The importance of getting a urine test during pregnancy
If a woman becomes pregnant, a urinary tract infection can be treated without consequences. For a pregnant girl, passing a urine test is one of the main tasks throughout the entire period. During this period, restructuring and changes occur in the woman’s body, which is why the organs are in disadvantaged conditions. The kidneys suffer from this.
A urine test reveals a sufficient number of diseases in the early stages of development, so the sooner the better, for example, in the early stages. Bacteria found in urine facilitate diagnosis during pregnancy and further treatment. Single microorganisms present in small numbers may mean a different kind of disease.
Baby under the protection of mom and doctor
Normal urine levels
During pregnancy, the norm of indicators differs from the same indicators in a non-pregnant woman, although slightly:
- The color of urine is straw-yellow, transparent.
- An uncomplicated pregnancy produces protein in the urine that is otherwise undetectable.
Pregnant women often have their urine tested to rule out possible pathologies in the child. To facilitate the study, a table of urine test norms, which every doctor has, will help.
How do bacteria get into the bladder?
The penetration of a bacterial infection into the urine is called bacteriuria. Normally they shouldn't be there. But if pathogenic microorganisms are still present in the discharge, it means that an inflammatory process of an infectious nature is developing in the urinary system.
But there are situations when foreign agents get into the tests not from the urethra at all. Often, if a patient uses a non-sterile container to donate biological material, bacteria are already present inside on the walls of the jar. Therefore, doctors recommend buying special sterile plastic cups with lids in pharmacies rather than using homemade jars.
Another way infection can enter the urine is through improper cleaning of the genitals before taking samples. First you need to perform a thorough toilet and collect not the first portion of urinary fluid in a container, but the middle one.
Microbes often accumulate in the anal area; their breeding ground and localization is the large intestine. If they get to the urethra due to improper hygiene of the external genitalia in women, then they easily rise up to the bladder. This route of penetration is called ascending.
For accurate diagnosis, the number of detected microbes is taken into account. With downward infection, only one type of bacteria is detected. If there are more of them there, it means that most likely pathogenic agents have entered the urinary canals due to improper intimate hygiene.
Causes of bacteria in urine during pregnancy
Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, favorable conditions have been created in the woman’s body for difficult passage of urine. This is due to the fact that the urethra is close to the rectum at this time. Here's where and why a lot of bacteria appear in the urine during pregnancy and what it means.
Each of the reasons for the appearance of bacteria in the urine during pregnancy is identified in a general urine test, which indicates the presence of the disease. Among these reasons are:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis.
If you find microbes in your urine for the first time, do not sound the alarm. The reason for the increased number of bacteria lies in these diseases. Changes occurring in the body are a common problem for pregnant women, which is why it is so important to find one factor in the occurrence of a bacterial disease.
Cystitis
A common disease of the urinary system during pregnancy is cystitis, which women of different ages are familiar with: 21, 30, 37 and 40 years old. The occurrence of this disease is associated with the physiological structure of the female body. Cystitis is caused by weakened immunity in the first and second trimester of pregnancy.
Symptoms of cystitis include frequent and painful urination, pain during pregnancy, blood in the urine, and fever.
Urethritis
It is an inflammatory disease of the urinary system, which is characterized by inflammation of the urethra. The symptoms of the disease are similar to cystitis, but a urine test is required to distinguish between them, since urethritis leads to the development of pathological processes and consequences for the child and other risks.
Most infections are associated with the bladder and urethra
Pyelonephritis
A general urine test during pregnancy sometimes reveals pyelonephritis, an inflammation of the kidneys. Taking antibiotics for this disease is mandatory, because antibiotics will protect against complications that arise during pregnancy. This is also due to changes that occur in the urinary system.
Causes
Very often, bacteriuria in pregnant women is observed due to the penetration of microorganisms such as staphylococcus and streptococcus, Klebsiella, enterococcus, and E. coli into the woman’s genitourinary organs. These microbes live on the skin, intestines and mucous membranes of every person. Under the influence of negative factors, microorganisms take on a pathogenic form and begin to multiply intensively, which leads to the development of the inflammatory process.
If bacteria are found in the urine during analysis, this may be due to the following factors:
- an increase in the level of progesterone in the body of a pregnant woman, resulting in a decrease in the tone of the ureters;
- increased growth of the uterus, which begins to put pressure on the kidneys and ureters;
- decrease in the protective properties of a woman’s body;
- stagnation of urine, changes in its composition;
- diabetes;
- caries;
- poor genital hygiene.
Often, bacteriuria during pregnancy affects those women who, before an interesting situation, had problems with the urinary system (cystitis, urethritis), as well as women who are promiscuous.
Main symptoms of infection in women
The appearance of bacteria in the urine manifests itself in the form of various signs and symptoms, and sometimes is asymptomatic. Main signs of infection:
- acute pain;
- changes in urine color;
- turbidity;
- unpleasant odor;
- sediment in the form of flakes;
- slime.
Urinary tract infections are the most common causes of white blood cells in urine
One or more of these symptoms indicate that there is a high likelihood of developing bacteriuria.
Diagnostics
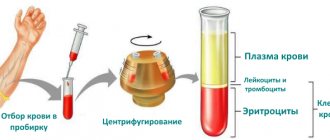
The main method for detecting bacteriuria in pregnant women is laboratory testing of their urine. Performed monthly, it is performed through rapid diagnosis and urine culture.
Express diagnostics of urine
Carried out using:
- TTX test. This technique is based on the ability of bacteria to give colorless tetrazolium crystals a blue color.
- Reduction glucose test. This study, related to rapid rapid diagnostic methods, is based on the ability of pathogenic microflora to reduce (absorb) small amounts of glucose. When testing a portion of morning urine, the laboratory technician puts a paper strip with a reagent into it, which shows whether there is glucose in this urine sample. If the glucose level does not reach the standard, it is believed that it has been absorbed by bacteria. This test does not belong to the category of studies that give 100% results. It is used only for initial diagnosis.
- Griess nitrite test. The essence of this method is the use of a complex of so-called Griess reagents, which detect the presence of nitrites in the urine. Their presence indicates that pathogenic bacteria contained in the urine of a pregnant woman interacted with nitrates, transforming them into nitrites.
Urine culture
A more reliable and reliable way to detect bacteriuria is urine culture.
- Culture of urine for bacteriuria, during which the laboratory assistant calculates the rate of bacterial reproduction, is the most informative. The main disadvantage of this method is the length of the process (the analysis is performed within forty-eight hours).
- A more simplified method is sowing performed using the Gould method. The test urine sample is placed in a Petri dish consisting of four sections and containing a nutrient substrate made of agar. To transfer the sample to the next sector, a sterile platinum loop is used each time. After a day (this is exactly the time enough for the incubation of pathogenic microflora at a temperature of thirty-seven degrees), using a special table, the number of microorganisms is counted.
- Another option for accelerated inoculation is that glass plates coated with a nutrient substrate are first immersed in the urine sample being tested, and then immediately transferred to special containers. The incubation time of bacteria is no more than sixteen hours. By comparing the results of the analysis with the data of the normative scale, the degree of bacteriuria is determined. The reliability of this test is 95%.
It is recommended to perform urine tests for bacteriuria at least twice to exclude the possibility of errors associated with improper collection of material (due to drinking plenty of fluids, taking antiseptics and antibiotics).
An adequately selected method of urine examination allows not only to determine the true culprit of infection of the genitourinary system of a pregnant woman, but also its sensitivity to drugs, which is necessary for choosing the only correct treatment tactics.
Additional diagnostic methods
If a laboratory urine test confirms the presence of bacteriuria, the pregnant woman’s body is subjected to a thorough examination. She is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
- Survey and excretory urography.
- Doppler measurements of the renal vessels.
- A number of screening tests.
- Laboratory blood test.
After laboratory and hardware diagnostics, the expectant mother is examined and advised by a whole group of specialists:
- urologist;
- nephrologist;
- gynecologist;
- therapist.
Having compiled a complete picture of the causes and clinical manifestations of the disease, the specialist managing the pregnancy outlines effective tactics for its treatment.
How is diagnosis done?
Bacteriuria during pregnancy requires mandatory treatment, which is carried out after diagnosis. The presence of bacteria indicates not one, but a large number of organ diseases:
- urethra;
- kidney;
- uterus;
- Bladder.
The main and primary diagnostic method is to give urine for analysis. Before doing this, you must follow the rules of hygiene.
Bacteriological tests
During pregnancy, bacteriological tests are more important than in other periods, as they show the factors causing the disease and will be the first diagnostic method. It is necessary to carry out:
- bacterial sowing;
- general blood analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- general urine test;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- if bacteriuria is suspected, a reaction with triphenyltetrazolium chloride is performed.
Women are at greater risk of developing UTIs than men
What does bacteria in small quantities mean?
A slight excess of the norm means the sample is contaminated. But bacteria in small quantities do not necessarily indicate the occurrence of bacteriuria. If urine exceeds 105 by 1 millimeter, bacteria can be a direct indicator of the development of the disease.
Symptoms
The presence of bacteria in the urine of a pregnant woman in most cases is accompanied by a clear clinical picture (true bacteriuria), but sometimes signs of bacteriuria may be completely absent (asymptomatic). Bacteria in urine also appear during the following inflammatory processes:
- Pyelonephritis is a disease that develops in the renal pelvis due to the active proliferation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, and various fungal infections. The first signs of inflammation of the renal pelvis are lower back pain, a sharp increase in body temperature, tachycardia, and chills.
- Cystitis is a disease that affects the bladder. The presence of cystitis is confirmed by painful and frequent urination, the presence of blood in the urine, high body temperature, and pain in the lower abdomen. If a woman had cystitis before pregnancy, the bacteria found in a urine test indicate a relapse of the disease.
- Urethritis is inflammation of the walls of the urethra. It is accompanied by the presence of pain during emptying of the bladder, a feeling of itching and burning when urinating, increased body temperature, and weakness of the body.
Other symptoms that it is important for pregnant women to pay attention to may indicate bacteriuria:
- urine separation occurs in small portions;
- severe pain occurs in the perineum;
- involuntary urination is observed;
- traces of pus are visible in the urine;
- urine acquires an unpleasant odor, becomes cloudy, and sediment may form;
- The pregnant woman experiences nausea, sometimes with bouts of vomiting.
Having noticed any of the listed signs, the expectant mother should contact the gynecologist managing her pregnancy as soon as possible. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as this will aggravate the course of the disease and cause serious consequences in the development of the fetus. In some cases, the baby may die right in the womb.
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women
It is imperative to eliminate the disease in women. The doctor prescribes pills; an additional method is a diet for bacteriuria during pregnancy. If the disease has not reached an acute form, you can completely or partially use folk remedies, but treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women with alternative options is possible only after consultation with your doctor.
Non-drug methods
Not all doctors consider it necessary to immediately begin treatment with antibiotics and offer non-drug therapy. The main task in the first stages is to normalize the pH of urine and increase its passage.
In this case, cranberry juice, lingonberry leaf, kidney leaf, and pickled foods that increase the pH of urine help. If, after two weeks, tests show that the non-drug method did not work, medications are prescribed that must be used according to the doctor’s prescription.
Medicinal treatments
The use of antibiotics guarantees relief from asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. The doctor prescribes the following medications:
| Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid | 375 mg 2–3 times/day |
| Cefuroxime | 250 mg 2–3 times/day |
| Ceftibuten | 400 mg 1 time/day |
| Cephalexin | 250 mg 4 times/day for 3 days |
| Nitrofurantoin | 100 mg 4 times/day for 3 days |
Advanced medical treatment
How to get rid of it using folk remedies?
Popular recipes are effective in cases where bacteriuria in pregnant women is diagnosed in the initial stages and early stages. An excellent method of treatment is the use of diuretic drinks - jelly, fruit drinks. It is useful to brew herbal mixtures from parsley, birch, and juniper fruits.
Do you need a diet?
Treatment with folk remedies is directly related to dietary restrictions. During treatment, a pregnant woman is recommended to exclude spicy and sour foods from her diet, drink more, and limit the amount of fatty and heavy foods.
Diagnostics: how are studies carried out?
Bacteriuria is a dangerous sign of a serious infectious and inflammatory process. Therefore, during pregnancy, the patient must undergo a urine test every month. Such a simple measure protects her from the development of a serious disease, and when bacteria are detected, it helps to prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
The laboratory performs rapid tests that show the level of bacteriuria and the number of bacterial colonies. If the indicators are elevated, and the woman had a chronic disease of the urinary system before conception, then doctors try to prevent an exacerbation.
How is diagnosis made? Two ways:
- Instrumental/laboratory . To do this, the patient is sent for an ultrasound, blood/urine test, and screening tests.
- Differential . To exclude the development of other pathologies that cause mucus and bacteria to enter the urinary fluid, the woman must be fully examined. Thus, it is possible to detect hidden inflammation and bacteriuria.
Diagnostic procedures allow timely detection of developing or worsening disease. A pregnant woman should consult with a therapist, gynecologist and nephrologist to prescribe the most effective and safe therapeutic regimen.
Prevention
It is not difficult to take preventive measures during pregnancy to avoid the occurrence of bacteriuria. Please meet the following requirements:
- Monthly blood and urine tests.
- Ultrasound of the fetus and kidneys.
- Use of antimicrobial agents.
- Following good hygiene is essential.
A urine test can help detect problems
Characteristics and types of bacteriuria
The urinary system of a healthy person does not contain any microflora, that is, it is sterile. The only exception is the distal urethra (urethra), which may contain bacteria from the skin of the perineum or genital mucosa. This is most typical for women due to their anatomical features - a short and wide urethra, close to the genitals and anus.
Most often, during pregnancy, bacteriuria or the presence of bacteria in the urine is caused by changes in the functioning of certain organs. However, infection with pathogenic microorganisms is not always a prerequisite. In most cases, there is an increase in opportunistic (present in a certain amount under normal conditions) flora due to, for example, stagnation of urine, etc.
Bacteriuria can occur in two forms: true, in which clinical manifestations prompt the doctor to search for the cause of the disease, and false, or asymptomatic, which has no signs. True bacteriuria is confirmed when, when tested twice within 24 hours, 105 or more microorganisms (no matter pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic) are detected in 1 ml of urine.
During pregnancy, asymptomatic bacteriuria is a fairly common condition, and it can only be determined by conducting a laboratory urine test. A general analysis can confirm the presence of bacteria in a pregnant woman’s urine, as well as the protein content and an increase in the number of leukocytes, which is usually combined with bacteriuria. To differentiate pathogens and determine their sensitivity to antibiotics, it is necessary to do a bacteriological analysis of urine, or bacterial culture.
Important! During the period of bearing a child, a woman should regularly undergo blood and urine tests in order not to miss the development of serious diseases against the background of infection.
How to treat bacteriuria during pregnancy
The presence of pathogenic bacteria in the urine is a serious reason for complex treatment. In uncomplicated pregnancy, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a urologist and obstetrician-gynecologist.
Medicinal treatments
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria is carried out with low-toxic antibiotics:
- Cefuroxime;
- Ampicillin;
- Ospamox;
- Cefaclor;
- V-mox;
- Ceftriaxone.
At the beginning of pregnancy, 2-3 generation cephalosporins and beta-lactam penicillins are prescribed.
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, synthetic nitrofurans are indicated - Solafur, Furagin, Furadonin. To disinfect the urinary tract, uroseptics are used - Urolesan, Canephron, Uroprofit.
Folk remedies
Self-treatment of bacteriuria during pregnancy is dangerous due to complications. Some herbs are strictly prohibited for pregnant women. Therefore, folk remedies are used only on the recommendation of a urologist.
To destroy pathogenic bacteria in urine, decoctions are used based on:
- bearberry;
- peppermint;
- pharmaceutical chamomile;
- juniper;
- birch buds.
The course of treatment is from 2 to 4 weeks.
Diet and drinking regime
During pregnancy, foods that alkalize urine and irritate the urinary tract mucosa are excluded from the diet:
- strong coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- spices;
- marinades;
- semi-finished products;
- greenery;
- onion.
To create unfavorable conditions for the growth of bacteria, they consume more products that shift the pH of urine to the acidic side - fruit drinks, fermented milk products, chicken eggs.
Indicators of clinical urine analysis
Laboratory testing of urine includes the study of its organoleptic properties (which are assessed using vision, smell, touch), physicochemical qualities, determination of biochemical parameters and microscopic assessment of sediment.
The table below contains indicators of the norm for general clinical examination
| Diagnostic parameters | Reference values |
| Hue | Straw yellow |
| Transparency | Transparent |
| Smell | Specific unsharp |
| Relative density | 1009–1029 |
| Medium reaction (pH) | 5,0–7,5 |
| Total protein | — |
| Glucose | — |
| Ketones | — |
| Bile pigments | — |
| Red blood cells | — |
| Leukocytes | Up to 6–8 in p/z. |
| Epithelium | 1–5 in p/z. |
| Cylinders | — |
| Slime | Slightly |
| Salt crystals | — |
| Bacteria, fungi | — |
And now we want to tell you sequentially what each final value of a urine test shows.
Color
The normal color of urine from a healthy woman is straw-colored. However, very often during pregnancy, the color of urine can be bright yellow or orange - this phenomenon is due to the use of vitamins before collecting biological fluid.
Drinking plenty of liquid dilutes the urine, and it becomes almost colorless, and drinking water in small quantities contributes to the high concentration of urine - its color becomes more saturated
The development of a pathological process may be indicated by such shades of urine as:
- whitish - characterizes the presence of a large amount of lipids and phosphates in the urine, which is observed with retention of lymphatic fluid in the kidney tissue or fatty degeneration of the kidneys;
- cloudy milk - indicates a urinary tract infection;
- lemon – characteristic of cholelithiasis;
- dirty pink (“meat slop”) – observed with glomerulonephritis;
- strong tea - for diseases of the gallbladder and liver.
Transparency
Normally, freshly collected urine is transparent; slight turbidity is observed when there is an excessive amount of mucus and epithelial cells in it. Significant turbidity can be caused by the presence of bacteria, mucus, red blood cells, salt crystals, a large number of white blood cells and epithelium in the biological fluid.
Cloudiness of urine occurs due to standing of the collected sample for a long time
Smell
In a healthy pregnant woman, the urine does not have an unpleasant pungent odor; its appearance may indicate the development of pathological processes not only in the urinary system, but also in other organs.
Relative density
The specific gravity of urine depends on the amount of fluid consumed per day and substances dissolved in urine. The range of parameters ranges from 1009 to 1029 g/l. Their level increases when:
- toxicosis;
- jade;
- diabetes mellitus;
- dehydration of the body.
A decrease in indicators is typical for nephropathy, renal failure, and excessive fluid intake.
Environment reaction
Depending on the diet, the urine of a pregnant woman ranges from 5.0 (acidic) to 7.5 (alkaline).
The ideal parameters for urine reaction during pregnancy are considered to be 6.0 (slightly acidic) or 7.0 (neutral)
Urine oxidation is facilitated by the consumption of protein foods (in particular, meat products). The constant presence of an acidic environment is undesirable - it is suitable for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Pathological conditions such as:
- tuberculosis;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- fever;
- diabetes.
Alkalinization of the environment is caused by the predominance of plant and dairy products in the diet, as well as the presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs and renal failure.
Total protein
Normal urine does not contain protein, however, during the period of bearing a baby, a small concentration is allowed - no more than 0.025 g/l. Its presence in the urine of a pregnant woman can be caused by:
- overheating of the body in the summer or hypothermia in the winter;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- consumption of raw domestic eggs or unboiled cow's milk;
- allergic reaction.
At the end of the second trimester of pregnancy, a small amount of total protein (“traces”) in the urine is due to mechanical compression of the kidneys by the growing uterus. However, this phenomenon is not constant and can only be dangerous in the presence of other clinical manifestations of kidney pathology.
What is bacteriuria?
Bacteriuria is a generally accepted medical term that refers to the presence of microorganisms of various types in urine. If a person is in absolute health, in the absence of any deviations from the norm, urine should be absolutely sterile. If, during the analysis, bacteria were found in the urine, this indicates disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary organs.
The indicator used in this analysis is called the titer of microbial bodies. The normal level for an adult is 100,000 CFU/ml of urine (CFU - colon-forming units). If this indicator is higher, then the urine contains microorganisms that are caused by an inflammatory infectious process of the urinary organs.
There are a variety of types of urine contamination that will cause an increased CFU count. The diagnosis of bacteriuria is made only in cases where the cause lies exclusively in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Prevention of pathology
To avoid the development of bacteriuria during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a routine examination with your doctor and conduct a full examination throughout pregnancy. If a girl has previously been diagnosed with any kind of inflammatory or infectious pathology of the genitourinary organs, she must be especially careful and take a number of preventive measures, which include:
- Maintain intimate hygiene using special products (cleansing gel, cream, wipes). Sometimes doctors prescribe special drugs that stimulate the immune system and improve the physicochemical properties of urine in order to avoid the active development of bacteria and infection in it.
- Full compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions, taking vitamins and multivitamin complexes that stimulate the immune system.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- No heavy physical activity, only general developmental exercises are acceptable.
- Proper nutrition and fluid intake.
According to statistics, bacteria are found in urine in every fifth pregnant woman. But don’t panic right away, because their presence can be caused by any other physiological changes in the body.
Prevention of bacteriuria: what should expectant mothers remember?
Everyone knows that preventive measures, especially during pregnancy, help get rid of various inflammations and prevent the development of serious infections in the body. By taking care of her health, the patient automatically protects the child from pathological changes in the intrauterine space, as well as from diseases that he may develop after birth. Immunity from the mother lasts a long time, so it is important to prevent bacteria from entering.
What can I do to prevent infections and increased protein in the urine from appearing?
- Get examined and tested regularly. Collect the material in a sterile container after hygiene of the external genitalia. Before going to the laboratory, avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, spicy foods, pickled foods, etc. All these types of food can distort test results.
- A pregnant woman should remove synthetic underwear from her wardrobe and regularly carefully observe intimate hygiene. Synthetics provoke the proliferation of infections and ascending infection by pathogenic microbes.
- It is necessary to follow all doctor’s recommendations and not self-medicate. If you suddenly feel pain when urinating, you should immediately see a gynecologist or urologist. The doctor will prescribe effective and safe treatment for the current stage of pregnancy.
- It is important to strengthen your immune system and exercise. These actions will speed up metabolism and prevent stagnation in the body, which can lead to infection.
It is worth recalling that bacteriuria, according to statistics, occurs in every fifth patient. This is not enough. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular examinations so that the asymptomatic course does not cause complications.