Home » Laparoscopy » Getting rid of bloating after laparoscopy
March 11, 2020 Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is considered the least invasive surgical procedure. With this method, the doctor can examine and study the abdominal cavity as well as the patient's abdomen. To perform a diagnosis or operation during laparoscopy, a special instrument (laparoscope) is used, which is a rough iron tube with a camera that connects to a computer screen. In this way, the entire abdominal cavity can be examined from the inside.
Indications for surgery
This modern operation has a number of advantages:
- detailed study and examination of organs,
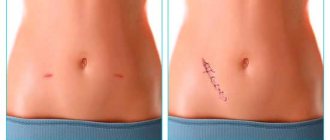
- no obvious scars,
- minor blood loss,
- reducing the risk of infection and ingestion of foreign bodies,
- fast recovery.
Laparoscopy may be prescribed for:
- adhesions. This disease causes pelvic pain and female infertility. Often the method allows you to completely cleanse the pelvic organs,
- cysts of different shapes and sizes,
- complicated pregnancy,
- various tumors,
- endometriosis of any stage,
- hysterectomy,
- oncology of the genital organs.
Laparoscopy is considered one of the most gentle interventions. Dangerous complications are very rare, the frequency is one case per thousand. Negative consequences can be expressed in injuries to internal organs or disruptions in the cardiovascular system.
Common symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, a person recovers within several days after laparoscopy; sometimes discharge can take place on the day of the intervention.
After the procedure, pain appears in the abdomen and in the area of postoperative wounds. Discomfort increases with movement, which is considered absolutely normal. To relieve pain, the doctor may prescribe additional painkillers.
Sometimes a sick person may have:
- prostration,
- attacks of nausea,
- anxiety.
To eliminate severe bloating, medications containing Simethicone should be prescribed.
A few days after the procedure, the person’s appetite returns, weakness and nausea go away. A distended abdomen after laparoscopy is a common consequence not only of laparoscopy, but also of many other surgical operations.
In addition, after surgical actions the following may occur:
As a rule, such symptoms disappear in a short time, literally within a few days.
Incisions made during laparoscopy usually heal quickly and without consequences. Sutures are removed approximately two weeks after the procedure or earlier. In the first months, there are small scars in the area of the incisions, which later fade and become almost invisible.
GB-40
Clinical case – patient R., 62 years old
What is laparoscopic surgery?
This is best explained by comparing this technique with traditional surgery.
When performing open surgery, the surgeon must make an incision that provides access to the organs on which the operation is performed. Until recently, cutting the integumentary tissue of the body was the only way for a surgeon to perform an operation.
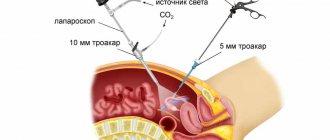
The laparoscopic technique eliminates the need to make large incisions. Instead, the surgeon can view organs from inside the body using a laparoscope, a thin instrument that resembles a telescope.
After introducing carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity (the abdomen is inflated), the laparoscope is inserted into the patient’s body through a small tube (trocar), with the help of which a puncture of the integumentary tissue is first made.
This requires a skin incision only 1 cm long. A small video camera and a light source are connected to the laparoscope, which allows the image from the video camera to be transmitted to the monitor via a fiber-optic cable.
The surgeon can perform the operation while looking at a monitor screen with an image magnification of 4-10 times.
For laparoscopic operations, special instruments are used, which are inserted along the same trocars through separate punctures.
Incision of the anterior abdominal wall during conventional and laparoscopic surgery
Appearance of wounds after laparoscopic gynecological surgery (4th day after surgery)
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
The large incision typically used in traditional surgery causes significant trauma to the muscle tissue. In this regard, pain occurs after surgery, and the wound healing period takes quite a long time. Small punctures made during endoscopic surgery do not injure muscle tissue. As a result, patients:
- experience much less pain after surgery, which may eliminate the need for painkillers;
- spend less time in the hospital (usually 1-2 days);
- recover faster, can return to normal activities and go to work faster;
- have no worries about the postoperative scar;
- avoid the formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity after surgery.
What gynecological operations can be performed laparoscopically?
The very first operations that were learned to be performed laparoscopically were gynecological operations. Today, about 95% of all gynecological operations can be performed laparoscopically.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy (examination of internal organs with an unclear diagnosis - infertility; chronic pelvic pain (suspicion of endometriosis of the uterine appendages or peritoneum, adhesions in the pelvis, etc.)
- Voluntary surgical sterilization (tubal ligation)
- Removal of ovarian cysts and tumors (in the vast majority of cases, laparoscopically).
- Checking and restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes in case of tubal infertility, preparation for IVF.
- Emergency laparoscopy can be performed in case of: (ectopic pregnancy; rupture or torsion of ovarian cysts; apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary with internal bleeding; in some cases - with purulent-inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages and pelvic cavities (in the absence of the effect of antibacterial therapy within 24-48 hours); differential diagnosis between acute gynecological and surgical pathologies).
- Removal of fibroids (conservative myomectomy), reconstructive surgery for abnormalities of the uterus.
- Removal of the uterus with appendages (hysterectomy) and without appendages: (for uterine fibroids; internal adenomyosis; recurrent (repeating) endometrial hyperplasia and polyps, pre-tumor and initial tumor changes in the uterus and cervix, for recurrent uterine bleeding)
- Removal of the uterus for fibroids (uterine amputation)
- Sacrovaginopexy (restoration of the mutual position of the pelvic organs when the vaginal walls prolapse)
Is laparoscopic surgery indicated for you?
These operations can be performed successfully on most patients. However, to decide whether laparoscopic surgery is appropriate for you, you need to consult with your attending physician and a surgeon who is fluent in laparoscopic techniques.
Before the operation, the patient signs a consent for the operation, which states that the doctor explained to her what the scope of surgical treatment will be (for example, with ovarian cysts, it is possible to remove the cyst, remove the cyst with part of the ovary, in some cases, remove the entire ovary), what complications are possible .
Also, before the operation, a conversation is held with the anesthesiologist, who explains what kind of medicinal preparation for the operation will be carried out (to stabilize the psycho-emotional status, prevent thrombosis and bleeding), and the patient also gives her consent to anesthesia.
Before surgery, the gastrointestinal tract must be cleansed, since a swollen intestine makes it difficult to see and blocks access to the genitals, increasing the risk of intestinal injury.
A cleansing enema is performed the evening before and the morning of the operation. The day before the operation, you can eat until 18:00, and you can drink water until 24:00 (?). On the day of surgery, you should not eat or drink anything.
It is also recommended to limit foods that cause flatulence (bloating) 3-4 days before surgery (brown bread, cabbage, legumes).
Before the operation, the patient must wear anti-varicose stockings on her legs or apply elastic bandaging. After the operation, the patient wears these stockings for at least another week, preferably two.
This is necessary because during surgery, microthrombi may form in the veins of the legs, and in the absence of elastic compression, these thrombi enter the general bloodstream; the most dangerous is their entry into the vessels of the lungs and heart.
Contraindications:
Absolute contraindications for laparoscopy are diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in the stage of decompensation, shock and coma, cachexia (severe exhaustion), disorders of the blood coagulation system, hernia of the anterior abdominal wall or diaphragm.
Contraindications for elective surgery are:
- acute infectious diseases suffered less than 1 month before surgery
- deviations in clinical laboratory tests (usually in these cases the patient is referred to a therapist to decide on the possibility of surgery and the need for further examination)
- bronchial asthma with frequent exacerbations
- hyperotic disease with high blood pressure values,
- pronounced adhesive process in the abdominal cavity
- significant size of the pathological formation of the internal genital organs)
← Back
Source: https://www.gb40.ru/services/ginekologiya/page/laparoscop/
Possible problems
After the procedure, a person often feels discomfort, which goes away within a few days. Some patients experience vomiting and nausea.
A certain category of patients complains of bloating after laparoscopy, as well as flatulence. The anesthesia used plays an important role here. Abdominal problems most often disappear within a week.
Sometimes it happens that the patient is constantly bothered by pain at the incision sites, as well as in the larynx. In rare cases, shoulder discomfort may occur.
After surgery, there is always carbon dioxide in the body. As a result of the processes associated with it, a person begins to experience abdominal pain.
Many patients are interested in when they can sleep on their stomach. The doctor allows this on an individual basis. If a person is in pain, he is allowed to sleep only on his back.
The recovery period after surgery depends on the method of therapy. Postoperative sutures should be treated with antiseptic solutions every day.
Wounds heal completely after 7-10 days. In the first days after laparoscopy, when the operation is related to the genital organs, there may be a slight discharge of blood from the genitals.
This is explained by the fact that at the beginning of the operation a manipulator is inserted into the uterus, which is removed at the final stage. For several days after surgery, women may experience unscheduled menstruation.
Contraindications
The main contraindications include:
- hemorrhagic shock,
- insufficient blood clotting,
- chronic pathologies of the respiratory or cardiovascular systems,
- acute kidney or liver failure,
Relative contraindications:
- high sensitivity to several types of allergens,
- malignant tumors,
- peritonitis,
- adhesions,
- pregnancy,
- uterine fibroids.
Nutrition rules
It is recommended not to eat on the first day.
Laparoscopy is a medical procedure that involves surgery to examine a patient's abdomen. During the operation, a special device (laparoscope) is used, which is inserted into the abdomen through small incisions in it. As a result of this, the doctor gets the opportunity to examine in detail the internal contents of the abdominal cavity, chest, and pelvic organs. The procedure is quick and has a higher degree of safety, since the patient loses a minimal amount of blood and can go home a few days after the operation. Therefore, laparoscopy has a number of advantages over other methods, such as ultrasound, computed tomography, and classical surgical interventions. The method is popular in diagnosing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and genital organs.
Bloating after laparoscopy
Many patients report the appearance of bloating and distension in the abdomen after laparoscopy. Don't panic right away. The procedure itself can give such a symptom. Before inserting an optical device into the abdominal cavity through a trocar (special tube), a small amount of carbon dioxide is pumped into it to create volume and improve visibility.
Often, in the first hours after laparoscopy, the remaining gas continues to put pressure on the walls of the internal organs, including the intestines, which causes bloating. The unpleasant symptom should disappear on its own soon. However, it may take about two weeks for the gases to completely leave the body.
This process can be accelerated with the help of medication therapy, rehabilitation exercises and traditional medicine recipes.
What is laparoscopy?
Laparoscopic surgery is an operation performed using a small puncture method in which an optical diagnostic device, gastroscope or laparoscope is inserted into the internal cavity of the body, which allows an examination of the organs from the inside.
In medicine, laparoscopy is used for diagnostics and surgical procedures. In the first case, a puncture and insertion of an optical device are used to make a diagnosis. During surgical laparoscopy, the doctor eliminates the pathological changes in the patient’s body.
Another difference is the method of anesthesia: during a diagnostic examination, he is given local anesthesia, and during surgery, general anesthesia is given.
What surgical interventions are performed using laparoscopy?
- Removal of ovarian cyst;
- Ovariectomy;
- Cholecystectomy;
- Hysterectomy;
- An operation to restore the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- Removal of fibroids, ectopic pregnancy, enlarged endometrium, malignant and benign formations in the abdominal cavity.
In general, almost all open surgical procedures are performed laparoscopically. Since laparoscopy involves the most delicate intervention in the body, it is considered the most gentle option.
Benefits of the procedure:
- Minimally invasive intervention;
- Acceleration of the healing and recovery process;
- Accessible and detailed study of the condition of internal organs;
- The process is not as traumatic as standard abdominal surgery;
- No large scars;
- Reducing the likelihood of infection.
Laparoscopy is the most popular diagnostic method in gynecology, but it is also used for endoscopic examinations in gastrology.
Discomfort during rehabilitation
Despite all the advantages of laparoscopy, a number of unpleasant symptoms arise during the rehabilitation stage. First of all, they are associated with the accumulation of gases in the stomach. This is due to the fact that during the operation, carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity through the incisions made. This is necessary in order to simplify surgeons’ access to the organs being operated on so that they can safely carry out the necessary manipulations. Carbon dioxide enters through one of the incisions, however, the formation of subcutaneous emphysema is possible due to gas entering the subcutaneous tissue (fat layer). In most cases, this process does not cause any particular trouble, since the amount of accumulated gases is minimal and is eliminated on its own. However, special measures are required to quickly remove gases.
Treatment of subcutaneous emphysema involves the prescription of painkillers that will allow the patient to calmly wait for the moment when the gases completely leave the body. In rare complex cases, the gas does not leave the body on its own, which may require repeated intervention, but practice shows that such situations arise infrequently.
Patients complain of a bloated abdomen and pain in it. In this case, at first you should not sleep on your stomach. It will take some time (five to seven days) before the condition stabilizes and you can return to your normal daily routine.
Pharmacological treatment of bloating involves the use of medications such as Espumisan, Polysorb, Simethicone, sometimes it is enough to simply drink activated charcoal. The use of any medications must be agreed with a doctor and carried out on the basis of his clear recommendations.
Gas after laparoscopy: how and how much comes out, what is important for patients to know
Currently, minimally invasive interventions are widely used in various fields of medicine. One of them is laparoscopy, which is used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
The technique has numerous advantages compared to open surgery. It allows you to reduce tissue trauma and shorten the rehabilitation period. But in the postoperative period, patients experience pain caused by gases in the abdominal cavity. Let's look at how quickly gas comes out after laparoscopy and how to alleviate the patient's condition.
Gases after laparoscopy
When people talk about gases after laparoscopy, they usually mean carbon monoxide (CO2), which is specifically introduced into the abdominal cavity during the procedure. But we must not forget that surgical intervention also causes disruption of intestinal motility, which leads to the accumulation of gases and flatulence.
The remaining carbon monoxide after the intervention is quite quickly absorbed into the blood and eliminated during breathing. Less commonly, if it penetrates the subcutaneous tissue, removal from the body is difficult and it takes 5–10 days for the bubbles to resolve. These bubbles cause pain, which worries patients.
Why is gas injection necessary during laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is an endoscopic intervention performed using a laparoscope. This is a device with a mini video camera at the end, the image from which is displayed on the monitor. There is also an additional device (grasper) for performing manipulations in the abdominal cavity. These devices are inserted through small centimeter incisions.
To ensure visualization, it is necessary to push back the intestinal loops; for this, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity. At the end of the intervention, it is released, but part of it may remain in the abdominal cavity.
This is not dangerous for the patient, although it sometimes causes pain and requires the administration of painkillers in the postoperative period. Therefore, in order not to become addictive, you need to know how long it takes for the gas to come out after laparoscopy.
If complications arise
In some cases, due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, micro-tears in the visceral layer of the peritoneum, gas enters the subcutaneous tissue and can even spread throughout it. This condition is called subcutaneous emphysema. This causes pain in the patient, so many are interested in how long it takes for gas to come out after laparoscopy, and whether it can be removed in any way.
Typically, gas bubbles spread within the subcutaneous tissue of the anterior abdominal wall, but cases of gas spreading upward to the chest and neck have been described. In such cases, drainage of the abdominal cavity and removal of carbon monoxide residues are sometimes required.
Such complications are now less common, this is due to improved quality of endoscopic equipment and laparoscopy techniques.
Gas removal methods
Despite the fact that during the operation the gas is removed from the abdominal cavity, after laparoscopy the patient is given recommendations on how to behave, eat, and organize a routine in order to quickly get rid of the remaining carbon monoxide. Recommended:
- Follow a diet . It is aimed at reducing gas formation in the stomach and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. This helps reduce intra-abdominal pressure and prevent remaining gas from entering the subcutaneous tissue. If an operation is performed on the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor prescribes a special diet, depending on the disease. In other cases, it is recommended to use only boiled, stewed products, with a minimum amount of fat. Fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt), cereals, and compotes are also allowed. You should avoid fresh fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Start getting out of bed earlier . When it will be possible to get up, sit in bed or walk, the attending physician decides. But as soon as the patient’s condition allows this, it is necessary, despite the fact that it hurts, to follow the recommendations. Usually in the first days the patient is prescribed painkillers so that he does not limit his movements. Physical activity, within reasonable limits, promotes the rapid removal of gases from the body and prevents the formation of adhesions.
- Medication support . Includes painkillers, adsorbents, which are prescribed by the attending physician. Charcoal (white, activated ), Espumisan, Polysorb , etc. are used
You can learn how to eliminate discomfort from this video.
Physical activity to combat gas
Physical exercise helps get rid of gases after laparoscopy, as it improves blood circulation and gas exchange. You can start exercising on the 5th–6th day after surgery. They should not be intense or long-lasting.
Bends in different directions, a bicycle, and pulling up your knees while lying on your side are useful. They also use breathing exercises with maximum abdominal exhalation, squeezing and unclenching the gluteal muscles, smoothing and massaging the abdomen clockwise. Exercises are repeated 10-15 times, 1-2 times a day.
Other ways to remove gases
If a patient after laparoscopy is bothered by bloating and gases are difficult to pass, you can use traditional medicine methods and take decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a carminative effect. Some of them can be purchased in pharmacies, for example, dill water, fennel tea. Teas made from chamomile, mint, and dry cumin are also useful.
Source: https://endoskop.guru/zhivot/laparoskp/posl/gaz-posle-laparoskopii.html
Procedures that accelerate the elimination of gases
The recovery period after surgery involves following special recommendations and changes to the regimen. Firstly, the patient follows a diet that includes easily digestible low-fat foods that accelerate metabolic processes; it is important to avoid overeating. It is necessary to exclude from the diet such products as: fatty meats, apples, cabbage, milk, cottage cheese, cheese, tea, coffee, soda. It is better to include low-fat yogurt, grapefruit, almonds, dried fruit compotes, and bell peppers in your diet. Secondly, you need to lead an active lifestyle, but avoid overload. Indeed, already on the second day after surgery, the patient can begin to walk, take walks in the fresh air, and light physical activity is acceptable. You should not spend time lying in bed after surgery, this will only slow down the removal of gases.
How should gas accumulations be removed from the body?
The problem regarding the removal of gases from the body occurs in almost all patients. During the recovery period after surgery, everyone must adhere to a diet. The food consumed should be easily digestible, and the food should also be gentle on the abdominal cavity. Thanks to this, additional gas formation can be avoided, because gases already remain in the body after laparoscopy. Their volume depends on how much gas was administered during the operation. And although at the end of the procedure doctors try to release gas from the abdominal cavity, its complete removal is still impossible. Generally speaking, it takes approximately two weeks to completely remove all accumulated gases from the body of the operated patient. When this happens, the patient will no longer feel discomfort.
To speed up the process of removing gases, follow these rules:
- spend your free time actively (but do not overwork your weakened body after surgery);
- eat foods that speed up metabolic processes;
Depending on the type of operation, doctors inject different amounts of gas, which spreads throughout the body and can cause pain in different parts of the body. It often hurts in the chest area, collarbone and, naturally, the abdominal cavity. It is because of these symptoms that gas formation needs to be removed.
Conducting special exercises
A set of simple but effective gymnastic exercises will help if gases slowly leave the body. These exercises can be done three or four days after surgery. Among such exercises, we note the following: “bicycle”, the usual bending of the torso forward and to the side, bending and extending the legs while lying on the back, relaxing and retracting the abdomen while lying down, tensing the buttocks. After a few days of performing such simple fitness, it is expected that the gases will completely leave the body.
What exercise can you do to get rid of uncomfortable gas?
If after laparoscopy gases come out very slowly, then light exercise will effectively solve this problem. They will improve intestinal motility. The restriction on physical activity after surgery applies to the first three to four days. And then light sports are not only not prohibited, but even recommended if you suffer from bloating after laparoscopy.
The most effective exercises that remove gases from the abdominal cavity:
- slight tilt of the body forward and in different directions;
- stand on one leg and bend forward (five on each leg);
- do the bicycle exercise (at least 15 spins);
- lie on your side and bend your legs under you (five to ten times);
- alternately draw in and relax your stomach while lying on your back;
- lie on your back, bend your knees and begin to relax and draw in your stomach;
- stroke your stomach in the direction in which the clock hand moves, gradually increasing the pressure;
- Squeeze your gluteal and anal muscles (about 50 times a day).
Such a simple and harmless selection of exercises will relieve you of pain and discomfort. Accumulations of gases will be completely removed in two to four days. Also, thanks to this complex, stools after laparoscopy are normalized, and the patient will finally feel better. By adhering to a special diet and doing these exercises, you will know for yourself and will tell everyone how to remove a bloated belly after surgery in a short time, only if you yourself do not specifically inflate it!
conclusions
Thus, laparoscopy is a popular and uncomplicated operation; today it is quite common. The accumulation of gases as a side reaction of this method is not dangerous. This is a normal process that can be easily eliminated. A week of minor inconvenience, after which you will be able to do what you did before the operation again, return to an active lifestyle, and your condition will return to normal. The main thing is to notify your doctor if you experience symptoms that cause discomfort.
Laparoscopy and its advantages
This modern surgical method has advantages over conventional methods. These include:
- detailed examination and thorough study of internal organs;
- absence of large scars and aesthetics of the method;
- minor blood loss;
- reducing the likelihood of infection and foreign bodies entering the body;
- short recovery period.
Causes of flatulence
Severe gas formation in the intestines can be caused by the following reasons:
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which products enter the lower intestine not fully digested and begin to sour. Hence the gases.
- High fiber content in some foods (beans, peas, cabbage, apples).
- Aerophagia is the swallowing of air while eating (when people eat in a hurry, drink liquids through a straw, talk while eating, or chew gum).
- Overeating (especially constant) contributes to the development of flatulence.
- Impaired intestinal motility.
- Lactose intolerance (a substance found in milk and dairy products).
- Stressful situations, depression.
- Celiac disease (gluten intolerance).
- Inflammation of the walls of the small or large intestine.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Recently undergone surgery to remove the gallbladder.
- Worms in the intestines.
- Peritonitis.
- Deformation of teeth and upper palate.
- Weakening of the intestinal muscles due to age (in older people).
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Oncology.
- Pancreatitis.
- Colitis and enterocolitis.
- Changes in hormonal levels in the body.
- Displacement of some internal organs (during pregnancy).
Main indications for the use of laparoscopy
This method is prescribed in the following cases.
- For pelvic adhesions. This disease can cause female infertility or pelvic pain. Very often, laparoscopy makes it possible to completely clean the pelvic organs.
- Endometriosis at different stages.
- The presence of cysts of different sizes.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Tumor of the uterus.
- Hysterectomy.
- Malignant formations in the genital organs.
Laparoscopy is a safe procedure. As for serious complications, they are rarely diagnosed - in about one case per thousand. Unpleasant consequences may include injury to internal organs or damage to the cardiovascular system.
How to prepare for surgery?
As for preliminary preparation, as a rule, the patient is recommended not to eat anything for 12 hours before the operation. Many patients after laparoscopy are discharged on the same day.
This surgical method involves the use of general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision (1 to 1.5 centimeters long) near the navel.
After the patient's abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas, a laparoscope is inserted using a needle. The gas makes it possible to disconnect the pelvic organs - this is necessary so that visibility is better and there is more space for performing surgical procedures. Using a laparoscope, the image is projected onto a computer screen.
If laparoscopy is used for the purpose of surgical therapy, additional incisions are made to insert instruments. Devices are also inserted through the genitals to allow the uterus to be moved during the operation. After the operation, gas is released from the abdomen. The incision is sutured and a bandage is applied.
You have questions?
You can ask them to me here, or to the doctor by filling out the form you see below.
Laparoscopy is considered the least invasive surgical procedure. With this method, the doctor can examine and study the abdominal cavity as well as the patient's abdomen. To perform a diagnosis or operation during laparoscopy, a special instrument (laparoscope) is used, which is a rough iron tube with a camera that connects to a computer screen. In this way, the entire abdominal cavity can be examined from the inside.
Rehabilitation stage
After laparoscopy is completed, patients may experience some discomfort, which often disappears after a few days. Some people experience nausea and vomiting. This is caused by the effect of anesthesia. Such symptoms disappear on their own after a certain time. Sometimes patients experience soreness in the area of the incision. Pain in the throat may also occur.
Abdominal pain and bloating are considered normal and common symptoms after surgery. Shoulder discomfort may also occur. This is due to the fact that after surgery carbon dioxide remains in the body. In most cases, the symptom disappears after a few days - but can be present for as long as a week. Regular painkillers help relieve such sensations.
The rehabilitation period after laparoscopy primarily depends on the method of treatment.
If diagnostic laparoscopic intervention has been performed, the person often returns to a normal lifestyle on the fifth day. Complete wound healing occurs after approximately a week. On the first day after the operation, slight bleeding from the vagina is observed. This is because a manipulator was inserted into the uterus at the beginning of the operation (and removed at the end).
After laparoscopy, bloating: causes
Nobody wants to undergo surgery. An operation is always an alarming moment associated with moral and physiological discomfort. However, in many cases, the patient can do with laparoscopy, which is not so traumatic. But this procedure has side effects, including bloating.
Laparoscopic surgery is an operation performed using a small puncture method in which an optical diagnostic device, gastroscope or laparoscope is inserted into the internal cavity of the body, which allows an examination of the organs from the inside.
In medicine, laparoscopy is used for diagnostics and surgical procedures. In the first case, a puncture and insertion of an optical device are used to make a diagnosis. During surgical laparoscopy, the doctor eliminates the pathological changes in the patient’s body.
Another difference is the method of anesthesia: during a diagnostic examination, he is given local anesthesia, and during surgery, general anesthesia is given.
What surgical interventions are performed using laparoscopy?
- Removal of ovarian cyst;
- Ovariectomy;
- Cholecystectomy;
- Hysterectomy;
- An operation to restore the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- Removal of fibroids, ectopic pregnancy, enlarged endometrium, malignant and benign formations in the abdominal cavity.
In general, almost all open surgical procedures are performed laparoscopically. Since laparoscopy involves the most delicate intervention in the body, it is considered the most gentle option.
Benefits of the procedure:
- Minimally invasive intervention;
- Acceleration of the healing and recovery process;
- Accessible and detailed study of the condition of internal organs;
- The process is not as traumatic as standard abdominal surgery;
- No large scars;
- Reducing the likelihood of infection.
Laparoscopy is the most popular diagnostic method in gynecology, but it is also used for endoscopic examinations in gastrology.
Why does my stomach swell after laparoscopy?
Many patients report the appearance of bloating and distension in the abdomen after laparoscopy. Don't panic right away. The procedure itself can give such a symptom. Before inserting an optical device into the abdominal cavity through a trocar (special tube), a small amount of carbon dioxide is pumped into it to create volume and improve visibility.
Often, in the first hours after laparoscopy, the remaining gas continues to put pressure on the walls of the internal organs, including the intestines, which causes bloating. The unpleasant symptom should disappear on its own soon. However, it may take about two weeks for the gases to completely leave the body.
This process can be accelerated with the help of medication therapy, rehabilitation exercises and traditional medicine recipes.
Caution: If you also experience other symptoms along with bloating, including chills, fever, nausea, and bloody vomiting, you should seek immediate medical attention. This may be a symptom of infection or internal trauma caused by the trocar or Veress needle through which the gas was injected.
What to do?
Abdominal bloating after anesthesia and laparoscopy can be eliminated on your own. The main principles of therapy are:
- Bed rest and rest on the first day after surgery;
- Eating foods that help speed up metabolism;
- Maintain moderate physical activity in the following days (approximately 7–10 days after laparoscopy) to reduce the risk of bile stasis.
If the patient is experiencing severe and painful intestinal cramps due to remaining gas in the abdominal cavity, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Espumisan;
- Polysorb;
- Disflatil;
- Sub simplex.
It is prohibited to choose your own medication without permission! The wrong choice of medication can cause infection of internal organs or other serious consequences that are life threatening.
You can help speed up the elimination of gases with light exercise. You should not give the body a strong load, as this will delay the healing process of the wound and internal microtrauma.
Exercises for bloating after laparoscopy:
In the first few days
- Squeeze rhythmically the muscles of the buttocks and the sphincter of the anus in a lying position (up to 50 times);
- Bring your knees together and slightly raise your pelvis. Do not overload the peritoneum!
7 – 10 days after surgery
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, place your hands on your waist, and bend slightly to the sides;
- Standing on one leg, bend forward (up to five times on each leg);
- Do the “bicycle” exercise in a lying position;
- Pull in and relax the peritoneum (up to 10 times in one approach). Performed with straight and bent legs;
- Lightly stroke the area around the navel, without pressing on the stomach.
Recovery after laparoscopy is impossible without following a therapeutic diet. Let's look at its main points.
Diet
For the first month and a half after surgery, the patient adheres to a strict diet, which is as close as possible to dietary nutrition. Failure to comply with the regimen can aggravate the condition and delay the healing process.
Each patient is informed of possible complications in the event of a dietary disorder. He is also informed that he must eat in accordance with diet number 5 . Subsequently, the menu can be expanded, but only by the decision of the attending physician.
If cholecystectomy has been performed, an extremely strict diet is required. The relaxation is carried out during the period when the function of the removed gallbladder will be taken over by the intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts. If the patient follows all the instructions, the likelihood of bile stagnation is minimized.
After a certain time, he will be able to return to his usual diet, which includes minor restrictions.
On the first day after laparoscopy, food is not taken; it is permissible to drink water without gas. On the second day, a light snack is allowed, including non-concentrated vegetable broth, boiled chicken fillet chopped or minced, light yogurt and low-fat cottage cheese. The portions are small, meals are taken every 3 hours (up to six times a day).
What should be excluded from the diet during the diet?
- Fatty varieties of fish, meat, poultry;
- Products containing solid animal fats;
- Dishes prepared by frying;
- Canned food of any kind, including meat and vegetables;
- Marinated, salted, smoked products;
- Spicy sauce;
- Animal entrails that are difficult to digest (offal, kidneys, stomachs, brain, etc.);
- Fresh baked goods;
- Confectionery;
- Raw vegetables and fruits;
- Caffeine;
- Cocoa;
- Alcoholic drinks.
On the third day after surgery and in the next seven days, the patient begins to adhere to the basic principles of treatment table No. 5 :
- Fractional meals (five to six times a day);
- You should try to eat at the same time every day;
- Portions should be the same size;
- Food is taken only warm;
- The products consumed are processed thermally (boiling, stewing, steaming, baking);
- Products are crushed, rubbed through a sieve (in a blender) or ground to facilitate digestion.
It is often difficult for a person to adapt to a changed lifestyle, not only physically, but also psychologically. The restrictions seem too harsh, so many people break the diet, refusing to acknowledge the temporary decrease in their activity and abilities due to illness.
However, the main purpose of the diet is not to deprive the patient of pleasure, but to reduce the load on the digestive tract. It should prevent stagnation of bile and the development of constipation.
It is necessary to accustom the body to work in a new mode and stimulate intestinal motility.
What can you eat?
- Dried bread made from wheat flour;
- Fish, meat, poultry of lean varieties (chicken, turkey, rabbit, pike perch, haddock, pollock, hake, etc.);
- Cereal porridges cooked in water (legumes are prohibited);
- Puree soups and low-fat broths;
- Stewed and boiled vegetables;
- Berry and fruit jelly, jelly;
- White marshmallows without chocolate;
- Apple marshmallow;
- Soft-boiled chicken eggs (one per day);
- Low-fat cottage cheese;
- Kefir, yogurt.
If the use of any product causes bloating, bloating and colic, then you should remove it from the diet or significantly reduce the portion.
Folk recipes
Treatment with medications gives more successful results if combined with techniques suggested by traditional medicine. When recovering and eliminating bloating after laparoscopy, you can try the following options:
- A tablespoon of dried immortelle flowers is poured with hot water and boiled for five minutes. After cooling and straining, drink one to two tablespoons before each meal;
- A decoction of 15 g of birch buds, prepared in 200 ml of water, relieves bloating and eliminates flatulence. 50 ml of liquid is taken before meals about three times a day:
- An infusion of fig fruits is useful for eliminating constipation after surgery, which is dangerous by causing stagnation in the bile ducts;
- An infusion of chicory root has a laxative and carminative effect. It is also drunk as tea (the raw materials can be purchased at a pharmacy or any grocery store). The main thing is to take pure chicory without additional flavoring additives. The plant contains inulin, which has a general regenerative effect, which is especially effective for recovery in the postoperative period;
- Increased gas formation, which worsens the patient’s condition after laparoscopy, can be quickly removed by an infusion of cinquefoil root. Drink 50-100 ml before meals no more than twice a day;
- An herbal infusion containing celandine, peppermint, lemon balm and the already mentioned bloodroot will do an excellent job of treating flatulence. Prepared in the proportion “1 tablespoon of phyto-raw materials per 300 ml of boiling water.”
Plant-based choleretic agents have a good effect. They are available without a prescription in every pharmacy. Possible options include:
- Biligin;
- Flamin;
- Turmeric-based preparations;
- Rosehip syrup;
- Corn silk extract in liquid form;
- Choleretic herbal teas.
Not a single folk recipe is recommended after laparoscopy unless its use is approved by the specialist who performed the operation or who monitors the patient’s condition after it. Uncontrolled use of herbal preparations and herbal preparations can lead to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, so before starting therapy you need to obtain an appropriate doctor’s prescription.
Source: https://hoove.ru/posle-laparoskopii-vzdutie-zhivota/
Non-serious complications
It was previously indicated what the likelihood of such deterioration in the patient’s condition is. Complications may be accompanied by the following symptoms.
- Postoperative infection can cause deterioration, resulting in an increase in body temperature, which is accompanied by chills, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
- Minor bleeding where the incision was made.
Laparoscopic surgery may be accompanied by abdominal bloating, increased discomfort and pain. This is due to the fact that at the time of the operation the abdominal cavity is filled with a special gas, which makes the work of surgeons easier. Once the operation is complete, it is pumped out, but residues may be present. Often, a large belly does not require treatment; the condition should return to normal within a week. Some changes in diet and taking special medications help smooth out the discomfort.
What it is?
Bloating is characterized by distension of the abdomen, cramping, cramping pain, and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. Often bloating is combined with belching or hiccups. In some cases, bloating is accompanied by such severe pain that the patient breaks out in a cold sweat and even falls into unconsciousness.
A healthy adult constantly has about 900 milliliters of gases in the intestines, which are released by microbes. Between 100 and 500 milliliters should be evacuated along with the feces. And with bloating, more than 3 liters of gas accumulates in the intestines.
Dangerous complications
Such deterioration is diagnosed in one case out of a thousand.
- Injury to internal organs, large blood vessels and pelvic nerves.
- Complications may occur after laporoscopy is completed if carbon dioxide gas was used during surgery. The use of anhydride may cause gas bubbles to enter the veins.
- The occurrence of a severe form of allergy to the administered anesthesia.
Subcutaneous emphysema
Swelling of subcutaneous adipose tissue occurs due to the fact that carbon monoxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. This phenomenon is dangerous because it has a wide distribution and can appear not only on the tissues of the membrane, but also on the neck, face and limbs. Often, such a complication disappears on its own within a period of several hours to several days.
Violation of the integrity of internal organs
There is a possibility of damaging organs due to the fact that the surgical instrument is inserted, one might say, blindly. In order to prevent such situations, special rules have been developed. So, you need:
- strictly follow the instrument insertion technique;
- use reliable and non-hazardous Veress needle and trocar devices;
- undergo testing before inserting the instrument.
For safety reasons, needles are equipped with blunt spring-loaded rods, and trocars are equipped with shielded caps. However, the possibility of damage is still present, especially if the operation is performed on the intestines, liver or blood vessels.
Thrombosis
Women over 50 years of age are more susceptible to thrombosis. In order to prevent such a complication, doctors bandage the sore leg. The patient is also prescribed medications that have a thinning effect. In addition to age, complications can be caused by the patient having diseases such as hypertension, arrhythmia, atherosclerosis and excess weight.
Burns
Most often, burns during laparoscopy occur due to poor visibility and malfunction of the device. If the doctor does not detect the burn in a timely manner, it takes on a more serious form and turns into inflammation.
Bleeding
Hemorrhage at the site of instrument insertion is a fairly rare occurrence, since during laparoscopy the trocar wound is sutured, capturing all damaged layers. But if such a complication does arise, first of all, it is due to a lack of homeostasis.
Inflammatory process at the wound site
This complication has several factors at once. Firstly, it is a weakened immune system. Secondly, the introduction of infection. These reasons may also include factors of a general nature.
The appearance of tumors
After laparoscopy, tumors may form in the incision area. This is due to the fact that organs that are malignant in nature are removed through the wound. The pathological cells remaining at the incision site cause the development of skin lesions.
In conclusion, it should be noted that despite the fact that much attention was paid to complications in this article, the benefits of laparoscopy are much greater. Clear advantages include the absence of large and unsightly scars, a quick recovery period that does not require the use of analgesics and compliance with the necessary routine after laparoscopy. This method is also characterized by a slight risk of developing adhesions and hernias at the incision site. In addition, complications largely arise due to the inexperience of surgeons. Remember! If you trust highly qualified specialists, the likelihood of postoperative complications is significantly reduced and is no more than 1%.
Abdominal bloating after laparoscopy – what are the dangers and how to avoid it?
Laparoscopy, despite being a low-traumatic surgical technique, has certain consequences or complications.
Regardless of the reason that necessitated such an intervention, the abdomen after laparoscopy may remain painful for some time, and bloating is often noted.
Even in cases where laparoscopy has a diagnostic purpose, a sufficient amount of carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. Most of it is pumped out after the operation, but a small amount still remains, causing discomfort.
Laparoscopy is a modern method of diagnosis and surgical treatment
Possible complications of laparoscopy
One of the most common complications is severe abdominal bloating after laparoscopy. Indigestion, pain, and infection are also noted. More rare but dangerous complications include:
- damage to blood vessels or intestines by the trocar;
- burns from power tools that are invisible to the surgeon;
- peritoneal injury due to exposure to cold gas.
After laparoscopic operations, the patient can remain in the hospital for some time, under the supervision of doctors, or go home, depending on the nature of the manipulations performed. Bloating, pain, and digestive disorders may not develop immediately, but 1-2 days after the intervention.
All complications that arise after such a low-traumatic intervention are much easier than those observed after abdominal surgery. When laparoscopy is performed by an experienced surgeon and the patient strictly follows the recommendations in the postoperative period, the consequences are minimal or completely absent.
When is a doctor's help needed?
Patient after laparoscopy
Symptoms such as flatulence, nausea, and slight pain in the lower abdomen are almost inevitable consequences of laparoscopy. In most cases, they go away on their own. You should immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur:
- chills, fever;
- disturbances of consciousness of varying degrees;
- constantly increasing acute pain in the abdomen;
- bleeding or purulent discharge in the area of the surgical wound.
The main part of the discomfort is due to the fact that the abdominal cavity is inflated quite strongly with gas - this is necessary to facilitate access to the internal organs and minimize the risk of accidental damage.
When the surgery is complete, the gas is pumped out, but some of it may remain inside, causing a feeling of bloating.
After the intervention, the overly swollen abdominal cavity returns to its normal size on its own within a few days.
How to avoid unpleasant consequences?
It is better to decide what to do if unpleasant symptoms do not go away on their own, together with your doctor. Immediately after laparoscopy, the doctor will give all the necessary recommendations that must be followed. Many of them are of a general nature, but their implementation can significantly reduce time and facilitate the recovery period.
- Move less for 2-3 days after surgery. This will minimize pain and avoid the need to prescribe strong analgesics.
- Sexual activity resumes after 1.5-2 weeks, not earlier. If the operation was performed on the uterus, the period may be extended.
After laparoscopy, it is necessary to maintain sexual rest
- Severe bloating and flatulence may require the prescription of antispasmodics, which will be selected by the doctor.
- Be sure to follow a diet. The first meal after surgery is allowed after 4-5 hours, and if the patient is able, it is better to wait a day. Food should be easily digestible - natural yogurt, low-fat kefir, light soups, meat and fish are allowed, but in boiled form. Carbonated drinks are excluded.
To alleviate your condition after surgery, it makes sense to follow a diet on the eve of the intervention. By limiting foods that cause excessive gas and also increase the volume of stool, you can avoid symptoms such as nausea, vomiting or bloating after laparoscopy.
In some cases, the introduction of large amounts of gas into the abdominal cavity causes the formation of subcutaneous emphysema. This phenomenon does not require active treatment and goes away on its own within a few days. If emphysema is localized in the neck or face, at a minimum, consultation with a specialist is required.
If no complications appear within 2-3 days, you should not think that the body has fully recovered from the intervention. Despite the absence of large incisions, after the operation you should not expose yourself to significant physical activity, excessive sun exposure, and swimming in the sea is not recommended. Following these simple rules will allow you to recover as quickly as possible after laparoscopy.
Source: https://diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/vzdutie-zhivota-laparoskopii.html