Features of ultrasound during pregnancy after IVF are significantly different from natural ones. During artificial insemination, ultrasound is often prescribed several times more often, and the first ultrasound is performed a little earlier than usual. It allows you to confirm the fact of successful embryo transfer and make sure that the pregnancy is proceeding successfully. When is the first ultrasound performed and what is looked at during the analysis?
What is IVF and why is it done?
To understand all the features of ultrasound, you need to know what in vitro fertilization is. The procedure began to be practiced in 1978. She helps infertile couples get pregnant. Feature of IVF: the egg is fertilized outside the woman’s body.
Eco is used for various types of infertility. Both partners or only the woman can be infertile. The main age of people who undergo the IVF procedure is thirty years or more.
The in vitro fertilization procedure proceeds in the following sequence:
- Initially, a woman’s follicle growth is enhanced with the help of hormones. By doing this, doctors achieve as much maturation of the eggs as possible. Only in this case the chances of getting pregnant increase significantly.
- Next, the doctor removes mature follicles from the woman’s body. To do this, he uses a very thin needle and an ultrasound probe.
- Next, specialists select eggs that differ in the required maturity. Sperm are collected from semen.
- Before sperm and eggs are united, the latter are kept for several hours in a specialized incubator. After crossing, the embryo is left to mature for 72 hours. It is then transferred to the uterus.
- From two to five embryos are usually implanted into the uterus. This number is necessary for more productive conception.
- At the last stage, the woman is prescribed hormone therapy so that the embryo is well established.
Ultrasound examination can be done 12-14 days after the procedure for introducing embryos into the uterus.
What examinations need to be completed
After the end of the next menstruation, which completed an unsuccessful protocol, the woman must do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, as well as hysteroscopy, which will show all the features of the uterus and endometrium. It is necessary to donate blood for hormones, general and extended blood tests, and urine tests.
Couples over 35 years old, as well as couples who have had three or more unsuccessful transplants, need to visit a geneticist and do the necessary compatibility tests and karyotyping. An immunogram done in the clinic will help identify possible immune factors in which a woman’s body rejects pregnancy as something foreign.
If a miscarriage or miscarriage occurs, the woman will have to do all the same tests, and in addition to them, it is advisable to obtain a conclusion from a genetic laboratory that examined embryonic tissue after miscarriage or spontaneous miscarriage. With a high degree of probability, such a study will show whether the baby had genetic pathologies or whether his death was due to other reasons.
HCG hormone
If the procedure is successful (IVF), the woman will soon begin to feel the first signs of pregnancy. This happens for the following reason. After replanting, time passes for the cell to implant. This takes about three days. But in some cases, the body takes up to 10 days. This time period is considered normal and does not cause concern to the doctor. After the cell enters the uterus and settles there, an important hormone begins to be released in the body: the hCG hormone. It is he who influences a woman’s well-being.
To determine this hormone, it is better to do a blood test for hCG rather than a pharmacy test strip. A blood test gives a more informative answer about pregnancy. It shows whether conception has taken place or not, the timing of pregnancy, and the course of pregnancy. Blood tests are effective at very early stages. The blood will give results 2 weeks after IVF. Then the pregnancy cannot yet be seen on an ultrasound. The test must be taken in the morning.
The test results are usually interpreted as follows: negative (there is 100% no pregnancy), positive (100% pregnancy) and weakly positive.
A weakly positive result may indicate the following:
- Laboratory error.
- The embryo implanted later than expected.
- The embryo is located outside the uterus.
- Spontaneous miscarriage.
If the blood test gives a weakly positive result, it should be repeated after 2-3 days.
How does IVF happen?
In vitro fertilization is popularly called in vitro fertilization. It is in laboratory conditions that the father's sperm merge with the mother's egg, which begins to divide and leads to the appearance of embryos. Next, the procedure of transferring embryos into the female uterus takes place, where one or several at once continue their natural development. But only in case of pregnancy. This is the most intriguing point. The fact is that, according to statistical data, not every embryo transfer process promises a woman pregnancy. The procedure ends with the successful implantation of embryos in the uterine cavity only in 35% of cases.
To ensure a higher success rate for the procedure, the expectant mother’s body is stimulated with hormones before the fertilized egg is transferred. It is thanks to this that several eggs can mature at once. Without hormonal drugs, doctors would not be able to plant several embryos into the uterine cavity, which means that the chances of pregnancy would be much lower. The stimulation process takes two weeks. The expectant mother injects the medications into the skin of the abdomen herself. Diferelin injections are usually prescribed. For pregnancy to occur, it must also be administered on the second and third days after embryo transfer.
What else can you do to help your body to make pregnancy more likely? One of the auxiliary drugs is piroxicam. It must be taken in tablet form an hour before IVF. It promotes better blood supply to the uterus and other female organs, so that the fertilized egg can take root with great success.
In general, stimulation of the body in medicine is called the IVF protocol. And there are two types: short and long.
The doctor prescribes a long protocol with drugs that suppress ovarian function. Seven days before menstruation, a woman begins to take hormonal medications that block the production of the hormone responsible for ovulation. After two weeks, the size of the follicles in the ovaries becomes no more than 15 mm. Then the doctor prescribes gonadotropin drugs, the dose of which is strictly regulated by test data and ultrasound. After some time, the required follicle size is formed, and the drugs are discontinued, and the hCG drug is administered for puncture. In general, a long protocol can last up to six weeks. It is worth noting that the role of ultrasound in this case is not replaceable. Folliculometry, or ultrasound of ovarian function, is prescribed even when infertility is established. Ultrasound also helps in the process of IVF preparation, during its process and after.
The short protocol in its implementation resembles the first option, only in this case the function of the ovaries is not suppressed. Stimulation of the body lasts four weeks and begins on the third day of the cycle. This protocol is prescribed to women over forty and those who have a poor reaction to a long protocol. The second option is much easier for the female body, and its side effects are minimized.
Pregnancy and signs
Typically, the expectant mother experiences the following symptoms:
- Mood swings: from good to terrible. Emotionality is harsh.
- Breast swelling.
- Signs of early toxicosis.
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Change in nipple color.
- Hot flashes and chills (speak of hormonal changes).
- Increase in basal temperature.
- Skin redness.
Often there are no first signs of pregnancy. In this case, an hCG test will allow you to find out about pregnancy. After receiving a positive result, you should go for an ultrasound examination.
Reaction of husband and loved ones after unsuccessful IVF attempt
It is no less difficult for the husband, because it is also difficult for him to come to terms with the fact that he will not have the heir that he and his wife have dreamed of for so long. A man can also experience a variety of experiences about this. And relatives who were expecting good news are faced with a harsh sentence. Their hopes and plans are destroyed. But no matter how difficult it is for relatives and husband, their experiences cannot be compared with what the woman herself feels.
The most correct thing in such a situation would be to provide her with moral support. We need to show the woman that she is not alone with her problem, that she is still loved and accepted. She should feel that the unsuccessful IVF procedure did not in any way affect the attitude towards her on the part of her relatives and her husband. In order not to further traumatize a woman, you should not often try to talk to her about such a topic, unless she herself does not want to.
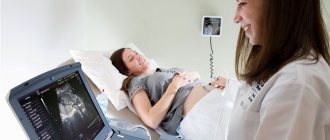
When do they do an ultrasound after IVF?
The IVF procedure is considered complex. Therefore, ultrasound examination after it is carried out with special care.
The first ultrasound is prescribed between 21-28 days after IVF. Further, in the process of bearing a child, 2 more examinations will be needed:
- Second ultrasound: 16-21 weeks.
- Third ultrasound; 32-36 weeks.
The ultrasound examination procedure is absolutely harmless to the mother and fetus. It is necessary because it allows you to accurately determine the condition of the fetus, identify its pathologies and provide information about the exact duration of pregnancy.
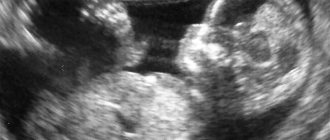
Ultrasound: first trimester
The first ultrasound confirms the fact of pregnancy and determines the viability of the fetus. In addition, other indicators are assessed:
- Where is the fertilized egg located (in the uterine cavity, in the tube or in the ovaries).
- How many embryos are there?
- What condition are the ovaries in?
In some cases, the ultrasound may be repeated. The purpose of a repeat examination after the first screening is:
- Confirmation of the fact of fixation of the fertilized egg and the positive nature of the process.
- Determination of the heartbeat and heart rate of the fetus.
At the first ultrasound, very dangerous pathologies are excluded. These include:
- Down syndrome. The child will have serious heart problems, a flat face and severe developmental delays.
- Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome. Downa's children can live 40 years, but babies with these diseases will not last even one year.
Ultrasound with high accuracy will give results about the health of the unborn fetus.
If the results of artificial insemination are negative, then you will still need to do another ultrasound screening. It will help the doctor determine the likely cause of the failure. Repeated ultrasound after unsuccessful IVF is an important step towards further successful conception.
Ultrasound: second trimester
Features of ultrasound after IVF in the second trimester look like this:
- First, hormone levels are determined.
- Next, hCG and free estriol are assessed. This once again eliminates the possibility of serious illnesses in the fetus.
- Then the following defects are excluded: absence of the cerebral hemispheres, underdevelopment of the abdominal wall, pathology of the neural tube. Other parameters of the study are determined by the doctor.
In the second trimester, they look not only at the woman’s organs (uterus, kidneys, ovaries), but also attentively examine the baby’s formed insides. The condition of the placenta, blood flow rate and oxygen supply to the baby are also assessed. For women after IVF, this ultrasound is performed with special care.
Ultrasound: third trimester
At 32-34 weeks a third ultrasound is performed. During it, the placenta is also examined, blood flow is assessed and the actual size of the fetus is compared with the gestational age. In addition, they look at the health of the fetal organs and the features of their structure.
Delivery after IVF occurs more often than after natural pregnancy. Therefore, the 37th week and beyond is a very dangerous period.
A pregnant woman is obliged to go to an ultrasound, prepared in material terms. She must bring with her to the procedure: slippers (to maintain cleanliness and sterility in the medical center), a diaper (in order to lie on it), a condom (you will need to give it to the doctor, he will put the product on the transvaginal sensor), a towel (in order to to wipe the special gel from the skin).
The procedure will end with the issuance of an ultrasound protocol. It will contain the following information:
- Biparistal size of the fetal head.
- Coccyx-parietal size.
- Dimensions of the nasal bone.
- The number of heart contractions (beats) per minute.
- Thickness of the collar space.
All data is indicated in mm. The ultrasound protocol must be shown to the doctor.
Thus, ultrasound not only confirms successful IVF, but also reveals dangerous pathologies. Particular attention is paid to multiple births. A woman should be ready for this. This is a common occurrence during IVF. Pregnancies with two or more fetuses usually do not last nine months. Delivery occurs a little earlier. There is also a serious risk of spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage).
In most cases, pregnancy does not occur after IVF. There is no point in stopping if you don't get the result.
Usually pregnancy does not occur for the following reasons:
- Incorrect actions when replanting.
- Pathology of the fallopian tubes.
- Poor quality embryo.
Most likely, pregnancy will occur after the second or third attempt.
If the first ultrasound was successful, this does not mean that subsequent studies are not needed. It is extremely reckless for a woman to think this way. It is necessary to visit a doctor and undergo repeated ultrasounds. In addition, the expectant mother should be careful about her body. It is imperative to inform your gynecologist about unusual symptoms. In this case, the doctor may prescribe a repeat ultrasound examination.
What the study shows
During IVF, several embryos are used. Sometimes only one of them begins to develop. In many cases, everyone takes root, so it is very important to know their exact number. This is necessary to remove excess embryos as early as possible. Ultrasound is used for this purpose.
Sometimes, if the replantation fails, an ectopic pregnancy may occur. In this case, the fetus, instead of the uterus, is attached to the fallopian tube or to the ovaries. Ultrasound examination helps to notice this pathology at an early stage.
The size of the embryo transferred to the uterus can indicate problems with its development. The following is considered the norm for the embryo:
- internal diameter is 18-22 mm;
- The coccygeal-parietal size is 3-6 mm;
- The diameter of the yolk sac is 3 mm.
Types of ultrasound
Ultrasound can be of several types:
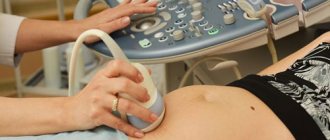
- Transabdominal ultrasound. The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall. A sensor moves across the woman's stomach. The recorded information is displayed on the monitor. This ultrasound is harmless and does not cause any discomfort. Transabdominal examination is used in the second and third trimester. By this time, the child has reached a large size and can be seen through the abdominal wall. No preparation is required for this type of ultrasound.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. The examination is carried out using a special sensor, which is placed in the vaginal area. Ultrasound is good for early pregnancy, when the fetus is still very small and cannot be viewed through the abdominal wall. The vaginal sensor allows you to see the uterine cavity and fertilized egg through a thin inner wall. The study requires little preparation. The woman should present for examination with an empty bladder and bowels. It is advisable to review your diet a few days in advance to avoid gas formation during the procedure.
- Combined ultrasound. If the picture is not entirely clear, then the above studies are combined.
An innovation has appeared in timely medicine - this is 3D research. It allows you to see on the monitor screen exactly where the embryo is and what size it is currently. Mom and dad will be able to see the birth of their baby and, if desired, take a photo of him. The third week of pregnancy will give the heartbeat of the unborn child using ultrasound.
After IVF, the transvaginal method is used as the first ultrasound. It is he who will help the doctor examine the fertilized egg and count the number of embryos.
It is known that IVF does not provide a 100% guarantee of pregnancy. A positive result is observed only in 40% of cases. Very often (25%) several embryos begin to develop in a woman’s uterus. This indicates a multiple pregnancy. A woman can become a woman of two or three children at once. Rarely does an ectopic pregnancy occur after IVF.
Further research
In addition to ultrasound, after successful IVF, the expectant mother undergoes the following examinations:
- fetal screening;
- analysis of hormone levels;
- Doppler.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo tests common to pregnant women - a general urine and blood test, blood for AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis, group and Rh factor.
Ultrasound after IVF is one of the most important diagnostic procedures. It allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of medical intervention and determine the order of further actions. There is no need to be afraid for the health of your unborn child. This method has no contraindications and is safe for everyone. It is better to undergo examination several times while carrying a baby. This will help detect any developmental pathologies.
If any of you have undergone an ultrasound after IVF, please share your experience with others. Leave feedback about the procedure in the comments, repost and be healthy.
Reviews
Yesterday I comforted my little sister. Her anxiety was caused by the upcoming ultrasound. She recently had IVF (this is her third attempt). The hCG test gave a joyful positive answer. She is shaking so much over her stomach that she even began to refuse to go to the ultrasound specialist. My mother and I tried to convince her that it was harmless. Not listening. She is simply afraid of any interference. My sister is especially against vaginal insertion of the sensor. She is afraid that the doctor will harm her something and this will certainly affect the fetus. In general, my sister is a modern girl. And that's not like her. I think it's all due to pregnancy hormones. And also the fact that she and her husband had been waiting for this moment for a very long time. If you can’t persuade her about the need for an ultrasound, you’ll have to force her to the medical center.
Yesterday I had my first ultrasound after IVF. I’m probably happy because IVF worked the first time. I didn't even expect it. Why did I wait so long for a natural pregnancy and didn’t go for IVF earlier? Now I blame myself for this. According to the ultrasound: everything is fine (as it should be in medical books).
Methods of carrying out the procedure
An ultrasound after IVF is performed as during a normal pregnancy. Diagnostic methods are divided into transvaginal and transabdominal. Both options are extremely rarely used. It is better to prepare for the examination in advance - refrain from eating immediately before the procedure, have a diaper, shoe covers and a condom with you.
With the transvaginal ultrasound method, a sensor placed in a special condom is inserted into the vagina. With this method, the most accurate results are achieved even at the initial stage. Due to the small size of the embryo, it is quite difficult to determine its location. To bring the ultrasound sensor as close as possible to the fertilized egg, it should be inserted transvaginally.
This method is also often used for overweight women. A regular ultrasound does not allow us to see the embryo due to fatty tissue in the abdominal area.
The transabdominal ultrasound method for IVF is used in late pregnancy. The examination is carried out in the supine position. A gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen to improve the passage of ultrasonic vibrations. As the sensor moves across the body, the resulting image appears on the screen.
Invasion of cells into the uterus
In order to obtain an embryo, male and female cells are needed, as during conception, for this purpose the mother's eggs and the sperm of the father of the unborn child are collected. For greater efficiency, several embryos are given the opportunity to form. After successful conception, the embryo remains in the laboratory for three to five days, where, under the supervision of specialists, it can develop at the initial stage.
The term of the embryo, when transferred to the uterus, is determined by the doctor himself, based solely on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body and the results of her tests. Also, the patient must undergo a preparatory course that guarantees a greater likelihood of successful implantation and engraftment of the embryo.
After the expectant mother has passed all the necessary tests and is ready for fertilization, the resulting embryo can be transferred to her uterus. This is done in a special medical center using devices designed for this purpose. During the procedure, the woman sits on a special chair, and light anesthesia is used. A special silicone tube is inserted into the cervical canal, through which the embryo is delivered to the body. The entire process can take no more than ten minutes. Up to three embryos can be introduced at the same time; if several embryos have taken root in the body, but the parents want one child, they can be removed.
After embryo transfer, the woman should be under the close supervision of specialists for two weeks. This time will be enough to find out whether the embryo has implanted and whether pregnancy has occurred. After the time has passed, you can find out the result using an ultrasound examination.
Unsuccessful IVF attempts reasons for non-pregnancy
Let us immediately note that each attempt at in vitro fertilization gives about forty percent probability of a successful outcome. At the same time, pregnancy after the first replantation is rare, and patients are always warned about this.
Let's look at the most common reasons for unsuccessful IVF:
- unpreparedness of the female body for pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diseases or pathologies of the endometrium;
- diseases of the fallopian tubes;
- decreased ovarian reserve;
- insufficient response of the ovaries to stimulation of ovulation;
- low sperm quality;
- low quality of obtained embryos;
- autoimmune factors (rejection of the embryo by the mother’s body);
- chromosomal disorders;
- similarity of histocompatibility antigens between parents;
- infections.
Why might the body not be ready for pregnancy? It is not recommended to carry out fertilization during an exacerbation of any diseases (not necessarily gynecological). This is why you need to undergo so many tests before preparing for IVF. It is better to take your time, fully recover and thereby increase the likelihood of successful conception. The presence of infection is also an easily eliminated factor: by the next cycle the chances of successful embryo implantation will be higher.
As for hormonal imbalance, most often it is caused by ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Perhaps the chosen protocol was not suitable for the patient, and the preparation plan for fertilization should be changed. The same applies to insufficient response to stimulation: a different protocol or replacement of drugs is needed.
For successful implantation of the embryo, the thickness of the endometrium must be from 7 to 14 mm. Doctors at the IVF Center clinic always closely monitor compliance with this condition, however, in general, unsuccessful IVF, according to reviews, is often due to the unpreparedness of the inner layer of the uterus.
To exclude autoimmune factors, it is necessary to donate blood for an immunogram, which reveals the presence of killer cells. To determine possible chromosomal abnormalities or antigen similarities, both parents should consult a geneticist.