlined, pubic and armpit hair appears, menstruation occurs, reproductive function is established).
Why you need to check your hormonal levels
Hormones are involved in all basic processes of the body: growth, development, metabolism, reproduction. For the body to function properly, the ratio of hormones must correspond to the gender and age of the person. There are standards for each hormone and each individual category of people.
Each indicator is important for a pregnant woman. Any changes in the analyzes reflect the process of fetal development. That is why hormones are monitored regularly by a doctor. Various methods are used to study hormonal levels.
Perinatal screening is mandatory - a group of studies that help determine the risk of developing defects in the fetus. Doctors recommend being screened at least twice. In the first trimester, studies are carried out at 11-12 weeks. In the second trimester, 16-19 weeks are appropriate.
In women, hormonal levels change after puberty, at the time of conception, and during menopause. A routine laboratory blood test can identify many diseases and even determine the location and nature of abnormalities. A blood test for hormones is an important part of the examination of a pregnant woman. Based on their results, the gynecologist can assess the condition of the mother and child and draw up the correct treatment plan.
What may deviations from the norm indicate?
Low levels of progesterone can indicate certain disorders, namely the threat of miscarriage, non-developing pregnancy, and delayed fetal formation. In addition, a low level of the hormone also indicates a post-term pregnancy, complications such as: gestosis, fetoplacental insufficiency, and may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
The use of hormonal agents and certain medications can significantly affect the results of the analysis. It would be appropriate to consult your doctor in these cases. A pregnant woman should know that a progesterone test is very important for identifying disorders in a woman’s body and preventing their development. Based on this, in the second and third trimesters it is necessary to donate blood for progesterone. You cannot interpret the results of the analysis yourself; only the doctor will make a conclusion after conducting additional research.
What tests are done for hormones during pregnancy?
Because the chemical composition of hormones varies, there are different ways to study blood. During pregnancy, tests for pituitary hormones may be necessary:
- prolactin;
- follicle-stimulating hormone;
- luteinizing hormone;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Tests for sex hormones:
- estradiol;
- estriol;
- testosterone.
Analysis for adrenal hormones:
- cortisol;
- progesterone;
- adrenocorticotropic hormone;
- DHEA sulfate.
Test for thyroid hormones:
- thyroid stimulating (TSH);
- triiodothyronine (T3);
- triiodothyronine (free T3);
- thyroxine (T4);
- free thyroxine (free T4).
Antibody test:
- thyroglobulin;
- thyroid peroxidase.
These hormones are studied as part of perinatal screening in the first and second trimesters. In the first trimester, PAPP-A and beta-hCG levels are measured. In the second, AFP, E3 and hCG hormones are examined. Control of 17-ketosteroids and 17-hydroxyprogesterone, as well as globulin, which binds sex hormones, is also necessary. At the same time, tests are carried out for hormones of the reproductive system (testosterone, estradiol) and the adrenal gland substance cortisol.
Hormones that are responsible for the normal course of pregnancy
Both after natural conception and after IVF, every woman should be under medical supervision. This is necessary to preserve the fetus
It is important to get tested regularly to monitor the health of the woman and child.
This appendage of the brain is located in the area of the sella turcica (bone pocket of the skull). The pituitary gland produces hormones that are responsible not only for reproductive function, but also for the growth of the body, as well as for the metabolic processes that occur in it. These are hormones that significantly affect pregnancy.
At the same time, the production of releasing hormones stops. This is necessary for a woman to stop menstruating. The level of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone decreases, which makes it possible to suppress the growth of ovarian follicles and stop ovulation. These changes are normal. If they do not occur, then the likelihood of miscarriage increases.
Progesterone is primarily responsible for maintaining pregnancy.
Estrogens
All changes that occur in the female body during gestation occur under the influence of three estrogens, which are produced by the placenta, ovarian follicles and adrenal cortex. These are types of hormones such as:
- estriol;
- estrone;
- estradiol
Pay attention to the hormone analysis for pregnant women. In this analysis, the reference (normal) values of progesterone and estradiol during pregnancy by trimester are indicated on the right
Estrogens are necessary in order to regulate metabolic processes, stimulate the growth of the uterus, and provide normal living conditions for the fetus. Hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and human chorionic gonadotropin are also of great importance for the mother.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Closer to the 10th week of pregnancy, the placenta begins to intensively produce hormones. The hCG hormone is produced by the fetal membrane (chorion). Secretion begins immediately after the embryo attaches to the inner layer of the uterus. HCG is one of the most important hormones for humans, especially for maintaining pregnancy. This hormone controls the production of other substances necessary for pregnancy - progesterone and estrogen.
During a healthy pregnancy, hCG levels constantly rise. By 10-11 weeks, the concentration of the hormone in the blood decreases and does not change until childbirth. If there is a lack of hCG, a miscarriage occurs: progesterone does not adequately prepare the endometrium, the egg does not hold and leaves the uterus, and menstruation occurs.
It is the hCG hormone that confirms pregnancy. A simple test detects the hormone in the urine by 5-6 days after conception, but a blood test is more reliable. The hCG level makes it possible to calculate the period when a woman cannot accurately determine the day of conception.
HCG levels reflect the condition of the fetus, so the analysis allows you to find out about complications. For each stage of pregnancy, the norm of hCG in the blood is established, which confirms the correct development of the fetus.
An abnormal increase in hCG may indicate multiple births, diabetes mellitus, or preeclampsia (microdamage to the placenta). Sometimes an increase in hormone levels indicates developmental defects and hereditary diseases, such as Down syndrome.
A decrease in hCG occurs with an ectopic pregnancy, as well as a frozen one. This may be a manifestation of developmental delay, placental insufficiency (violation of the functionality of the placenta), spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
If your hCG level is high or low, there is no need to be alarmed. Perhaps the date of conception was entered incorrectly.
Norms
| Index | Normal values |
| hCG | for adult men and non-pregnant women - less than 5 mU/ml. |
| free β-hCG | in non-pregnant women and after menopause - 0-2 ng/ml; in men - 0-2 ng/ml. |
| free PAPP-A | range from 1.02 to 17.8 mIU/ml |
| alpha fetoprotein (AFP) | in the blood of an adult - up to 10 ng/ml or up to 8 IU/ml |
| free estriol | varies depending on the duration of pregnancy, gradually increasing from 0.45 to 40 nmol/l |
Placental hormones
Progesterone
During a certain period of the menstrual cycle, progesterone levels increase. The hormone is produced by the corpus luteum, which matures at the site of the follicle after it releases the egg on the day of ovulation.
This hormone is responsible for the readiness of the uterus for implantation and is considered essential during pregnancy. Progesterone promotes better attachment of the fertilized egg to the endometrium of the uterus. The hormone prevents miscarriage by reducing the tone of the uterus.
Without normal levels of progesterone, conception does not occur. The hormone sends signals to the central nervous system to prepare for conception. It preserves pregnancy and creates the necessary conditions for bearing and feeding a child. Progesterone also worries about a woman’s psychological state. It calms the pregnant woman, creates affection and love for the fetus.
On the other hand, progesterone affects the psyche, making a woman irritable and depressed. The hormone also retains salts and liquid, causes headaches, drowsiness, nausea, and increases urination. Thanks to progesterone, the mammary glands swell and hurt.
The concentration of progesterone doubles by 8 weeks, and increases gradually by 38 weeks. In the first trimester, the norm is 9 nmol/l and increases to 770 nmol/l by the third trimester.
Lack of progesterone is associated with pregnancy complications. It is possible to replenish hormone reserves with medication. Otherwise, the pregnancy ends in miscarriage or underdevelopment.
Placental lactogen
The level of placental lactogen determines the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. The hormone is secreted by the placenta. It is present in a woman’s blood from 5-6 weeks. Normally, the maximum placental lactone in the blood is observed at 37-38 weeks. After this period, the hormone level drops.
Studying the level of placental lactogen is aimed at assessing the condition of the placenta. The analysis allows for timely diagnosis of deficiency. A sharp decrease in the hormone by two times or more (compared to normal levels on a certain day of pregnancy) may indicate a delay in the development of the child. A decrease in the level of placental lactogen by 80% can lead to fetal death. The doctor must notice the decline in time to urgently prevent the reduction of the hormone.
The norm of placental lactogen is 0.05 mg/l in the early stages, increasing to 11.7 by 40 weeks. A lactogen test is performed if there are two history of miscarriages.
Estrogens
Estrogen levels are important during pregnancy. The hormone supports labor activity and helps the uterus grow. Estrogen also normalizes blood pressure, removes fluid, and relaxes blood vessels. Estrogens are produced by the baby's placenta and adrenal glands.
Free estriol improves blood circulation in the vessels of the uterus. The hormone affects the mammary glands and helps the body adapt to feeding the baby. Analysis for free estriol reveals fetoplacental insufficiency (impaired blood supply to the placenta), developmental delay, post-term pregnancy. At 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, the estriol norm is 0.6-2.5 nmol/l. By week 40, the hormone level rises to 111 nmol/l.
Testosterone
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of the hormone that underlies sex differences and is male. In women it is found in small quantities. Testosterone determines the libido and sexual activity of men, being responsible for their sexual activity. Controlling normal hormone levels in the body is the primary task of every representative of the stronger half.
To do this, you need to know what the norm looks like, ensuring the smooth functioning of the body. The generally accepted indicators are 11-32 nmol/l, when they decrease, it is necessary to actively increase them.
A decrease in the hormone provokes:
- erectile dysfunction;
- reduction in weight and strength;
- irritability;
- baldness;
- obesity;
- breast enlargement.
To avoid this, appropriate tests must be taken and the body's production of testosterone must constantly increase.
Ovarian hormones
In normal times, estradiol (estrogen) is produced by the ovaries and, after conception, also by the placenta. It supports the normal course of pregnancy, so its level is constantly increasing. First, an estradiol test can tell you about the condition of the placenta. A decrease in estradiol in the early stages may indicate a risk of pregnancy termination.
In the first week the norm is 800-1400 pmol/l, and in the last week 57100-99100 pmol/l. Immediately before birth, estradiol levels increase to the maximum. It is he who needs to be thanked for relieving pain during childbirth, since estradiol is a natural pain reliever.
At the psychological level, estradiol is responsible for readiness for the birth of a baby. The hormone affects the woman, and she begins to buy things, arrange the room and prepare for the birth of the child.
If you have a history of miscarriages, you need to monitor progesterone and estradiol both before and after conception. It is necessary to monitor the state of hormonal levels during preparation for fertilization, as it affects implantation and development of the fetus.
Prolactin
Exceeding the norm during pregnancy, it actively maintains the amount of progesterone. This contributes to the preservation of the fetus and its normal development. Three fractions of prolactin can be found in the female body:
- three-dimensional;
- two-dimensional;
- monomeric.
The most active of them is the last type, it contains about 80%. With the proper amount of prolactin, a woman is able to conceive, bear and feed a baby. In men, this hormone affects sexual function and sperm formation.
Various factors associated with stressful situations, as well as the use of certain contraceptive and psychotropic drugs, lead to its increase.
The main reasons for increased prolactin are:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver failure;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- oncological problems;
- abortion;
- breast surgery;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- increase in sugar;
- tuberculosis.
Excess weight, mastopathy, menstruation irregularities and infertility are a signal to conduct tests for prolactin levels. In men, a lack of the hormone is signaled by decreased libido, infertility, impotence, and low sperm count.
Adrenal hormones
Pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the production of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids by the adrenal glands. Under stress, ACTH levels increase and the secretion of adrenal hormones increases. Pregnancy is such a stress.
Effect of adrenal hormones:
- suppression of immunity, prevention of fetal rejection;
- regulation of water-salt balance through salt and fluid retention;
- weakening of hair;
- formations of stretch marks (stretch marks);
- skin hyperpigmentation;
- strong hair growth.
Thyroid hormones
During pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the functionality of the thyroid gland. Insufficiency and excessive production of hormones by this organ can cause malformations in the fetus. The condition of the thyroid gland can be assessed using thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
An analysis of hormones during pregnancy of this gland is prescribed to those patients who have a history of problems with the organ. Indications may include severe fatigue, drowsiness, problems with hair, skin and nails, low blood pressure, swelling and sudden weight gain. All these signs may indicate thyroid dysfunction.
During pregnancy, a deficiency is often diagnosed, although an excess of thyroid hormones is also possible (hyperthyroidism). An excess is dangerous due to premature birth. Advanced hypothyroidism (lack of hormones) leads to fetal death in the womb and mental retardation.
The following hormones need to be examined:
- thyroid-stimulating (TSH), which stimulates the secretion of thyroid hormones (the norm is 0.4-4.0 mU/l, in pregnant women the norm is 0.4-2.0 mU/l);
- free thyroxine (free T4), which accelerates metabolism (normal 9-22 pmol/l, during pregnancy 8-21 pmol/l);
- triiodothyronine (free T3), which also accelerates metabolism, but is more active (the norm is 2.6-5.7 pmol/l, during pregnancy the values remain normal).
Sometimes the endocrinologist also prescribes testing for antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG) and thyroid peroxidase (AT-TPO) - proteins that appear in the blood when the gland is inflamed.
When necessary
Disturbances in hormone production in pregnant women rarely occur after conception. As a rule, a similar problem already exists in the body.
Pregnant women are prescribed medications to reduce the amount of progesterone in the blood. The pathology entails improper formation of the corpus luteum, and, consequently, pathologies in the further development of the baby.
The main causes of progesterone deficiency are:
- excessive physical activity;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes;
- poor nutrition and low-calorie diets.
If women have repeatedly experienced miscarriages or fading, appropriate hormonal therapy is prescribed without fail.
Some expectant mothers need products to support the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Pituitary hormones
Hormones from the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland located in the brain, also participate in the process of fetal growth. During childbirth, the uterus contracts under the influence of oxytocin. Postpartum lactation is carried out thanks to prolactin. Lack of prolactin reduces the amount of breast milk.
Oxytocin and prolactin are the so-called motherhood hormones. They help a woman feel love for her child, feel like a mother and enjoy feeding. These hormones tell a woman how to behave and how to set priorities. Nature, through hormones, forces a woman, like any female on the planet, to love and protect her child. In this way, the continuation of the species and the preservation of each population are carried out.
A woman’s desire to be close to her child and protect him depends on the concentration of maternal hormones. The concentration of maternal hormones changes gradually so that the woman’s psyche can prepare for the birth of the baby.
Possible complications
Like any medicine, hormonal medications can negatively affect the human body. During gestation, the following complications may occur during therapy:
- increased manifestations of early toxicosis;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- decrease in blood pressure in the vessels;
- the appearance of anxiety, psycho-emotional stress;
- changes in the nature of the heart rhythm;
- increased concentration of white blood cells;
- reducing the amount of calcium ions in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the visual apparatus.
This is a serious therapy that requires close medical supervision.
Only a doctor can determine the required dosage and duration of treatment.
If there is a need to take them, then you should not neglect it.
Possible risks of hormonal imbalance during pregnancy carry a poor prognosis.
Preparation for analyzes and recommendations
The hormonal system reacts acutely to external stimuli and internal changes. Therefore, a blood test for hormones during pregnancy is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. A few days before the procedure, you need to refrain from physical and emotional stress, eliminate alcohol and cigarettes.
It must be remembered that hormonal levels primarily depend on a woman’s mood. Its importance for the development of a healthy pregnancy is great, but almost any hormone can be replenished with medication. Therefore, do not panic if the analysis shows an excess or lack of the active substance.
The intensity of positive as well as negative effects from the growth of hormones during pregnancy depends on many factors: heredity, health status, mood, individual characteristics.
Reasons for getting tested
Not all couples are given a blood test for hormones when planning a pregnancy: this only happens in certain cases that pose a problem. This may apply to both unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child and to carrying a child during previous pregnancies. Most often, examination is offered when:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- signs of hyperandrogenism are observed: excessive obesity, severe acne, increased hair growth;
- available - problematic conception: pregnancy does not occur with active sexual activity for a whole year;
- previous pregnancies were unfavorable, which resulted in consequences such as fetal death or miscarriage;
- The woman is over 35 years old.
Any of the above reasons is a reason to undergo a number of additional examinations. An endocrinologist will advise which hormone tests and when to take them when planning a pregnancy: it is best to do this about six months before the expected date of conception of the baby. In this case, it will be possible to identify the problem and begin to completely eliminate it. Blood from a vein and a urine test will show whether everything is in order with the hormonal background of the future parents and whether they are ready for the birth of a new life.