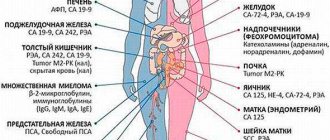
Conducting an accurate differential diagnosis of oncological pathologies of pelvic organs and tissues in women is one of the most difficult tasks in modern medicine. The most reliable biopsy method, which involves excision of a piece of tissue followed by microcopying, cannot be used in routine gynecological diagnostics. Tumors of the internal genital organs in women are quite common and are often not malignant. Therefore, in order to conduct a quick differential diagnosis, a blood test for the He 4 tumor marker is used.
Tumor marker for epithelial ovarian cancer He 4 is a modern criterion sufficient for the primary diagnosis of a patient in order to determine the risk of developing cancer.
Description and advantages of the marker
This is a modern criterion that is considered sufficient for making a preliminary diagnosis, determining the risk and dynamics of the development of a malignant tumor. It is used in cancer screening studies in fertile women and postmenopausal patients.
HE-4 is a tumor marker (deciphering the analysis provides valuable diagnostic information) of epithelial malignant hyperplasia, inhibiting proteolytic enzymes. Its chemical structure is made up of glycoprotein protein molecules.
The main advantage of a blood test for HE-4 is its high information content. In the recent past, the CA-125 tumor marker was used for early diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which does not allow distinguishing malignant from benign hyperplasia.
This biochemical protein compound, secreted by pathologically altered cells, is one of the most studied criteria for the formation and development of tumor diseases of the pelvic organs.
The disadvantage of CA-125 is its low sensitivity. It does not allow diagnosing the early stages of the pathological process. The combination of HE-4 and CA-125 indicators makes it possible to reliably determine the malignant nature of the epithelial neoplasm and its morphological characteristics.
The diagnostic technique does not respond to germ cell tumors that form during intrauterine development. The analysis does not detect hormonally active hyperplasias resulting from mutagenesis of granulosa cells.
Additional studies on CA-125 are prescribed if an increased concentration of the HE-4 tumor marker is detected in the hematological fluid. The complex methodology is considered the most reliable and informative.
A significant portion (about 90%) of clinically documented cases of ovarian cancer are epithelial hyperplasias, which until recently were considered a difficult diagnostic task to recognize at an early stage.
A glycoprotein protein compound allows one to determine the degree of development of the pathological process, the level of metastasis, and the likelihood of relapses after therapy.
For the utmost accuracy of diagnostic testing, American scientists have developed the ROMA algorithm. This is a mathematical model of the likelihood of developing malignant epithelial hyperplasia, based on a combination of tumor markers HE-4 and CA-125.
The ROMA index takes into account the patient's age and her menopausal status. Initially, the model was built on a set of 7 marker criteria. It is the combination of HE-4 and CA-125 indicators that provides maximum predictive accuracy.
Application
The tumor marker He-4 (Human epididymis protein) is considered the most sensitive at the very initial stages of the formation of malignant tumors, which helps to detect the disease early. Its main disadvantage is that it is not susceptible to germ cell and mucoid malignancies.
The He-4 tumor marker identifies malignant neoplasms of the ovaries and uterus in women. According to statistics, epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) ranks 5th among pelvic cancers, with a mortality rate of approximately 50%. The reason for such a high mortality rate is the absence of symptoms at the initial stage of the disease. Malignant neoplasms of the ovaries occur most often in women 55-70 years old.
Important! The He4 tumor marker detects ovarian cancer in the early stages, when the disease responds positively to treatment. Other tumor markers make it possible to detect malignant tumors much later, when symptoms of the disease have already appeared.
To identify ovarian cancer, the CA-125 marker was used in many cases, but in our time it has become clear that it is the He-4 marker that diagnoses the presence of pelvic cancer much more correctly.
Studies have shown that CA-125 levels increase a short time before a definitive diagnosis of ovarian cancer, and He-4 levels increase 2 or 3 years before the diagnosis of a cancerous tumor. The combination of two studies (He-4 and Ca-125) is especially effective in epithelial ovarian tumors. The marker CD 15 (leukocyte antigen Sidi) is also used. With ovarian cancer, it is common to have no symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Malignant neoplasms of the ovaries cannot be detected during a routine gynecological examination. Therefore, it is very difficult to diagnose them in time without analysis to determine the level of the HE-4 tumor marker. Symptoms appear in the later stages of the disease, and metastasis occurs early (to the uterus, peritoneum, liver, intestines).
Indications for analysis
Laboratory testing is not included in the mandatory diagnostic complex and is prescribed only if there is reasonable suspicion of epithelial hyperplasia in the pelvic area and organs of the reproductive system.
Clinical symptoms that serve as a reason for testing:
- periodic nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
- menstrual cycle disorders in women of reproductive age;
- inter-cycle blood or purulent discharge;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse;
- general weakness;
- abdominal swelling and protrusion determined by palpation;
- sudden weight loss for no apparent reason;
- sharp deterioration in appetite;
HE-4 is a tumor marker, the decoding of which provides not only basic diagnostic, but also important prognostic information. A private basis for prescribing a laboratory blood test is to assess the likelihood of developing malignant tumor pathology of epithelial tissue.
It is recommended for women during menopause to undergo such a study periodically. Oncologists often prescribe a HE-4 test to monitor the effectiveness of ovarian cancer therapy. The examination is indicated for patients at risk who have an increased likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm.
These include chronic diseases of the pelvic organs, congestive and inflammatory processes in this area.
The risk group includes:
- patients with a hereditary predisposition to pathological proliferation of epithelial cells;
- women living in regions with excessive technogenic saturation;
- working in hazardous industries;
- those who have suffered severe injuries;
- regularly exposed to toxic chemicals and carcinogens.
Gynecologists refer for analysis when pathological lumps or thickenings are detected during an ultrasound examination of the pelvic area or a manual medical examination of the vaginal cavity.
Preventive actions
In order to minimize the risk of ovarian cancer, the following rules must be observed:
- Periodic examinations by gynecologists.
- Regular blood donation for analysis (general, biochemistry). This procedure is also indicated for people undergoing rehabilitation for ovarian cysts.
- Maintaining genital hygiene.
- Taking hormonal and contraceptive medications only after consultation with a therapist.
- In winter, choose a wardrobe with warm clothes, and not for the sake of fashion. Keep the pelvic organs warm.
- Complete cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Maintaining a routine and balanced diet. Increasing the consumption of plant antioxidants (vegetables, fruits, dried fruits).
- Losing excess weight. According to American researchers, overweight women are at risk of developing ovarian cancer. Moreover, the excess weight may be small. There is also a direct connection between excess kilograms and diseases such as breast cancer, colon cancer, endometrial cancer, kidney cancer, etc.
With the proper level of care for the body, timely and regular examinations and studying the research of international scientific organizations in the field of combating cancer, you can overcome the disease and live a full life.
What types of abnormalities does a tumor marker signal?
The laboratory indicator is used for early diagnosis of oncological pathologies of epithelial tissue, malignant tumors of the ovaries and endometrium. It signals hyperplastic changes of a type of carcinoma, which ranks 5th in the world among the causes of female mortality.
This disease is primary in nature and serves as the main focus of metastasis of the pelvic area or secondary with its capture by a progressive pathological process. The cause of ovarian carcinoma is not fully understood. Given the high mortality rate and the complexity of treatment, early diagnosis is of fundamental importance.
Ovarian carcinoma is a dangerous malignant pathology. Such a deviation can be determined in its infancy using a blood test for the HE-4 tumor marker. The risk group includes patients with a genetic predisposition and nulliparous women.
HE-4 tumor marker
Scientific evidence suggests that the development of ovarian carcinoma is facilitated by excessive amounts of certain animal fats ingested through food. The formation of pathological deviations is provoked by gynecological diseases of various origins.
Using the HE-4 tumor marker, early diagnosis of hyperplastic changes in endometrial tissue is possible. A malignant neoplasm in the uterine organ is manifested by bloody discharge from the vaginal cavity.
If this symptom is detected, you should immediately contact your gynecologist to receive a referral for a tumor marker blood test. Signs of such tumor abnormalities are characteristic of other oncological processes.
HE-4 is a tumor marker, the decoding of which allows for highly accurate and informative differential diagnosis.
Among the etiological factors of such deviations are:
- benign tumor of the reproductive organs and pelvis;
- excess weight;
- chronic endocrine pathologies;
- hormonal disorders;
- infertility;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- menstrual irregularities.
An increased concentration of glycoprotein protein may indicate the development of cancer hyperplasia in the lower respiratory system, large intestine, and mammary glands. HE-4 has a fairly wide diagnostic spectrum.
It has low sensitivity to benign tumors and endometriosis, which ensures accurate differentiation of abnormalities. The tumor marker is used in the diagnosis of non-oncological diseases - ovarian cysts, benign uterine fibroids and others.
Tumor marker characteristics
The chemical structure of this tumor marker is a special protein - a glycoprotein. It belongs to the family of acidic 4-sulfide proteins. This protein is associated with polysaccharides. Polysaccharides, in turn, contain from two to ten monosaccharide residues (monosaccharides are the simplest forms of sugar in the body).
HE4 is found in small amounts in the genitourinary system, pancreas and upper respiratory tract of healthy men and women. It supports the function of the oral mucosa, respiratory organs, and epithelium.
It is also important to note that an increased concentration of such a protein in the body indicates precisely malignant formations, while other markers react to both oncological and benign tumors. This is the advantage of this marker.
Rules for donating blood for analysis
Biological sampling is carried out in the morning. For maximum reliability of the diagnostic result, you should adhere to the established rules for preparing and taking a blood test.
They are as follows:
- Biological material is collected on an empty stomach.
- 3 days before the scheduled date of the study, it is necessary to stop the course of medication, taking hormonal contraceptives and any other medications.
- Before donating blood, you should not smoke or drink alcohol, including low-alcohol drinks.
- It is not recommended to conduct research during the active menstrual cycle.
- 24 hours before donating blood, you should not eat fatty foods or smoked foods.
Before the laboratory procedure, you can drink only still water. It is advisable to stop drinking alcohol 5 days before the appointed date. You should take the test in a calm state.
In 30 min. Before the procedure, you should avoid emotional excitement, psychological stress and significant physical activity. 48 hours before donating blood, it is necessary to exclude sexual contacts that affect hormonal levels.
Basic recommendations before taking the test
To test for the He-4 tumor marker, blood taken from a vein is used. It is very important that the blood is delivered to the laboratory within an hour of collection. Usually the results of the study can be obtained already on the second day. To ensure that the analysis is as accurate as possible, doctors advise adhering to the following recommendations:
- 4 hours, and preferably 8 hours before the test, refuse to eat;
- Give up tea, sweet carbonated drinks, coffee and juices 8 hours before. Drink only boiled water;
- Stop using any medications several days before the test;
- Do not drink any alcoholic beverages for a week;
- A few hours before the test, stop smoking;
- Avoid fried, fatty, spicy and sweet foods;
- A day or two before the analysis, it is recommended to abstain from sexual activity;
- Avoid heavy physical and emotional stress.
There are cases when testing for the He-4 tumor marker is prescribed for children. Half an hour before the test, the child needs to drink at least a glass of boiled water.
Need to know! An analysis to determine the level of He-4 cannot be taken during menstruation, since the result is likely to be increased. It is recommended to take the test 5–7 days after your period. A repeat study is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician after 2 to 3 months.
Features of the analysis
The biomaterial is collected from the ulnar vein. The procedure is extremely simple, has been practiced many times and causes minimal discomfort. It takes no more than 5 minutes. Results are usually ready within 2 days.
Biological material is analyzed using the immunochemiluminescence method. It involves the use of special reagents that cause a glow reaction upon contact with glycoprotein compounds. They are produced as a protective response to the production of cancer antigens.
The sensitivity and specificity of the analysis is not less than 90%. The material is venous blood serum.
The technique is used not only for early diagnosis of oncological processes, but also for:
- detection of urogenital infections;
- determining the functional state of the thyroid gland;
- the presence of TORCH infections in pregnant women, which can cause severe intrauterine damage to the embryo;
- planned prenatal monitoring.
Chemiluminescent immunoassay plays an important role in the diagnosis of hepatitis B and C. The technique is well established and ensures high accuracy of laboratory research.
What tests are needed if you suspect ovarian cysts and tumors?
Cyst, cystoma and tumor are pathological growths on the ovary. Actually, a “cyst” is essentially a bubble attached to an organ. A tumor is a cystic formation containing a dense component.
Contents: 1. Classification of neoplasms 2. Diagnosis of cysts and other neoplasms - Ultrasound - Tumor markers - Determination of hormonal levels - Blood test - Pregnancy test 3. Normal 4. Pathologies for which the gynecologist prescribes tests
Classification of neoplasms
There are a number of classifications of neoplasms, but the most universal is the division according to the degree of malignancy.
Cysts and tumors are divided into 3 main types:
- benign formations (which include cysts);
- borderline ovarian formations;
- malignant tumors.
In young patients, cysts are most common. They may be a consequence of irregularities in the menstrual cycle or endometriosis (pathological growth of the uterine endometrium).
We recommend reading: Ovarian cyst: causes, types, diagnosis, treatment
Borderline neoplasms are in most cases diagnosed in women after 30 years of age. Upon microscopic examination of the material, these formations can be determined as malignant, but the nature of the course is more reminiscent of benign. Metastases are rare, but there is a high probability of relapse (localization may vary), which requires repeated surgery. A remedy such as chemotherapy for borderline tumors does not bring the expected effect.
Ovarian cancer is more common in women during menopause (menopause). The main problem is that most patients come only after the appearance of pronounced symptoms - and they are characteristic of stage 3-4 cancer. For malignant ovarian tumors, complete excision of pathological formations within healthy tissue is indicated. In some cases, chemotherapy is indicated before and after surgery. Cure rates range from 30% to 40%.
Diagnosis of cysts and other neoplasms
The main diagnostic method for suspected ovarian tumors is ultrasound examination - transabdominal and transvaginal.
Ultrasound
Please note: transabdominal ultrasound is performed directly through the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. Transvaginal requires the use of a special sensor that is inserted into the vagina.
During the study, the specialist pays attention to the following parameters:
- ovarian size;
- structure of the cyst capsule;
- thickness of the neoplasm capsule;
- blood circulation in the capsule;
- the nature of the contents of the bubble;
- the presence or absence of growths on the inner wall of the capsule.
Clinically, several types of cysts are distinguished:
- corpus luteum cyst;
- follicular;
- dermoid;
- mucinous;
- paraovarian;
- serous;
- Serosocella.
Important: functional formations - corpus luteum and follicular cysts undergo spontaneous involution over 3-4 months, i.e. they disappear on their own without additional treatment.
Tumor markers
To establish the nature of the process, an analysis is carried out for the presence of specific tumor markers (in particular, CA-125 and CA-19).
To exclude or confirm the malignant nature of the tumor, a test for the presence of the CA-125 tumor marker is required. If its content exceeds the reference values (especially in patients during perimenopause), this is highly likely to indicate a cancerous tumor.
In young women, the content of the CA-125 marker may be slightly increased against the background of benign neoplasms, adnexitis or salpingoophoritis, or with endometriosis.
Please note: the terms “adnexitis” and “salpingoophoritis” imply inflammation of the ovarian appendages.
Thus, the detection of a tumor marker in cysts cannot be a reliable sign of tumor malignancy.
Determination of hormonal levels
If ovarian cysts or tumors are suspected, it is necessary to establish the patient’s hormonal background.
The doctor needs to determine the level of the following hormones in the woman’s blood:
- luteinizing hormone (LH);
- estrogen;
- follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH);
- testosterone.
Blood analysis
All women who are suspected of having diseases of the reproductive system must undergo a blood test for coagulability and hemoglobin levels (to rule out anemia).
Pregnancy test
Clinical manifestations of such a dangerous pathology as ectopic pregnancy may be similar to the symptoms of ovarian cysts and tumors. In this regard, all patients of fertile age must undergo a pregnancy test.
Norm
- Repeated transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound examination does not reveal any cysts or tumors on the ovaries.
- The level of tumor markers is not increased.
- The content of testosterone and estrogen does not increase, and the content of LH and FSH does not decrease.
- Blood tests are normal; hemoglobin is not reduced, and blood clotting is normal.
Pathologies for which the gynecologist prescribes the listed tests
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Cystic ovarian abnormality.
Betsik Yulia, obstetrician-gynecologist
4, total, today
(172 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
okeydoc.ru
Decoding the results
A small amount of the HE-4 tumor marker in the blood of women is considered normal. The concentration depends on age, concomitant pathologies and the current physiological status of the body.
Normal by age
The acceptable value for a healthy woman is considered to be 0-140 pmol/l. The level of HE-4 in the blood is strongly influenced by hormonal levels. Up to 40 years of age, increased secretion of estrogen is observed.
Therefore, young women have lower levels of cancer antigen than older patients. Established age standards are shown in the table below.
| Age | HE-4 content in pmol/l |
| 18-40 | 0,1-60,5 |
| 41-49 | 60,6-74,0 |
| 50-59 | 74,1-76,0 |
| 60-70 | 76,1-104,0 |
| Over 70 | 104,1-140,0 |
A ROMA index value exceeding 29.89 indicates a low probability of the formation and development of hyperplastic pathologies.
Deviations
Decoding He-4, a tumor marker, sometimes demonstrates an excess of established physiological standards. More than 90% of these clinical indications are for ovarian cancer.
Deviations from the norm are observed with any hyperplastic changes in the pelvic organs and reproductive system. The synthesis of a glycoprotein compound is regulated by a specific gene, available only in the biological structure of mutated cells.
This explains the high accuracy of laboratory research. When pathologically altered cytological elements multiply, the glycoprotein antigen is actively released into the intercellular space with further penetration into the blood channels.
Primary clinical manifestations of the pathological process are determined even in the phase of manifestation of hyperplastic abnormalities. Complete suppression of the physiological functions of the ovaries occurs in the later stages.
They are characterized by extensive metastasis involving nearby and even distant organs. Any therapeutic tactics for such a course of the disease do not demonstrate adequate effectiveness.
Therefore, early diagnosis of oncological pathologies is of fundamental and fundamental importance for successful treatment. In order to clarify the clinical picture with an increased concentration of the HE-4 glycoprotein antigen, additional instrumental studies are prescribed:
- ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography screening;
- X-ray examination.
The results of a laboratory blood test cannot serve as a basis for making a final diagnosis. A biopsy is performed - a sample of biological tissue is taken. It is sent for histological examination, which makes it possible to accurately determine the presence of a pathological process and the degree of its malignancy.
Norms of values
To correctly evaluate the result of a blood test for the he 4 tumor marker, you need to know the norm. This will help avoid mistakes when making a diagnosis.
The normal limits for protein formation he 4 directly depend on the woman’s age and her hormonal status.
During childbearing age, when female sex hormones are produced in sufficient quantities, the levels of this substance are lower than during premenopause and menopause.
Table for deciphering the norm of tumor marker he 4 depending on the woman’s age:
| Age, years | Normal, pmol/l |
| Up to 40 | No more than 60.5 |
| 40 – 49 | No more than 76 |
| 50 – 59 | No more than 74 |
| 60 – 69 | Up to 83 |
| After 70 | No more than 104 |
An increase in the normal limit indicates that with age, a woman’s risk of developing cancer of the reproductive system, and more precisely of the ovaries, increases.
Causes of false blood test results
Errors in laboratory testing of biological material taken are common. The test can give either a false positive or a false negative result.
Methodological and technical reasons for the error are a malfunction of diagnostic equipment and violation of established rules for preparing for the blood sampling procedure. Hematological diseases, hormonal fluctuations, and specific conditions of the body lead to research errors.
An increase in the concentration of the HE-4 tumor marker in serum blood is provoked by the following pathological factors:
- cystic fibrosis is a systemic hereditary disorder that is caused by a mutation in the transmembrane gene regulator of cystic fibrosis and is characterized by inhibition of the exocrine glands with severe respiratory impairment;
- Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor in the muscle fibers of the organ called the myometrium;
- functional failure of the renal apparatus;
- chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary system;
- uterine fibroma is a benign hormone-dependent neoplasia that develops from the muscular layer of the organ with a predominance of connective tissue;
- ovarian cyst - a bubble-like formation with liquid exudate or jelly-like contents;
- inflammatory and infectious processes in the pelvic area.
In rare cases, a malignant tumor does not provoke an increase in HE-4. In such a situation, a blood test gives a false negative result. The accuracy of the study is affected by the use of hormonal contraceptives, antibiotics, cytostatic and other medications.
False deviations from the norm are possible during the active menstrual cycle. Urogenital infections and inflammation of the urinary canals lead to increased levels of HE-4. They must be treated before being tested for tumor markers. The results are interpreted by a specialized specialist - a gynecologist or oncologist.
Tumor marker HE 4: what is it, the norm in women, interpretation of the analysis for the marker
Cancer diseases are widespread throughout the world. More and more cancers are diagnosed every year.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect malignant neoplasms in the early stages, when clinical signs are still absent. One such method is a blood test for tumor markers.
The specific tumor marker he 4 helps to identify a disease of the female reproductive system, such as ovarian cancer.
What is he 4
The he 4 tumor marker is a protein formation that can be present in a small concentration in the body of any healthy person. This glycoprotein blocks the proteinase enzyme.
Normally he 4 is located in:
- Epididymis in men. This protein is involved in sperm production;
- Endometrium - the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- Fallopian tube cells;
- Cells lining the bronchi.
The he 4 protein is specific for oncological processes, since it is actively produced in the presence of cancer cells, by these cells or by the human body. He 4 is produced under the influence of a special gene WFDC2, which is activated in malignant cells.
The he 4 tumor marker is used to diagnose ovarian cancer in women, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of therapy during treatment.
It should be noted that he 4 is extremely rarely synthesized by healthy cells of the female body, therefore, if its levels increase, additional examination should be carried out to clarify the diagnosis. If the concentration of this protein increases, then this laboratory sign alone does not indicate the presence of a cancerous tumor. The diagnosis is made after a comprehensive examination.
It is important that the collected blood is delivered to the laboratory for testing no later than 1.5 hours after its collection, and the tube must be stored in a special box where the temperature is maintained no higher than 8°C.
The protein structure of he 4 is not a sign of any malignant ovarian formation. It is more than 90% specific for epithelial cancer.
Only the tumor marker he 4 is detected in the blood long before the spread of the pathological process (early stage), that is, before the formation of metastases in neighboring organs and tissues. This in turn makes it possible to cure the patient and avoid serious complications.
Indications for the study
A blood test to determine the he 4 tumor marker is not performed on all women.
It is ineffective to conduct tumor marker testing in the following cases:
- If a woman has any cancer, except for the reproductive system;
- If you suspect cystic fibrosis and germ cell ovarian cancer.
Experts have identified several situations in which analysis for he 4 is mandatory:
- If a woman has a high probability of developing ovarian cancer (hereditary predisposition, complicated gynecological history);
- If there is a risk of deterioration of a woman’s condition (spread of metastases) diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer;
- If there is a suspicion of the development of a malignant neoplasm in the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium);
- If a woman is undergoing treatment for ovarian and endometrial cancer.
Sometimes the he 4 marker helps identify cancer of the bronchi, lungs and mammary glands.
Rules for taking a blood test for tumor marker he 4
To study he 4, venous blood is taken. To do this, you need to contact the laboratory, where a medical worker with the appropriate qualifications will perform this manipulation under sterile conditions. The biological material is sent to the laboratory, where a laboratory assistant examines the blood and calculates the substance.
In order for the test result to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare several days before donating blood:
- Stop taking medications (after consultation with your doctor) 2–4 days before the laboratory test;
- Avoid drinking alcohol the day before;
- Donate blood on an empty stomach or 5-8 hours after eating; you can only drink clean water. You cannot drink juices, tea, coffee, carbonated drinks;
- You should not smoke on the day of blood collection.
Women undergoing treatment need to monitor the level of this tumor marker every 3 months. After completion of treatment, monitoring is carried out every 6 to 12 months. This is necessary for early detection of relapse.
Norms of values
To correctly evaluate the result of a blood test for the he 4 tumor marker, you need to know the norm. This will help avoid mistakes when making a diagnosis.
The normal limits for protein formation he 4 directly depend on the woman’s age and her hormonal status.
During childbearing age, when female sex hormones are produced in sufficient quantities, the levels of this substance are lower than during premenopause and menopause.
Table for deciphering the norm of tumor marker he 4 depending on the woman’s age:
| Age, years | Normal, pmol/l |
| Up to 40 | No more than 60.5 |
| 40 – 49 | No more than 76 |
| 50 – 59 | No more than 74 |
| 60 – 69 | Up to 83 |
| After 70 | No more than 104 |
An increase in the normal limit indicates that with age, a woman’s risk of developing cancer of the reproductive system, and more precisely of the ovaries, increases.
Explanation of the analysis and reasons for deviation of indicators from the norm
In the laboratory, only the he 4 tumor marker is counted per unit volume of blood using a chemiluminescent research method. A specialist (oncologist) deciphers and evaluates the obtained analysis result. This takes into account the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
An increase in the content of the he 4 marker in a blood test can indicate the presence of both benign and malignant formations.
Reasons for increasing the concentration of tumor marker he 4
If an increase in indicators is detected, this indicates the development of a malignant neoplasm and some other diseases (much less frequently). Let's consider each of the possible diseases in more detail.
Ovarian cancer
Tumor marker he 4 indicates the presence of epithelial cancer. In this case, the indicators significantly exceed the norm.
At the beginning of the formation of epithelial cancer, there are no pathological symptoms. This is why ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at stages 3 or 4, when treatment is extremely difficult or impossible.
With ovarian cancer, there is a disturbance in menstrual function, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, disruption of the pelvic organs (compression of the intestines, bladder, inflammation, and so on).
HE 4 for ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation, which is a cavity filled with fluid. Often this pathology has an asymptomatic course.
Symptoms that may indicate the presence of an ovarian cyst:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen;
- Increase in abdominal size;
- Constipation;
- Frequent urination;
- Menstrual dysfunction (uterine bleeding, heavy periods).
In the case of cyst formation, the he 4 indicator increases slightly, and in some situations it may be at the upper limit of normal. It is advisable to identify other tumor markers during laboratory blood tests.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign tumor formation of the muscular layer of the uterus. This pathology is diagnosed quite often in women after 30 years of age. The cause of its occurrence is an imbalance of female sex hormones.
Uterine fibroids can be asymptomatic for a long time or manifest themselves with few pathological signs:
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Heavy periods, which can lead to anemia;
- Painful sensations in the abdomen and lower back.
In the case of fibroids, an increase in tumor marker values is an auxiliary diagnostic sign. The basis of diagnosis is a bimanual (two-handed) gynecological examination and ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a pathological condition in which endometrial cells grow in places they are not supposed to (outside the uterus). This disease is common in women of childbearing age.
Symptoms of endometriosis:
- Severe pain during menstruation;
- Spotting before and after menstruation;
- Heavy periods;
- Infertility.
With endometriosis, the he 4 tumor marker remains normal or increases slightly. However, this gives reason to examine the woman more carefully.
HE 4 is not a specific indicator for liver and kidney diseases, but may increase. In this case, the patient must have appropriate symptoms.
Reasons for false research results
Such a serious diagnosis as cancer is not made on the basis of an increase in just one he 4 indicator. It is advisable to conduct a blood test for other tumor markers, as well as perform instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound examination, biopsy, cytology, MRI and others).
It should be remembered that in some cases, a blood test may reveal a false result. For example, with chronic renal failure, uterine fibroids, inflammatory process in the pelvic organs.
A false positive result, that is, an increased level of this tumor marker is determined, but the malignant tumor is absent in the body.
Reasons for a false positive test result:
- Ovarian cyst;
- An inflammatory process occurring in the pelvic organs;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Chronic renal failure.
It is also necessary to remember that the test result may be false negative.
Reasons for a false negative result:
- The growth of this indicator has not yet reached values that exceed the norm;
- A cancer tumor does not synthesize this protein.
If there are corresponding symptoms, a hereditary predisposition, a complicated medical history and a doctor’s suspicion of oncology, then a negative result does not exclude its presence.
The resulting error may also be due to:
- Human factor (the laboratory technician made a mistake during the analysis);
- Malfunction of the equipment used for the research;
- Failure to comply with the rules for preparing for blood collection.
HE 4 in combination with other tumor markers
The most optimal way to diagnose ovarian malignancy is to study a combination of tumor markers he 4 and ca 125. However, it should be noted that an increase in the concentration of ca 125 occurs at a later stage in the development of the pathological process than he 4. But he 4 is not sensitive to some types of ovarian cancer ( germinogenic and mucoid), and ca 125 increases.
Tumor markers he 4 and ca 125 are necessary to calculate the ROMA index. It is a calculation of the prognosis of the disease. To calculate this index, you need to know the results of the analysis for tumor markers and the woman’s age.
ROMA index in premenopausal women:
- If this index is less than 11.4, then the risk of developing epithelial ovarian cancer is very low;
- If this indicator is 11.4 or more, then this indicates a high risk of developing this pathology.
ROMA index in postmenopause:
- If ROMA is less than 29.9, then the risk is low;
- If this index is equal to or greater than 29.9, then the risk of developing ovarian cancer is extremely high.
Studying a combination of tumor markers leads to more accurate and timely detection of such a dangerous disease as cancer.
vseanalyzy.com
Deviations
When specialists detect a deviation from the norm in the blood in the form of an increase in the number of HE-4 tumor markers, patients are prescribed the following diagnostic measures:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- radiography.
After analyzing the marker level, the results do not provide a basis for making an accurate diagnosis. All these values can only indicate the need to conduct a full examination.
Deciphering the analyzes of already adult women, a decrease in indicators is not provided; additional diagnostic measures are prescribed only if an increase in the number of markers is detected. More accurate diagnosis requires the combined use of blood tests for tumor markers HE-4 and CA 125.
How to get tested
To determine the level of HE-4 in a woman's body, venous blood is taken. It must be taken on an empty stomach (in the morning before going to the laboratory you can only drink water). On the eve of the study it is recommended:
Completely eliminate smoking and alcohol.- Do not take medications (for women undergoing any treatment, this point must be discussed with their doctor).
- Limit physical activity.
What does he4 tumor marker show?
The he4 marker is encoded by the WFDC2 gene, which is found in cancer cells. Due to this, at a he4 concentration of more than 150 pmol, the sensitivity of the assay for ovarian cancer is 80%. However, the specificity of the analysis is high only for epithelial ovarian cancer.
Attention. Normally, the he4 marker is present in small quantities in all people.
From a biochemical point of view, he4 is a glycoprotein involved in blocking protein kinase and contains:
- in the epididymis in men (participates in the formation of sperm)
- in the uterus and fallopian tubes in women
- in epithelial cells of the ovaries
- in bronchial cells.
It is worth emphasizing that despite the fact that this marker can be produced in the female genital organs normally, an increase in its level occurs extremely rarely. Therefore, if it is detected, it is worth conducting a full comprehensive examination.
Important. An increase in he4 concentration in repeated tests is also not a sufficient criterion for diagnosing cancer. The detection of this tumor marker should always be accompanied by a complete examination of the woman.
As the experience of modern medicine shows, the h4 tumor marker is of great importance for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. The fact is that with early diagnosis, the percentage of successful treatment is 90%. In addition, based on its concentration, one can draw conclusions about the effectiveness of the therapy.
For reference. The he4 marker is the only one that appears in the blood before tumor metastasis and, thus, allows treatment to begin at the earliest stages.
The he4 marker test is not a screening test and is not performed unless prescribed.
This study must be carried out in women:
- with a hereditary predisposition;
- with a history indicating the possible development of endometrial cancer;
- with established epithelial ovarian cancer with suspected metastasis;
- with an established diagnosis and started treatment to assess its effectiveness.
Alarming symptoms, after which the doctor may prescribe tests for the h4 marker, are:
- Weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Malfunctions of the female cycle.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
For reference. To prescribe an analysis for he4, a combination of these complaints is required, since they are collectively characteristic of the first manifestations of cancer of a woman’s reproductive system.
An increase in the he4 tumor marker may indicate the presence of cancer:
- Endometrium;
- ovaries;
- mammary gland;
- lungs (rarely).
Despite this list, this tumor marker mainly increases in ovarian cancer. However, it is worth remembering that there are types of cancer in which it will not be elevated even in the terminal stages - germ cell and mucoid.
For reference. Therefore, if you suspect the presence of a malignant process in the ovaries, it is advisable to study the tumor marker CA 125 in parallel with he4.
To receive an informative analysis, you need to prepare for it.
When the analysis is wrong
Based on data from the diagnostic results solely of tumor marker He 4, a diagnosis of ovarian or other organ cancer is not made.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that an increase in the level of a tumor marker is possible in the absence of an oncological neoplasm. False positive results can be detected by:
- cystic fibrosis is a hereditary genetic disease characterized by disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands and severe pathologies in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- infectious lesions of the genitourinary organs, after successful elimination of which a control measurement of the He 4 criterion is carried out;
- chronic liver or kidney failure;
- less often with a cyst. It was noted that the He 4 norm in women with cysts is similar to the reference values for healthy people. However, in rare cases, an increase in the level of this tumor marker is observed, and it is important to reliably exclude cancerous abnormalities;
- fibroids are benign tumors of the uterus.
False negative results are also possible when the level of the He 4 tumor marker is not high enough to be registered by test systems. Therefore, if the development of mutant cells is suspected, an additional examination is prescribed after 1 month.