Diseases of the hip joints occur less frequently than diseases of other joints of the legs, so ultrasound of the hip joints is prescribed when the causes of pain become unclear. Elderly people and children are most susceptible to diseases of the pelvic joints.
Ultrasound examination of the hip joint involves diagnosing the muscles, tendons, and joints of the pelvis. Most often it is prescribed together with Doppler ultrasound, which allows more accurate determination of pathology.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the diagnostic method
Ultrasound visualization of articular cartilage and subchondral layers in adults and children allows us to evaluate a wide range of destructive and degenerative changes. Ultrasound of the hip joint is prescribed to identify hyperechoic inclusions in hyaline cartilage. Using a non-invasive study, the thickness of the joint space and even the slightest deformation of the contours are determined. Ultrasonographic images, the processing of which uses spatial densitometry, are characterized by high information content in the diagnosis of joint diseases.
Medical ultrasound devices use frequencies from 2 to 29 MHz. The operating capacity of modern devices is characterized by values measured in fractions of mm.
Preparing for the examination
The ultrasound examination procedure is simple, so an adult patient does not need preparation. The only condition is to avoid injections into the joint 4–5 days before diagnosis.
Ultrasound results are affected by body position, so when performing this procedure on children, it is important that the child does not move. Infants need to avoid foods that can cause colic a few days before the test; you need to feed the baby half an hour before the procedure to avoid regurgitation.
Advantages of the method
Ultrasound is used as an independent research method, and as a supplement to radiography, if the resulting images turned out to be uninformative and did not allow one to accurately determine the stage of the pathology and assess the degree of joint destruction. Ultrasonography has many advantages over other diagnostic methods for detecting diseases of the hip joint:
- affordable price (in private clinics from 550 rubles);
- short period of examination;
- convenient operation of ultrasonic diagnostic equipment;
- the ability to simultaneously measure the morphological and functional characteristics of the hip joint;
- a small list of contraindications for examination.
An important advantage of ultrasound of the hip joint is the absence of harmful radiation to the patient during the diagnostic procedure . The widespread use of ultrasonography in examining newborns and older children is explained by the availability and safety of the method, and the ability to provide the doctor with objective information about the condition of the child’s bone and cartilaginous structures.
Ultrasound of the shoulder joint
It is the most complex in the human body. Due to its high mobility, it is rarely subject to degenerative disorders. But unfortunately, the shoulder is injured quite often, especially among athletes. The advantage of the method over classical x-ray examination is the ability to study the articular surfaces and the bursa during shoulder movement. In this way, even minor joint defects are identified and treatment is started in a timely manner.
Picture. shoulder ultrasound:
Flaws
This research method in orthopedic practice is used to determine the main sonographic indicators of the hip joints, identify structural changes provoked by the development of arthrosis and arthritis, and study the dynamics of sonographic criteria against the background of conservative treatment and surgical interventions. Its main problems:
- requirement of a certain accuracy of measurements;
- low quality of the resulting images;
- inaccurate installation of sensors in standard ultrasonic positions, as a reason for low repeatability of results.
Ultrasound images are characterized by specific distortions, interference and artifacts, which are closely related to the characteristics of ultrasonic wave propagation in biological tissues. The inaccuracy of images is influenced by the characteristics of the ultrasonic sensor, the difficulty of obtaining a standard position, and the psychophysical state of the human visual organs. An in-depth analysis of the conditions for studying the hip joint and the use of modern equipment that allows the implementation of the latest techniques for digital processing and quantitative assessment of images helps to gradually solve all the problems of ultrasonography.
Ultrasound of the ankle
These connections are injured very often, and ultrasound of the ankle joint helps doctors establish the correct diagnosis and choose treatment tactics.
Subluxations and dislocations of the ankle are the most common, and with the help of an ultrasound, the doctor will identify possible ruptures of the ligaments and tendons. Another common indication for the use of ultrasound in the ankle area is degenerative diseases of the lower extremities. These include rheumatoid arthritis, heel spurs and others.
Ultrasound examination of the ankle joints is also used to diagnose pathological formations such as cysts and inflammation of the articular surfaces - epicondylitis, tendonitis and bursitis. In conjunction with x-ray examination, it is also possible to use ankle ultrasound to monitor surgical interventions on the joint.
Indications for use
The structural formations of the hip joint are the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. The acetabular lip is attached to its edge, which is reflected in the depth characteristics. The acetabular labrum is the site of attachment of the joint capsule, filled with synovial fluid. The hip joint is one of the largest joints of the bone surfaces, constantly experiencing increased loads with increasing human motor activity. Main indications for ultrasound examination of the hip joint:
- limited range of motion, the appearance of uncomfortable feelings of stiffness, especially in the morning;
- the occurrence of pain of varying intensity both at night, at rest, and when walking;
- the need to assess the condition of the hip structures after a fall, impact, or prolonged compression;
- the appearance of a characteristic crunch when moving or trying to change the position of the body;
- regular or periodic swelling in the hip joint;
- damage to muscle tissue;
- spasms of the striated muscles of the buttocks and lower extremities that occur from time to time;
- pathological change in leg length.
When serious diseases of the hip joint occur, changes in its structures are visualized even during an external examination of the patient.
An ultrasound is necessary to assess the extent of damage and select treatment methods - conservative therapy or surgery. This diagnostic study is indicated when identifying a pathology that provokes the gradual destruction of joints, including the hip. These may be endocrine diseases or disturbances in the absorption of biologically active substances.
The images obtained during diagnostics make it possible to reliably establish not only damage to bone and joint structures, but also damage to soft tissues as a result of the developed inflammatory process. This is important when drawing up a therapeutic regimen and choosing pharmacological drugs. What does an ultrasound of the hip joint show in adults:
- dysplasia;
- bursitis;
- synovitis;
- arthrosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- protrusion;
- coxarthrosis;
- arthritis.
Ultrasonography can be used to evaluate soft tissue damage by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The development of destructive-degenerative changes of any severity in the hip joint provokes disruption of the entire musculoskeletal system. Loads are gradually distributed to the knees or ankles, which causes the rapid spread of pathology. This is visualized in a change in gait, limping.
When is ultrasound performed in adults?
Ultrasound does not have any radiation effect on the human body and is a non-invasive diagnostic method. The procedure does not require the patient to perform complex preparatory measures, violate the integrity of the skin and bone structure of the joint, or administer contrast agents. It is these advantages that make it possible to use sonography to obtain objective data on the condition of the hip joints at any time without limiting the number of procedures, without fear of causing harm to the body as a whole.
An ultrasound of the pelvic joint structures is necessary if an adult has:
- hip injuries;
- painful sensations in the lumbar region, lower limb and joint, which appear not only during movement, but also at rest;
- intermittent claudication;
- problems with crunching, grinding or crackling in cartilage tissues;
- contractures – restrictions on passive movements in a joint;
- swelling (permanent or periodic) of the lower extremities;
- muscle spasms in the pelvic area;
- limb deformities;
- violation of rotational movements in the hip joint;
- changes in the external shape of articular elements;
- symptoms of pathological processes that lead to destruction of the hip joint.
The most important indication for an ultrasound of the hip is a sudden change in a person’s gait - this is a signal for the need for a comprehensive examination, since it may lead to further destructive changes in other bone structures
Ultrasound examination of the hip joint in children
The main indication for ultrasound of the hip joint in newborns is dysplasia, or congenital dislocation. This is one of the most common pathologies among all malformations of the musculoskeletal system. According to statistics, dysplasia is diagnosed in 15 out of 1000 newborns, and in environmentally disadvantaged areas this figure increases significantly. Ultrasound examination allows for timely detection of congenital dislocation and immediate treatment.
The etiology of the disease is different; The medical literature even describes cases of the formation of pathology of the hip joint as a result of perinatal damage to the central nervous system, which is called neurogenic dysplasia. It was confirmed by experiments by A. Yu. Ratner and his colleagues in 1992-2005.
For a long time, congenital dislocation was diagnosed during an external examination of the child by an orthopedist, and an X-ray examination was performed to confirm the initial diagnosis. This method involves irradiation of children, and difficulties arose in interpreting the resulting images due to the predominance of cartilaginous tissue in the hip joint of infants. Therefore, safe ultrasound examination is increasingly used. Indications for its implementation may be one of the following circumstances:
- the birth of a child as a result of multiple or premature pregnancy, as this is a factor provoking the development of congenital dislocation of the hip joint;
- gluteal or pelvic position of the fetus before birth, increasing the likelihood of dysplasia as the child passes through the birth canal;
- complicated pregnancy occurring against the background of severe toxicosis and (or) vitamin deficiency;
- a woman taking pharmacological drugs (diuretics, cytostatics, antibiotics, immunomodulators) during pregnancy, including for the treatment of chronic diseases;
- periodic or regular need to maintain (correct) pregnancy;
- viral, bacterial, fungal severe respiratory or intestinal infections diagnosed in the mother in late pregnancy, during the formation of the main articular structures in the fetus and the formation of foci of ossification of the femoral head.
Any of these factors causes an ultrasound examination to be performed as soon as possible after the birth of the child. For children under 6 months of age, a diagnostic procedure is indicated if, during the next medical examination, they are found to have asymmetry of skin folds in the gluteal or groin area, shortening of one of the lower limbs in relation to the other, or difficulties arising when abducting the hip. The pediatrician refers the child for ultrasonography if specific clicks appear when trying to abduct the hip, or if there is increased or decreased activity of the leg muscles. For older children, ultrasound of the hip joint is prescribed in the following cases:
- injury;
- retardation in physical development, accompanied by failure to walk or crawl;
- lame, unsteady gait, frequent falls;
- slowdown or cessation of physical development as a result of severe infectious pathologies that have caused a decrease in the range of motion in the hip joint.
Quite rarely, situations arise when hip dysplasia is not detected either by ultrasound or X-ray examination, despite the severity of the symptoms of the pathology. In this case, constant monitoring of the child’s condition and the timely appearance of ossification nuclei is carried out before the onset of 6 months.
Long-term follow-up is necessary during the rehabilitation and treatment phases to evaluate the recovery of the pediatric hip joint. The table shows a breakdown of the parameters obtained during ultrasound of the hip joint in young children:
| Type of childhood pathology | The obtained results of ultrasound of the hip joint |
| Normal (correct formation of the hip joint) | Expanded and shortened cartilaginous plate |
| Excessively slow formation (pre-luxation) | Delayed ossification |
| Subluxation | Displacement of the femoral head relative to the acetabulum, unchanged cartilaginous structure |
| Dislocation (dysplasia) | Incorrect development of the hip joint, the cartilage protrusion does not cover the head of the femur |
Ultrasound of the knee joint
Often affected by degenerative and inflammatory diseases, it is injured less frequently than the elbow and ankle.
For knee pain, ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed very often, since it is impossible to assess the quality and quantity of joint fluid using an X-ray examination. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, these surfaces are deformed by special growths; during inflammatory processes in the cavity, a decrease in the amount of joint fluid and cords, visible only on ultrasound, etc., is observed.
Picture. Structure of the knee joint:
Procedure
No special preparation is required to perform an ultrasound of the hip joint in adults and children. The only contraindication to this diagnostic study is individual sensitivity to the inert transparent gel used, which facilitates the movement of the sensor, improves sound conductivity and the quality of the resulting images. To carry out the procedure, a referral from the attending physician, a package of wet wipes or towels, a diaper or sheet are sufficient.
To optimize ultrasound diagnostics, to ensure full contact of the sensor with the patient’s body at the micro level, a gel consisting of glycerin, sodium tetraborate, styrene copolymer with meleic anhydride and distilled water is used.
To generate ultrasonic waves, a special sensor is used, which the doctor moves in the area of the hip joint. The principle of the ultrasonography technique is based on the different densities of bone, cartilage and soft structures. They are characterized by a certain level of absorption of sound waves, which are transformed into echo signals that differ in strength and phonogram. These signals are visualized on the monitor in the form of structural images, which make it possible to determine the pathology, the stage of its development and the number of complications that have arisen. To obtain the necessary images, a diagnostic laboratory specialist uses one or more access options:
- front . The patient is asked to take a horizontal position, placing the roller in a longitudinal projection relative to the femoral surface. This positioning helps to better visualize the structural elements of the hip joint. The resulting images clearly show the iliac bones, femoral heads, ligaments, muscles and lymph nodes of the groin;
- rear . The patient is placed on his side and asked to pull his knees towards the lower abdomen. This position allows you to obtain photographs in which the sciatic nerve, tubercle, surface of hyaline cartilage, superficial and internal structure of muscle fibers in the gluteal region are visualized in great detail;
- medial _ The patient is asked to lie on his back, bend his leg and abduct it slightly. This diagnostic method allows for a detailed examination of the pelvic flexor muscles and articular ligaments if an inflammatory process is suspected;
- lateral . The patient is asked to lie on his side and rotate the hip inward. In this position, the protruding elements of the tibia and the trochanteric bursa are clearly visualized.
The duration of an ultrasound examination is 15-25 minutes, depending on the diagnostic tasks and the degree of destructive-degenerative changes identified. The choice of examination technique and access option is made directly by the doctor after studying the preliminary diagnosis and the location of the area of suspected damage to the hip joint.
The discoverers of ultrasonic waves were the Curie brothers, who in 1880 discovered the piezoelectric effect, which arose in quartz crystals under mechanical influence.
If the ultrasound procedure is indicated for a newborn or small child, then during the examination the parents help maintain proper immobility. This is necessary to obtain high-quality images to avoid repeated ultrasound or other examinations. It is often necessary to examine other joints in adults or children to confirm the initial diagnosis. In this case, the procedure takes longer.
Medial surface of the thigh on ultrasound: adductors
The patient is in a supine position, with the hip bent at the knee and rotated outward - “frog”. Place the sensor transversely above the main mass of the adductors. Three muscle layers are visible: superficial long adductor (lateral) and thin (medial) muscles, in the middle part - short adductor muscle, deep - adductor magnus muscle.
The transducer is then moved upward to the tendon insertions at the level of the pubis and placed longitudinally along the long axis. Adductor injuries usually occur in combination with hip hyperabduction and abdominal hyperextension, sometimes with forced external rotation of the leg. The adductor longus and gracilis muscles are most often affected. In tentopathy, the tendon is hypoechoic and thickened compared to the asymptomatic side. Ultrasound has low sensitivity for minor injuries or chronic tendinopathy compared with contrast-enhanced MRI. In the left thigh, the long adductor tendon of the left femur is thickened (8.3 mm, compared to the right femur 7.2 mm), hypoechoic.
We scan the adductors in the longitudinal plane until they attach to the pubic bone. Attachment of the longus tendon in the form of a hypoechoic triangle. At the pubis, move the sensor laterally to see the transverse and internal oblique abdominal muscles; the symphysis is visible medially.
Decoding the results obtained
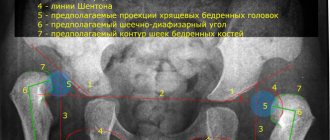
The obtained ultrasound values of the hip joints in children are taken as the norm, and the development of the hip joint occurs in accordance with age if the echogenicity of the femur and acetabulum is increased. On the oscilloscope screen they are visualized as white spots, and the femoral head and hyaline cartilage tissue look like dark, slightly blurred areas. The older the child, the more pronounced the contrasting outlines of the hip joint are due to the formed foci of ossification. The deciphering of the obtained values is carried out by a diagnostician who measures the angles obtained after drawing linear segments on the photographs. When connecting the lower part of the small ischial muscle to the ilium, only straight lines should be obtained, and the hyaline cartilaginous structures with the acetabulum should be curved. When lines intersect in such projections, alpha and beta angles are formed, measured by a diagnostician using the Graph method. The norm is characterized by the following digital parameters:
- an alpha angle of more than 60°, formed by bends and horizontal straight lines, indicates the correct formation and hardening of the surfaces of the acetabulum;
- a beta angle of less than 55° indicates the degree of development of the cartilaginous zones in the acetabulum and is normal.
Alpha angles with values of 39-40° are considered deviations from the norm during ultrasound of the hip joints. Such parameters of a diagnostic study indicate the presence of a subluxated joint in a child. When the alpha angle is less than 43°, children are diagnosed with hip dysplasia. Beta angles in these diseases are almost always greater than 77°.
In adult patients, the increased echogenicity of the acetabular labrum, the fibrous arrangement of the ligaments of the synovial capsule, and the lack of visualization of the synovial membrane are taken as the norm for the structure of the hip joint. The normal distance from the femoral neck to the articular capsule is 0.6-0.9 cm. The main task of the doctor when examining adults is to carry out differential diagnosis, which makes it possible to separate intra-articular pathology from extra-articular one. This helps the doctor choose treatment tactics and the best medications. What intra-articular pathologies are detected by ultrasound:
- the presence of effusion in the joint cavity, or synovitis. A thickened joint capsule indicates accumulation of foreign fluid. The thickness of this structural element is compared with a similar one in a healthy joint. If the difference is more than 0.2 cm, then the synovial joint capsule is not functioning properly. The resulting images measure the length of the line connecting the joint capsule and the femoral neck. Values above 1 cm allow us to establish developed synovitis;
- the presence of foreign fragments in the synovial fluid. This pathological condition is usually preceded by fractures, avulsions of particles of cartilage or bone. The cause of the appearance of tiny foreign bodies is osteoarthritis, accompanied by an acute or chronic inflammatory process. Foreign particles penetrate the joint capsule and are visualized on the resulting images in the form of an intra-articular mobile hyperechoic structure;
- formation of a false joint. With delayed fusion of fragments, irregular extraneous joints are formed. Their formation is provoked by surgical reposition of bone fragments with the help of various fixing structures for closed fractures of the femur, the complication of which was suppuration and osteomyelitis. Ultrasound of the hip joint reveals false joints. Signs of their formation are intermittent outlines of bone structures with uneven calluses. Areas of inflammation and swelling of nearby soft tissues are also well visualized.
Ultrasonography is prescribed to detect necrotic changes in the femoral head, a pathology that most often affects men. The disease progresses quickly and severely, causing decreased ability to work and disability. An ultrasound scan of the hip joint allows you to identify pathology at the initial stage and begin treatment immediately. With necrosis, the symptoms are dominated by pain, atrophic muscle damage, limited range of motion and gait disturbance. When deciphering the results of an ultrasound, the disease is indicated by a violation of the symmetry of the contours of the joint, narrowing of the joint space, and uneven outlines of the head.
What does the diagnosis show?
An ultrasound of the joints shows what is happening to them at the moment. With the help of an examination, injuries, pathologies, cysts, degenerative and inflammatory processes can be identified. Let's look at each point in more detail.
Pathologies in the joints
Ultrasound of joints is also done to identify pathologies. These can be transformations after operations, inflammatory processes, dystrophic changes.
Based on the results of the examination, heterogeneity of the structure, hyperechoic formations, edema, displacement of ligaments and tissues can be revealed. These changes may indicate degenerative processes.
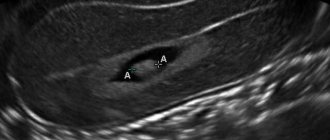
Detection of a cyst
A cyst is a hollow tumor, usually filled with fluid. Using ultrasound, you can identify a cyst in the joints and evaluate its development. Most often, cyst removal is only possible through surgery. If left untreated, it can grow and/or become malignant.
Injuries
Joint injuries can occur for various reasons: a fall, high load, awkward movement. During ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to identify the consequences of these injuries: rupture of ligaments, tendons, hematomas.
Degenerative processes
Factors in the development of degenerative diseases are osteoporosis (decreased bone density) and wear and tear of the joint with subsequent destruction of cartilage. Mostly elderly people are susceptible to these processes. Subsequently, various types of arthrosis arise. Ultrasound clearly shows these processes and the condition of the joints (for example, narrowing of the gap between the joints, irregularities).
Joint inflammation
Inflammation is a normal reaction of the body to the ingress of pathogenic bacteria. For any manifestations of inflammatory processes in the joints (pain, swelling, redness, limited mobility, crunching, fever), you must immediately consult a doctor to undergo an examination and receive the necessary treatment. Neglected inflammatory processes lead to chronic diseases (gout, various arthritis) and even disability. During an ultrasound of joints and limbs, inflammation is indicated by free fluid in them.
#!UZIseredina!#
Advantages of ultrasound over other examination methods
Pathologies in the hip joints can be identified using the following research methods:
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT;
- arthroscopy.
The advantages of ultrasound research are the following:
- No contraindications.
- Painless.
- Safety. Compared to x-rays, since it does not irradiate the patient.
- Affordable price. Compared to MRI and CT, the price is approximately 5-6 times lower.
- Without violating the integrity of skin tissue structures. Compared to arthroscopy.
- Speed. Allows the doctor to see the pathology during the examination.
Due to the fact that this type of diagnosis is safe, it can be prescribed to pregnant women who very often have pain in the pelvic bones.
What is better, ultrasound or x-ray?
Very often, the doctor prescribes x-rays of the hip joints. This method, like ultrasound, is accessible, but has the following disadvantages:
- X-ray irradiation. Radiation occurs in small doses, but therefore such diagnostics cannot be carried out frequently.
- Insufficient information content. The surrounding tissues overlap the joint being examined.
- It is impossible to assess joint function.
- The surrounding tissues are not visible without the introduction of special contrast.
X-ray examination has the following contraindications:
- allergy to iodine;
- kidney and liver pathology;
- tuberculosis in the open stage;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- serious human condition.
These contraindications are relative, and the appointment of an x-ray examination remains the prerogative of the doctor.
The final decision on whether to prescribe an ultrasound or an x-ray should be made by the doctor, because there are diseases that are not visible on an x-ray, and pathology can only be seen using sonography, due to the fact that it clearly shows the tissue surrounding the joint.
Fluid in the joint capsule
Synovitis is a set of symptoms indicating inflammation of the synovial bursa, which contains synovial fluid. Sonography clearly shows the presence of fluid in the synovial capsule. Therefore, with this disease, an x-ray examination may not show anything, since only the bone structure and articular surfaces are visible on the x-ray.
Bursitis
Bursitis is an inflammation of the synovial fluid that prevents the joint from rubbing against bone, muscle, and tendon. More often, this disease affects women who are intensely involved in sports.
Soft tissue injuries
Ultrasound of the soft tissues surrounding the joint allows us to assess their condition in various injuries and injuries. On an ultrasound of soft tissues, the doctor can see the following indicators:
- Hematoma size.
- Is there blood around the joint?
- Are soft tissues affected by tuberculosis and cancer of the bone structures of the pelvis?
- The condition of the lymph nodes located near the hip joint.
- Whether the soft tissues have been affected by joint inflammation and the degree of inflammation.
- Is there a systemic disease in the hip joint that also affects the soft tissues surrounding it?
Thus, we can conclude that diagnostics using an ultrasound device is fundamentally different from diagnostics using X-rays, as it allows the doctor to more accurately make a diagnosis.
Ultrasonography has firmly established itself in rheumatology as an accessible and informative method for studying joints and surrounding tissues. The availability of this method allows doctors to timely detect an incipient disease, which significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment and the patient’s recovery rate.