One of the key blood test indicators that a doctor evaluates to determine if there are any abnormalities in a patient's health is PCT (the percentage of whole blood volume occupied by platelets). This is a criterion through which it is possible to detect not only current inflammatory processes in the body, but also to examine the general state of the human immune system.
The ability to decipher the results of the analysis, as well as an understanding of what usually causes the actual concentration of platelets in the blood to deviate from the generally accepted norm, will help to identify the onset of the disease and begin its treatment as soon as possible.
Pct - what is it, role and functions in the body
PCT (the abbreviation used to refer to the results of a platelet test) illustrates the status of the portion of the total blood volume that contains platelets. This is an indicator whose level in the analysis is most often determined in an automated way rather than by manual calculation. Its main role is to prevent the progression of dangerous diseases.
The most common among them are:
- thrombosis;
- stroke;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- causeless internal bleeding.
The criterion under consideration helps to determine:
- How prone a particular person’s body is to bleeding . In cases of obvious predisposition, doctors usually prescribe corrective medications in order to minimize the existing risk.
- The degree or speed of the thrombus formation process . Based on blood clotting, we can predict how likely the patient’s body is to develop a vascular blockage that prevents free blood circulation.
Due to the objective importance of the result obtained, accurate platelet counting, provided by advanced technologies, is more popular than manual counting.
PCT in a blood test is the number of platelets per liter!
If there is insufficient or excessive number of platelets in the body, a person suffers from:
- frequent headaches, migraines;
- changes in skin color of the extremities;
- causeless bleeding (most often from the nose);
- apathy, drowsiness;
- decreased performance;
- severe itching on the fingers or toes;
- pain in the kidneys or liver;
- enlargement of the liver or spleen.
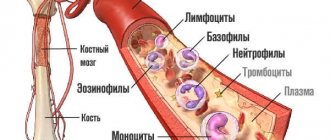
Blood platelet levels
At the birth of a child, platelets have indicators of 100-420 units/μl. In the second month of life, the bar decreases to 350 units/μl. Indicators in adolescents are approaching the values of adults.
The platelet rate in women by age is presented in the table:
| Woman's age (years) | Platelet count (units/µl) |
| 15-18 | 180-340 |
| 19-80 | 180-320 |
The normal cell content in men is slightly higher.
The indicators may be affected by third-party factors:
- menstrual cycle;
- pregnancy period;
- chronic diseases;
- diet.
In pregnant women, the blood volume in the body is increased; flat cells in the required quantity do not have time to recover, so there is a slight decrease in them. Low levels are normal.
Norm of thrombocrit in women, men and children
Despite the similarity in the structure of the circulatory system in children, women and men, the generally accepted norm of thrombocrit varies depending on the age and gender of the individual patient.
In a healthy child, the quantitative value of platelets is usually equal to:
| Child's age | PCT reference value |
| From birth to 12 months | 100 – 421*109 cells per liter of blood |
| Over 12 months | 181 – 321*109 cells per liter of blood |
Children often fall, causing them to get cuts, scratches and wounds on their bodies. With a normal thrombocrit, the skin regenerates on its own in the shortest possible time. In addition, platelet cells prevent infection from entering the child’s body through the site of a violation of the integrity of the skin.
For adults, generally accepted reference values are:
| The age of an adult or the characteristics of his condition | Thrombocrit reference values |
| Men from 20 to 75 years old | 0.14 – 0.39% to 1 liter of blood |
| Women from 20 to 75 years old | 0.14 – 0.39% to 1 liter of blood |
| Women during pregnancy or menstruation | 0.07 – 0.21% to 1 liter of blood |
| Elderly people over 75 years old | 0.18 – 0.31% to 1 liter of blood |
When assessing the obtained thrombocrit results, one should take into account not only the patient’s gender and age, but also his lifestyle, as well as factors that have a potential impact on this indicator.
Factors influencing the indicator
As with other blood tests, a thrombocrit test may give a distorted result due to the presence of circumstances that influence a temporary change in blood composition.
Among them:
- time of day when biological material is submitted (in the evening, the platelet count may decrease by 5-7% or be at the lower limit of normal);
- seasonal period (in spring and autumn, due to internal physiological changes in the body, the thrombocrit indicator may differ from its normal value);
- menstruation period , during which a woman donates blood (at the beginning of the cycle, the PCT indicator usually decreases significantly by 20 - 40%);
- pregnancy (during gestation, the female body activates all its protective functions, in particular, thins the blood to prevent blood clots);
- excessive physical activity (if biological material is taken after sports, especially cardio exercise, the resulting thrombocrit may be 2 or more times greater than the reference value).
Proper organization of a blood test will allow you to obtain a reliable result, identify abnormalities (if any) and promptly begin treatment of pathological processes that pose a danger to human health.
When is the test ordered?
A PCT blood test (this is a test that involves counting platelets), usually carried out as prescribed by a physician or hematologist, is considered mandatory for evaluation by a specialist.
According to the recommendations of doctors, it is necessary to take a general blood test for preventive purposes every 5 to 6 months. This will help to adjust its composition in time, without waiting for obvious deviations in health and the development of dangerous diseases.
Therapists usually prescribe this type of study when the patient complains of:
- frequent occurrence of bruises and bruises on the body that are not associated with external influences;
- periodic nosebleeds that cannot be quickly eliminated;
- irregular menstrual cycle (in this case, both the duration of the periods themselves and the number of days included in the menstrual cycle are important);
- excessive bleeding of the gums (if there are abnormalities in the composition of the blood, this occurs every time you brush your teeth, regardless of the type of hardness of the toothbrush used).
If there are no deviations in the result of the thrombocrit test, the therapist refers the patient to a specialist for subsequent identification of disturbances in the functioning of a specific body system (for example, if the gums are bleeding for no reason, the general practitioner will recommend that the person see a dentist).
Important Features
Platelets are cells that are shaped like small plates. Their main task is considered to be protection against blood loss. When a vessel is damaged, platelets move to the painful area. They are held together, creating a barrier that protects against bleeding.
In addition to this function, platelets are needed for the liquid state of the blood and the dissolution of existing blood clots, so regular analysis is required. Increased and decreased indicators negatively affect human health. In case of deviations, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations, which will help normalize the cell level.
Preparing for the study
PCT in a blood test (this is the number of platelets that most often occurs per liter of blood) is an indicator that can only be identified if properly prepared for the study.
On the eve of submitting biological material, you should:
- refuse to eat food and liquid (at least 8 hours must pass from the last time food and water entered the body);
- avoid stressful situations and emotional stress;
- minimize physical activity;
- get enough sleep (the optimal length of time for sleep is 8 hours);
- avoid fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- minimize the consumption of flour products and products with a high sugar content;
- make sure there is no elevated body temperature or symptoms of an incipient disease (at least a week should pass from the moment of complete recovery even from a simple ARVI).
If one of the points of the general recommendations is not followed, the resulting thrombocrit indicator will be unreliable, which may subsequently lead to incorrect treatment.
What does thrombocytosis mean?
An increase in the number of platelets in the blood leads to thrombocytosis.
This is a serious disease that causes blood clots. With this disease, the platelet level reaches approximately 500,000 per mm3. The cause of the disease may be the production of platelets in the bone marrow, slowing down their breakdown, or disrupting the movement of cells in the bloodstream. Thrombocytosis can develop into thrombosis, characterized by poor blood circulation and blockage of blood vessels. Treatment of thrombocytosis consists of preventing thrombosis and treating the underlying disease that causes an increase in platelet levels.
With the pathology of secondary thrombocytosis, the number of blood platelets increases, which is most often caused by chronic diseases.
The causes of this disease are the following:
- low-quality tumors;
- operations for diseases associated with tissue necrosis;
- bone fractures;
- heavy bleeding;
- infectious diseases;
- splenectomy;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids;
- long-term inflammatory process.
A good cause of secondary thrombocytosis is meningococcal infection, which often develops in children. In the presence of anemia associated with iron deficiency, the likelihood of such thrombocytosis increases several times.
Thrombocytosis is classified into 3 types:
- clonal;
- primary;
- secondary.
The first two types are characterized by a similar pathogenesis - the disease develops due to a disorder in stem cells. In the clonal form, cells are affected by tumor processes, platelets begin to form uncontrollably and their interaction with other cells of the system is disrupted. There is a tendency to form blood clots.
Primary thrombosis occurs due to a disruption in the functioning of brain stem cells, in which the proliferation of hematopoietic areas is recorded. This risk group includes older people. The secondary type develops against the background of chronic pathologies that bother the patient.
In the primary stage there are no symptoms, but the secondary form has pronounced manifestations, because occurs against the background of the development of chronic inflammatory processes.
The following manifestations are typical:
- fatigue;
- acute stage of a chronic disease;
- general health deteriorates;
- problems with blood vessels;
- bleeding;
- swelling;
- bruises and hematomas not associated with contusions;
- heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right;
- shortness of breath and tachycardia;
- migraine and hypertension.
Most patients learn about the manifestation of the disease from the results of a clinical blood test. It is important that the primary form of the disease can develop into a chronic stage. A patient with secondary type thrombocytosis complains of symptoms that are associated with the underlying disease. It is quickly diagnosed, treated in a timely manner, and blood clotting does not occur.
There are a number of recommendations that are useful for stabilizing the number of platelets in the blood. The effect will be positive only if all points are completed simultaneously.
- diet - eating at the same time during the day, taking into account individual characteristics, needs and distribution of proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- avoidance of foods with large amounts of carbohydrates and fats;
- inclusion in the diet of foods that reduce and normalize the level of platelets containing iodine and organic acids;
- consumption of clean drinking water daily.
The menu should contain:
- vegetable oil;
- onion garlic;
- fish fat;
- green vegetables;
- persimmons, tomatoes;
- cottage cheese, cheese, kefir;
- cereals and legumes;
- liver and other offal;
- seafood and kelp.
In addition, natural herbal tea, orange, pomegranate, tomato juices, and decoctions of fresh berries are useful.
Along with medications, traditional methods are also used to treat this disease.
An effective element in the fight against thrombocytosis is ginger, the method of preparation of which is as follows:
- Grind natural ginger into powder.
- Mix with cane sugar in equal parts.
- 2 tbsp. l. pour 250 ml of boiling water over the mixture.
- Take small sips before lunch.
In addition, traditional healers advise using the following ingredients to prepare medicinal medicines:
- a decoction of Ginko Biloba leaves, taken 2 times a day;
- cocoa without milk and sugar should be drunk before meals in the morning;
- garlic tincture (pour 2 crushed heads with 200 g of vodka and leave to infuse for 1 month). Drink it 1/2 tsp. 2 times a day;
- use of leeches;
- Make a paste from garlic, onion, honey and lemon and use 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
Reducing platelets using folk remedies is necessary in combination with diet and traditional medicine.
What biomaterial is taken for analysis?
To conduct a study on the volume of blood containing platelets, laboratory assistants take blood from a patient's finger.
This method of collecting biological material allows you to obtain the required amount of capillary blood quickly and without additional financial costs for medical equipment (in particular, syringes).
Considering that in some cases the detection of PCT is necessary in small children, a second puncture of the ring finger will allow all the necessary manipulations to be carried out without the need to restrain the resistance of the small patient for a long time.
Classification
Thrombocytosis can be:
- Primary (essential) - occur when the functioning of the stem cells that make up the bone marrow is disrupted. The primary form of the disease is detected mainly in patients of older age groups.
- Secondary (reactive) - occur under the influence of some pathological condition.
- Clonal - accompanied by defects in the development of stem cells, which differ in tumor properties. It is not possible to control the process of platelet production in this form of the disease.
Thrombocytosis can provoke the development of complications when chronic leukemia, polycythemia vera, etc. are detected.
How is the analysis carried out?
The standard sequence of actions when taking biological material for a general blood test involves the simplest steps.
Among them:
- Clean your hands before taking biological material.
- Make sure that your hands are not cold (the temperature of your fingers should not be lower than 36.6 degrees).
- Disinfect one of the fingers with alcohol or an alcohol-containing product.
- Use a scarifier (a medical instrument that resembles a blade) to make a puncture in the pad of any (usually ring) finger. The depth of the cut should be approximately 2-3 mm.
- Using light pressure on the pad of the selected finger, collect the required amount of blood with a pipette.
- One part of the obtained biological material must be placed in a sterile flask, the other - on laboratory glass.
- Apply an alcohol pad to the cut to stop the bleeding and bandage the finger.
Restoration of the integrity of the skin usually occurs within a few days after taking capillary blood. Sometimes a small hematoma forms at the puncture site, which disappears on its own without the use of medications.
Analysis transcript
PCT in a blood test is a number that can be deciphered by assessing the ratio of platelets to the amount of blood being tested. Under normal conditions in an adult, its value should fall within the range from 0.14 to 0.39.
Any deviation from the reference value, subject to compliance with the rules for preparing for the delivery of biological material, as well as conducting the study itself, is considered a sign of the presence of a pathological process in the body. A single discrepancy with the norm is usually confirmed by repeated analysis, but not earlier than a week later.
A little about platelets
Platelets are a type of blood cell. The blood of any person contains red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets, which “float” in the blood plasma. Each type of cell is responsible for performing a specific function in the body.
The main task of platelets is to regulate blood clotting. When bleeding occurs, cells rush to the site of damage to the vessel and form a plug that blocks blood flow.
Platelets increase the coagulability of blood plasma, which ultimately leads to stopping bleeding and promote the regeneration of damaged tissues.
When these cells are destroyed, the nutrients needed to form new cells are released.
Platelets are involved in many other processes in the body: they are able to attach to potentially dangerous proteins and reduce inflammation, saturate blood vessels with nutrients and maintain their elasticity, nourish tissues and, if necessary, release unique enzymes that ensure rapid cell repair.
A platelet test is performed in a laboratory. This can be an independent study (for example, platelets according to Fonio) or a detailed analysis of blood composition (coagulogram).
Preparation for analysis, regardless of the type of study, is the same. Blood must be donated on an empty stomach, i.e. at least 8 hours after eating.
It is best to contact the laboratory in the morning, since stress and physical activity provoke fluctuations in the number of cells, which can distort the overall picture and reduce the effectiveness of the study.
You should avoid alcoholic beverages 24 hours before blood collection. If you are taking medications, you should consult your doctor: some medications affect the composition of the blood, so to obtain reliable results, you must temporarily stop taking them.
When is additional research needed?
It is advisable to carry out additional examination in the case of the actual platelet concentration, which is significantly higher or lower than the generally accepted norm.
In addition to a repeat general blood test, the patient is recommended to do:
- ultrasound examination of a potentially unhealthy system or organ;
- analysis to determine serum iron levels;
- blood clotting test.
Additional health studies are also needed for people at risk. This is due to the likelihood of transmission of the blood disease at the genetic level.
Low values
An insufficient concentration of platelets per 1 liter of blood negatively affects its clotting. At low thrombocrit values, the risk of causeless bleeding (both external and internal) increases, which will be very difficult to stop.
Depending on the age and gender of the patient, hematologists and therapists differently characterize the identified indicator as low.
According to the standards:
- for women it is less than 0.14%;
- for men - similarly;
- for pregnant women or girls taking a blood test at the beginning of the cycle - below 0.06%;
- for people over 75 years old - less than 0.16%;
- for children aged from birth to 12 months – below 0.1%;
- for children older than one year – less than 0.17%.
The platelet count may decrease due to existing pathological processes or due to previously suffered diseases.
Most often, such changes in the composition of the blood are caused by:
- a tendency to develop anemia (low hemoglobin or “anemia”);
- renal failure;
- liver problems;
- deficiency of vitamins, in particular folic acid;
- infectious or viral disease;
- lupus erythematosus disease;
- existing leukemia or hemoblastosis;
- indiscriminate use of antibacterial and diuretic drugs;
- recently completed chemotherapy;
- intoxication of the body;
- radiation damage;
- underweight;
- the presence of intestinal parasites.
It is possible to normalize thrombocrit levels only with the help of an integrated approach. The patient is usually recommended to review his diet and undergo a course of drug therapy.
In your daily menu you should focus on:
- fruits (bananas, apples, pomegranates, melons);
- vegetables;
- seaweed;
- gluten-free porridges (buckwheat, rice, corn);
- nuts (hazelnuts, walnuts);
- peas;
- beans;
- lean meat (in particular beef);
- fresh herbs;
- green tea
Among the drugs used to increase the level of platelets in the blood, the most effective are:
- "Dicinon" (a drug for the treatment of capillary bleeding);
- "Derinat" (remedy for parasites);
- "Vikasol" (medicine for hemorrhagic disease and hypovitaminosis).
After treatment, it is necessary to take a blood test again to ensure that the thrombocrit level has returned to normal.
Diagnostics
If platelets are elevated, patients are referred for a comprehensive examination. With its help, it is possible to determine what provoked such changes in the circulatory system and what measures should be taken to eliminate the disorder. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will decide what to do and what treatment tactics to resort to.
It should be understood that for thrombocytosis, therapy differs significantly from the tactics used for thrombocytopenia, that is, a low platelet count in the patient’s blood. Comprehensive diagnostics consists of:
- mandatory external examination of patients;
- submitting samples for platelet testing;
- aspiration biopsy of bone marrow samples;
- trepanobiopsy of bone marrow;
- oncological examination in order to identify or refute the presence of malignant tumors.
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will determine what type of thrombocytosis your particular case belongs to. It is divided into two types:
- Primary. In this case, high platelet counts are caused by dysfunction of human bone marrow cells. There are practically no characteristic symptoms for this disorder. In rare cases, headaches and deterioration in general health are possible.
- Secondary. In this case, thrombocytosis occurs as a symptom of an ongoing disease, is a consequence of surgery, or a side effect of improper use of a medication.
Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
First of all, you should contact a therapist. After an examination and medical history, the general practitioner issues a referral to a specialist. With such a pathology, you may need to consult the following doctors:
- hematologist;
- oncologist;
- cardiologist;
- medical geneticist - if there is a suspicion of a congenital disease.
The diagnostic program may include the following activities:
- general blood analysis;
- detailed biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis and Nechiporenko test;
- analysis of stool for occult blood;
- tumor marker test;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
The specific diagnostic program will depend on what clinical picture is present and on the data that were collected during the initial examination. It should be noted that not only personal, but also family history is collected.
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, it is possible to determine why platelets are elevated and what therapeutic measures to take to eliminate the pathological process.
A general blood test is the most accurate way to detect elevated platelets in an adult or child. However, diagnosis is not limited to this study; if platelets are elevated, other research methods are also used.
In order to make the correct diagnosis as accurately as possible, if platelets are elevated, doctors send their patients for the following examinations:
- Complete blood count - also determines how quickly the increase occurs;
- Three blood tests for platelets with an interval of 4 days;
- Bone marrow biopsy;
- Determination of ferritin and serum iron levels;
- Coagulogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- Analysis for C-reactive protein;
- Consultations with a gynecologist or urologist.
Diagnosis of thrombocytosis begins with collecting anamnesis: the doctor asks the patient about previous diseases, emerging complaints and suspected reasons that could provoke this or that manifestation. In the future, the following examinations may be recommended:
- General blood test.
- Ultrasound examination of the peritoneal and pelvic organs.
- Molecular research.
- Bone marrow biopsies.
A complete blood count can determine platelet levels
For this purpose, the following methods and analyzes are used:
- A blood test for platelets, which is done three times at intervals of 3 to 5 days to obtain accurate data.
- A blood test to check the level of iron it contains.
- Test for the presence and amount of C-reactive protein.
- Urinalysis - general.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
In some cases, to clarify the data obtained and make a diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe some additional studies and tests. Their number and direction depend on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and are selected as necessary.
As a rule, these are very serious diseases with a high level of risk for the health and life of the patient, so their treatment is always complex, sometimes including not only drug therapy, but also surgical intervention.
If platelet levels rise due to disorders that are not caused by serious illnesses, for example, due to obesity or a large dose of alcohol, you need to take care of switching to a healthy lifestyle.
Tags: quantity, blood, man, elevated, platelet
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Increased values
PCT in a blood test is a value that, if exceeded, can cause blockage in the cardiovascular system. In the vast majority of cases, obstructed blood circulation leads to the death of the patient.
Depending on the age of the person, an increased thrombocrit value is:
- for middle-aged men and women – more than 0.39%;
- for people over 75 years old – over 0.31%;
- for children from birth to 12 months – more than 0.41%;
- for children over 1 year old – over 0.31%.
The reasons for the increase in this indicator may be the initial stages of serious diseases in both children and adults.
| Patient's age | Potential body dysfunctions that provoke an increase in platelet levels |
| Children (from birth to 15 years) | Pathological changes in the structure of the bone marrow and disruption of its normal functioning; initial stage of tuberculosis; iron deficiency in the body; blood loss during surgery. |
| Adults (from 16 to 75 years old) | Consequence of removal of one of the organs (usually the spleen); early stage diabetes mellitus; ulcer; gastritis; benign or malignant tumor; purulent-inflammatory processes in the skeletal system; atherosclerosis; consequence of long-term use of steroids. |
To adjust the composition of the blood, doctors recommend that patients eat as much as possible:
- fresh berries (lingonberries, cranberries, blackberries);
- white fish;
- dark chocolate.
If an elevated platelet level persists after adjusting the diet, a therapist or hematologist usually prescribes Angiox to patients. It is used to normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular and circulatory systems. Drugs containing argotroban are considered no less effective in restoring normal AST levels.
Despite the fact that the PCT indicator in the test results may not always reflect a reliable concentration of blood platelets, it is necessary to monitor its level.
This is due to the ability of such a criterion to signal existing pathological processes in the body. By normalizing the thrombocrit indicator in time, a person will be able to avoid not only subsequent drug treatment, but also, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Can a single analysis be considered sufficient to make a diagnosis?
After the biomaterial is taken from a vein or finger, the absolute number of blood platelets is calculated. The norm of platelets in the blood for women and men is the same and is 170–320x10 9 cells/l. Another analysis allows you to determine platelets and their number in relation to red blood cells. Per 1 ml of red blood cells, the platelet norm in women and men is 60–70 thousand PLT.
We suggest you read: Running and hypertension: benefits and harms
Minor decreases or increases in the number of blood platelets are not a cause for concern. If platelets have decreased to 140x10 9 or increased over 400x10 9, then you cannot do without the help of a specialist, since we are talking about a serious pathology.
A condition in which platelets are low is called thrombocytopenia. With low platelets, their volume in men and women is below 200 × 10 9 per liter of blood.
A low PLT level is a very alarming symptom that increases the duration of bleeding. When platelets are below normal, I diagnose the following diseases in a person:
- Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Leukemia of acute and chronic forms.
- Reduced level of platelet formation in the bone marrow in hypoplastic and plastic conditions of unknown cause, metastases of a cancer tumor in the bone marrow, folate deficiency anemia.
- Increased activity of the spleen, which is affected by causes such as liver cirrhosis, chronic and acute viral hepatitis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleroderma.
- Impaired functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Viral diseases.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
- The use of various drugs whose action is aimed at toxic or immune damage to the bone marrow (Vincristine, Mercaptopurine, Vinblastine, Levomycetin, Sulfadimethoxine, Biseptol, Aspirin, Butadione, Analgin, Reopirin).
To determine the level of platelets in the blood, you need to take a test, during which biological material will be collected for further research.
Blood can be tested for platelets in two ways. The first is a general blood test, which includes the platelet count. For this type of study, blood is taken from a fingertip.
The second method is a coagulogram, which reveals the level of platelet aggregation. Normally, this figure should be from 30 to 60%.
If the level is lower or higher, this indicates thrombocytopenia or thrombocytosis, respectively.
Blood for coagulation is taken from a vein; this study studies exclusively platelets.
The collection of biological material should be carried out in the first half of the day, from a patient who did not eat in the morning. You can only drink plain purified water without additives.
In order for the analysis to provide correct data, you should stop drinking alcohol-containing drinks a couple of days before the test.
You should also avoid taking medications that can affect your platelet count.
These drugs include diuretics, analgesics, corticosteroid painkillers and other medications.
If for health reasons you have to constantly take certain medications, you should consult with your doctor before taking the test.
Since platelet levels are affected by stress, for an accurate result it is recommended to avoid heavy physical activity and strength training for three days before the test.
It is recommended to be less nervous, since psycho-emotional stress has a great influence on the hormonal background of the female body, and, accordingly, affects the level of platelets.
You should also refuse to take the test if an injury with a large loss of blood or an extensive burn occurred less than three days before the blood draw.
The body, in defense mode, will increase the number of platelets, and the analysis will be incorrect.
When receiving the analysis results, the main line in the conclusion will be the PLT indicator. This number indicates the number of platelets in the blood.
If PLT deviates from the norm, the attending physician will recommend additional studies to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate drug therapy.
- saturating the body with oxygen;
- nutrition of all organs and tissues;
- removal of metabolic products from the body;
- regulation of body temperature;
- protecting the body from foreign biological invasions.
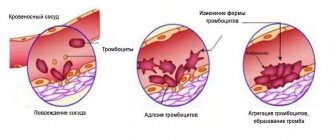
Platelets occupy a worthy place among the defenders of the “citadel” of the human body. They are the first to appear on the affected areas of the vessels and form the primary plug.
Platelets promote rapid plasma coagulation by secreting enzymes that convert soluble blood plasma protein into insoluble one.
Scientists have concluded that platelets secrete “growth factors” that promote repair processes in damaged tissues.
But what happens when there are too many platelets in women, men, children, in other words, the thrombocrit is higher than normal? What is the quantitative criterion for these blood cells?
We’ll talk about the normal platelet count in the blood of a healthy person below. Now let's try to figure out what happens when there are too many of them.
The main function of these anucleated cells is to protect the body from blood loss in cases of superficial injuries or internal bleeding. Receiving a signal from the affected vessels, platelets are instantly activated and sent to the “distressed” area.
Having reached the front line, they are firmly attached to the walls of damaged vessels. The platelets following in the “rearguard” cling to the first wave, and so on, until a reliable clot is formed.
However, this positive quality of blood platelets can create serious problems if their number is too large.
The fact is that the process of platelet activation is virtually irreversible. And the activation factor may be reasons unrelated to the case described, for example:
- hysterical state;
- physical activity associated with muscle tension;
- artificial stimulation of the body with drugs of plant and synthetic origin.
Activated platelets do not find somewhere to go, but their desire for aggregation remains. High density provokes them to action. Blood cells stick to each other, creating clots that get into the ducts of blood vessels, blocking them, forming a blood clot.
A critically high number of platelets in the blood plasma is called thrombocytosis.
- repeated general clinical;
- biochemical;
- serological;
- analysis for tumor markers.
A comprehensive study of blood composition is extremely important for drawing up an overall picture and accurate diagnosis.
A repeat analysis will confirm (or not confirm) the constant quantitative composition of the blood.
Biochemical analysis helps to identify sluggish inflammatory processes, without external manifestations. Determines the level of iron in the body. It is not fully scientifically substantiated, but through long-term laboratory studies it has been proven that the iron content in the blood is directly related to the level of platelets.
Serological analysis is carried out to identify viral and infectious diseases that suppress the human immune system.
A tumor marker test detects the presence of cancer cells in the blood. Malignant and benign tumors can cause elevated platelet levels.
A temporary increase in blood platelet levels is often a consequence of physical and emotional stress, poor diet, and alcohol and tobacco abuse.
In women who are struggling with swelling of the face and legs with the help of diuretics, reducing fluid intake to a minimum, blood thickening is the result of thoughtless methods.
We suggest you read: What calcium shows in the blood
Symptoms accompanying thrombocytosis, such as general weakness, numbness of the extremities, dizziness, accompany many other diseases.
Until the reasons are fully clarified, you should abandon any attempts at self-medication using traditional and non-traditional methods. Otherwise, you may not only experience aggravation of the situation, but also get unwanted side effects.
- Eliminate cigarettes and alcohol from your life.
- Avoid carbonated drinks, as well as tea and coffee.
- Increase the consumption of juices rich in ascorbic acid (apple, lemon).
- Remove smoked foods and carbohydrate-rich foods from the menu.
- Include seafood, garlic, ginger in the menu.
If the course of the disease does not require emergency measures, limit medication use to a small dose of aspirin to thin the blood.
Platelets are inhabitants of the Universe, which is called the human body. Without seeing us, they transmit to us signals indicating disturbances in the life support system. We need to learn to understand them, and not rush into a reckless fight when they are elevated.
The number of platelets in a man's blood is counted during a clinical analysis. To do this, blood is taken from a finger and a small amount is applied to a special glass slide in the form of a smear. It is then stained with aniline dyes (Romanowsky-Giemsa stain) and platelets are counted in the smear under a microscope.
In modern laboratories, this study is performed using a special hematology analyzer, in which platelet counting is carried out automatically. To obtain reliable test results, it is advisable to donate blood on an empty stomach, so it is usually carried out in the morning.
In this case, the patient does not have breakfast (still mineral water or unsweetened tea is allowed). If taking medications that can affect the number of platelets in a man’s blood, the patient must inform the attending physician, who will determine the need to temporarily stop using the medications.