Rating: 5/5 (2)
A pregnant woman undergoes a lot of medical examinations, which are mandatory for this group of the population in our country. Ultrasound (ultrasound diagnostics), as one of the many modern diagnostic methods, is especially important for a woman during her pregnancy and is called the “gold standard” for diagnosing fetal pathology. It is he who is able, without a detrimental effect on both the expectant mother and the fetus, to tell the doctor about the satisfactory or poor condition of the baby in the womb. When and how many times are ultrasounds performed during pregnancy?
What is ultrasound
An ultrasound examination is a visualization on the screen of a special ultrasound machine of structures that differ in their echogenic (that is, reflect ultrasonic waves) activity of structures.
The operation of ultrasound is based on the phenomenon of different echogenicity of the tissue elements of the organ under study, as a result of which they are displayed differently on the screen, which provides the specialist with the convenience of most accurately assessing the visualization results. This is a non-invasive technique, which means it is absolutely harmless for mother and baby .
There are several types of ultrasound scanning in pregnant women, which include:
- Fetometric study , in which the doctor can determine with absolute accuracy the timing of gestation and the presence of pathology in the development and growth of the baby by measuring the size of various parts of his body.
- Ultrasound with Doppler , which helps to analyze the state of vascular blood flow.
- Three-dimensional , the indication for which is a gestation period of more than 24 full weeks.
- Four-dimensional , which visualizes the child in the mother’s womb even more accurately and in detail.
This type of diagnostic study of a pregnant woman and baby shows the doctor how the pregnant uterus is located, what size it is, what is the condition of its contour and the structure of the amniotic membranes. The length of the cervical canal and its structure are assessed. It is possible to analyze the condition of nearby groups of lymph nodes.
What not to eat before the test
The diet a few days before an abdominal ultrasound should not contain foods that contribute to increased gas formation:
- milk and products made from it;
- cauliflower and white cabbage;
- beans, peas;
- onion;
- radish, radish;
- mushrooms;
- whole grain bread and boiled cereals (except rice);
- apples, pears;
- grape;
- peaches;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- juice, sparkling water.
If other screening tests (blood tests) are performed simultaneously with ultrasound, the list of dietary restrictions will be expanded.
How to perform an ultrasound on a pregnant woman
Ultrasound scanning can be divided according to the method of introducing the device into the female body into transvaginal (through the vagina), transrectal (through the rectum) and transabdominal (by driving along the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall).
More often, the technique is performed transabdominally and is one of the most painless and safe for both subjects, and it is also quite simple and short-lived. The patient is asked to lie down completely on the couch, but a semi-sitting position is also possible. After taking the desired position, the pregnant woman exposes her tummy, and a special transparent gel is applied to the skin and the sensor itself for a better signal.
Using the sensor, the specialist moves through the area under study several times, making repeated drives in those areas that need additional attention. Having recorded his observations, the doctor removes the sensor. A pregnant woman wipes the gel from her skin with a paper napkin or an ordinary towel and gets dressed. All that remains is to wait for the results of the examination.
How is the ultrasound procedure performed?
The expectant mother most often comes to the sonologist's office by appointment.
Ultrasound diagnostics can be carried out in a clinic, which includes an antenatal clinic, or in a specialized diagnostic center with modern equipment (for example, if there are special indications).
How long does it take
Typically, the research procedure takes up to half an hour. The duration of the process depends not only on the quality of the equipment, but also on the experience of the diagnostician. Sometimes his assistant takes dictation.
How to do it
The first ultrasound is usually performed transvaginally. The specialist inserts the device with a condom on it into the vagina. This method, of course, can cause unpleasant experiences for shy women, but it should be remembered that the child’s health is a priority. The usual method of examination (abdominal), when the device is moved over the pregnant woman’s abdomen, is less effective in the first trimester. Signals from a small fetus are “muffled” by the layers of the uterus and muscles.
What are they watching?
During an ultrasound, the doctor records indicators indicating the condition of the embryo and the conditions of its development.
The number of embryos, the presence of a placenta and yolk sac are determined, and the size of the uterus and its appendages is measured. The size of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone and the diameter of the abdomen are recorded. The bones of the arms and legs are measured and their symmetry is established. Among the internal organs, the heart, stomach and brain are primarily examined - their location and size. Key indicators that are markers of trisomy (cases of excess number of chromosomes) and other pathologies:
- collar area size;
- development of the neural tube, its closure;
- visualization of the nasal bone.
The doctor is required to report in the conclusion about all detected abnormalities, for example, blood clots or detachment of membranes. Some of them are not fatal and can be corrected if doctors are informed in a timely manner.
Some additional information, for example, data on the smoothness of facial contours, indicating Down syndrome, cannot be obtained with outdated equipment.
Decoding
A gynecologist interprets the ultrasound results, but in case of anxiety and doubt, a pregnant woman can independently compare the parameters indicated in the conclusion with the normative ones (although only a specialist can give an accurate assessment of this information).
The coccyx-parietal size is designated by the abbreviation KTP. Its normative indicators differ at different times:
- At the beginning of the 10th week, the CTE is 3-4 mm.
- At week 11 – from 4.2 to 5 mm.
- Week 12 – CTE is 5-6 mm.
- At week 13 the figure is up to 7.5 mm.
The thickness of the nuchal translucency (TN) also varies depending on the period. At 10 weeks it ranges from 1.5 to 2.2 mm, at 11 weeks it can reach 2.4 mm, at 12 weeks - up to 2.5 mm, and in the middle of the 13th week - up to 2.7 mm.
The presence or absence of a nasal bone is considered one of the most important markers of pathologies, but a pregnant woman should not be alarmed if its size is not indicated - normally, the nasal bone cannot be accurately measured. From 12 weeks the bone size is 3 mm or more.
An important parameter is the heart rate (heart rate), in other words, the pulse of the embryo, which gradually becomes less intense in the first trimester:
- at 10 weeks – from 161 to 180 beats per minute;
- at week 11 – from 158 to 170 beats;
- 12 week – 149-173 beats per minute;
- at week 13 - from 146 to 170 beats per minute.
During a multiple pregnancy, some of these indicators may be lower, which is acceptable.
If the indicators go beyond the specified ranges, it is a reason to prescribe in-depth studies, sometimes with introduction into the placenta. Unfortunately, the consequence of procedures such as amniocentesis (puncture with amniotic fluid collection) can be fetal death or miscarriage.
At what stage is the embryo visible on ultrasound?
At what stage of pregnancy can you have an ultrasound? At 6 obstetric weeks, a pregnant woman is 100 percent sure that she is carrying a baby under her heart, since it is at this moment that his developing heart begins to beat . Ultrasound in the first weeks of pregnancy can only give results using the transvaginal method.
The transabdominal method visualizes pregnancy by the 8th obstetric week, although this is also considered a fairly early period. In general, an early ultrasound scan is necessary for a woman to not only verify the presence of a fetus, but also to exclude an ectopic pregnancy, determine the number of formed embryos and the risk of miscarriage.
How many times are ultrasounds performed during pregnancy? In the Russian Federation there is a special program for examining pregnant women, according to which they undergo 3 mandatory screening ultrasounds . Additional studies during periods of pregnancy not established by law are not excluded.
Frequency of ultrasound procedures during pregnancy
Carrying out an ultrasound of the fetus for pregnant women is often undesirable. Each pregnancy is carried out individually; after an examination, the doctor decides whether an examination is necessary and how many times it will be necessary. Possible risks to the fetus are always assessed, and the ultrasound procedure is never abused, even if the expectant mother wants to look at her baby.
There are situations when, in order to diagnose unfavorable conditions of the mother or fetus, it is vital to conduct ultrasound many times, in such cases it is harmful to ignore the study. It could be:
- with premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
- blood discharge from the genital tract;
- developmental delay of the child;
- signs of intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- presence of a developmental defect in the baby;
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus;
- harmful working conditions for the mother during pregnancy;
- gestosis.
An ultrasound helps to manage pregnancy, timely diagnose dangerous conditions for the mother and fetus, and determine the method of delivery, which is necessary for every expectant mother. Ultrasound is a diagnostic procedure that is used strictly according to indications. In this case, it is not harmful to the fetus.
How many times did you have an ultrasound scan during pregnancy? Share in the comments what you think - is ultrasound harmful to the fetus? Share the article with your friends, all the best.
First scheduled ultrasound during pregnancy
When and how many weeks is the first ultrasound done during pregnancy? It is carried out during 10-14 obstetric weeks of the baby’s intrauterine life. This stage of the study is necessary to assess placenta previa and signs of hereditary pathology of the fetus in the form of developmental anomalies. The place where the pregnancy began is also monitored, that is, the location of the implanted embryo, the presence of motor activity of the child, and the usefulness of the chorionic villi.
The first screening can reveal such pathological conditions of the fetus as:
- abnormal placenta previa;
- abnormal structure of the fetus;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- reduction in the baby's movements until death;
- chorionic insufficiency.
Is there any harm from ultrasound to the fetus?
Many opponents of this diagnostic method argue that the potential harm of ultrasound in early pregnancy is based on the thermal and mechanical effects of ultrasound.
The thermal effect is determined by the ability of human tissues to absorb energy emanating from an ultrasonic wave. Thus, the degree of heating of organs and other internal structures directly depends on the amount of ultrasound energy. At the same time, the intensity of the ultrasonic waves used for the study does not exceed the boundary values.
The mechanical effect is explained by the vibrations of small particles. If the ultrasound pressure exceeds the maximum limit, a cavitation effect will occur, or the formation of microcavities. Subsequently, they collapse under the pressure of the tissues surrounding them.
However, all modern devices are equipped with limiters that prevent acoustic power limits from being exceeded. This means that the safety of ultrasonography depends on two criteria.
- A medical institution must use only certified ultrasound devices tested by a special metrological service.
- The doctor who conducts the study must be perfectly aware of the safety rules and follow all instructions for operating the equipment.
Since only certified and highly specialized equipment is used in obstetric practice, the doctor will in no way be able to exceed the permissible power and harm the fetus . Therefore, talk about how harmful ultrasound is during pregnancy is completely unfounded.
Second planned ultrasound during pregnancy
At what stage of ultrasound during pregnancy? It is carried out in the period from 20 to 24 obstetric weeks .
The diagnostic value of this episode of research on a pregnant woman is increased due to the greater possibilities in determining the abnormal structure of individual parts of the baby’s body. This is due to the active differentiation of all organs and systems of the baby by this time. The child is already more clearly visible; assessing the condition of its membranes is no less important.
At this stage, it is possible to detect the pathology of anencephaly, polycystic and hydronephrosis of the kidneys, megacystic (enlarged bladder of the baby), pathology of the respiratory and digestive systems. Confirmation of the four-chamber structure of the heart is especially important.
The effect of ultrasound on the fetus
The negative impact of ultrasound on the fetus has not been proven.
Ultrasound only slightly heats the cells, which can cause an unpleasant sensation during the procedure and nothing more. But experts do not agree on a single opinion; there are those who are for and those who are against. The cause-and-effect relationship of pathologies and diseases from ultrasound has no scientific basis.
Most doctors and physicians have a positive attitude towards this type of research. Timely ultrasound, thanks to its accuracy, has more than once saved the lives of patients and children in the womb.
In the first months
The first months of pregnancy are the most important: the formation of organs and vital systems of the fetus occurs. Numerous external factors can negatively affect development.
The first ultrasound is done to confirm the presence of pregnancy. The procedure allows you to detect the fertilized egg at 3-4 weeks. But it is possible to determine whether it is empty or not only by the fifth week. The examination is most often carried out vaginally: a narrow tube with a sensor at the end is inserted into the vagina and examines the internal organs. This method is the most effective and is allowed 2-3 weeks after a missed menstrual cycle.
Experts have not proven the negative impact of ultrasound on the fetus.
The procedure is repeated between 10-13 weeks to:
- ensure fetal development;
- consider its position;
- exclude ectopic pregnancy.
An ultrasound may be prescribed in case of sudden bleeding and deterioration of the mother's condition in order to find out the cause and condition of the embryo.
In the second trimester
Routine midterm ultrasound examinations are performed between 19 and 23 weeks. This is necessary for:
- assessment of the formation of fetal organs and systems;
- determination of size and length;
- identifying the functionality of the placenta and its attachment site;
- to eliminate the risk of chromosomal pathologies and abnormalities;
- determining the amount of amniotic fluid;
- to find out the sex of the child (at the request of the expectant mother).
Gynecologists consider this procedure safe for the child and woman. There have been no recorded cases of negative effects of ultrasound on the fetus.
Before birth
The last planned ultrasound is done shortly before the expected date of birth, approximately from 32-36 weeks.
This allows you to see the condition of the child and identify deviations that appear at this stage. You can also examine the umbilical cord and detect entanglement. The main importance of the study in the last period is to clarify the date of birth, the location and readiness of the child, monitoring the placenta and choosing the method of delivery: natural or cesarean section.
Third planned ultrasound during pregnancy
At what stage is the third ultrasound screening during pregnancy? A woman is sent to it at 30-34 obstetric weeks . Usually everything goes like a transabdominal examination. Particular attention is paid to fetometric parameters, such as:
- biparietal size (BPR);
- length of humerus and femur;
- length of forearm bones;
- abdominal and head circumference;
- chest diameter;
- fronto-occipital size (FOR).
The condition of the woman’s birth canal, amniotic membranes, uterus, respiratory and cardiovascular systems is not excluded from the study. At this stage, it is very important to exclude intrauterine hypoxia of the child, which is a trigger factor for many dangerous conditions in a newborn child.
Ultrasound - 2nd trimester of pregnancy
The timing of pregnancy ultrasound in the 2nd trimester corresponds to 20-24 weeks of gestation. At this stage they look and track:
- growth and weight gain of the fetus in dynamics compared with the indicators of the first study;
- intrauterine defects are more accurately determined;
- the amount of amniotic fluid is diagnosed;
- The placental membrane is assessed.
In the middle of pregnancy, you can clearly listen to the baby’s heartbeat and, if the baby is in the right position, determine the gender. It is also necessary to perform an ultrasound so that the doctor compares the norms of anatomical indicators with these parameters of intrauterine formation. During the decoding of the study, specialists evaluate the blood circulation between the mother, placenta and fetus, study the placenta according to the degree of maturity, its structure and location, since normal intrauterine formation depends on these parameters. Often, thickening of the placental membrane is associated with infectious and pathological processes in the body or with the presence of diabetes.
Ultrasound before birth
This is the last ultrasound examination during the pregnancy period. It is carried out at 34 weeks with the aim of assessing the condition of the placenta, fetometric parameters, fetal position before birth, and preventing the umbilical cord from being entangled around the fetal neck.
This ultrasound is important, first of all, because in the period before birth the baby’s condition is especially unstable, because at any moment he can be born. And the specialist can determine not only pathological presentation and entanglement, but also severe hypoxia of the baby, which significantly complicates the early neonatal period and places the newborn in the neonatal pathology department.
Unscheduled diagnostics
Three scheduled ultrasound examinations must be completed. However, in addition to scheduled visits to the diagnostic room, there may be additional ones. They are prescribed in cases where some pathologies are identified or the diagnosis needs to be clarified. Often, after a planned examination, repeat examinations are carried out two to three weeks later to obtain confirmation or denial of suspicion.
Sometimes pregnant women refuse an ultrasound, citing the fact that it will have a negative impact on the development of the child. But modern diagnostic devices are absolutely harmless. This has been proven by numerous studies in this area. On the contrary, diagnostics helps not only to monitor the development of pregnancy, but also to identify parallel dangerous diseases. The observing gynecologist will not prescribe an ultrasound examination without good reason.
Why might you need an unscheduled ultrasound?
The normal course of pregnancy usually excludes the use of episodes of additional ultrasound examination of the fetus. However, if there is vaginal bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort, the doctor not only has the right, but also must prescribe an additional ultrasound. The use of additional procedures when there is a threat of premature termination of pregnancy and suspicion of an ectopic location of the ovum is not discussed.
How often are ultrasounds performed throughout pregnancy?
During the nine months of bearing a child, ultrasound examinations are performed at least three times, one in each trimester. For confirmation or additional control, the number of ultrasounds may be greater.
During pregnancy, ultrasound allows timely detection of pathologies and diseases, some of which can be treated in utero. Therefore, there is no exact number of procedures. This is purely individual. The main periods for carrying out the procedure by week:
- 12-13. During this period, one can consider the features of the formation of organs,
- 20-22;
- 32-33.
Indications for additional ultrasound examination:
- bleeding;
- threat of premature birth and termination of pregnancy;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- lack of fetal activity or a sharp decrease;
- if the placenta is located incorrectly.
Video about ultrasound during pregnancy
In order to better understand the essence and significance of the screening periods established by the protocols using ultrasound in pregnant women, you can watch the video. It describes in detail the timing of routine ultrasound during pregnancy, evaluation parameters, the advantages of this method and its wide range of capabilities.
And to find out even more information about planned and additional ultrasound examinations, discuss this issue with each other in the comments. Share your impressions after undergoing this diagnostic procedure and ask questions that interest you, because a live discussion of the topic with those who have undergone this procedure is very useful for women planning a pregnancy.
We recommend reading:
- Discharge during early pregnancy Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) for pregnant women: what is it Hiccups in the fetus during pregnancy Norm of TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) during pregnancy
Third ultrasound
In the absence of any deviations from the normative indicators, the next ultrasound scan is carried out according to plan between the 32nd and 34th weeks of pregnancy, and Doppler measurements - no earlier than a month later, since the development of any circulatory disorders occurs gradually and they are diagnostically significant become within a month, if during this time no other complications have arisen, for example, changes in the hemostasiogram (blood clotting test) have not appeared. In this case, the doctor will recommend Doppler testing earlier than scheduled. If during the research any disturbances are revealed (reduced blood flow in the vessels being studied, retardation of the fetus in growth and development), and the patient needs therapeutic measures, which can be carried out both outpatiently and inpatiently, depending on the degree of the identified disturbances , the doctor will prescribe a repeat ultrasound examination and Doppler ultrasound at least one more time after the appropriate course of treatment. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated, and the number of ultrasound examinations increases accordingly.
High precision research
In cases where a first-level ultrasound scan (in a antenatal clinic) has detected certain problems or the doctor has any doubts about its results, the patient is referred to an ultrasound scan of the second level of obstetric screening - to prenatal diagnostic centers, medical genetic centers and other similar institutions equipped with high-resolution ultrasound scanners and staffed by expertly qualified medical personnel.
In such cases, the number of ultrasound examinations increases accordingly. In the third trimester, the diagnosis of congenital malformations of the fetus is still relevant. Although all gross malformations are detected, as a rule, during earlier ultrasounds, such malformations as hydronephrosis of one or both kidneys (fluid accumulation in the renal pelvis), megaureter (enlargement of the fetal ureter) may not be detected in earlier stages of pregnancy for a number of reasons. diagnosed. One of these reasons may be the inconvenient location of the fetus in the uterus for examination during examination in the second trimester. In the case of diagnosing any defect, depending on its complexity, the question of its correction is decided: is urgent surgical intervention immediately after birth necessary to save the baby’s life, or is it possible to delay the operation somewhat if this defect does not pose a danger to the life of the newborn? . Sometimes, if severe defects are detected, the issue of terminating the pregnancy early (before the 40th week of pregnancy) is decided by introducing medications that promote the onset of labor.
The objectives of ultrasound examination in the third trimester are:
- assessment of fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow, since disturbances in this system can cause pregnancy complications such as intrauterine growth restriction;
- assessment of the size of the fetus, its correspondence to the gestational age;
- the location of the placenta (complete or partial (marginal) placenta previa, which is important for choosing the method of delivery - vaginal delivery or cesarean section), its “maturity”, i.e. readiness for the upcoming birth;
- the position of the fetus in the uterine cavity (its presenting part; what faces the exit from the uterus - the head or pelvic end), which is important for determining the tactics of labor management.
The last point is very conditional, since the child in the womb and later in pregnancy (after the 34th week), although rarely, can turn over from the correct position (head down) to the incorrect one - oblique or transverse position. In some cases, the baby can even turn 180º and position his legs towards the exit of the uterus.
Three-dimensional ultrasound
Separately, it is worth mentioning three-dimensional ultrasound examination, which is currently a new, modern and, importantly, fashionable research.
Many future parents attend this procedure with interest, sometimes forgetting that it is an additional study, although a qualified specialist with modern diagnostic capabilities (a good ultrasound machine) can take all the necessary measurements, examine everything and draw appropriate conclusions using two-dimensional ultrasound. What attracts future mothers and fathers so much? Firstly, such a study allows you to obtain an image on the screen in three projections at once, i.e. voluminous, which means more revealing, close to photographic, which is what future parents strive for. Secondly, this test allows real-time recording of fetal movements in digital photo format, as well as VHS (video cassette), CD or DVD in three-dimensional format. And finally, such a study makes it possible to view and analyze the resulting images over long periods of time, which can be important for the doctors conducting the study. All abnormalities detected by ultrasound at this stage of pregnancy, in particular those related to the condition of the placenta, require qualified medical intervention to avoid the birth of an immature baby with low weight.
In conclusion, I would like to say that ultrasound during pregnancy is of great importance and should not be neglected. No matter how large, in your opinion, the number of these studies is - three (for physiological pregnancy) or many more (in the presence of pathology), you should undergo all the procedures prescribed by the doctor. After all, a timely ultrasound examination can help you give birth without complications, and your baby can be born healthy.
The last planned ultrasound is performed at 32-34 weeks, however, in some cases, additional research may be necessary before birth, for example, to clarify the position and presentation of the fetus (more often in overweight women), as well as the state of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus and placenta and intrauterine condition of the fetus, which may affect the choice of delivery method (cesarean section or vaginal delivery).
Obtained results
An ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman includes examination of the uterus with the fertilized egg inside, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. If necessary, an examination of the kidneys, bladder, and cervix is prescribed. Ultrasound shows pathologies on the part of the fetus and the maternal body.
Pregnancy criteria
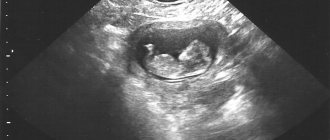
The fact of pregnancy is confirmed by the detection of a fertilized egg with an embryo inside the uterine cavity. The fertilized egg in the picture is represented by a rounded gray spot with light and dark inclusions. It is located on one of the uterine walls. The image does not show intrauterine pregnancy if the fertilized egg is attached inside the fallopian tube or in the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound results for certain weeks of pregnancy:
- 4 weeks - an embryo is detected inside the fertilized egg;
- Week 10 - major organs are formed, genetic abnormalities can be identified;
- 16 week - formation of the placenta;
- Week 20 - determination of anomalies of internal organs and skeleton;
- 30 week - fetal position, developmental defects.
From the third month, all parts of the embryo’s body are visible inside the fertilized egg. The largest spot is the head. The smaller elongated spots are limbs on which fingers are visible.
Table of obstetric ultrasound parameters:
| Index | Characteristic |
| Fetus | Quantity, transverse or longitudinal position |
| Presentation | Pelvic or head |
| Fetometry | Size of head, torso, limbs |
| Collar width | Determined at 12 weeks - no more than 3 mm |
| Heart rate | Normal - 110-180 per minute |
The gestational age according to ultrasound is always slightly longer than according to menstruation. Delayed menstruation is detected by a woman 2 weeks after conception. Ultrasound determines the period from the moment the egg enters the uterus - 3-5 days after conception.
Pathology indicators
Deviations in the development of pregnancy are detected at any stage.
- False pregnancy. A fertilized egg is formed, but there is no embryo inside it. It can be determined from 10-12 weeks. Inside the light gray spot in the picture there is a black space instead of white-gray inclusions.
- Bubble drift. Anomaly in the development of membranes. The picture shows many dark bubbles in the place where the embryo should be.
- Down syndrome. The earliest time for determination is 12 weeks. A sign is a thickening of the collar area of more than 3 mm. At week 20, the syndrome is determined by the length of the nasal bone.
- A marker of IUI (intrauterine infection) is an insufficient amount of amniotic fluid.
- Placenta previa is its location at the uterine os. The photograph shows an oval dark spot in the throat area to which the fetus is attached. Occurs due to multiple scars on the uterus.
- Cervical insufficiency. Determined by its shortening of less than 12 mm.
- Umbilical cord entanglement. The photo shows a dark tourniquet around the child's neck.
- Defects of the heart, limbs, brain.
The specialist conducting the examination provides a description of what he saw. A diagnosis cannot be made based on this conclusion alone. A sonologist can make a mistake for a number of reasons. Visualization of the uterus can be difficult due to the patient’s obesity and excessive gas formation. The child may lie in such a way that his position seems pathological.
After the procedure, you should contact a gynecologist so that he can confirm or rule out the detected pathologies. Often it is necessary to perform ultrasound in dynamics. During pregnancy, the fetus turns several times, and by birth it takes the desired position. If chromosomal abnormalities are suspected, a woman is recommended to consult a geneticist.
Watch a master class from a gynecologist on identifying pathologies using ultrasound:
Ultrasound 3rd trimester
Ultrasound in the third trimester is done between 31 and 34 weeks of gestation in order to exclude the presence of pathological processes or to be prepared for complications as labor progresses.
Ultrasound is used to look at the size of the fetus, its location in relation to the cervix, and calculate a more accurate date of delivery. Basically, deciphering the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is associated with the functional characteristics of the placental membrane. The location of the placenta and the degree of maturity are studied, since not only the choice of birth method, but also the further development of the baby depends on these parameters. The last ultrasound helps assess the formation of the baby’s internal organs and how ready he is for independent living. If hypoxia or malnutrition is detected, drug therapy is prescribed, and doctors prepare to provide emergency care immediately after birth.
Cost of the procedure
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes an ultrasound examination at the antenatal clinic at her place of residence. If she is registered, the examination will be free. The procedure is performed by private medical centers. The cost depends on the type of examination.
| City | Cost, rubles |
| Moscow | 500-3500 |
| Saint Petersburg | 550-4000 |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-3500 |
| Novosibirsk | 550-4500 |
| average price | 525-3875 |
Ultrasound examination is an important procedure during pregnancy. It can be done for the first time in the fifth obstetric week, that is, 35 days after conception. A woman has the right to refuse the study. In this case, she will not know the gender of the unborn child, and there will be no way to timely identify abnormalities in the baby’s development.
Ultrasound is performed once per trimester, more often if necessary. When to do the test is determined by the gynecologist when registering the woman. The diagnosis is safe for the expectant mother and child.
Share your experience of undergoing an ultrasound in the comments. Tell your friends about the information you read on social networks; it will be useful not only for expectant mothers, but also for fathers.