What is the name of the technique designed to study the filling of an organ with blood? This is plethysmography. Within its framework, the volume of an organ is measured at different stages of the functional cycle. These indicators help determine both the volume of blood inflow and outflow from it (the moment of inhalation and exhalation), as well as changes in permeability and electrical resistance. All this together makes it possible to diagnose a wide range of diseases. Let's look at the indications for plethysmography, characteristics of its varieties, preparation for the examination, and the significance of its results.
Indications for the procedure
Why is plethysmography prescribed? This examination helps identify the following pathologies and diseases:
- Phlebeurysm.
- Vascular thrombosis.
- Raynaud's disease.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Vasculitis.
- Atherosclerotic pathology of arteries.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain.
- Neuropathies and angiopathy observed in diabetes mellitus.
- Lung diseases (the information obtained about the capacity of the organ is valuable) - emphysema, obstructive bronchitis, bronchial asthma, pneumosilicosis and other occupational injuries to pulmonary tissues.
- Low erection in men. By assessing conditioned reflex activity, the technique allows us to determine the causes of dysfunction.
By the way, plethysmography is used to diagnose a number of mental and sexual disorders - pedophilia, homosexuality, and a tendency to sexual violence. The subject is shown images, and the plethysmograph records signs of sexual arousal at this moment.
First and modern devices
The first devices were completely mechanical. The principle of their operation is quite simple: the research chamber was equipped with rigid walls, between which the research area was located. The water chamber was filled with water, and the air chamber was sealed.
As soon as the organ expanded, it began to displace part of the air or liquid mass from the chamber. Under the influence of this, the moving part of the device began to move, which was recorded on tape or photographed.
Modern plethysmography is a combination of models. That is, electrical mechano- and cardiographs equipped with photo recorders. They are distinguished by a wider range of applications. The devices help analyze the blood flow of such large areas as the head, abdominal, chest areas, etc.
Electrophotoplethysmographs—combined photoelectric systems—are also considered a very useful discovery. They allow you to examine flat areas of the body - for example, the ear, skin folds, hands. But this method is not yet perfect - it does not provide certain quantitative indicators. The results obtained provide only general data about blood circulation - whether it is normal or whether there is some kind of disorder.
Types of research
Today there are several methods of plethysmography. Each one is aimed at a specific examination of the heart, kidneys, and other organs. This or that type is prescribed by the treating specialist based on the goals of the procedure and the need to conduct a stress test.
Methods for studying vascular reactions (rheography, plethysmography) are divided into the following types:
- Impedance form.
- Venous impedance form.
- Integral form.
- Occlusal form.
Each of these examinations has its own set of contraindications. The referring specialist - a vascular surgeon, therapist, neurologist, phlebologist - should inform you about them.
Next, we will analyze each of the presented categories in detail.
Impedance method
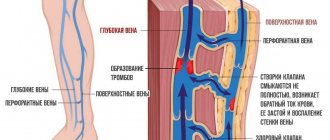
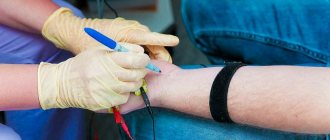
Another name is rheography. The operating principle is based on a change in impedance (resistance) to electric current. What does it mean? With an influx of blood mass, electrical conductivity increases. This is due to the fact that blood has the highest ability to conduct a pulsed electrical wave (among all other biological fluids).
The rheogram is recorded using electrodes that are placed on the subject’s body. An electric cardiograph with a special attachment can also be used for this task.
The resulting graph is a sine function. A rise in it is the flow of blood from the arteries, a decline is, accordingly, venous outflow. To judge the patient’s condition from the graph, a specialist should study a considerable volume of such fluctuations, evaluate their similarities and differences, the dynamics of growth, as well as the presence of additional waves during decline.
The main purpose of rheography is to study the filling of the heart chambers with blood. It is most often carried out in parallel with an electrocardiogram.
Diagnostic capabilities of the method
A pulse wave is a wave of increased pressure that propagates through the aorta and arteries due to the ejection of blood from the left ventricle during systole (contraction of the heart muscle). A short-term expansion of a section of the arterial wall can be recorded in the form of a pulse impulse. The speed of propagation of the pulse wave through the vessels depends on the width of the lumen and elasticity of the vessel, the thickness of its wall and blood density.
The pulse wave is formed as a result of the interaction between the left ventricle and the vessels of the systemic circulation. It consists of two peaks: the first is formed due to the systolic wave, the second corresponds to the reflected wave due to the blood transmitted to the lower extremities and directed back to the aorta. It is known that the intensity of reflection is determined by the tone of arterioles, therefore analysis of the pulse waveform makes it possible to assess the functional state and structural changes of the peripheral vascular bed.
It is believed that the duration and frequency of the pulse wave depend on the work of the heart, and the shape and size of its peaks depend on the condition of the vascular wall. When assessing the photoplethysmogram, narrowing of the arteries, including vascular ischemia of the lower extremities, can be determined. The properties of the waves when measured on the right and left legs should be the same, and if one of them is affected, asymmetry occurs.
To assess vascular reflexes using this method, various functional tests are used (for example, a compression and decompression test with determination of pressure in the brachial artery allows one to study the state of venous blood flow, a drug test with nitrogycerin - to assess tolerance to nitrates, etc.).
When monitoring treatment, photoplethysmography helps to select the optimal dose of the influencing factor and prevent negative reactions associated with its overdose.
Rheography results
All rheograms obtained during the examination can be divided into main categories:
- Normal. It is characterized by a smooth descent and ascent, as well as the presence of a small depression on the round top.
- Hypovolemia. Indicates low blood flow. The waves are small, with steps visible on the ascending part, while the descending half will be completely flat.
- Hypervolemia. The volume of blood supply to the organ is higher than normal. This is indicated on the graph by a curve with sharp peaks, sharp descents and a large amplitude.
- Hypertension of the pulmonary vessels. Pathology is determined by a sharp rise, slow descent and a rounded top.
Impedance method results
The results of impedance plethysmography are interpreted as follows:
- Insufficiency of outflow through the veins is determined by the descending side of the graph and the presence of additional fluctuations on it. Attention is paid to the distance from the top to the lowest point of the curve.
- If oxygen supply to the tissues under study is impaired, the rheographic index will be reduced. For a specialist, this is a sure indicator that blood flows into these tissues poorly and does not flow out of them through the venous vessels.
Features of photoplethysmography
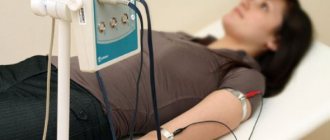
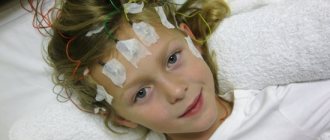
When photoplethysmography is performed, a number of special conditions must be observed. Since the vessels of the superficial layers of body tissue (skin, visible mucous membranes) are quite sensitive to ambient temperature and subtly respond to its changes, photoplethysmography of the skin and mucous membranes, especially in the mode of recording reflected light, is carried out in a room with a stable air temperature in the range of 19-23 ° C and humidity 50-60%. To control these conditions, a thermometer and a psychrometer are installed in the photoplethysmography room, the readings of which are recorded in the patient’s functional examination card.
There should be no sources of infrared radiation in the room for photoplethysmography studies.
When examining the oral cavity, dental lights are used. Photoplethysmography is carried out in normal daylight, and in the evening when the room is illuminated with ordinary lamps.
To prevent direct light from entering the photo-plethysmographic sensors, they are covered with dark (black) paper or thick fabric (in the form of napkins, sterilized together with the dressing material).
Photoplethysmography (like rheography) is carried out in a horizontal position of the subject on a medical couch. Synchronously with the photoplethysmogram, it is necessary (as with rheography) to record an ECG in standard lead II.
When performing photoplethysmography of the skin in reflected light, it is wiped with cotton swabs moistened with alcohol or ether to remove fat and sweat, which can significantly change the reflective properties of the skin. Since the evaporation of alcohol and ether cools the skin and spasms of superficial vessels occur, the study is carried out some time (8-10 minutes) after a normal level of blood supply to the tissue has been established. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is carefully (without pressure) wiped with dry cotton swabs and during the study is isolated from saliva with cotton swabs, rollers or using a saliva ejector. If the skin or mucous membrane is discolored (pigmented, coated with dyes, such as methylene blue, etc.), these factors are taken into account during photoplethysmography and noted on the examination card. Usually, to exclude these factors, a control registration of the PPG of a symmetrical or nearby area of tissue that has not changed in color is carried out.
When examining children, the significant lability of the photoplethysmogram is taken into account. In children, functional tests are the most unstable, especially for holding the breath, etc. Therefore, to obtain background PPGs, 5-6 recordings are necessary.
To check the stability of the photoplethysmograph and eliminate artifacts, a filter is placed between the sensor and the illuminator, equivalent in its optical density to the tissue being studied, the sensor is covered with black paper or cloth, and a test recording is made; When the device is in working order, the recorder records an isoelectric line with minor fluctuations not exceeding 3% of the main amplitude.
Displacement of the sensors can cause artifacts, so their reliable, stable fixation in relation to the tissue area being examined is necessary. When establishing photoplethysmography techniques, it is advisable to compare the results obtained using simultaneous recordings of the photoplethysmogram and rheograms for their mutual correlation and comparability.
Occlusal method
In what cases is occlusion plethysmography used? To assess the stage of expansion and blockage of venous vessels, their reaction to a certain load. The method involves creating an artificial obstacle to the outflow of blood. To do this, a cuff is placed on the vein a little further from the area being examined.
After air is inflated into it (the cuff), the specialist re-measures the resistance to electric current on the device. The data obtained are compared with those obtained before the impact of the obstacle. As a result of this comparison, the doctor can judge the risk of developing venous insufficiency or its presence.
Varieties
Plethysmography of the veins of the lower extremities can be performed in various ways, depending on the indications for its implementation. Types of diagnostics:
- Mechanical. During the examination of the lower limb, the entire part being examined is placed in a hermetically sealed vessel with solid walls. The vessel can be filled with liquid or air. Fluctuations in air (the method is called air plethysmography) or water, occurring as a result of blood circulation, are transmitted to a recording system, where they are analyzed.
- Electric or induction. As a result of the test, changes in the electrical conductivity of the lower limb are recorded. Another name for the study is electroplethysmography or impedance plethysmography. During inductive plethysmography or rheoplethysmography, tissues are exposed to high-frequency currents, in contrast to classical rheovasography, when currents of lower frequencies are used. Like all biological fluids, the tissues of the lower limb have a high coefficient of electrical conductivity. Therefore, plethysmography allows one to quickly and clearly determine dynamic changes in blood supply and microcirculation.
- Photoelectric method (densography). The method is based on determining changes in the light transmission of the lower limb that occur as a result of blood filling the veins of the legs.
Occlusion plethysmography is one of the variants of vein plethysmography.
A variant of mechanical plethysmography of veins is occlusion plethysmography. A distinctive feature of this diagnostic option is that the limb is examined mechanically after a belt or cuff is placed on it, creating an obstacle to the outflow of venous blood from a part of the body.
Integral method
It is also called bodytest, plethysmography of the whole body. The purpose of such a study is to study the patient’s pulmonary respiration.
How is whole body plethysmography performed? The patient is inside a special sealed chamber of the device, and his respiratory tract is connected to a pneumotachometer - a device that records air movement. A special catheter with a balloon is placed into the human esophagus, the pressure in which will be close to pleural.
This study (plethysmography of the whole body) helps to obtain a set of valuable indicators:
- Volume of inhalation and exhalation.
- Lung reserves.
- Extensibility of pulmonary matter.
- The degree of resistance to bronchial air flow.
How is it carried out?
During the procedure in the room, the air temperature should not exceed 19-23 degrees, which will avoid a distorting effect on the reaction of blood vessels. At lower temperatures, the patient is more likely to develop arteriolar spasm. When taking measurements, make sure that the sensor is not exposed to direct sunlight.
When performing the procedure, the patient must be in a calm state in a lying or sitting position. During photoplethysmography, you must relax, and the limb with the sensor must be motionless.
The fact is that muscle contraction can distort the final results of the study when analyzing the photoplethysmogram.
Preparation for the procedure
Thus, in modern medicine, the study of venous outflow is mostly carried out using plethysmography. The method is distinguished by high information content coupled with complete patient safety. When compared with common angiography, this method does not require the introduction of a contrast agent through a catheter, for which a number of contraindications are prescribed. Unlike radiography, it does not involve radiation harmful to humans.
Another significant advantage is that you do not need any special preparation for plethysmography. There are no restrictions on diet, lifestyle, activity, or taking medications on the eve of the procedure.
The only wish is that the patient should be in a relaxed and calm state during the examination. If pain or muscle tension in a specific disease does not allow this, then it makes sense to administer sedatives.
Indications for the study
Photoplethysmography is used to identify changes in blood vessels that occur with varicose veins, hypertension, atherosclerosis and other pathologies. In addition, if the condition of the blood vessels improves, we can talk about the effectiveness of the therapy and rehabilitation techniques.
In sports medicine, using a photoplethysmograph, it is possible to select an individual training regimen for an athlete. With increased physical activity with an increase in muscle volume, severe overload of the veins and even their rupture are observed. In order to prevent the development of varicose veins and many complications, it is necessary to regularly monitor their condition.
Using photoplethysmography, it is possible to identify contraindications for certain rehabilitation procedures and fitness. Particular attention is paid to the body's tendency to form blood clots in blood vessels. The main place where a blood clot appears is the walls of the veins of the lower extremities, and after it breaks off, it can clog a vessel along its path. In such a situation, a dangerous condition develops that threatens human life.
It is recommended to undergo a computer photoplethysmograph test before starting training or other exercises that increase the likelihood of a blood clot breaking off.