Dynamic spectral colposcopy (DYSIS) is an innovative technology used to diagnose cervical cancer and precancerous conditions. This procedure combines high-quality spectral imaging and a digital colposcope.
Colposcopy Dysis 4,000 rub.
All prices Make an appointment
In our International Hemostasis Clinic, the procedure is performed by Sencha M.V., Baimuradova S.M. and Jijihia L.K. – experienced obstetricians-gynecologists with the necessary qualifications to interpret the results obtained.
Preparing for colposcopy
If you are planning to have a colposcopy in the coming days, you need to prepare for it:
- 1-2 days before the examination, refuse sexual intercourse;
- Avoid douching and using gels for intimate hygiene. Use only clean water;
- A few days before colposcopy, refuse vaginal suppositories, foams, tablets and sprays, unless your doctor recommends them.
Most often, colposcopy is performed in the first days after the end of menstruation. This test does not cause pain and only minor discomfort is felt during the test, but if necessary, you can take painkillers before the procedure.
How is colposcopy performed?
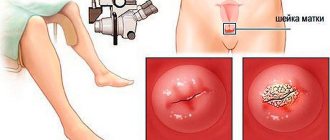
You will be asked to remove clothing from the waist down and lie down on a gynecological chair. The doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina and place a colposcope in front of it. The image will be broadcast on the monitor screen, you will be able to monitor the progress of the procedure.
Colposcopy can be simple or extended. During extended colposcopy, additional tests are performed: with 3% acetic acid, iodine. This should not cause pain or severe discomfort.
On average, the procedure lasts 10-20 minutes.
If the doctor finds an abnormal area, he will perform a biopsy: remove a fragment of suspicious tissue and send it to the laboratory. This procedure may be slightly painful.
Depending on the results, the doctor will prescribe treatment or additional tests to clarify the diagnosis.
How is colposcopy performed?
The first stage of the examination consists of examining the patient by a doctor who examines the woman’s internal genital organs using special dilators.
The specialist inserts a colposcope inside and carefully examines the vaginal walls and cervix, paying special attention to areas with pathologically altered tissues.
During extended colposcopy, the doctor applies a solution of acetic acid or iodine to the cervix with a gauze swab, and after a few minutes examines the cervix and determines the location of the changed areas, which, after contact with the applied mixture, look like visually noticeable spots against the background of healthy tissue. At the same time, material is taken for a biopsy, which can be a little painful.
The entire procedure usually takes no more than 30 minutes.
Colposcopy
Colposcopy: how is it performed and how to prepare?
Modern medicine can prevent cervical cancer in almost all cases. This requires regular cytological screening, that is, a preliminary examination of the cells of the cervix and cervical canal. According to the clinical examination program, a smear from the surface of the cervix is taken once every three years from all women. A cytological examination of a smear from the surface of the cervix and analysis for the human papillomavirus help to suspect diseases of this organ, in particular cancer. A simple examination is not enough to confirm or exclude such a diagnosis. In such cases, cervical colposcopy is used. Often it is supplemented by a biopsy followed by histological examination. In doubtful cases, repeated procedures are carried out.
What is colposcopy
Colposcopy is an examination of the cervix under a special microscope. A colposcope is a specially adapted binocular microscope with illumination. It helps to examine the surface of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, and vulva under high magnification. The colposcope was invented specifically for the diagnosis of precancerous conditions and cervical cancer. In modern conditions, this procedure makes it possible to diagnose benign, precancerous and tumor processes.
During a colposcopy, a biopsy can be taken and photographs of the affected areas can be taken. Computerization of the process and data archiving in modern devices can improve the quality of diagnostics. However, the primary role in performing the procedure and interpreting the data belongs to the doctor. The results of the study largely depend on his experience and qualifications.
The colposcope magnifies the image 6-40 times. Low magnification helps to initially orientate, determine the presence of pathological foci, evaluate their shape, color, surface and location. The doctor examines suspicious areas under high magnification. A green filter is applied to improve visualization of the vascular network. The use of a color filter is particularly helpful in diagnosing invasive cervical cancer.
Types of colposcopy:
- simple
- extended
A simple one allows you to visually assess the surface of the cervix, its shape and size, examine the area of the cervical canal, and determine the border between flat and tall columnar epithelium.
The technique for performing simple and extended colposcopy differs in that during extended colposcopy, additional treatment of the cervix is carried out with a solution of acetic acid and Lugol's solution. These methods help to distinguish normal vessels from pathologically altered ones, and also limit the foci of affected epithelium. This subsequently makes it easier to select a biopsy site.
Who is the study for?
Indications for colposcopy:
- unfavorable cellular changes according to cervical smear data;
- suspected cancer and other diseases, such as genital warts;
- positive test for human papillomavirus;
- bleeding after sexual intercourse in women over 40 years of age;
- bleeding outside of menstruation;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the cervix;
- vaginal discharge and itching;
- prolonged pain in the lower abdomen.
Research objectives:
- diagnosis of precancerous conditions and cancer in women with a positive Pap smear result;
- examination of the vagina and cervix;
- monitoring the effectiveness of drug treatment for neoplasia;
- monitoring the health of women whose mothers took diethylstilbestrol during pregnancy.
A contraindication for the procedure may be a woman’s refusal. Extended colposcopy should be performed after clarifying the allergic history, in particular, reaction to iodine.
How to prepare
No special preparation is required for colposcopy. The diet and diet are normal.
The following restrictions must be adhered to:
- two days before the test, do not douche or wash yourself with intimate hygiene products;
- use a condom during sexual intercourse;
- stop using suppositories, vaginal tablets and other medications for intravaginal use.
How is colposcopy performed?
When is the best time to do the procedure? Colposcopy is performed outside of menstrual bleeding. The doctor decides on which day of the cycle the examination is planned, but it is usually carried out on the seventh to tenth day after the start of menstruation. During this period, cervical mucus is transparent and does not complicate examination.
The manipulation can be performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Before the procedure, the woman is informed about the study, convinced of its diagnostic value, necessity and safety. The patient should be warned about the possibility of taking biopsy material during the procedure.
Women often wonder if it hurts. Colposcopy is painless and does not cause any unusual discomfort. There may be some minor pain when the biopsy is taken.
The research time is about half an hour. An examination is carried out on a gynecological chair. The cervix is examined using mirrors. It is advisable that the mirror be warm. The woman should relax well so as not to create obstacles for the insertion of speculum or colposcope.
A smear is taken only when necessary to avoid unnecessary complications (infection, bleeding).
Examine the cervix and upper part of the vagina at low magnification. The discharge is dried with a cotton ball. Large lesions and leukoplakia are assessed. Using a green filter, the vasculature is examined. Benign formations are described - polyps, Nabothian cysts and others.
If an extended colposcopy is performed, then the surface of the cervix is moistened with a 3-5% solution of acetic acid using a cotton ball. Wait 10 seconds and remove the remaining mucus. Individual characteristics and foci of pathology on the surface of the mucous membrane are recorded or remembered. The vinegar test is the main one in the diagnosis of pathological conditions of the epithelium.
After this, a Schiller test is performed by applying Lugol's aqueous solution to the mucous membrane. It contains 1% iodine, 2% potassium iodide and water. After a minute, dry the surface with a cotton ball. Iodine stains normal squamous epithelium well in a dark brown color. The iodine-negative zone during colposcopy is represented by atypical or columnar epithelium. It is examined in more detail under high magnification. If necessary, a biopsy is taken - small pieces of tissue are “plucked off” for histological examination.
The biopsy may be mildly painful. In addition, bloody or mucous discharge is possible after colposcopy with biopsy. To stop bleeding, electrocoagulation or vaginal tamponing is used.
What the study will show
Colposcopy helps in diagnosing cervical ectopia. This is a physiological condition. However, if the ectopic lesion is large, bloody discharge after sexual intercourse or excessive mucous discharge from the vagina may be observed. If these symptoms are absent, ectopia does not require treatment. A study of erosion helps to clarify the diagnosis and the extent of damage to the cells of the mucous membrane, and to exclude precancerous processes. Colposcopy is performed after treatment of erosion to assess its effectiveness.
Colposcopy is very important in diagnosing precancerous conditions of the cervix (dysplasia). A special classification of changes detected during colposcopy and the degree of their severity has been developed. Based on it, the doctor establishes an accurate structured diagnosis that determines further treatment tactics.
Current guidelines call for greater attention to colposcopic examination of the vaginal walls, as cancer of this organ is increasingly spreading.
Normally, the mucous membrane of the cervix is smooth, pink, with a uniform network of vessels. Ectopic areas have a grape-like appearance.
Pathology reveals whitish areas (leukoplakia), mosaic or point changes. Keratinization or irregular vascular patterns are characteristic of cancer.
During manipulation, you can see atrophy of the epithelium, erosion, inflammation, tissue proliferation (papillomas, condylomas). The result of the study is confirmed by histological analysis of tissues. Colposcopy and pregnancy
Is it possible to do the test during pregnancy? Colposcopy in early pregnancy is performed if the results of a cervical smear are questionable or poor. Its main goal is to diagnose cancer in a timely manner and clarify the tactics for managing the patient before childbirth. Research in later stages (2-3 trimesters) is not carried out due to technical difficulties and the risk of complications (infection, bleeding).
Colposcopy during pregnancy is more technically complex and less comfortable for the patient. No preparation for the study is required. Most often, only a simple colposcopy is performed, which does not pose a danger to the pregnant woman and the fetus. If necessary, some time after birth, a repeat colposcopy with a biopsy is performed.
What to do after the study
If only colposcopy was performed, the woman can lead a normal life. It is recommended to use sanitary pads for 1-2 days to ensure that the discharge stops. If a biopsy was taken, for ten days after colposcopy you should not take baths, go to a bathhouse or sauna, have sex, use tampons, douche, take aspirin and medications containing it, or engage in heavy physical labor. The tampon inserted to stop bleeding must be removed the next day.
The result of the study is ready in 10-14 days. You should schedule a follow-up visit to your doctor at this time.
After the examination, there are rare non-dangerous consequences - slight mucous, bloody, dark brown or even greenish discharge, aching pain in the lower abdomen of a spastic nature.
Complications are rare and are mainly represented by an infectious process (vaginitis, cervicitis), bleeding after a biopsy, or an allergic reaction to iodine or other liquids used.
You should immediately consult a doctor in the following situations:
- profuse bleeding that did not stop during the day;
- any spotting that lasts more than five days;
- purulent vaginal discharge;
- increased body temperature;
- intense pain in the lower abdomen;
- chills, dizziness and severe weakness.
Recommendations after the examination
After colposcopy, a woman may experience spotting and spotting from the vagina. She may also be bothered by a nagging pain in the lower abdomen. These phenomena are normal and usually disappear after 1-2 days without medical intervention.
In order to speed up recovery after colposcopy, for a week or two after the procedure you should avoid sex, the use of vaginal tampons, douching, baths (it is better to shower instead), heavy physical labor and fitness.
Types of procedure
Survey colposcopy
Survey colposcopy (simple) includes examination of the cervix and cervical canal (no reagents or additional means are used).
A simple colposcopy allows you to:
— determine the shape, size and condition of the cervix;
— identify the presence of injuries or ruptures;
- determine the nature of the discharge;
- assess the condition of blood vessels and mucous membranes.
Colposcopy with color filters.
A green filter is used to determine and assess the condition of blood vessels.
Extended colposcopy
It involves examining the cervix and assessing its condition through the use of special tools that treat the cervix. The procedure takes place in two stages:
- The first stage is the use of a 3% acetic acid solution, which makes it possible to evaluate the vascular reaction and determine whether there are areas of neoplasia.
- The second stage is the use of an aqueous Lugol solution, which allows you to clearly see the pathological areas.
Chromocolposcopy
Chromocolposcopy involves the use of special dyes when only healthy areas of tissue are stained.
Colpomicroscopy
Colpomicroscopy is a method when it is necessary to evaluate and analyze the structure of cells and their composition (cytoplasm, nuclei, inclusions). For this, a special colposcope with up to three times magnification is used.
What recommendations should be followed when performing colposcopy?
Before prescribing a procedure for examining the uterine cervix with a colposcope, the doctor conducts a preliminary consultation to identify possible limitations.
Colposcopic examination is not recommended if a woman is prescribed local treatment for inflammation of the genital organs or an insufficient amount of time has passed since its completion (according to experts, at least a week should have passed since the end of treatment).
A few days before the set date of the study, you should refrain from douching, baths and sexual contact. It is also not recommended to use any local contraceptives (spermicides, creams, suppositories).
Following the listed recommendations and performing colposcopy within the prescribed time frame will allow you to obtain reliable diagnostic results and select appropriate treatment.
Video: Colposcopy is...
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 50408 Date of publication: 10/11/2017
Gynecologists - search service and appointment with gynecologists in Moscow
The main differences between colposcopy and pelvic ultrasound
An ultrasound can be performed by a sonologist . Using a sensor, he can see the pathology of the reproductive system, urinary tract, and the pathology of surrounding tissues - the pelvic organs. Colposcopy is aimed primarily at viewing the cervix and vagina and is usually performed by a specially trained gynecologist, who then prescribes and adjusts treatment.
Using a colposcope it is impossible to examine and diagnose pathology of the bladder, ureters and, if necessary in the future, kidneys. Those. Ultrasound is a primary screening examination. Often it is thanks to this examination that ovarian fibroids and cysts are first identified. Colposcopy is a more targeted method, during which you can take a biopsy, smears, conduct an examination at high magnification and identify the oncological process.