Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is found in all tissues of the human body, but to a greater extent in the liver, bones and placenta. When at healthy levels, alkaline phosphatase protects your intestines from harmful bacteria and aids digestion. However, high levels of this enzyme in the blood usually indicate problems with the liver, kidneys or bones. Read on to learn about the causes of elevated alkaline phosphatase levels and how to lower these levels in ways that are natural to your body.
The article is based on the findings of 42 scientific studies
The article quotes authors such as:
- Department of Biochemistry, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- Department of Neurology, Cha Bundang Medical Center, Cha University, South Korea
- Kwangtung Catholic University St. Mary's International Hospital, Incheon, South Korea
- Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, USA
- Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepaticas y Digestivas-CIBERehd, Campus de Cartuja, Spain
Please note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, 3, etc.) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific studies. You can follow these links and read the original source of information for the article.
What is alkaline phosphatase?
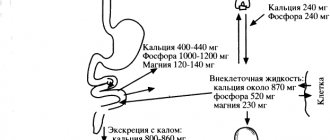
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is found in all cells of our body, but is mainly concentrated in the bones , kidneys , liver , intestines and placenta . It exists in different forms depending on where it originates. ()
When found in cells such as the liver and biliary tract, alkaline phosphatase catalyzes certain biochemical reactions in these cells. When cells are destroyed, phosphatase enters the blood, but it does not work in it. Gradually, all our cells are renewed, being destroyed in the process, so the blood constantly contains a certain level of alkaline phosphatase. But if massive cell death occurs, the amount of alkaline phosphatase in the blood increases greatly. What often happens in various diseases, for example, cholestasis, liver cancer, bone metastases or bone fractures.
For example, circulating alkaline phosphatase is known to be a reliable and independent predictor of all-cause mortality in the general human population and in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
EFFECT ON ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE LEVEL - A NEW TREATMENT STRATEGY TO REDUCE BLOOD VESSEL CALCIFICATION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE OR TYPE 2 DIABETES ()
The following alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes are found in humans and other mammals:
- ALPI—intestinal
- ALPL—in liver, bones and kidneys
- ALPP—placental
Some of the main functions of alkaline phosphatase include protecting your intestinal tract from bacteria, helping with digestion, breaking down fats and some B vitamins, and promoting bone formation. () Most doctors order an alkaline phosphatase test to assess the health of a patient's bones and liver, but many promising studies are emerging that support the positive role of this enzyme in gut health.
What it is?
First of all, it is worth finding out what the substance is. This is a protein compound that acts as a catalyst in metabolic processes involving calcium and phosphorus. This enzyme is located in the cell membranes of a wide variety of tissues. Therefore, several fractions of alkaline phosphate are distinguished:
- bone;
- hepatic;
- placental;
- intestinal, etc.
The substance molecule is a dimeric compound; it consists of two parts, each of which has several (most often three) active nuclei.
Advice! In the blood, the substance is contained mainly in two forms - bone and liver. The ratio of these isoenzymes is approximately one to one. The content of other isoforms is insignificant.
Functions of alkaline phosphatase
Supports brain function
You need to maintain a healthy amount of alkaline phosphatase to keep your brain functioning at its best. Elevated levels of this enzyme are associated with inflammation of small blood vessels in the brain, while lower levels may be beneficial for the brain. (, )
One of the isoenzymes of tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase helps the generation of new neurons , enhancing neurogenesis in both children and adults. Another isoenzyme, intestinal alkaline phosphatase, promotes healthy brain-gut communication by reducing inflammation and balancing microflora in the intestinal tract . ()
Maintains healthy teeth and bones
Alkaline phosphatase plays an important role in the development of bones and teeth , as this enzyme is necessary for their mineralization. During mineralization, substances such as calcium and phosphorus are deposited in bones and teeth to keep them strong. ()
Supports blood cholesterol levels
Pregnant women show higher alkaline phosphatase activity in the blood. Both triglyceride and total cholesterol rise in parallel with alkaline phosphatase levels, so cholesterol values correlate with the activity of this enzyme. ()
How to donate blood for alkaline phosphatase - preparation for analysis
A blood test for ALP is performed as part of a routine biochemical blood test.
- Blood is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach, from a vein.
- The day before donating blood, you should not drink alcohol, abuse fatty foods, or take multivitamins, medications, or dietary supplements without a doctor’s prescription.
- If you are undergoing treatment or regularly take life-saving medications, please inform your laboratory doctor on the day of donating blood.
A decrease or increase in alkaline phosphatase in the blood is a significant, but not the only marker of various diseases, including pathology of the liver and bones.
- Tags:
Save the article for yourself!
2 comments
Tatyana07/02/2018 at 18:01
Thank you very much for the article! Excellent like others on this site. I look here all the time, thanks for answering the questions!!! Good luck and health to you!
Antonina02.10.2019 at 11:10
thank you very useful article!
Add a comment Cancel Reply
Read more…
Norm and interpretation of general urine analysis in adults
Properties of intestinal alkaline phosphatase
There are several types (isoenzymes) of alkaline phosphatase, but the ALPI type found in the intestines is the most studied to date. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase is produced by enterocytes (intestinal epithelial cells).
Modern animal studies have demonstrated the very important role of intestinal alkaline phosphatase, which is naturally present there. The enzyme interacts with the intestines, the food we eat, and the microbes found in our bodies.
INTESTINAL ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE (IAP) REGULATES THE HOMEOSTASIS OF THIS ORGAN ()
Additionally, several animal and human studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of alkaline phosphatase supplementation. However, these studies have been limited and more research is likely needed.
Unlike other types of alkaline phosphatases, intestinal alkaline phosphatase is primarily associated with the intestinal mucosa, and approximately 1-2% may be present in the blood. ()
Some studies show that curcumin increases the level of intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity in the cells of this organ. ()
Protects against bacterial infection in the intestines
Many harmful gram-negative bacteria produce lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which can cause either an acute episode of infection (sepsis) or chronic inflammation.
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase is able to remove phosphate groups from these liposaccharides (LPS), which reduces their inflammatory effects . ()
In addition, intestinal alkaline phosphatase can also prevent bacteria such as Salmonella typhimurium and Clostridium difficile from entering the intestinal lymph nodes. ()
In a study on human intestinal cell lines, it was found that intestinal alkaline phosphatase can control cellular resistance to LPS in harmful bacteria. It is known that the presence of LPS in the blood can stimulate inflammatory processes in the body. ()
Helps restore intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics
Supplementing intestinal alkaline phosphatase to mice that were given antibiotics to fight salmonella and clostridia helped these mice recover their gut microbiota .
Mice given an oral calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase supplement during antibiotic treatment had fewer infections and lower mortality compared to mice not given the supplement. ()
Helps restore intestinal integrity in cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis impairs intestinal barrier function and increases intestinal permeability, which can lead to intestinal damage. It also causes a decrease in intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity. ()
In mice with cystic fibrosis, supplementation of intestinal alkaline phosphatase was associated with improved protection against intestinal permeability . This enzyme also reduced bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine by more than 80%. ()
ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE (IAP) IN THE INTESTINE PROTECTS THE BODY FROM THE PENETRATION OF WASTE PRODUCTS OF HARMFUL BACTERIA INTO THE BLOOD
Removes toxic microbial chemicals
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase removes phosphate groups from toxic microbial molecules such as leftover DNA and parts of harmful bacteria. This helps protect the body from inflammation . ()
Slows down the absorption of fats in the intestine
Mice without intestinal alkaline phosphatase absorb fat very quickly. As a result, these mice exhibit higher blood cholesterol levels ()
Reduces kidney damage from bacterial infection
In a clinical trial of people with severe bacterial infection (sepsis) that leads to acute kidney injury, administration of alkaline phosphatase through the blood helped improve overall kidney function . () This fact speaks of intestinal alkaline phosphatase as a promising substance for protecting the kidneys during sepsis.
Protects against type 2 diabetes
Mice deficient intestinal alkaline phosphatase can develop type 2 diabetes. Oral intestinal alkaline phosphatase supplementation prevents metabolic syndrome in mice fed a high-fat diet. ()
In another study, researchers examined the stool of 200 patients with diabetes and 400 people without diabetes. They found that compared to healthy controls, diabetic patients had lower levels of intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity. ()
In another study, intestinal alkaline phosphatase was good protection against type 2 diabetes even in obese patients. ()
Reduces inflammation in the intestines
Supplementation of intestinal alkaline phosphatase reduces levels of inflammatory proteins (TNF-alpha, IL-5, and IL-1beta) in infants suffering from increased intestinal cell death (necrotizing enterocolitis). However, the injection did not cure this disease, but only reduced its manifestations. ()
Reasons for deviations from the norm
Alkaline phosphatase can be reduced for various reasons.
Possible diseases:
- The development of hypothyroidism – swelling of the mucous membranes, mental and physical underdevelopment.
- Severe anemia.
- The formation of intestinal enzymopathy is celiac disease.
- Anomalies in the structure of the skeletal system.
Other causes of pathology:
- Lack of vitamins in the body, especially vitamins B and C.
- Lack of useful macro- and microelements - zinc, magnesium.
- Increased production of vitamin D.
- Reduced protein formation and, as a consequence, the development of dystrophy.
- The formation of placental insufficiency during pregnancy.
- Beginning of menopause.
- Kidney failure.
- Diabetes.
- Abuse of hormonal drugs containing high levels of estrogen.
- Previous bypass surgery or blood transfusion.
Among cardiovascular pathologies, the development of tachycardia, heart failure, increased cholesterol levels, and blood vessel diseases are noted.
It is extremely rare that the cause of pathology is congenital hypophosphotization. The process is caused by hereditary or genetic factors. The condition poses a high risk to the patient’s life, is accompanied by disruptions in the mineralization of bone tissue, breathing problems and requires immediate treatment.
In more rare cases, the cause of low enzyme levels may be improper storage conditions for the patient's blood serum or incorrect display of test results.
Causes of increased alkaline phosphatase
An increase in the concentration of the isoenzyme can occur for various reasons, including drug abuse (barbiturates, sulfonamides, nicotinic acid). Increased levels can also be observed in cases of alcohol poisoning during pregnancy.
Pathology often develops against the background of internal diseases. In this case, several main groups are distinguished: liver disorders, changes in the skeletal system, and other forms of diseases.
Liver disorders, bile duct disorders:
- The development of cirrhosis is the inhibition of most liver functions, the replacement of damaged tissue with scar tissue.
- Hepatitis formation - the activity of the isoenzyme increases 3 times.
- The presence of tumor processes (cancer) - metastases move from other organs.
- Cholangitis is an extremely rare occurrence and is characterized by inflammatory processes in tissues.
- Development of biliary cirrhosis - pathology is formed due to complications caused by cholangitis. In this case, an increase in the enzyme by more than 4 times is noted.
- An infectious form of mononucleosis - the process affects all liver tissues, a change in the properties of the blood is noted.
- Stagnant processes of bile – cholestasis.
- Damage to the biliary system. The formation of stones that provoke stagnation and outflow of bile.
Disorders in the skeletal system:
- Development of Paget's disease. The protective and regenerative properties of bone tissue are disrupted, and the process leads to further degeneration of the skeletal system and inhibition of basic functions.
- Osteomalacia. The pathological process is characterized by softening of bone tissue. The condition is complicated by a significant loss of phosphoric acid. Vitamins.
- The formation of sarcoma is internal damage to bones by cancer cells.
- Penetration of metastatic processes into the skeletal system from other organs.
- Enhanced metabolic functions.
Other forms of pathologies:
- Endocrine disorders that provoke disruptions in the metabolic processes of the thyroid gland and cause disturbances in the production of phosphorus and calcium are the primary form of hyperparathyroidism.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Development of ulcerative colitis.
- Pathological changes in intestinal functions.
According to official statistics, in most cases, the development of the disease is provoked by disorders caused by inhibition of liver function.
Normal alkaline phosphatase levels
Typically, a total alkaline phosphatase (ALP) blood test is performed to detect all types of this enzyme. And it is used to diagnose bone and liver disorders.
If your total alkaline phosphatase level is elevated, your doctor may order tests to determine if the specific type of alkaline phosphatase is elevated.
The normal range for total alkaline phosphatase in the blood is 30-140 U/L , although this may vary depending on the laboratory. It should be noted that children and pregnant women may show significantly higher levels of the enzyme in their blood and have their own standard of a “normal” range. ()
When the liver does not function properly, alkaline phosphatase enters the bloodstream and its levels increase significantly. In addition, any condition that affects bone growth or causes increased bone cell activity can increase alkaline phosphatase levels in the blood. For this reason, this test is commonly used to diagnose liver/gallbladder diseases and bone disorders. ()
Higher levels of ALP can be observed in people with blood groups 1 and 3. ()
In children
In young patients, changes in alkaline phosphatase concentrations are much more common. It must be borne in mind that initially the level of alkaline phosphatase in this category is much higher.
About 1.5-2 times. You need to start from the formal indicator. For the most part, the causes of deviations are natural. But not always.
More specifically, the factors are as follows:
- Active growth during childhood. It occurs in everyone, but to varying degrees. The more significant the process, the higher the ALP levels. There is no need for medical correction. This is the norm.
- Transition to puberty. The period of puberty is associated with enormous stress on all systems of the human body. Deviations in alkaline phosphatase are considered a clinically acceptable option.
To talk about disorders, you need to consider the patient’s condition, his well-being, and study other objective indicators. That is, it is possible to differentiate between normal and pathological conditions only through diagnostics. Usually everything is fine. You don't need to do anything.
- Poor or unhealthy diet. Nutritional factors in childhood and adolescence pose a huge threat. Because there is a lack of “building material” necessary for the development of the body in physical and mental terms. To eliminate the problem, you need to adjust your diet and diversify it.
- Mononucleosis. Infection with the fourth type of herpes virus. It is especially common in children due to a weak immune system. However, the disease is tolerated somewhat less frequently when compared with adults.
- Intestinal infections. Including colitis caused by poisoning.
Usually, in a child, alkaline phosphatase increases due to the active growth and development of the whole organism, but this is not always the case; it is necessary to monitor the person’s condition and, if necessary, carry out targeted diagnostics. In order not to miss possible problems.
Diseases for which elevated alkaline phosphatase levels are diagnosed
If it is unclear why total alkaline phosphatase levels are elevated, additional isoenzyme studies using electrophoresis can confirm the source of the increase.
Bone phosphatase (which is localized in osteoblasts and extracellular layers of newly synthesized matrix) is released into the blood by an as yet unclear mechanism.
Placental alkaline phosphatase is often elevated in seminomachi and active forms of rickets.
The list of diseases in which an elevated level of total alkaline phosphatase is detected:
- Bile duct blockage
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder)
- Fractures and cracks of bones
- Bone tumors
- Bone metastases
- Osteomalacia
- Osteoporosis
- Hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
- Liver cancer
- Gallbladder cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Chronic kidney disease
- Acute cholecystitis
- Myelofibrosis
- Leukemoid reaction
- Lymphoma
- Paget's disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hodgkin's lymphon
- Wilson's disease
- Myocardial infarction
- Ulcerative colitis
- Pregnancy
- Alcoholism
When is a test ordered?
Very often, doctors recommend taking this test before performing a planned operation, as well as as part of a preventive examination. But it is considered more appropriate to prescribe alkaline phosphatase in the presence of complaints and anamnestic data.
The first group of diseases in which determination of phosphatase may be valuable are those accompanied by stagnation of bile.
Therefore, the doctor has the right to prescribe an analysis if the following complaints and symptoms are present:
- yellowness of the skin;
- icterus of the sclera and mucous membranes (slight yellow staining);
If the alkaline phosphatase level is exceeded, jaundice appears
- presence of discolored stool;
- pain in the abdomen, more on the right and above;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- severe skin itching, in which even antihistamines do not always help.
Doctors recommend an alkaline phosphatase test to confirm or rule out liver dysfunction. In parallel, it is important to know the level of cholesterol, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, as well as conduct a thymol test and determine the content of protein and its fractions.
To exclude bone diseases and metastases of tumors to the bones, the described analysis is also recommended. The examination is complemented by determining the amount of phosphorus and calcium in the serum as part of a biochemical analysis.
Other Causes of Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Levels
While alkaline phosphatase may not necessarily cause harm to the body itself, elevated levels of this enzyme have been linked to cancer , bone , liver , and kidney . () Additionally, lifestyle factors, medications, and some supplements can increase alkaline phosphatase levels.
Birth control pills
Birth control pills can raise alkaline phosphatase levels many times above the normal range. (8)
Exercise stress
Exercise increases bone alkaline phosphatase levels after thirty and fifty minutes of moderate to vigorous exercise in male cyclists, but these values quickly return to normal. ()
Thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones stimulate alkaline phosphatase. (, ) Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase also correlate with the severity of hyperthyroidism . ()
Colon cancer
Alkaline phosphatase levels are often high in patients with metastatic colon cancer . Elevated alkaline phosphatase values correlate with increasing cancer stage and may indicate that the cancer has spread to the liver. ()
Mammary cancer
Women with breast cancer had elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase compared to healthy women. An increase in enzyme activity also indicates that metastases have occurred and have spread to either the bone or the liver. (, )
Alzheimer's disease
Patients with Alzheimer's disease have higher levels of alkaline phosphatase compared to healthy patients. The higher the alkaline phosphatase activity, the lower the brain function in these people. ()
LIST OF BASIC ANALYSIS WHEN ASSESSING LIVER HEALTH:
AST , ALT , ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE , GGT (Gamma-glutamyltransferase)
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is usually accompanied by an increase in the level of total alkaline phosphatase in the blood. However, this is not the best indicator for identifying a deficiency of this vitamin. ()
Heart diseases
Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase are associated with a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease .
In a prospective study of more than 3,000 older men, higher alkaline phosphatase levels predicted a greater risk of heart attacks, strokes, and increased mortality. ()
Liver problems associated with celiac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the lining of the intestines when gluten . In cases of uncontrolled celiac disease, when patients continue to consume gluten in food, other liver and biliary tract diseases may occur. Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase are associated with these two disorders. ()
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is associated with high levels of alkaline phosphatase. Higher levels of alkaline phosphatase correlate with worsening bone and other tissue health in patients with sickle cell disease. (, )
In patients with sickle cell disease, higher levels of alkaline phosphatase are associated with vaso-occlusive crises. ()
Epilepsy
Children with epilepsy show higher levels of alkaline phosphatase compared to children without the condition. ()
Symptoms and signs of elevated ALP
High ALP levels may accompany pain in the right hypochondrium
- Presence of symptoms of damage to the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts:
- pain in the right hypochondrium, pain or discomfort when palpating this area;
- intolerance to fatty foods;
- jaundice;
- sometimes increased body temperature;
- in severe cases - signs of liver failure (encephalopathy, edema, ascites, increased bleeding), dilation of the veins of the esophagus and stomach.
- Presence of symptoms of bone tissue damage:
- pain in the projection of the bone;
- deformation of the affected area;
- dysfunction, especially when the bones of the extremities are involved;
- pathological mobility during fractures;
- fever;
- sometimes - external signs of inflammation - redness, swelling, local increase in temperature.
- Symptoms of intestinal damage:
- spasm-type pain along the small or large intestine, less often dull or nagging pain;
- increased intestinal motility, rumbling;
- poor absorption of food, resulting in weight loss;
- diarrhea, stool frequency can be dozens of times a day;
- pathological impurities in the stool - blood, pus, mucus, or the release of helminths living in the intestines.
- Common symptoms of blood diseases:
- asthenia (weakness, lethargy, drowsiness);
- slight increase in body temperature;
- enlargement of lymph nodes of various locations, they can be elastic or dense, numerous or single, mobile or immobile;
- possible enlargement of the spleen and liver;
- possible bone pain due to bone marrow growth;
- anemic syndrome (weakness, pallor, heart murmurs), hemorrhagic syndrome (increased bleeding of mucous membranes, hemorrhagic rash, easy bruising in places of physical impact on the skin);
- change in the number of certain types of cells in a general blood test;
- identifying the pathological picture of a bone marrow or lymph node biopsy.
- Detection of an increase in alkaline phosphatase in the blood serum when taking blood for testing.
Rumbling in the stomach is one of the unpleasant symptoms of high ALP
Patients may indicate weakness
| Floor | Age | High values of alkaline phosphatase in the blood, U/l |
| Both sexes | Children up to 2 weeks of life | > 270 |
| Children from 2 weeks to 1 year | > 520 | |
| Children 1-10 years old | > 370 | |
| Children 10 - 13 years old | > 460 | |
| Female | Girls 13 - 15 years old | > 280 |
| Girls and women over 15 years old | > 150 | |
| Male | Boys 13 - 15 years old | > 520 |
| Boys 15 - 17 years old | > 360 | |
| Boys 17 - 19 years old | > 160 | |
| Boys and men over 19 years of age | > 150 |
How to reduce alkaline phosphatase levels?
Manage your condition that causes elevated alkaline phosphatase levels
Elevated alkaline phosphatase is usually a symptom of some disease. Therefore, to reduce your alkaline phosphatase levels, you need to treat the underlying condition. For example, if your doctor determines that your high titers of this enzyme are caused by liver disease, he will prescribe you a medicine to treat your liver. High alkaline phosphatase levels will normalize on their own after liver disease reduces in severity or is treated.
Find out if your medications cause an increase in alkaline phosphatase
Some medications have the side effect of increasing phosphatase levels. If you experience a side effect like this, your doctor will likely ask you to stop taking one or more of these drugs for a certain amount of time (for example, a week) and then ask you to take a new blood test. If your alkaline phosphatase levels do not decrease, you may need to stop taking another medication for a week to determine if there is a drug cause for the enzyme increase.
Medicines that can cause high alkaline phosphatase levels (3):
- Birth control pills and hormonal drugs
- Antidepressants and anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Various steroids and drugs
Help your liver work
If your alkaline phosphatase levels are high because you have been diagnosed with liver damage due to disease, then look into additional options to support liver health. Your liver has the ability to regenerate, so taking a variety of protective herbs and nutrients, adapting your diet, and reducing your alcohol intake will help.
Additional substances to protect the liver:
- Milk thistle
- NAC (N-acetyl-cysteine, approximately 300 mg per day according to studies)
- Taurine(500 mg)
- Vitamin C(500 mg)
- B vitamins (low doses)
- Lipoic acid
Vegetables such as broccoli (), onions (), dandelion greens, cabbage, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts () also have a cleansing and regenerating effect on the liver.
WHAT WORSES THE WORK AND HEALTH OF YOUR LIVER
Eliminate foods high in zinc from your diet
Zinc is a structural element of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase . This means that eliminating foods high in zinc from your diet will automatically reduce the amount in your body (). Check food labels if you are unsure how much zinc they contain.
Foods that contain large amounts of zinc:
- Mutton
- Beef
- Pumpkin seeds
- Oysters
- Spinach
Eat foods high in copper
Copper is important in regulating the levels of various enzymes in our body, and it has been shown to help reduce high levels of alkaline phosphatase. ()
Complications without treatment
Changes in the biochemical blood test themselves do not pose a threat to human life. Diseases that cause an increase or decrease in alkaline phosphatase are dangerous.
Bone tumors can be aggressive. Early detection and initiation of specific treatment minimizes early disability and mortality in these cases and provides a chance for a high five-year survival rate. Identification of the primary site within metastasis also allows timely initiation of therapy and achievement of a favorable prognosis.
Hepatitis is dangerous and can lead to cirrhosis. This applies to viral hepatitis C, which goes unnoticed for a long time.
Cirrhosis is complicated by loss of liver function, development of bleeding, decreased protein levels, and failure of heart function.
Bone tumors are dangerous due to skeletal deformation. If metastases occur, complications depend on their location. Foci in the brain and liver are especially dangerous.
Alkaline phosphatase is not a specific marker for any disease. But this indicator indicates to specialists in which direction to look for pathology. It is important to understand that the norms differ for men and women of different ages. An additional examination is ordered to find the cause. As a result, the causative factor is identified and its specific treatment begins.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Low ALP levels during pregnancy
ALP levels during pregnancy are higher than normal
During a pregnancy that is proceeding well, the alkaline phosphatase level should be higher than in the normal state. This is explained by the fact that an additional substance begins to be produced by the placenta. In this condition, a reduced level is an indicator of placental insufficiency, which is dangerous due to termination of pregnancy or the birth of a child who will not be viable.
What to do
An increase in phosphatase levels is not a disease, but it is an accurate indicator of the condition of the baby’s body.
In order to reduce its level, it is necessary to diagnose the reasons for the increase in the indicator. Typically, treatment of pathologies found in the body occurs through surgery, elimination of symptoms of concomitant diseases, and treatment with medications (antibiotics, injections, anti-inflammatory drugs).
Treatment is prescribed to each patient individually by the attending physician and depends entirely on the underlying cause of the condition.
The attending physician must take into account that there are a number of natural factors in which the level of the component may increase, but this does not entail any threat to the life and health of the baby.
If the doctor doubts the reasons for the increase, he will prescribe an additional examination. After diagnosing the root cause of the disease, the therapist can redirect the patient to a more highly specialized specialist, for example, an orthopedist, surgeon, or oncologist.
Features of increase in adults
There are a number of nuances that need to be taken into account when deciphering the results of an alkaline phosphatase blood test. First, in men the content of isoenzymes in the blood is always higher than in women. The difference is approximately 20-25 points. With age, the amount of alkaline phosphatase increases in everyone. This means that the concentration of this element depends on the age and gender of the person.
The most popular natural causes of high blood enzyme levels in adults are:
- Avitaminosis;
- Poor nutrition;
- Excessive physical activity.
The list of possible reasons for increased levels in women is supplemented by the following “moments”:
- Pregnancy, the period before the birth of a baby;
- Breast-feeding;
- Climax;
- Taking hormonal contraceptives. With long-term use, complications in the form of diseases are possible, for example, cholestatic jaundice and intrahepatic cholestasis.
For more information about changes in phosphatase levels during pregnancy, read the article Alkaline phosphatase is elevated during pregnancy: norms, symptoms, causes.
Men over 50 years of age are at risk. They are more likely to develop Paget's disease (skeletal deformity).