What are red blood cells
Erythrocytes are red blood cells in the form of a biconcave disc. These cells differ from others in that after maturation they can lose their intracellular structure. The lifespan of cells is 100-115 days. The main function of red blood cells is to carry hemoglobin protein. In turn, the protein carries oxygen, thanks to which many biochemical reactions take place in the cell. An increased width of distribution of red blood cells is not an independent disease, it is only a consequence of the development of another serious pathology. When the number of red blood cells decreases or increases, a person's overall health deteriorates.
What determines the width of the distribution of red blood cells
And so the term described is determined by a certain index, the use of which allows doctors to obtain information about the actual distribution of blood cells of various volumes and shapes. That is, when deciphering this index, you can obtain information about the percentage of red blood cells in the hematopoietic system - the size and volume of these cells, which can be increased or decreased.
To fill existing blood cells with oxygen, blood particles need to have a secure passage even into the smallest vessels of the human body. That is why, both physiologically and in size, the described bodies must fit the so-called vascular openings.
If excessively large or very small described elements are formed in the hematopoietic system, this leads to all sorts of changes in the described structural units of the human body. As a result, a person needs to designate the cellular component of plasma by using an indicator in the form of RDW CV.
Main symptoms
If the level of red blood cells in the blood increases, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- migraine;
- poor appetite;
- restless sleep.
If one of the symptoms of increased red blood cell distribution appears, it is important to consult a doctor and get treatment. Since such a phenomenon may indicate that a serious pathology is developing in the body.
RDW blood test transcript
The Rdw indicator should be at the same level. However, doctors have established certain standards by which this indicator should be limited. Deviations are excluded; if they are present, we can talk about a serious disruption in the functioning of the body.
On average, the Rdw rate is 11-15%.
If a person’s indicator is decreased or increased by 1-2%, it is necessary to immediately re-examine and contact the attending physician for a detailed diagnosis. Such a deviation may indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
If Rdw is normal, then the body functions normally and does not require any additional therapy.
If Rdw decreases by several percent, you should also consult a doctor. However, this condition does not indicate a serious deviation in the functioning of the body.
In the vast majority of cases, this phenomenon indicates the individual characteristics of the body, with which a person can live calmly. Normal indicators of the degree of heterogeneity of erythrocytes include the following:
| Age | Norm |
| Up to six months | 11,5-14,5% |
| From six months to 10 years | 14,9-18,7% |
| Over 10 years old | 11,6%-14,8% |
Possible diseases
Quite often, the level of red blood cells in the blood increases due to the development of serious diseases. In older people, the level of these cells increases if heart or pulmonary failure occurs. Erythrocytosis often develops as a result of impaired water-salt metabolism (dehydration). If the functioning of the kidneys and bone marrow is impaired, the number of blood cells increases. Among the most basic reasons for the increase in the width of the distribution of erythrocytes are:
- water imbalance;
- heart disease;
- tumor neoplasms;
- kidney disease;
- problems in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- massive burn.
Erythrocytosis does not always appear due to the development of the disease. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on the patient's test results.
RDW in blood test increased causes
If Rdw is elevated in a person’s blood, this indicates a persistent and serious disorder. He needs to immediately contact his doctor to determine what exactly caused this increase.
In the vast majority of cases this can be explained by:
- Iron deficiency anemia. In this case, the indicator may increase even before the hemoglobin concentration drops. It is the reduced width of distribution that is often called the first harbinger of anemia.
- Megaloblastic anemia - caused by a lack of B vitamins.
- Hemoglobinopathy is a hereditary disease characterized by a disorder of protein structure.
Increased levels of Rdw are observed in people who have serious liver problems: cirrhosis, hepatitis, fatty dysplasia. Also, this condition can occur after a blood transfusion, when the two masses have not yet had time to mix. The width of erythrocytes can also increase after treatment of nutritional disorders.
Very often this indicator is determined incorrectly, since cold agglutinins may be present in the blood.
Climate change is a common cause of increased blood cell levels
In some situations, red blood cells increase due to the body’s adaptation to the conditions of the surrounding world. In mountainous areas, a person's red blood cell levels may increase, since mountain air often causes a lack of oxygen. As a result, hypoxia (lack of oxygen) occurs.
The increased width of distribution of red blood cells negatively affects the general well-being of the patient and disrupts the functioning of internal organs. As the body adapts to new conditions, the hormone erythropoietin is released. This substance provokes the formation of new red blood cells and hemoglobin. Thanks to increased levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin, the body effectively binds oxygen and transports it to cells.
Reasons for the decrease in the indicator
When RDW - CV is below normal, the existing elements of the hematopoietic system are indicated by the same sizes without any differences in cell volume. When the volume indicator under consideration is reduced, doctors most often diagnose a condition in the form of microcytosis, in which the elements present in the blood, indicated by small sizes, cannot fully saturate the tissues of the human body with oxygen.
Also, when the indicator decreases, a disease often occurs accompanied by the unification of the main blood elements of small sizes, along with a reduced RDW rate in the form of thalassemia. Which refers to diseases of a hereditary nature, and manifests itself as disturbances in the processes of synthesis of iron-containing protein chains, with reduced activation in relation to oxygen. In light of this, plasma is no longer able to participate in the process of gas exchange in a normal and adequate manner, which ultimately leads to a change in the functioning of existing human organs.
This disease is also characterized by changes in the morphological properties of blood cells, with inhibition of their growth and decreased activity. The clinical picture of this disease is caused by the deformation of the human skull, the growth of organs such as the liver and spleen, as well as the icteric color of the skin.
Also, with a reduced ratio of such blood cells, a disease called microspheracytosis, which is a hereditary disease, can develop. When such a disease appears in the hematopoietic system, there is an increase in the small size, a certain shape of red blood cells, along with a decrease in the RDW coefficient, due to their insufficient vital activity. As a result, intravascular cell death occurs and so-called hemolysis develops.
In this condition, a person feels weakness, anemia, and jaundice characteristic of this condition, along with changes in the activity of all organs of the human body.
If any of the above symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help from doctors and, for your own safety, conduct a complete examination of the entire body. Only in this way can you protect yourself, thereby preventing one or another possible already emerging disease.
Source: diagnosis-med.ru
Smoking is harmful to health
Doctors concluded that smoking provokes an increase in red blood cells. Carbon monoxide, which is contained in tobacco, negatively affects the functioning of hemoglobin. Instead of oxygen, hemoglobin can carry carbon monoxide to cells. In this case, hypoxia occurs and general health deteriorates. Due to the fact that the body is trying to independently cope with the pathological process in the body, a compensatory mechanism is launched, which is aimed at increasing the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Nicotine not only disrupts the functioning of the lungs, but also provokes an increase in the width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume.
Red blood cell indices
Red blood cell indices measure red blood cell size and hemoglobin content and include mean erythrocyte volume (MCV), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin content (MCHC), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and red blood cell distribution by size (RDW).
The determination of the above indicators is an integral part of the general blood test and is not performed separately.
Average erythrocyte volume, average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes, average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes, distribution of erythrocytes by size, erythrocyte morphology index.
English synonyms
General information about the study
Erythrocytes are red blood cells, which are the main formed elements of blood. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs. It consists of the protein globin and a heme complex containing iron, which can bind to oxygen. In some people, the process of hemoglobin “assembly” may be disrupted, which affects the appearance and size of red blood cells.
Changes in the number of red blood cells are usually associated with changes in hemoglobin levels. When the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin level are reduced, the patient has anemia; when they are increased, the patient has polycythemia.
Erythrocyte indices allow you to estimate the size of red blood cells and the hemoglobin content in them. They characterize the cells themselves, and not their number, as a result of which they are relatively stable parameters.
Mean erythrocyte volume (MCV)
MCV is the average volume of one red blood cell. It can be measured directly by the analyzer by assessing many thousands of red blood cells, or it can be calculated using a formula as the ratio of hematocrit to the number of red blood cells.
This indicator is measured in femtoliters (10 -15 / l). One femtoliter is equal to one cubic micrometer (one millionth of a meter).
When there are large numbers of abnormal red blood cells (eg, sickle cell disease), the MCV count is unreliable.
Average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (MCH)
MCH reflects how much hemoglobin is contained on average in one red blood cell. It is measured in picograms (one trillionth of a gram, 10 -12 ) per red blood cell and is calculated as the ratio of hemoglobin to the number of red blood cells. It corresponds to the color indicator that was previously used to reflect the hemoglobin content of red blood cells. Typically, MCH in the erythrocyte is the basis for the differential diagnosis of anemia.
Mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
MCHC is an indicator of the saturation of an erythrocyte with hemoglobin; unlike MCH, it characterizes not the amount of hemoglobin in the cell, but the “density” of filling the cell with hemoglobin. It is calculated as the ratio of total hemoglobin to hematocrit - the volume occupied by red blood cells in the bloodstream. It is measured in grams per liter and is the most sensitive indicator for disorders of hemoglobin formation. In addition, it is one of the most stable hematological parameters, so MCHC is used as an indicator of analyzer errors.
Red blood cell distribution by volume (RDW)
RDW is the degree of dispersion of red blood cells by volume. There are different options for calculating this indicator. RDW-CV is measured as a percentage and shows how much the red blood cell volume deviates from the average. RDW-SD is measured in femtoliters, the same as mean red blood cell volume (MCV), and shows the difference between the smallest red blood cell and the largest.
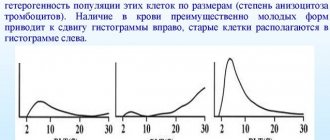
In general, RDW corresponds to anisocytosis, which is determined on the basis of blood smear microscopy, but is a much more accurate parameter.
What is the research used for?
Evaluation of erythrocyte indices allows you to get an idea of the characteristics of erythrocytes, which is very important in determining the type of anemia. Red blood cell indices often respond quickly to the treatment of anemia and can be used to assess the effectiveness of therapy.
When is the study scheduled?
As a rule, erythrocyte indices are included in a routine general blood test, which is prescribed both routinely and for various diseases, before surgical interventions. This test is repeated for patients undergoing treatment for anemia.
What do the results mean?
Mean erythrocyte volume (MCV)
Genetic predisposition
An increased level of red blood cells may be due to a hereditary factor. Some people's bodies produce erythropoietin in large quantities. This hormone often provokes the active formation of red blood cells. This phenomenon often occurs in congenital renal pathology. If there are problems with the blood supply to the kidneys, the level of erythropoietin increases. If the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume is increased, then this may indicate that someone in the family had erythrocytosis.
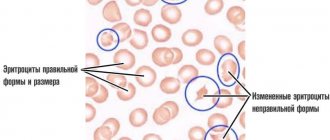
Anisocytosis of red blood cells
Anisocytosis of erythrocytes is a specific laboratory sign that is detected after deciphering the results of a general clinical blood test.
Changes in parameters can occur either up or down. Every person is susceptible to this disorder, regardless of gender and age. In most situations, the sources of deviation are pathological processes, including oncology, diseases of the hematopoietic system and other internal organs.
The clinical picture includes constant weakness and drowsiness, pale skin and shortness of breath, dizziness and decreased concentration. However, such signs often go unnoticed or are attributed to other conditions.
Diagnosis in children and adults is based on a general blood test. To identify the source, a complete examination of the body may be required, i.e., there is a need for additional laboratory and instrumental procedures.
Normalization of such values is achieved by conservative therapeutic methods, but it is not possible to completely get rid of the problem without eliminating the provoking disease.
In a healthy person, the concentration of normal red blood cells in the blood should be at least 70%, macrocytes and microcytes - no more than 15%. In children under 6 months of age, RDW SD ranges from 14.9 to 18.7%. Starting from the age category of six months, the parameter approaches the norms of adults and amounts to 11.6–14.8%.
The relative width of the distribution of erythrocytes by volume is increased in the following cases:
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- hemolytic form of anemia;
- megaloblastic anemia;
- chronic kidney disease;
- blood transfusion;
- myelodysplastic syndromes;
- malignant neoplasms of any location;
- chronic alcoholism;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- hemoglobinopathies;
- severe poisoning with lead and other chemical or toxic substances;
- metaplasia, which often develops with bone marrow or cardiovascular pathologies;
- cardiac ischemia.
When the distribution of red blood cells by volume is reduced, clinicians recommend retaking a general clinical blood test, since the RDW CV is almost never reduced.
If the indicator is slightly reduced and no other laboratory changes are observed, doctors consider this state of affairs as a variant of the norm.
It follows that low anisocytosis of erythrocytes has no diagnostic value.
During the course of some diseases, the distribution of red blood cells throughout the blood volume does not change. This is an extremely rare occurrence:
- with anemia that accompanies the chronic course of any disease;
- with beta thalassemia;
- with microspherocytosis;
- with sickle cell anemia;
- for acute aplastic or hemorrhagic anemia.
It is advisable to relate all etiological factors to persons of any age category and gender.
Based on the degree of severity, anisocytosis of erythrocytes has several course options:
- + or minor type - the pathological process affected no more than 25% of blood cells;
- ++ or moderate type - 50% of red blood cells are involved in the disease;
- +++ or pronounced type - modified blood particles predominate in number over healthy ones, their concentration is 75%;
- ++++ - pronounced or critical type, complete replacement of cells is observed.
By size they are distinguished:
- normocytes - volumes range from 7.1 to 9 micrometers;
- microcytes - less than 6.9 micrometers;
- macrocytes - more than 8 micrometers;
- megalocytes are cells with sizes of 12 micrometers and above.
Based on the above data, the rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis is divided into:
- microcytosis;
- macrocytosis;
- mixed form.
A person can suspect anisocytosis of erythrocytes by the presence of certain clinical manifestations, which, regardless of the cause, will be the same for everyone.
However, the peculiarity of this condition is that sometimes symptoms may be completely absent or disguised as an underlying disease, which is why it remains ignored.
People note:
- constant weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- inability to endure prolonged physical activity;
- decreased concentration;
- shortness of breath both during activity and at rest;
- causeless increase in heart rate;
- headaches and dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, nail plates and sclera;
- sleep problems;
- decreased appetite;
- impaired skin sensitivity to external irritants;
- lack of sexual attraction to the opposite sex;
- muscle weakness;
- hepatosplenomegaly - this may be indicated by an increase in abdominal volume, heaviness in the left or right hypochondrium;
- pain in the abdomen;
- redness and dryness of the tongue.
The severity of such clinical manifestations depends entirely on the index of erythrocyte anisocytosis.
It is possible to determine that RDW is increased or decreased using a laboratory examination of a smear of the main biological fluid, but to obtain more accurate results, a general clinical blood test is performed.
The test material is collected from a finger - it is best if the procedure is carried out in the morning and always on an empty stomach.
Deciphering the meanings is the responsibility of a hematologist, but to find out the cause, you should undergo a comprehensive examination, which begins with the following measures:
- familiarizing the clinician with the medical history - this will make it possible to identify the main pathological source, which can occur in acute or chronic form;
- collection and analysis of life history - to identify those provocateurs that are not associated with the course of a particular disease, for example, alcoholism or a previous blood transfusion;
- assessment of the general appearance of the patient - the specialist pays close attention to the skin and mucous membranes, tongue and sclera, nails;
- percussion and palpation of the abdomen will help determine hepatosplenomegaly;
- measurement of heart rate and blood tone;
- detailed interview with the patient - to obtain information regarding the full range of symptoms.
In addition, a number of specific laboratory tests and instrumental procedures are required. Consultation with clinicians from various medical fields may be required. This diagnostic program is individual.
If the erythrocyte distribution index is low or above normal, the first step should be to treat the underlying disease. In some situations, therapy is limited only to:
- changing your usual diet;
- refusal to consume alcohol;
- introducing foods fortified with iron and other micronutrients into the menu;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
In other circumstances, therapy will be purely individual:
- when cancerous tumors are detected, they turn to medical intervention, radiation treatment and chemotherapy;
- for gastrointestinal pathologies, drug tactics and diet therapy are used;
- myelodysplastic syndrome is eliminated through the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and other conservative methods.
Recovery is spoken of in such cases: improvement in well-being and complete absence of clinical signs, positive dynamics regarding changes in general blood test parameters.
To prevent anisocytosis of red blood cells, it is enough to strictly adhere to a few simple rules. Preventive recommendations:
- lifelong cessation of bad habits;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- constant strengthening of the immune system;
- avoiding physical and emotional stress;
- regularly undergoing a full preventive examination in a medical institution with visits to all specialists and the mandatory implementation of the necessary laboratory and instrumental procedures.
Regardless of whether the concentration of modified red blood cells is decreased or increased, the outcome of the condition will completely depend on the original source of the problem. Patients should not forget that the lack of treatment for the underlying disease is fraught with the development of complications that can lead to death.
Source: https://MedAnaliz.pro/krov/eritrotsity/anizocitoz
Water imbalance
Lack of water in the body causes blood volume levels to decrease. In this case, the blood is more viscous and thick. Under such conditions, a clinical blood test will indicate that the level of red blood cells is elevated. Doctors recommend monitoring the water balance in the body and drinking at least 1 liter of clean water per day. This will help prevent an increase in the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume. Even if you are slightly thirsty, you should take a few sips of water. Most often, dehydration occurs due to overheating of the body, an intestinal infection or a burn.
Kinds
There are two varieties of this indicator:
- RDW CV, that is, the relative value of the width of the red blood cell distribution by volume, demonstrating the coefficient of heterogeneity in the size of red blood cells. This indicator in the analysis is required to establish the nature of the differences between blood cells.
- RDW SD. Determines deviations from the standard norm, which reveal differences in the distance between the maximum and minimum volume of red blood cells.
So, RDW in the blood test is increased. The reasons for this are presented below.
Diagnostic process
If any signs of dehydration appear, it is important to consult a doctor immediately, as this can lead to the development of serious complications. Doctors recommend regularly taking a general clinical blood test. This will help prevent the development of serious diseases. If the patient has donated blood and is diagnosed with erythrocytosis, it is necessary to begin treatment.
Taking into account the individual physiological characteristics of each patient, the doctor prescribes specific treatment. It is not recommended to buy medications yourself from a pharmacy and take them without a doctor’s prescription. Because this will lead to the development of serious complications. First of all, it is important to fully examine the patient. The main goal is to identify the main disease that provoked an increase in the level of red blood cells in the blood. Many people are interested in what does increased distribution width of red blood cells mean? You should know that this phenomenon indicates that the cells are larger than each other.
Lower RDW
Situations where the RDW indicator is reduced are rare. A deviation from the norm to a lesser extent indicates the development of dangerous diseases and pathological processes in the body that require diagnosis and immediate treatment.
Why is this happening
The resulting value is below normal means that red blood cells lose their function due to some congenital and acquired diseases. The main reasons why a reduced CV occurs in a blood test:
- Profuse bleeding due to injuries or wounds. Bleeding in the uterine cavity or stomach poses a threat to health, and in some cases, life.
- Previous surgical interventions, during which resection of an internal organ was performed.
- Disturbances in metabolic processes, as a result of which food entering the body is poorly digested and remains in the stomach, where it ferments, thereby provoking a purulent process.
- Changes in hormonal levels - this factor is typical for women.
- Low concentration of vitamins and iron.
- Blood diseases characterized by the loss of red blood cells of their functions.
- Oncological neoplasms, mainly tumors of the lungs and brain.
- Pathologies of an autoimmune nature, as a result of which new red blood cells do not receive enough important components, which affects their parameters and functionality.
Important information: The normal number of red blood cells in the blood of a healthy person (how much should it be)
The cause of low RDW may be anemia - microcytic hypochromic anemia. In this pathological process, red blood cells have an irregular shape, differ in size and quickly die due to the fact that such blood cells do not represent biological value in the body.
If there is a suspicion that the test result was false positive, the blood will have to be taken again, carefully following the doctor’s recommendations. Factors such as smoking before taking the test, excessive psycho-emotional arousal, and eating food immediately before taking biological material can affect the result of the analysis.
Taking certain medications can also cause a false positive result. Therefore, if a patient is forced to constantly take medications for medical reasons, the laboratory assistant must be informed about this.
How it manifests itself
Low RDW levels are manifested by:
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- lethargy and apathy, drowsiness;
- rapid fatigue even without physical activity;
- frequent attacks of dizziness;
- decreased degree of performance;
- shortness of breath;
- dry cough;
- increased blood pressure;
- rapid heartbeat.
All these signs arise due to disturbances in biological processes. Red blood cells become much smaller in size, which is why they cannot fully perform their functions. Due to their insufficient size, red blood cells cannot deliver enough oxygen to cells and soft tissues. First of all, the central nervous system suffers from this, which, due to a lack of oxygen, cannot fully transmit impulses along the nerve fibers.
If RDW is reduced in a blood test in a 3-month-old baby, this sign may indicate congenital blood diseases. If the indicator deviates from the norm to a lesser extent, first of all it is necessary to exclude a diagnostic error by retaking the analysis. If a repeat analysis again shows an abnormality, it is important to determine the cause, especially to pay attention to possible oncological neoplasms, most often accompanied by a low level of RDW.
Important information: What do decreased (increased) segmented neutrophils in an adult indicate in a blood test?
What to do
An underestimation of red blood cells in the blood is a rare phenomenon, but it signals dangerous diseases and pathological processes that can occur in a latent form until some point and do not have a pronounced symptomatic picture.
There is no single scheme of measures that can be used to increase the level of red blood cells. In order for RDW to be brought to normal levels, it is necessary to determine the cause of the deviations and eliminate it. Given the wide range of causes, therapy is selected individually.
Prevention
Cases where a low RDW result turns out to be only a diagnostic error occur more often than situations where severe illnesses lead to discrepancies with the norm. To avoid a false result, it is necessary to follow all recommendations regarding preparation for the process of collecting venous blood for analysis.
Low red blood cell distribution is a fairly rare phenomenon. It is difficult to prevent the occurrence of this pathological symptom. But some preventive measures will help, if you do not maintain health, then identify the disease in a timely manner and treat it at an early stage of development, avoiding complications.
Prevention of low RDW levels is a set of measures that help maintain good health and prevent the development of many diseases. Such measures include:
- A proper, balanced diet, including foods enriched with vitamins and minerals.
- Fractional meals so as not to put a strain on the organs of the digestive system.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle. It is necessary not only to exercise regularly, but also to take walks in the fresh air, which have a positive effect on the circulatory system and the heart muscle.
- Regular preventive examination.
Even if no symptoms bother you, it is important to undergo a medical examination and laboratory tests at least once a year. There are diseases that last for a long time without a pronounced symptomatic picture. They can be detected in the initial stages only through timely and regular blood tests.
Preparing for the study
Doctors recommend not eating food several hours before donating blood. It is better to take the test early in the morning on an empty stomach. It is important not to exercise or get nervous the day before going to the hospital, as this may affect the results of the study. Most likely, the doctor will give a referral for:
- general clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the respiratory system;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Considering the fact that most often erythrocytosis appears due to dehydration, using a special form, doctors determine the water balance in the human body. To carry out this analysis, a person needs to collect urine throughout the day and determine its volume. If the color of the urine is too dark, this indicates that the body does not have enough water.
How to prevent the problem?
A value below normal is extremely rare, and it is quite difficult to prevent it. It is important to undergo regular preventive examinations and monitor your general health. To avoid false blood test results, you must follow your doctor's recommendations.
But it is important to adhere to the basic preventive rules that doctors advise:
- eat properly and balanced; your diet should include fresh vegetables and fruits;
- take walks in the fresh air;
- lead an active life;
- do gymnastics;
- At the first symptoms of illness, contact a medical facility.
Many serious diseases are hidden and do not manifest significant symptoms. Only with a complete examination can a pathological abnormality in the body be identified. Having determined the cause of the disorder, the doctor will be able to correctly prescribe drug therapy. Self-medication will only aggravate the situation; often lost time leads to serious consequences.
Treatment process
During the treatment process, it is important to exclude the influence of the etiological factor that provoked the onset of the disease. If hypoxia is detected in the patient, oxygen treatment is necessary. If the level of red blood cells in the bone marrow has increased, it is necessary to treat with a blood replacement solution and glucose. In case of advanced disease, the patient must be prescribed medications that thin the blood. This will help prevent the formation of blood clots. During the treatment process, it is important to follow the diet prescribed by the attending physician. Physicians often prescribe bloodletting - this will help reduce hemoglobin levels. When using oxygen inhalation, the functioning of oxygen transport into human cells is restored. Specific medications are prescribed by the doctor depending on the identified disease and the general health of the patient.
Therapeutic diet
With proper nutrition, you can lower the level of red blood cells in the blood. During the treatment process, doctors often prescribe special diets that help to positively affect the functioning of blood vessels. Proper nutrition thins the blood and strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
To reduce the level of red blood cells in the blood, doctors recommend including in the diet:
- dairy products;
- fish;
- walnuts;
- potato;
- watermelon.
There are foods that can increase the number of blood cells in the blood. If a patient is diagnosed with erythrocytosis, then the following should be excluded from your diet:
- beets;
- apples;
- meat soups;
- buckwheat porridge;
- chicken eggs;
- tomatoes;
- dried fruits.
The detailed menu can be discussed with your doctor. In addition to proper nutrition, doctors recommend regular blood tests. Patients are often interested in the question: if the width of the distribution of red blood cells is increased, what does this mean? Many people do not know that this may indicate that a serious disease is developing, which can only be cured under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Reasons for the increase
The described coefficient of blood cells is higher than normal with an increase in the percentage correlation between small and enlarged cells, in relation to the described elements having sufficient volume. Due to the so-called redistribution of iron-containing protein, which is the basis of blood cells, the smallest number of them in the body begins to be synthesized, which subsequently leads to the manifestation of various anemias, to anisocytosis - when the main part of the cells have characteristic differences from each other.
According to the above, the main feature of such bodies is their sufficient size, as well as the period of life. As a result of their death, a decent amount of bilirubin is released, which has a very bad effect on all organs of the human body.
The coefficient that distributes blood cells by volume can be high, since there are:
- Lack of components in the body such as iron, folic acid, vitamins belonging to group “B”. Such a condition may, not without reason, give a chance for the development of a disease such as anisocytosis, in which an increase in this index of elements of the hematopoietic system occurs;
- Oncological diseases leading to the formation of red blood cells of various sizes and volumes in the hematopoietic system;
- Intoxication with chemical elements in the form of heavy metals (such as lead).
All of the above signs of disease should be stopped with the use of professional therapy. Otherwise, they will seriously harm the body and lead to death.