Elevated thyroid hormone indicates a malfunction of the endocrine organ, and any deviation in one direction or another provokes disharmony in the body.
The main function of the thyroid gland is to maintain stability within the body. When the production of hormones increases, disorders of various systems begin.
The rhythm of thermoregulation and metabolism is disrupted, problems with blood vessels and the heart begin, and a disorder of the nervous system appears. The list of problems may be longer.
Functions and role of the hormone TSH in the body of women
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is an active substance produced by the brain. It controls the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and supports metabolism.
An elevated TSH level indicates a decrease in the amount of thyroid hormones (triiodothyronine and thyroxine). Thyrotropin stimulates the organ to produce more active substances. Elevated hormone levels, on the contrary, reduce the effect of TSH on the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Thyrotropin supports the following body functions:
- protein synthesis;
- vitamin A production;
- control of motility in the gastrointestinal tract;
- functioning of the central nervous system, its growth and development;
- supporting energy balance in the female body;
- the entry of iodine into the thyroid gland from blood cells;
- accelerated production of phospholipids and nucleic acids.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone takes an active part in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and affects the menstrual cycle. Specific nuclei of the hypothalamus (neurosecretory) are responsible for its production. They control the level of hormones in the blood. If necessary, active substances are released to stimulate or slow down the process of thyroid-stimulating hormone production.
Symptoms
The manifestations caused by excess hormone levels will depend on the disease that caused it. With goiter (diffuse or nodular toxic), the thyroid gland enlarges, exophthalmos (bulging eyes) appears. If a person has elevated thyroid hormone, then this condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- feeling of hunger, in some cases - refusal of food;
- diarrhea mixed with blood;
- loss of body weight;
- abdominal pain;
- increased arousal, feeling of anxiety;
- worsening sleep, trembling hands;
- disturbances of the menstrual cycle (possible development of amenorrhea), in men - decreased potency;
- the appearance of shortness of breath, fatigue;
- low-grade fever;
- inability to bear a child;
- heart failure, tachycardia;
- memory impairment;
- decreased response;
- increased sweating;
- thinning hair and nails, rapid aging of the body;
- arterial hypertension.
An increased level of thyroid hormones leads to protrusion of the eyes, a feeling of dryness and pain in the eyeball, and blurred vision. In old age, such symptoms may not be present, which corresponds to latent hyperthyroidism. Depression, drowsiness, rapid fatigue, and disorders of the cardiovascular system become more typical.
Hyperthyroid crisis occurs as a complication as a result of improper or insufficient treatment of high levels of thyroid hormones. Its appearance is possible as a result of stress, mechanical intervention (examination, surgery).
Symptoms may get worse. Delirium and hallucinations develop, a sharp drop in blood pressure, and trembling in the body. The temperature rises to 41 degrees, diarrhea and vomiting occur, and the urine smells of acetone.
As a result of liver damage, jaundice and the development of adrenal insufficiency may occur. In the absence of timely medical care, a crisis can turn into a coma and lead to death.
Norm TSH in women by age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There is a certain norm for the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood of women, depending on their age or position:
| Age | TSH level (mU/l) |
| Newborns | 1,1-17,0 |
| 5-14 years | 0,4-5,0 |
| 14-25 years old | 0,6-4,5 |
| 25-60 years | 0,4-4,0 |
| From 60 years old | 0,5-8,0 |
| Pregnancy planning period | 2,5 |
| Carrying a baby | 0,2-3,5 |
During pregnancy, TSH levels change due to increased functioning of the thyroid gland. Thyroxine takes part in the physiological development of organs and systems of the fetus.
The level of thyroid-stimulating hormone changes throughout the entire period of gestation:
| Pregnancy | Thyrotropin level (mU/l) |
| 1st trimester | 0,3-2,5 |
| 2nd trimester | 0,5-4,6 |
| 3rd trimester | 0,8-5,2 |
Day and night, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the human body also changes. The maximum concentration is observed between 2 and 4 am. Lows at 6 p.m. TSH levels in women are influenced by bad habits, physical activity, and emotional changes.
Features of taking analysis
On the eve of the procedure, there is no need to fast or limit any activity, but it is important to remain calm and limit stress. Although this test does not require any special preparation, some medications may affect the test results, so your doctor should be aware of the medications you are taking.
It is especially important to notify about the intake of radioactive substances or exposure to X-rays over the past two weeks - this will ensure more accurate analysis results, which can be affected by existing acute or chronic diseases, therefore, when assessing the indicators, the doctor must take into account the presence of pathologies.
Blood is collected using a special lancet - for this, a small puncture is made on the skin of the finger. For a full-fledged study, a few drops of biomaterial are enough: the blood is placed in special containers and sent for analysis.
It is important to note that a blood test for TSH will allow you to fully display all the internal processes of the dynamics of the endocrine system. Test results may vary from person to person
However, the limits of reference values may not be the same between different laboratories because some of them use different reagents for measurement or examine different numbers of samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of specific test results.
TSH levels should be maintained within the normal range. If thyroid-stimulating hormone is higher than normal, proper functioning of most body systems cannot be expected. Its excess will not only affect many bodily processes, but also lead to complications.
A complete blood test for the hormone TSH is one of the best screening tests for diagnosing any thyroid disorder. Thanks to the results of the procedure, the doctor will be able to correctly read indicators of the state of the endocrine system and assess the functional activity of the pituitary gland.
TSH testing is an important part of the diagnosis and treatment of any thyroid disorder. In addition to such basic indications as enlargement of the thyroid gland, monitoring the treatment of previously diagnosed hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, the analysis can also be ordered for newborns: its purpose is to check for congenital endocrine diseases
Causes of elevated TSH
Elevated TSH in women (diagnostics will help determine the reasons for changes in thyroid-stimulating hormone levels) is more often a consequence of the development of a serious disease. Rarely, pathological deviations are observed due to the influence of minor factors.
The most serious reasons for increased TSH levels in women include the following sources:
| Name | Description |
| Tumors | Malignant or benign neoplasms in the pituitary gland prevent it from functioning properly. |
| Endocrine pathologies | In most cases, hypothyroidism develops against the background of hypofunction of the thyroid gland and reduced production of T3 and T4. |
| Hashimoto's thyroiditis | The pathology is of an autoimmune nature, accompanied by a long-term inflammatory process in the thyroid gland. |
| Surgical intervention | After removal of the gallbladder and thyroid gland, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood of women increases. |
| Intoxication of the body | Pathological processes develop against the background of severe poisoning with heavy metals (lead). |
| Excess iodine | Excessive intake of this element into the human body provokes disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland. |
| Genetic factor | Lack of sensitivity of the adenohypophysis to the influence of thyroid-stimulating hormone. |
Elevated TSH in women may indicate Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.
Elevated TSH in women (the reasons are important to establish with the help of an endocrinologist and medical diagnostics in order to select the most effective treatment) is also observed as a result of a malfunction of the adrenal glands. Pathological changes occur in severe forms of late toxicosis during pregnancy.
Treatment methods
If an increased level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is detected, you must contact an endocrinologist and undergo a full examination to find out the reasons for the increase in the level - you should remember that only a specialist can prescribe treatment. Self-medication in this case is dangerous. It can cause great harm to health.
Against the background of elevated TSH levels in the body, various diseases of internal organs arise that require immediate treatment.
If we are talking about a subclinical form of hypothyroidism (there are no clinical manifestations, only changes in the blood are observed), then treatment with hormonal drugs is not carried out. Patients are monitored by an endocrinologist, the level of hormones in the blood is monitored.
Treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism includes:
- Diet;
- Use of vitamin complexes and minerals according to indications;
- Elimination of stress. The use of sedatives based on medicinal plants: valerian, motherwort.
If hypothyroidism is observed in a pregnant woman, treatment with hormones is carried out in any case, regardless of the form of the pathology.
In case of hypothyroidism manifest (detailed clinical picture), treatment is carried out with the help of synthetic thyroid hormones. Most often prescribed: Eutyroxy and L-thyroxine.
First, the minimum dosage of the drug is prescribed. A month later, a blood test for hormones is performed to monitor the therapy. Based on the results of which, the doctor decides whether to change the dosage or continue the treatment. Most often, patients require lifelong use of synthetic hormones.
If an increase in the amount of this hormone occurs against the background of iodine deficiency, then iodine-containing medications are prescribed.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed: excision of a lobe or complete removal of the thyroid gland.
Signs of increased hormone levels
Changes in thyrotropin concentration in the first days occur without obvious symptoms. The woman has no complaints, her condition is satisfactory. With a prolonged increase in TSH, the concentration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine decreases.
In this case, the following clinical signs appear:
- performance decreases, general well-being worsens, weakness appears in the body;
- it is difficult for a woman to concentrate, memory deteriorates, and the thought process slows down;
- sleep disturbance leads to increased irritability;
- apathy towards the outside world periodically appears;
- Appetite worsens, sometimes disappears completely;
- the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted, nausea, vomiting, and constipation occur.
During the examination, the endocrinologist notes noticeable pathological changes:
- the skin swells all over the body;
- body weight increases, the likelihood of obesity is high;
- body temperature is constantly low;
- the skin becomes pale.
When clinical signs appear, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to determine the cause of the pathological changes and establish an accurate diagnosis. Correctly selected treatment increases the chances of a full recovery without serious complications.
Thyrotoxic crisis
Sometimes, in severe forms of the disease, treatment is ineffective. The content of T3 and T4 in the blood sharply increases. This condition threatens the patient's life.
Sometimes occurs in newborns if the mother did not receive treatment for thyrotoxicosis during pregnancy.
Provoke a crisis
The following can lead to the occurrence of a pathological condition:
- stress:
- physical stress;
- infections;
- injuries;
- surgical treatment of thyroid diseases;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- accompanying illnesses.
Often, thyrotoxic coma occurs after the use of radioactive iodine, if it was carried out without taking into account the hormonal status.
Attention! Surgical treatment of diffuse toxic goiter or therapy with radioactive iodine - only after stabilization of the hormonal status! Otherwise, there is a risk that you will create a life-threatening situation with your own hands.
Main symptoms
The deterioration of the condition progresses rapidly.
The following clinical manifestations indicate a crisis:
- Initially, there is increased excitability, tremors of the limbs, and delirium. Then the patient becomes inhibited. Subsequently - loss of consciousness, coma.
- High tachycardia. The heart rate reaches 200 per minute.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Dyspnea.
- Fever.
- Nausea, abdominal pain.
- Sometimes jaundice develops.
If left untreated, thyrotoxic crisis is fatal. In order to establish a diagnosis, an examination is carried out.
Diagnostic measures
Helps you identify the problem:
- Hormonal study. An increase in T4 and T3, a decrease in TSH and cortisol are determined.
- Increased blood sugar.
- An ultrasound examination will reveal an enlarged gland and increased blood flow.
- Reducing cholesterol.
Treatment
Timely and correct therapy will help stabilize the patient’s condition and prevent death. If signs of a thyrotoxic crisis appear, the patient is urgently hospitalized in a hospital.
Emergency instructions:
- Reduced production of thyroid hormones: intravenous administration of sodium iodite.
- Suppression of thyroid activity (mercazolyl).
- Infusion with prednisone or hydrocortisone.
- For severe agitation, droperidol is used.
- Combating rhythm disturbances.
Plasmapheresis gives a good result: it ensures rapid removal of hormones and reduces toxic effects.
Elevated levels after thyroid removal
After removal of the thyroid gland, the synthesis of thyroid-stimulating hormones completely stops. The pituitary gland produces TSH to restore the level of iodine-containing hormones. The patient is prescribed to take medications for life. In the absence of replacement therapy, the risk of thyroid coma increases.
The complication is characterized by the following symptoms:
- cold sweat;
- loss of consciousness, drowsiness, general weakness;
- breathing becomes slow;
- muscles relax;
- memory deteriorates;
- kidney function is impaired;
- decrease in body temperature.
Against the background of hypotension, the intestines stretch. Clinical symptoms appear gradually if there is no treatment or the therapy is incorrectly selected. At risk are older women or those who have experienced menopause.
Why is the test done?
Your doctor may order this test if you have symptoms of an endocrine disorder. The most common problems are hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Read more: Symptoms of thyroid disease - how to correctly identify?
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the body produces too few hormones, resulting in a slow metabolism. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weakness, and difficulty concentrating.
Below are some of the most common causes of this condition:
- Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to attack its own thyroid cells. As a result, it cannot produce enough hormones. The condition does not always cause symptoms, so it can progress for several years before it causes noticeable damage.
- Thyroiditis is an inflammation that is often caused by a viral infection or an autoimmune disorder such as Hashimoto's disease. This condition interferes with the production of hormones and ultimately leads to hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism.
- Postpartum thyroiditis is a temporary form of thyroiditis that may develop in some women after childbirth.
- The thyroid gland uses iodine for its work. Iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism.
Read more: Hypothyroidism: diagnosis and treatment.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces excess hormones, causing the metabolism to speed up. Symptoms include increased appetite, restlessness and trouble sleeping.
Below are some of the most common reasons:
- Graves' disease is a common condition in which the organ becomes larger and significantly more productive. The condition has many of the same symptoms as hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis eventually leads to hypothyroidism, but in the short term it can also cause hyperthyroidism. This can happen when inflammation causes the thyroid gland to produce too many hormones and release them all at once.
- Too much iodine in the body can lead to hyperactivity. This usually occurs as a result of chronic use of medications that contain iodine. These are some cough syrups, as well as amiodarone, which is used to treat cardiac arrhythmias.
- Thyroid nodules are benign lumps that sometimes form in the thyroid gland. When these lumps begin to increase in size, they can become overactive.
Read more: Hyperthyroidism: diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
In what other cases is an examination prescribed?
- For male and female infertility, problems with potency.
- If the patient is undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
- For various heart problems.
- Myopathy (muscle damage).
- Hypothermia (low body temperature).
- Alopecia (baldness).
- Amenorrhea (lack of menstruation).
- Prolonged depression.
- Delayed sexual and mental development in children.
Analysis for hormone determination
Elevated TSH in women (a blood test will help determine the cause of the deviation) requires diagnostics. The examination is necessary to assess the functioning of the endocrine system, on the functioning of which the activity of the whole organism depends.
Tests also help determine the condition of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Deviation of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels from the norm indicates a malfunction in the reproductive and cardiovascular system. The results obtained will help the endocrinologist select the most effective treatment.
Rules for taking the analysis, preparation
To obtain the most accurate results, the endocrinologist recommends adhering to certain rules for preparing and donating blood.
Namely:
- the analysis is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- the day before the procedure, you should give up alcoholic beverages, smoking and physical activity;
- It is not recommended to take hormonal medications for a month before the analysis;
- a couple of days before the examination, do not take medications that contain iodine;
- Immediately before the procedure, you should rest for 20-30 minutes.
The reliability of the results will be ensured by compliance with all these simple rules.
Collection of biomaterial
Blood for research is taken from the right or left vein in the elbow area. The frequency of the procedure is determined by the attending endocrinologist, taking into account the complexity of the pathological processes.
Every year it is recommended to have a blood test for women who are at risk, especially after 50 years.
How long should I wait for research answers? Decoding the results
Only a qualified endocrinologist can establish an accurate diagnosis based on the results obtained. The normal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone depend on the age of women, so a specialist will help decipher the data.
Disease prevention
Basic instructions for the prevention of thyroid diseases:
- eat foods high in iodine; doctors recommend using iodized salt;
- do not worry about trifles, do not be nervous, avoid stressful situations;
- take vitamins;
- walk in sunny weather;
- undergo a routine examination by an endocrinologist, do preventive ultrasounds, and take hormone tests at least once a year.
source
How to bring the hormone back to normal?
Treatment for elevated thyrotropin is prescribed by an endocrinologist after a thorough medical examination and based on the diagnosis. In most cases, the cause is impaired functioning of the thyroid gland.
Considering the degree of damage by pathological processes, patients are prescribed special medications to adjust the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. If there are no serious contraindications, the use of folk remedies is allowed. It is also important to adhere to dietary nutrition and change your lifestyle.
Drug treatment
Elevated TSH in women (an endocrinologist will help determine the causes) is restored with the help of replacement medications:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Levothyroxine" | The adult dosage ranges from 12.5 to 25 mcg per day. The medicine is taken 30 minutes before meals. |
|
| "Thyreotom" | Adults are recommended to start treatment with 1 tablet. Every 2-4 weeks the dosage is increased by 1 tablet. The medicine is taken for a long time 30 minutes before meals. |
|
| "Bagotirox" | The drug is taken in the morning before meals, 30 minutes, 1 tablet. |
|
In rare situations, in the absence of positive dynamics after using medications, the patient is offered surgical intervention.
ethnoscience
There are numerous recipes from healers and healers that affect the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. But the use of traditional medicine should be discussed with an endocrinologist.
The following recipes help restore the concentration of thyrotropin:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal collection | Mix parsley, cocklebur and agrimony flowers in equal proportions. Pour 1 tbsp. from the resulting collection with hot water (200 ml). Place the resulting mass in a water bath and heat for 10-15 minutes. Cool and strain thoroughly. | Before use, the decoction should be diluted with liquid. It is recommended to take the medicine 1 tbsp. 3 r. per day. The course of therapy lasts 2-3 weeks. |
| Beet juice tincture | Mix fresh nectar (100 ml) with vodka (200 ml) and leave for 2 days. | The tincture is taken 20-30 ml 3 times a day. per day, washed down with water. The course of treatment is 14 days. |
| Herbal decoction | Mix equal amounts of chamomile, yarrow, mordovnik root, rose hips and chicory. Pour 1 tbsp. hot water, leave and strain. | It is recommended to drink the medicine 3 times a day. per day. |
Elevated TSH in women can also be reduced by tea with dandelion, chamomile, rose hips, St. John's wort or celandine. Therapy is carried out comprehensively; folk recipes alone will not help restore the functioning of the thyroid gland and eliminate the causes of pathological processes. You should not engage in self-treatment, as there is a high probability of causing serious complications.
Diet
A slight increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone can be restored with proper nutrition.
An endocrinologist recommends adding the following products to your diet:
- chicken;
- tofu;
- beans;
- whole grains, nuts, seeds can be added to salads;
- fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to eat seaweed every day; it contains iodine. Low vitamin D levels have been linked to thyroid dysfunction. It is recommended to add foods containing it to the diet or go out into the sun every morning (20-30 minutes).
Lifestyle
During treatment, it is important not only to remember the doctor’s recommendations, but also to adhere to a healthy lifestyle:
- refuse strong physical and emotional stress;
- eliminate bad habits (alcoholic drinks, cigarettes).
Regular and moderate physical activity has a positive effect on metabolism. It is enough to exercise for 30 minutes every day. They mitigate side effects due to impaired thyroid function. Helps cope with fatigue, depression and prevent weight gain. You can run or ride a bike.
Favorite activities (drawing, knitting, painting) will help reduce stress and anxiety. Emotional stress can be relieved through breathing exercises or yoga.
Calcitonin
The most important tumor marker
This hormone is produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland. Its meaning is not well understood. Calcitonin affects the exchange of calcium and phosphorus: it increases the deposition of calcium in the bones and reduces its concentration in the blood. A lack of thyroid hormone is a symptom of a mineral metabolism disorder (can lead to osteoporosis).
Calcitonin is usually produced in small quantities. An increase in its level in the blood indicates the development of medullary thyroid cancer. Determination of this hormone helps to diagnose a dangerous disease in the early stages, which increases the chances of recovery.
Consequences
Lack of medical care for elevated TSH in women leads to serious complications:
| Name | Description |
| Skin and hair | Redness and swelling of the skin occurs. In most cases, pathological processes affect the feet and legs. Hair begins to fall out, even intensive therapy does not stop this process. |
| Reproductive sphere | Against the background of a prolonged increase in TSH, a woman experiences a failure of ovulation. The egg matures, but it is not capable of fertilization. There are also no favorable conditions for artificial implantation. High levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone lead to secondary infertility. |
| Heart and blood vessels | Complications caused by elevated TSH include tachycardia (atrial fibrillation) and congestive heart failure. The heart's ability to pump enough blood decreases. The likelihood of developing thrombosis, hypoxia, blood stagnation, and atherosclerosis increases. |
| Vision | The eyes become swollen and red, and sensitivity to light increases. The vision is double, the image is blurry. Lack of therapy provokes complete loss of vision. |
| Nervous system | Constantly high levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone provoke a malfunction of the central nervous system. The woman becomes irritable, loses interest in life, and experiences frequent mood swings and depression. |
A complication of elevated TSH in women is also thyrotoxic crisis. Clinical symptoms increase (fever, rapid pulse). In such a situation, the patient needs urgent medical attention.
Treatment of hormonal imbalance is carried out exclusively by an endocrinologist. Elevated TSH in women requires properly selected therapy using synthetic drugs. It is important to identify the causes that suppress or activate the thyroid gland. Without medical care, pathological processes will progress and cause serious consequences.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Signs of a hormonal surge
Thyroid hormones increase, as a result of this process the work of all internal secretion organs is gradually disrupted. With normal functioning, the thyroid gland is characterized by harmonious functioning of the whole organism, good health in a person and an excellent appearance. If the hormone levels are increased, metabolism accelerates.
Changes occur to a person:
- changes in body temperature;
- sudden weight loss;
- tremor of the limbs;
- excessive skin moisture;
- lack of calcium, resulting in broken nails and hair;
- high blood pressure;
- uncharacteristically high heart rate;
- the appearance of goiter;
- sudden mood swings.
Elevated thyroid hormones in women lead to menstrual irregularities. Symptoms are common to all thyroid problems. Below are the same signs that appear according to an increase in any one indicator.
Enlargement of element T4
An increase in this indicator causes many different complications - acceleration of the metabolic process, sudden weight loss or gain. The changes occur due to the fact that a large amount of energy is released in the human body, which, in turn, is obtained through the breakdown of important reserves of the body.
The process of decay leads to a change in human behavior. He exhibits aggression, playfulness, and frequent mood swings. Changes in human bone tissue are often observed - they become fragile and can often be injured. There are cases of sweating, both of the whole body and of individual parts, but sweating does not depend in any way on the ambient temperature. Difficulty breathing occurs, the person begins to wheeze, and the heart rate increases sharply.
A person of any age may experience tremors in the upper or lower extremities. If a person experiences at least one of the symptoms listed above, they should immediately consult a doctor. An endocrinologist deals with issues and problems with the thyroid gland.
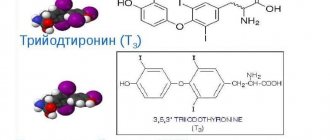
T3 element boost
T3 or triiodothyronine has a strong relationship with the human nervous system; increasing its level affects the functioning of this system. An increase in the level of a certain thyroid hormone affects the functioning of the entire body. Often, it all starts with a deterioration in overall health. Characteristic signs: weakness, fatigue,
excitability increases. These symptoms rarely cause alarm and a person ignores them, but it is worth remembering that this is only the first “call”. It doesn't need to be ignored. General health will deteriorate, weakness and fatigue will occur. Increased excitability is rarely perceived as a separate symptom, but this is a misconception.
The human heart and blood vessels are closely related to triiodothyronine. The level of this hormone increases, and the heart begins to work in an accelerated, emergency mode. This rhythm of the heart muscle does not allow the body to be sufficiently saturated with oxygen. Oxygen starvation begins, with the ensuing consequences - ailments, fatigue, weakness, muscle pain.
There is a decrease in local immunity and the patient begins to cope poorly with the viruses and infections around him, i.e. often exposed to all sorts of diseases. The lack of this hormone leads to rapid burning of fat, resulting in rapid weight loss. A person experiencing problems with a sharp jump in T3 levels may experience frequent headaches, fever, sudden changes in blood pressure, frequent urination and an overwhelming feeling of hunger.
When a person has increased T3 element in the body:
- a goiter appears;
Changes do occur, the main thing is to be attentive to your inner feelings. Otherwise, the functioning of the thyroid gland will be impaired. It is important to identify and eliminate all symptoms and the source of their occurrence in time. There is no way to deal with thyroid problems without the help of a specialist.
A table reflecting signs of an increase in the TSH element in the human body:
| System | Symptoms |
| Nervous system | Memory deterioration, depression and low mood, drowsiness, weakness, slow speech. |
| The cardiovascular system | Changes in blood pressure, sudden changes in heart rate. |
| Gastrointestinal system | Constipation or diarrhea, loss of appetite. |
| Reproductive system | Decreased libido, menstrual irregularities, infertility. |
| Appearance | Dry skin, lack of calcium. As a consequence: brittle nails and hair, swelling, increased adipose tissue, and the appearance of a goiter. |
| Feeling | Decrease in temperature. |
Reasons for increasing TSH hormone levels:
- excess or deficiency of iodine;
- diseases of the liver, lungs, kidneys, heart, etc.;
- late toxicosis, characterized by increased thyroid hormones during pregnancy;
- malignant or benign tumors;
What danger does a high TSH level pose?
If quick measures are taken to reduce thyroid-stimulating hormone to the required level, there is no threat to human health. And if you ignore the symptoms of such a problem, first of all, a person’s mood and general well-being will gradually deteriorate. Elevated TSH levels will lead to slower metabolism, weight gain, diabetes and hypertension.
Elevated levels of TSH in the blood lead to slower metabolism
Important ! Hyperthyroidism in a small percentage of cases ends in death - only in very advanced cases. The most likely threat lies in hypertension and diabetes.
Preparing for the test
Knowing what TSH is, it is very important to properly prepare to take TSH tests. Since the hormonal levels in the human body are influenced by many factors, if the recommendations are not followed, it will be impossible to understand what the results of the study indicate.
The results of the analysis are interpreted based on the fact that the patient followed certain recommendations the previous day before taking blood. The doctor giving the referral will tell you how to take the test correctly. If this has not been done, information on how to properly donate blood for a TSH test can be obtained from the nurse collecting the material.
First of all, the level of the hormone in the blood is affected by food intake, and therefore, when preparing to take tests for hormones, you should stop eating food at least 12 hours in advance. Also, in order for the test to show TSH correctly, 5 days before the test they refuse foods that negatively affect the hormonal system, and therefore exclude fatty foods, alcohol, lemonade and fast food. If this is not done, then the values shown by the TSH test result will not correspond to the real picture and you will have to take the TSH test again.
For cigarette lovers, the relevant question is how long you should not smoke before donating blood for the TSH hormone. Ideally, of course, give up the bad habit a few days before the collection of the material, but if this is not possible, 4 hours before the procedure, which will be spent without a cigarette, will be enough.
When an analysis is done, there are no restrictions on liquid, unless, of course, a person drinks only clean, still water. You can drink it in any volume and even immediately before taking a blood test. If the desire to eat before the procedure is irresistible, you are allowed to drink a cup of warm, weak green tea. In this quantity, it will not change the blood picture, but will eliminate the unpleasant feeling of hunger. This drink, but already strongly brewed, is recommended after blood sampling if you feel weak and dizzy after it.
When a person is preparing for an analysis, for a period of 5 days before it, it is necessary, if possible, to stop taking medications, since they can disrupt the picture, which means the unreliability of the results and, as a result, the incorrectness of further treatment. If you cannot give up medications, there is still a way to get a TSH test done correctly. In such a situation, the rules for taking a biochemical analysis establish the need to inform the doctor taking the blood what drugs and in what volume were taken and how long before the analysis, which means that the result will be determined taking into account possible errors using a special table. Most often this concerns adults taking life-saving medications.
Taking material for analysis from women deserves special attention. They are often interested in the question of how to donate blood during the menstrual cycle. This condition does not affect the TSH level, which allows analysis.
The test is taken in the morning, when hormonal levels have not yet been changed by physical activity and stress, from 8 am to 12 noon. Blood is taken from a vein. After the procedure, you can eat immediately.
Knowing how to take the test correctly, you can get the most accurate result, which will give the doctor all the necessary data for competent therapy.
How to reduce TSH with folk remedies
Folk remedies for lowering hormonal levels are widely used and show excellent results. Various herbal preparations are most effective in treating this disease.
In order for the use of traditional medicine to truly bring positive results, it is important to make sure before using them that they do not cause individual intolerance to the body. Reduced hormone levels can be stabilized with the help of folk remedies purchased at the pharmacy, but you can prepare them yourself, there is nothing complicated about it
There can be many recipes for such medicines; below is a simple and not complicated method:
take angelica root, birch leaf, licorice roots and celandine (these 4 components are the main ones here). Then rose hips (its fruits), coltsfoot, all this is complemented by yarrow
It is important that all these ingredients are mixed in equal proportions. After this, the herbs are used to prepare a decoction, which should be drunk three times a day, then the level of TSH in the blood will be reduced
Treatment using folk remedies has long been recognized as effective and safe. But once again it should be said that before using any means, it is necessary to undergo medical consultation. And you shouldn’t rely only on folk remedies; traditional medications are more effective.
Normalization of TSH levels
If the hormone level is too high, the specialist will prescribe a thyroid examination. Impaired functioning of the gland increases TSH levels.
Only a qualified specialist can prescribe treatment, and then only if the cause of the increase in hormone levels is accurately detected. A course of treatment is selected for each patient individually. If the cause of the surge is a tumor in the mammary glands, inflammation of the thyroid gland, then treatment will take a lot of time, patience and effort. Benign tumors require complex therapy. The appearance of small tumors does not require surgery.
A doctor can help normalize TSH levels in the blood.
If the level of the hormone discussed in the article is high and slightly below the norm, as a rule, the doctor prescribes a corrective diet. In addition, the doctor prohibits the patient from taking certain medications and exercising.
Important ! A slightly increased TSH will not have a serious impact on a person’s health, and there will be a lot of time left to bring it back to normal.
A slight increase in TSH caused by iodine deficiency requires taking medications that contain this substance. They should be taken for 6 months. At the end of the course, it is worth doing a repeat ultrasound of the thyroid gland and undergoing a TSH examination.
Diagnostics
If you suspect an elevated TSH level, you should be examined by a specialist as soon as possible to make a diagnosis. The analysis is carried out in the morning. Blood is taken from a vein. If the analysis confirms that the hormone is contained in quantities exceeding the norm, an additional examination is prescribed to understand the reasons for this deviation.
Blood for analysis is taken from a vein in the morning
You need to know that at night, even in a healthy person, TSH will have high values. This is due to the slowing down of the body during sleep. Therefore, there is no point in taking tests in the evening and at night, since the hormone level will always be slightly elevated. This is especially worth considering during urgent examination as a result of hospitalization.
The results of the analysis also give a general idea of other features of the work of the organs.
There are 3 types of antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone:
- stopping the action of TSH receptors and increasing T3 and T4;
- promoting long-term increases in T3 and T4;
- stopping the activity of the thyroid gland and reducing susceptibility to TSH.
The threat from antibodies is expressed in the possibility of their penetration through the placenta to the developing fetus, which can cause pathology in the baby. Therefore, checking TSH levels for pregnant women is mandatory.
Antibodies to TSH can negatively affect fetal development
Diagnosis of hormone levels in childhood is of particular importance. Its normal value varies depending on the age of the child. Young children are tested for delayed physical and mental development, anemia of the arms and legs at normal body temperature, emotional disorders, weakness, and drowsiness.
Elevated TSH levels may be associated with mental disorders and adrenal disease. The greatest danger for children is the presence of hyperthyroidism in one of the parents. For such babies, analysis is carried out while they are still in the womb.