Ekaterina Smolnikova
Practicing endocrinologist (10 years of experience). He has extensive experience working in private and public clinics in Russia.
Ask a Question
Last updated August 22, 2020 at 3:20 pm
Often, a blood test shows that the leukocytes in the blood are elevated. The reasons for women are very diverse - from banal acute respiratory infections to serious diseases. What elevated white blood cells indicate should be understood in each individual case. For this purpose, additional laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out.
What are leukocytes?
Leukocytes are white blood cells. They protect the body by absorbing pathogenic microbes. They were first discovered by scientists I. Mechnikov and P. Ehrlich, who in 1908 received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. Scientists have developed a theory of immune defense and described different types of leukocytes.
Leukocytes can penetrate the cell wall and engulf foreign microorganisms. This process is called phagocytosis, and the leukocytes involved in it are called phagocytes. To maintain immunity, white cells are constantly synthesized in the bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes.
How long do white calves live?
Their lifespan is 10-12 days.
Where are leukocytes destroyed?
If too many pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the cells, the phagocytes grow in size and are destroyed.
The result of destruction is a local inflammatory reaction, expressed in redness and swelling of the tissue. An even larger number of white cells join the site of inflammation, they die, destroying foreign cells. Purulent discharge is nothing more than dead leukocytes.
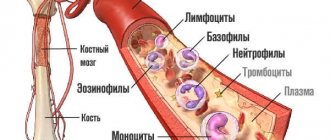
Leukocytes are diverse in their appearance and functions. Some of them provoke phagocytosis, others synthesize antibodies. Based on this feature, white cells are divided into two large groups:
- Granular: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
- Non-granular: lymphocytes, monocytes.
Increased levels of various white cells are found in various diseases. For example, the number of eosinophils increases with allergies and parasitic infections. An increase in lymphocytes indicates the presence of a viral infection.
Therefore, a blood test examines the leukocyte formula, that is, the balance of different types of leukocytes. If a so-called shift to the right is detected, then they speak of an increase in the number of young leukocytes; with a shift to the left, mature “old” cells predominate in the blood.
Brief information about leukocytes and their position in blood tests
Blood is divided into plasma, that is, the liquid part, and the cellular component, represented by the formed elements.
| Varieties of shaped elements | Name | Designation | Purpose and functions |
| red cells | red blood cells | R.B.C. | transfer of iron-containing protein (hemoglobin) through the bloodstream to provide the body with oxygen, regulation of the acid-base composition of the blood (ABC) |
| blood platelets | platelets | PLT | ensuring normal blood clotting, preventing vascular damage |
| white (another name for colorless) cells | leukocytes | WBC | phagocytosis – protection of the body from antigens (viruses, bacteria, parasites, allergens), through their capture and destruction |
An extended clinical blood test includes all types of leukocytes:
- NEU – neutrophils (band and segmented). Responsible for “protection” from infections and viruses;
- LYM – lymphocytes. Provide an immune response (differentiation and elimination of allergens, bacteria, viruses that have entered the body);
- MON – monocytes. Responsible for the production of interferon, tissue regeneration, and suppression of cancer cell activity.
- EOS – eosinophils. They form antiparasitic immunity (detect and eliminate parasitic infestations).
- BAS – basophils. Serve as markers of allergic reactions.
The totality of the listed blood cells makes up the leukogram (leukocyte formula). Neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils represent a group of granulocytes (leukocytes containing granules in their nuclei, otherwise known as grains). Lymphocytes and monocytes belong to agranulocytes (non-granular, colorless cells).
Norm of leukocytes in the blood (table)
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of adults and children differs. In children, the number of white cells is always higher and changes with age. White blood cells also increase slightly in pregnant women, especially in the third trimester, and this is considered normal and does not require treatment.
Article on the topic:
What is leptin? How is the hormone related to weight loss in women?
The content of leukocytes by age is presented in the table:
| Patient category | Norma (10 9 l) |
| Children up to 5 days | 8-29 |
| Children 5-8 days | 8-14 |
| Child under 1 year | 5-12 |
| Child 1-6 years old | 4-12 |
| Child 6-12 years old | 4-11 |
| Men | 4-9 |
| Women | 4-9 |
| Pregnant | 7-11 |
What does high content mean? This pathology is called leukocytosis. If the white cells in the blood are much lower than expected, then we are talking about leukopenia.
After childbirth
During childbirth, all the protective forces in the mother’s body are activated, so slightly increased values of the indicator are the norm. However, if the analysis registers elevated leukocytes in the blood within several days after birth, this is an alarming signal. The reasons may be infection or exacerbation of a chronic disease, which requires immediate further examination and medical care.
Read further: About increased leukocytes in urine during pregnancy
When is promotion normal?
Leukocytosis can be physiological. White cell levels fluctuate several times a day, which may be due to the following factors:
- A hearty lunch.
- Exercise stress.
- Visiting the sauna or being in the sun.
For these reasons, the blood test is performed on an empty stomach after rest.
The level of leukocytes is also affected by:
- Smoking.
- Sports activities. In athletes, the number of these cells always fluctuates.
- Prolonged stress.
- Eating large amounts of red meat. The body perceives the components of meat dishes as foreign and reacts to this by releasing white cells.
- Pregnancy after 6 months. This is due to the increased load on a woman’s body.
- Use of medications.
- Last days before menstruation.
- The first days after vaccinations. This is due to the entry of a small number of microbes into the blood.
As for leukopenia, the physiological reasons are:
- stress;
- taking antibiotics;
- following a strict diet.
How to raise them
There are several ways to increase low white blood cells, but only a doctor can prescribe an effective treatment regimen. Treatment should include medications, dietary and lifestyle adjustments.
Medication
Treatment of low white blood cell levels in many cases is impossible without prescribing drugs that stimulate the production of white blood cells. Popular stimulators of leukopoiesis - the process of producing leukocytes - include:
- Leukogen;
- Methyluracil;
- Tevagrastim;
- Neupomax;
- Sodium nucleinate;
- leucite;
- Zarcio;
- Filgrastim;
- Sargramostim;
- Lenograstim.
In drug therapy for a reduced number of leukocytes, doctors also use auxiliary drugs:
- means to strengthen the immune system (tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus, echinacea);
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants (Immunal, Estifan, Galavit);
- vitamin and mineral complexes containing thiamine (vitamin B₁), pyridoxine (vitamin B₆) and folic acid;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Important information: How to quickly raise white blood cells at home (what foods increase them)
The treatment regimen, method of administration and duration of medication must be agreed with your doctor. Self-prescribing even the most harmless medications can lead to dire consequences.
On your own with diet
In order to bring low levels of leukocytes back to normal, you need to reconsider your usual diet - exclude high-calorie and carbohydrate foods, supplement the menu with protein foods, berries, fruits, citrus fruits, and vegetables with a high fiber content.
Doctors recommend eating foods that increase the concentration of white blood cells every day:
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- oatmeal;
- whole grain porridge;
- beets;
- celery;
- pumpkin;
- garlic;
- spinach;
- liver;
- nuts;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- chicken eggs;
- turkey and rabbit meat;
- river and sea fish.
Animal fats should be replaced with sunflower, corn or olive oil, soups should be cooked in fish, meat or vegetable broth. To prevent the body from experiencing hunger, it is advisable to eat fractionally, dividing the daily amount of food into 5-6 meals. It should be remembered that any fasting and long-term mono-diets can provoke a persistent decrease in leukocytes in the blood.
Right way of life
It is possible to increase the concentration of white blood cells only with an integrated approach, therefore, when leukocytes in the blood decrease, it is important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle:
- stop drinking alcohol, smoking, and drugs;
- do not overheat or overcool;
- avoid intense physical activity;
- minimize contact with people who have influenza, ARVI, chickenpox, measles and other infectious diseases;
- eat well;
- take a walk in the fresh air every day;
- Avoid large crowds of people; when visiting crowded places, wear a medical multi-layer mask.
These easily implementable measures will help prevent weakening of the immune system and the development of dangerous bacterial, viral and fungal infections, which, against the background of a low level of leukocytes in the blood, can lead to irreversible consequences.
How is a blood test for leukocytes performed?
A standard blood test is ordered to measure white blood cell levels. Blood is drawn in the morning.
Before the study you cannot:
- Exercise.
- Be nervous.
- Eat food.
- Take medications.
If a deviation from the norm is detected in the blood, the analysis should be repeated after 5-7 days. With a physiological increase, everything will return to normal. Maintaining an elevated level indicates pathological conditions.
How is the analysis performed?
Checking for leukocytes is carried out using a diagnostic procedure such as a general blood test. The sample is taken from a finger using a capillary medical device. The resulting material is used for laboratory testing, during which the number of required blood cells is automatically counted. For the indicator to be as accurate as possible, the patient must properly prepare for the procedure.
- Blood donation is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. It is forbidden to eat at all, you can only drink a little still water or tea without sugar.
- The day before the procedure, it is not recommended to consume fatty, fried and smoked foods.
- Smoking provokes an increase in the level of leukocytes, so it is better to give up cigarettes in the morning.
- If the woman is taking medications, the nurse should be notified.
Causes of pathological increase in leukocyte levels
Pathological leukocytosis can be true and redistributive.
In the first case, the synthesis and release of leukocytes from the bone marrow increases. In the second case, the cells that are on the surface of the vessels enter the blood, but their production is not increased.
The causes of true leukocytosis are leukemia and other oncological diseases, as well as the first period of radiation sickness.
Important! In chronic leukemia, the number of white cells increases tenfold. However, in the acute period, on the contrary, the number of leukocytes is much lower than normal.
Causes of redistributive leukocytosis:
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza, sore throat). After recovery, leukocytes remain above normal for another 10 days, then the level gradually decreases.
- Inflammatory processes caused by bacterial infections (otitis media, pharyngitis, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, gynecological problems, etc.).
- Infected wounds, internal inflammation (appendicitis, boil, peritonitis).
- Heart attack.
- Severe burns or frostbite.
- Significant blood loss.
- Autoimmune diseases: lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Chemical poisoning.
- Rubella, mumps, chickenpox, hepatitis.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Kidney failure.
- Diffuse mastopathy.
- Allergy.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- HIV AIDS.
- Condition after removal of the spleen.
Article on the topic:
What is anti-Mullerian hormone responsible for? What are the normal AMH values in the female body?
With purulent inflammation, the level of leukocytes is significantly increased; a slight increase indicates a chronic inflammatory process when the body is fighting infection. Leukemia and other oncological diseases are characterized by a multiple increase (up to 300 units).
Also, against the background of a general increase in leukocytes, an increase in the number of lymphocytes may be observed. This happens when:
- Asthma.
- Tuberculosis.
- Whooping cough.
- Lymphocytic leukemia.
- Drug use.
An increase in the level of neutrophils is usually associated with purulent processes and indicates the following pathologies:
- Peritonitis.
- Internal purulent inflammation.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Intoxication.
- Suppression of bone marrow activity.
Important! A large number indicates deadly pathologies and requires a thorough examination and urgent medical care.
Leukocytosis in women
In addition to an increase in white blood cells in the blood, women often have a large number of these cells in the smear. Normally, they should not be more than 15 units. Otherwise, we can talk about STIs (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, herpes, trichomoniasis, etc.).
Leukocytosis in the urine means diseases of the urinary organs (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis).
How to treat leukocytosis
Only a specialist can determine. Elevated white blood cells are not treated unless the condition is caused by a pathological malfunction in the body. In such cases, white blood cells perceive their cells as foreign.
Systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid polyarthritis develop according to this principle. To defeat the disease, drugs are prescribed that block the production of leukocytes.
If you have had an operation to transplant donor tissues or organs, you may experience increased production of white blood cells. They interfere with recovery, so they are blocked for a while. When the transplanted tissue takes root, the medications are stopped, and the functioning of the circulatory system is normalized.
In most cases, it is enough to find the source of inflammation and treat the underlying disease. A full examination is necessary, since elevated white blood cells can be caused by both carious teeth and malignant neoplasms . Because of this, self-medication is prohibited, and taking medications without the supervision of specialists will only worsen the condition.
Symptoms of elevated white blood cell levels
A slight increase in cell levels is almost not felt by a person and is detected during a blood test.
If there are a lot of white cells, the patient feels the following symptoms:
- Temperature increase.
- Weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Pain in joints, muscles.
- Sweating.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Poor appetite.
In addition, inflammation and pain may occur in the affected area (for example, pain in the throat or stomach).
Symptoms
In the early stages, leukocytosis in women is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- visual impairment;
- headache;
- low-grade body temperature;
- poor appetite;
- excessive sweating.
At later stages of leukocytosis, the symptoms of the underlying disease come to the fore, which are determined by the nature, severity, localization of the pathology, and require special treatment.
Low white blood cell counts (leukopenia) in women pose a serious risk. The body is deprived of protection, bacterial and viral infections are possible.
In the early stages, the symptoms of leukopenia are:
- general weakness;
- pale skin;
- enlargement of the spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils;
- joint pain.
When infections occur:
- conjunctivitis, rhinitis, sinusitis;
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- enteritis, colitis;
- herpes, respiratory infections.
Not only the body’s defense against infections suffers, but also antitumor immunity. In women with leukemia, the incidence of tumors of various origins is twice as high as in healthy women. An insufficient number of leukocytes in the blood after cancer chemotherapy significantly increases the risk of progression and metastasis of the malignant neoplasm for which therapy is being carried out.
Reasons for decreased leukocyte levels
Why does a decrease in leukocytes occur? Pathological leukopenia is said to occur when the level of white cells remains below 4 for a long time. This is usually associated with diseases such as:
- Acute leukemia.
- Bone marrow aplasia.
- Anemia.
- Metastatic tumor.
- Thyroid pathology.
- Anaphylaxis.
- Typhoid fever.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Diabetes.
Symptoms of decline
Some symptoms of leukopenia are similar to those of leukocytosis:
- Temperature.
- Prostration.
- Increased heart rate.
- Chills.
This condition usually means a decrease in immunity, which is fraught with infection. Therefore, leukopenia requires careful examination and treatment.
Why is the level decreasing?
Possible reasons for a decrease in the number of white blood cells can be divided into several groups.
Bone marrow diseases
The most dangerous cause of low white blood cells is the inability of the bone marrow to produce, i.e. create new cells. Distortion of the leukocyte blood formula occurs as a result of:
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- malignant neoplasms;
- precancerous conditions (myelofibrosis, myelosarcoma);
- germination of metastases into the bone marrow and replacement of leukopoietic tissue with tumor cells;
- transferred radiation exposure;
- radiation or chemotherapy for cancer.
It should be remembered that the absence or reduced number of leukocyte cells in the bloodstream, resulting from bone marrow dysfunction, is rare. Therefore, with a small deviation from the norm, there is no reason to panic. To exclude the presence of dangerous pathologies, it is enough to consult a doctor and, if necessary, undergo an examination.
Intoxication
A reduced number of white cells in the blood often indicates possible intoxication - poisoning with poisons of various categories. Among the provoking factors of leukopenia in adults, doctors include:
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- taking narcotic drugs and medicinal poisons;
- smoking;
- contact with household insecticides;
- food poisoning that was prepared without following technology or stored in violation of the temperature regime;
- intoxication with arsenic, heavy metal compounds, mercury vapor, benzene, toluene and other harmful substances.
Toxic compounds can enter the body for a long time from food, water or air and gradually poison the body. Leukocytes, rushing to fight pathogenic agents, will die en masse, and the number of white cells in the blood will decrease.
Diseases of internal organs and systems
No less significant factors, as a result of which leukocytes can be reduced, are viral and bacterial infections:
- flu;
- ARVI;
- pneumonia;
- measles;
- malaria;
- hepatitis;
- typhoid fever;
- sepsis;
- tuberculosis.
White blood cells are often reduced in patients suffering from diseases of the endocrine and digestive systems:
- thyrotoxicosis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- Graves' disease;
- acromegaly;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- cholecystitis;
- peptic ulcer.
The level of leukocyte cells also decreases in HIV infections, allergic conditions and anemia caused by deficiency of folic acid and cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12).
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, a low level of all types of leukocytes most often indicates the presence of anemia. In 90% of cases of leukopenia detected during pregnancy, the cause is iron deficiency anemia. It is characterized by a sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood and a decrease in hemoglobin levels. This harmless phenomenon can be easily corrected with a special diet and taking iron-containing medications.
Important information: What does it mean to have low lymphocytes in the blood of an adult (reasons for the decrease)
Lactation
The reason for the decrease in white blood cells during breastfeeding is most often general exhaustion. The body lacks useful substances, which are the “building material” for the synthesis of a sufficient number of neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, eosinophils or monocytes. With minor deviations from the norm, the leukocyte formula is restored to optimal levels within 2-4 months after the end of breastfeeding.
Lack of substances
If white blood cells are low, then the most common cause of this phenomenon may be a lack of nutrients necessary for the synthesis of white and red cells. This means that the body is deficient in certain vitamins and microelements:
- ascorbic acid;
- folic acid;
- arachidonic acid;
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- gland;
- copper;
- manganese;
- Selena;
- zinc;
- Yoda.
To compensate for the lack of nutrients, it is necessary to supplement the diet with products that are leaders in the content of the listed substances. In addition, you need to consume more protein foods, giving up high-calorie, fatty, fried and high-carbohydrate foods.
If there are few leukocytes in the blood, and dietary adjustments do not give the desired effect, you should resort to the help of multivitamin complexes - they will provide the body with the necessary nutrients and accelerate the synthesis of white blood cells.
Taking medications
If the leukocytes in the blood are less than normal, the cause of the deviation may be long-term use of medications. The risk group includes:
- analgesics;
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- drugs from the sulfonamide group;
- barbiturates;
- anticonvulsant and antiepileptic drugs;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- antidepressants;
- antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs;
- antitumor drugs;
- thyreostatics;
- antiviral tablets;
- medications with interferon;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- drugs for chemotherapy.
The extensive list of medications that lower the number of white blood cells means that any therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. As a result of self-treatment of even the most harmless, at first glance, diseases, the number of white blood cells decreases, and this leads to adverse consequences.
How to detect?
Treatment for leukocytosis depends on the underlying cause. To do this, a number of additional examinations are carried out:
- Biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
- Tests for STIs.
- Enzyme immunoassay blood test to detect autoimmune diseases and allergies.
- Blood test for parasites.
- Ultrasound.
- X-ray.
- If leukemia is suspected, a spinal cord puncture is performed.
Article on the topic:
What do elevated platelets in women indicate? Causes, symptoms and treatment
How to identify deviation
A decrease in leukocytes is determined in 2 ways - by characteristic symptoms and a general blood test.
Signs and symptoms
You may not be aware of a low white blood cell count as long as the disease is mild. But if the process enters the chronic stage, then the following signs may indicate a decrease in the number of leukocytes:
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- general weakness, lethargy, fatigue;
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating under comfortable temperature conditions);
- increase in body temperature to +37…+38°C, accompanied by chills;
- pain in the chest or joints;
- rapid pulse and heartbeat (90 beats per minute or more);
- headache;
- dizziness;
- causeless anxiety;
- the appearance of pustules on the face, torso or limbs;
- hoarseness of voice;
- bleeding gums;
- enlarged lymph nodes, tonsils, projections of the liver or spleen;
- frequent colds.
Important information: What does it mean to have elevated eosinophilic cationic protein (protein) in a blood test?
These symptoms can accompany not only a decrease in the level of leukocytes, but also other diseases. Therefore, to make a correct diagnosis, you should go to the clinic and undergo the necessary tests.
Analysis
To diagnose leukopenia, doctors first of all recommend taking a general blood test with a detailed breakdown of all indicators. This method of diagnosing disorders of the leukocyte formula is more reliable and reliable.
If necessary, additional manipulations may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs;
- serological and biochemical blood tests;
- collection of cerebrospinal fluid (puncture, trephine biopsy);
- detection of blast cells in the bone marrow and peripheral blood;
- liver tests for bilirubin, transaminases, markers of viral hepatitis.
The feasibility and procedure for conducting certain tests is determined by the doctor.
Treatment of elevated white blood cells in women
If the increase in white blood cells is caused by bacterial or viral infections, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics or antiviral drugs. For severe allergic reactions, corticosteroid therapy is prescribed. In some cases (appendicitis, peritonitis) urgent surgical intervention is required.
If leukemia or another cancer is confirmed, the question arises of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
How to bring leukocytes back to normal?
When the increase in white cell count is associated with physiological conditions, no special treatment is required. Therapy consists of eliminating provoking factors. In particular, the following rules should be observed:
- Get more rest and sleep.
- Establish proper nutrition.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day to speed up the removal of toxins from the body.
- Minimize spicy and salty foods in the menu.
- Take vitamins and minerals to strengthen your immune system.
- Take walks in the fresh air every day.
The patient's diet should contain foods rich in B vitamins, especially B12. These are meat, dairy, seafood.
Folic acid also reduces leukocytosis. It is found in foods such as legumes, greens, vegetables, fruits. Copper has a positive effect on the level of leukocytes. To compensate for the deficiency of this element, it is recommended to consume more fish, seafood, liver, and buckwheat porridge.
Folk remedies for elevated leukocytes
It is also possible to reduce leukocytosis using folk remedies. Since the increase in these cells is associated primarily with inflammatory processes, agents are used that reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
The following recipes will help you cope with the problem:
- A mixture of birch leaves, lingonberries and strawberries. A tablespoon of raw material is steamed with boiling water, cooled and taken ½ cup before meals.
- Linden blossom decoction. A spoonful of herbs is poured with water and placed in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then cool and filter. Drink as tea during the day.
- Horsetail decoction. A spoonful of raw materials is brewed with hot water and left for at least 8 hours. Drink 1 tbsp. before meals.
- Alcohol infusion of propolis. It has powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Dissolve 20 drops of tincture in water and drink. Can be consumed up to 3 times a day.
Leukocytes perform one of the main functions - they protect the human body from bacteria and viruses. An increase in their level indicates health problems. To bring white cells back to normal, it is necessary to detect and treat the disease that caused the imbalance.
Types of leukopenia
In the modern medical classification there are the following types of leukopenia, they are discussed in the table:
| According to the nature of the flow | By time of appearance | By severity | |||
| Acute | Up to 3 months | Congenital | Kostmann's syndrome, cyclic neutropenia | Lightweight | 1-1,5*109 |
| Chronic | Progresses over 3 months | Acquired | Under the influence of factors such as the activity of fungi, viruses, bacteria | Average | 0.5-1*109/l |
| Heavy | Less than 0.5*109/l | ||||
If the concentration of blood cells in the blood decreases to less than 0.5*109/l, this means that agranulocytosis develops.
Features of leukopenia in women
The reasons for the decrease in the proportion of blood cells in women may not only be inflammatory processes. The female body can independently turn on protective mechanisms that provoke both a decrease and an increase in the content of blood components.
Attention! A decrease in leukocytes in a woman’s blood during pregnancy is normal, especially if there is a Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus. In the case of such a deficiency, the picture normalizes after childbirth. The condition does not require correction.
Deviation from the norm can be provoked by prolonged use of painkillers and antispasmodics on the days of menstrual bleeding. Gynecologists report that the disorder is often detected in women who uncontrollably take contraceptives.
Often the reason for changes in marks is poor nutrition, and this factor specifically affects the female gender. This is due to the fact that girls, more often than men, neglect the need for adequate nutrition in favor of diets. Against this background, vitamin deficiency with a lack of vitamin C and B appears.
White blood cells are low in a child
A general blood test is an important marker of a child’s health because it allows a preliminary diagnosis or confirmation of health status. An important indicator is the concentration of leukocytes, the norm of which varies depending on the age of the child. The disease in a child is diagnosed when the indicator decreases by 2 * 109/l from the norm for age.
List of main reasons:
- Lack of vitamins and microelements, namely: vitamin B and C, iron, iodine, zinc, selenium and protein.
- Destruction of blood cells as a result of the activity of pathogenic flora.
- Destruction of leukocytes and other blood components as a result of toxic effects.
- Bone marrow disorders.
- Genetic diseases.
Violation of the blood formula often accompanies the following processes:
- viral infections;
- lack of vitamins;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- hypotension;
- purulent and septic processes;
- tumors;
- systemic, autoimmune diseases;
- transferred radiation exposure;
- acute allergic reactions.
The cause of development in children often lies in an incorrectly defined treatment regimen for the underlying disease. Leukopenia can be the result of long-term use of antibacterial, hormonal, anticonvulsant drugs, or drugs that enhance immunity. The prescription of any drug must be agreed with the pediatrician; the consequences of self-medication can be irreparable.