Any person can develop a malignant neoplasm. The danger of the disease lies in its long-term development without the manifestation of characteristic symptoms. The disease can be detected already at stages 3 or 4, which reduces the patient’s chance of a full recovery. A blood test for the tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) can detect cancer at an early stage. An increase in the indicator is observed with a benign neoplasm, but its concentration in the blood is lower compared to the oncological process. The study must be performed under the supervision of an experienced oncologist. It is difficult to decipher the analysis on your own.
Characteristics of alpha-fetoprotein
AFP tumor marker is a molecular compound produced by cancer pathogens. The protein is present in low concentrations in the blood of adults and children, and in pregnant women it is secreted by the developing embryo. In a normally developing pregnancy, the fetus produces alpha-fetoprotein after 2 weeks of development. The substance allows you to control the immunity of the expectant mother. An increased level of 10 or more times can provoke rejection of the fetus by the woman’s body, which ends in fading of pregnancy or miscarriage.
In women during pregnancy, the AFP tumor marker is monitored through a screening test performed at least 3 times during the period of gestation. It is possible to use saliva, bile or urine as the material, but this is done exclusively under the supervision of the attending physician and according to medical indications.
In other cases, protein protects the human body from external and internal irritants. The substance secretes a specific protein enzyme that destroys pathogens of the formed tumor. The protein is able to destroy malignant compaction in the tissues of the liver and lung.
AFP in the adult human body
The alpha-fetoprotein indicator during diagnosis shows the presence of oncology in the tissues of the breast, pancreas, and liver. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on a single parameter. If the level of AFP increases, it is recommended to undergo additional examination using instrumental diagnostic methods.
The body of an adult contains a low concentration of this glycoprotein in the blood or the element is completely absent. An increase in protein by several positions means the presence of a benign tumor in the body. Deviation from the norm by tens of times is a dangerous oncological process with the formation of metastatic sprouts.
The liver and other organs, when affected by a malignant tumor, produce cells with the properties of embryonic pathogens. This leads to the production of a large volume of peptides and alpha-fetoprotein. Therefore, this glycoprotein is classified as a tumor marker that can detect pancreatic, breast and liver cancer.
The AFP tumor marker shows the presence of a malignant or benign neoplasm in the body in men or women, but the size and extent of the lesion must be determined using instrumental diagnostic techniques. This indicator is considered the main one in assessing the chances of recovery of a patient with cancer in the genital organs and breast tissue.
What are tumor markers
06/29/2011 | Author Redaktor
Each type of cancer has its own characteristic “marks”, which are called tumor markers.
In recent years, tests for tumor markers have become fashionable. Doctors prescribe them “for insurance” for any reason. What are tumor markers? How accurate are tumor marker tests? And if the test result is normal, can you be absolutely sure that a person does not have cancer? Let's try to figure it out.
Tumor markers are specific substances - proteins, enzymes and protein breakdown products that are produced by cancer cells. Moreover, each type of cancer has its own characteristic “marks”. Detection of certain tumor markers in the blood or urine helps to identify cancer at the earliest stages, which facilitates treatment and improves further prognosis.
However, such studies are informative only in the complex diagnosis of cancer, since the reliability of most of them is low. After all, various tumor markers can be found in the blood of any healthy person, albeit in small quantities. And even if any of the tumor markers is elevated, this does not always indicate the development of cancer. Sometimes tumor markers increase in the presence of cysts, benign tumors, infectious diseases, and even after a common cold.
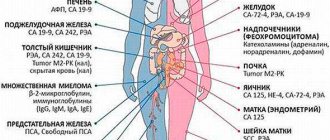
Doctors identify only 5 tumor markers (out of the 20 most common) that are highly reliable: for prostate cancer - PSA, for ovarian cancer - CA-125, for chorionepithelioma (choriocarcinoma) of the uterine body - CHG, for hepatocellular liver cancer - AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) and for rectal cancer - CEA.
However, not everything is so simple here either. Thus, an increase in CA-125 can be detected in benign ovarian tumors and even in healthy women. And with moderately elevated PSA values, it is necessary to take a more accurate “free PSA” test, since total PSA sometimes increases in benign diseases, such as prostate adenoma, prostatitis, and even after prostate massage.
Unfortunately, there is no absolutely accurate marker for cancer yet. Therefore, without additional methods (history collection, instrumental examination, biopsy, etc.), it is impossible to diagnose cancer or a predisposition to it. Only an oncologist can assess the significance of the results of enzyme immunoassays and determine the tactics for further examination and treatment. Taking tests to “just check for cancer” is a waste of money and nerves.
Tests for tumor markers should be done in a specific situation: for example, if a tumor is suspected as one of the diagnostic stages. Or when monitoring a disease after treatment: a decrease in the concentration of a tumor marker in the blood indicates a positive result of treatment, and a repeated increase indicates a relapse of the disease. Regular monitoring of the level of specific tumor markers makes it possible to detect a returning disease in time and quickly begin treatment (for example, an increase in the CA-15-3 marker after treatment for breast cancer indicates a future relapse in 6–10 months).
The most commonly used tumor markers:
• CA 125 is a marker of ovarian cancer.
• AFP – alpha-fetoprotein – a marker of hepatocellular liver cancer.
• CEA – carcinoembryonic antigen – tumor marker for rectal cancer.
• PSA – prostate-specific antigen – tumor marker for prostate cancer (normal – no more than 4 ng/ml.).
The most commonly used combinations of tumor markers:
• For chronic prostatitis, adenoma and tumor diseases of the prostate gland – total PSA + free PSA.
• For tumor diseases of the large intestine, rectum, stomach – CEA + CA 72-4.
• For lung diseases – CEA + CA 19-9 + AFP.
• For breast tumors – CA 15-3 + CEA.
• For tumor diseases of the pancreas and biliary tract – CA 19-9 + CA 125.
• For diseases of the ovary, cervix, endometriosis – CA 125 + CA 72-4 + b-hCG.
• For liver diseases – CA 19-9 + AFP.
• For testicular cancer (in men) – AFP + hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
• For chorionepithelioma, hydatidiform mole – hCG.
• For lung cancer, melanoma, neuroblastoma - NSE (neuron-specific enolase).
***
Other articles on this topic:
Indications for prescribing a blood test for AFP tumor marker
Doctors do not recommend donating blood yourself for testing using the described method. There are good reasons for diagnosis. They will be determined by the attending physician who knows the medical history well.
Indications for studying the tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein are considered to be the following:
- It is necessary to identify possible pathologies in the development of the embryo until the moment of birth - mutations of the chromosomal DNA series, disturbances in the formation of the neural tube, anencephaly, absence or incomplete development of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Monitor pregnancy for possible abnormalities.
- There is a suspicion of a malignant neoplasm in the liver tissue.
- Confirmation of oncology in pancreatic cells is required.
- A man is suspected of being at risk of developing a malignant tumor in the testicles or prostate gland.
- There are confirmed benign lumps in the human body that require monitoring to prevent degeneration into a malignant form.
- It is necessary to detect metastatic branches to distant areas of the body.
- Diagnostics helps to monitor the treatment process to ensure the correctness of the chosen tactics.
People who are at risk for developing a dangerous malignant pathology are indicated. In this case, doctors recommend regularly checking the level of the AFP marker. The group includes:
- people with positive HIV status;
- there is a confirmed diagnosis of hepatitis;
- severe liver diseases - enzyme deficiency, cirrhosis;
- there are tumors with a risk of spreading metastatic branches to distant organs;
- patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy;
- people who have undergone a therapeutic course for malignant pathology in order to determine the effect of treatment;
- after surgical excision of cancer to prevent recurrence;
- women during pregnancy during the period of 14-22 weeks.
Additionally, to confirm or reject the diagnosis, a man over 45 years of age should examine the following markers:
- CA72-4 is required to test for cancer in stomach tissue or testicles.
- CA19-9 allows you to check the pancreas and confirm or exclude metastases in distant organs.
A woman donates blood for examination of the CA125 marker together with alpha-fetoprotein. This will check for the presence of cancer in the ovaries, breast, liver and pancreas. The doctor will also evaluate the chosen therapy method for effectiveness.
Decoding the results
You should not try to decipher the research results yourself. Deciphering AFP tumor markers should be done by a highly qualified specialist; only he knows exactly when the level of this protein increases or decreases. As a rule, in a public clinic it can take up to three days to decipher the result, while in private clinics the result will be ready within 24 hours. The tumor marker level in different laboratories can be measured in IU/ml or ng/ml.
Normal value for the tumor marker alphafetoprotein
Thanks to solid-phase chemiluminescent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, normal values can be determined. The norm depends on age and gender. On analysis in men, normal values will be as follows (in IU/mg of blood):
- up to one month - 0.5 - 13600;
- from one month to one year - 0.5 - 23.5;
- after a year - 0.9 - 6.67.
In women, the AFP norm is as follows:
- up to one month - 0.5 - 15740;
- from one month to one year - 0.5 - 64.3;
- after a year and in adults in the absence of pregnancy - 0.9 - 6.67.
In pregnant women, the tumor marker rate depends on the length of pregnancy in weeks:
- 1-12 — 0,5 -15;
- 12-15 — 15 — 60;
- 15-19 — 15 — 95;
- 19-24 — 27 — 125;
- 24-28 — 52 — 140;
- 28-30 — 67 — 150;
- 30-32 — 100 — 250.
In different laboratories, normal values may vary slightly. If the analysis shows that there is more AFP in the blood than normal, you need to see a doctor and undergo a full examination, including ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and a blood test for other tumor markers. Do not forget that during pregnancy some diagnostic measures may be contraindicated.
We recommend reading: What tumor markers should be tested for breast cancer?
Level exceeding normal
An increase in AFP in non-pregnant women in ninety percent of cases means liver cancer, in ten percent the occurrence of metastases, ovarian cancer, malignant neoplasms in the mammary or pancreas, intestines, and lungs. In addition to oncological pathologies, an increase in tumor markers sometimes indicates biliary cirrhosis, exacerbation of chronic hepatitis, liver dysfunction due to alcoholism, surgical or mechanical injuries to the liver, as well as the development of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
If AFP is elevated in a woman during pregnancy, this indicates in eighty-five percent that there is some kind of anomaly in the formation of the neural tube of the embryo. Also, an increase in tumor marker can be an indicator of cancer in the fetus, mutations in the organs of the urinary system, absence of kidneys, intestines, or esophagus. The tumor marker may increase if there is a threat of spontaneous abortion, pathologies of the placenta, or if the formation of the skeletal system in the fetus is imperfect.
Reduced rate
A decrease in this protein in the blood can occur due to gene mutations in the embryo, for example, with Patau, Edwards, or Down syndrome. In a pregnant woman, AFP may fall if the pregnancy is frozen and the child dies, as well as with abnormal growth of the chorionic villi filled with amniotic fluid (this pathology leads to the arrest of fetal development). If a pregnant woman is severely obese or has diabetes, the tumor marker level also drops.
Normal tumor marker level in an adult
In adulthood, alpha-fetoprotein protein is usually absent or remains in both men and women. The norm of the indicator for a person is individual. The required level will be determined by the attending physician, who is familiar with the history of all diseases and human development from birth. On average, individual characteristics are within the generally accepted norms for diagnosing the marker.
For women aged 20-45 years, the normal level of alpha-fetoprotein is considered to be in the range of 6.3-6.6 IU/ml.
In men aged 20-40 years, the range of the substance should not exceed 6.67 IU/ml.
In older people, the protein norm is the same as for men and women of reproductive age.
Protein norm for children
In children under 1 year of age, the indicator depends on age. Girls usually have higher levels than boys. After a year, the child’s indicator is equal to the adult norm – 6.67 IU/ml.
In boys, from the moment of birth until 1 month of life, the substance parameter is considered to be 13600 IU/ml. From 1 month to a year, the figure should not exceed 23.5 IU/ml.
For girls, a level of 15,740 IU/ml is considered normal in the period up to 1 month of life. At the age of 1 month to 12 months, the protein level should be up to 64.3 IU/ml.
If a significant deviation from the norm in the direction of increasing or decreasing protein parameters is detected, an urgent examination of the body is required for the presence of a malignant neoplasm. First of all, it is worth checking the abdominal organs, then the pelvis and other areas of the body.
Norms for men and women, during pregnancy, in children
The normal level of AFP in the blood of women, men, and children varies. In women, the norm for alpha-fetoprotein ranges from 0 to 7.3 IU/ml. Ideally, the concentration is zero, but there are nuances associated with a woman’s lifestyle. In addition, the AFP norm in women allows for errors.
| Woman's age | Norm in IU/ml |
| From 18 to 25 | 0-7,25 |
| Up to 40 | 0-7,26 |
| Up to 55 | 0-7,27 |
| At 60 and older | 0-7,29 |
During pregnancy, AFP levels are correlated by trimester:
| Trimester | Norm in IU/ml |
| I | 0-12 |
| II | 15-25 |
| III | 50-130 |
In men, AFP is normally approximately the same as in women.
| Man's age | Norm in IU/ml |
| From 18 to 25 | 0-7,26 |
| Up to 40 | 0-7,27 |
| Up to 60 | 0-7,28 |
| Over 60 | 0-7,29 |
| Child's age | Norm in IU/ml |
| Newborns | Boys: 13,500 Girls: 15,500 Slight excesses of the specified value are possible |
| From 1 year to 18 | No more than 6.6 |
Blood test for the tumor marker AFP in pregnant women
AFP tumor marker during pregnancy is a special indicator. It is included in the mandatory screening program. Diagnostic testing differs from standard testing of people with cancer. A significant deviation from normal parameters warns of the presence of serious disturbances in the development of the fetus with the formation of severe pathologies.
Basically, when there is a significant difference from the normal parameter, a number of these pathologies are detected:
- high risk of miscarriage;
- fading of pregnancy and death of the embryo;
- the fetus has a congenital umbilical hernia;
- there may be a disturbance in the formation of brain cells - anencephaly, or absence of the cerebral hemispheres;
- pathologies in the development of kidneys and bone tissue;
- autoimmune disorders.
If it is detected that the tumor marker parameter exceeds the norm, the doctor conducts an additional examination to assess the woman’s condition. In addition, amniocentesis is required, an invasive prenatal examination procedure. Using a long thin needle, a puncture puncture of the amniotic membrane is performed to obtain part of the amniotic fluid for study for possible pathologies in the embryo.
This diagnostic method reveals a serious contraindication in the form of a high risk of miscarriage. But it is considered the only accurate method for diagnosing congenital pathologies before the birth of a child. If serious diseases that threaten the life of the unborn child are detected, the woman is offered an artificial termination of pregnancy.
Reasons for increasing AFP levels in the human body
The atypical cell begins to actively produce the AFP tumor marker protein, which poses a particular danger to human health.
Cancer cell metastases
An increase in protein in the body indicates the following pathologies:
- Malignant formation in liver tissue.
- There is oncology in the ovaries and mammary gland in women.
- There is a high probability of cancer in the cells of the lungs, intestines, and stomach.
- Shows the spread of metastatic branches to distant areas of the body.
- A malignant tumor in the liver or a serious disease of the organ - enzyme deficiency, cirrhosis, alcohol poisoning, hepatitis.
- In pregnant women, it warns of the presence of pathological disorders in the development of the fetus or a high risk of miscarriage.
- In men, it shows cancer in the testicles or prostate gland.
- The presence of squamous cell carcinoma on the mucous membrane of the esophagus and in the tissues of the pancreas is possible.
- Inflammatory processes in the gallbladder with blockage of the lumen - cholelithiasis.
- Deficiency of adipose tissue in the liver.
- Formation of adenoma in the area of hepatic pathogens.
- There are cystic neoplasms in the pelvic organs.
- Malignant pathologies in the genitourinary system.
A sharp increase in the marker can be provoked by taking specific medications, an inflammatory process against the background of cholelithiasis, with a diagnosis of cholecystitis and diseases of the endocrine system.
UBC (Urinary Bladder Cancer)
Bladder cancer marker. A highly specific test, effective in the early stages. UBC is determined in urine that has been in the bladder for at least 3 hours; the level of 0.12 * 10-4 μg/μmol is considered normal; with malignant lesions of the bladder, the concentration increases to 20.1-110.5 * 10-4 μg/ µmol
* * *
It must be taken into account that one tumor marker can appear in various diseases, so a combination of markers is used for accurate diagnosis. For example, when defining
- stomach cancer – REA and CA 242,
- pancreas - SF 242 and SA 19-9,
- testicular cancer – AFP and hCG.
- a simultaneous increase in the tumor markers CA 19-9, CEA and AFP indicates liver metastases.
Another subtlety is that elevated levels of tumor markers do not necessarily mean cancer. Therefore, biochemical studies must be supported by clinical ones.
Cases of decreased AFP marker levels
A deviation towards a strong decrease in the indicator also warns of the presence of serious disorders in human health. A similar fact is usually recorded in women during pregnancy, but sometimes it can be present in other cases.
The test result with a sharp decrease in the parameter indicates violations:
- genetic disorders in the formation of the chromosomal DNA series - Patau, Down or Edwards syndrome;
- fading of pregnancy with subsequent death of the fetus;
- excess weight during pregnancy;
- active growth of the chorion, which causes inhibition in the development of the embryo;
- Mechanical injury to the body can provoke a sharp decline.
A low level of protein indicates disturbances in the development of the unborn baby, so additional examination will be required. This will allow you to identify deviations and assess the severity of the pathological process. After the research, a decision is made on further actions.
What can influence the results?
The results obtained are influenced by many factors.
- For example, representatives of the Negroid race have higher levels of this protein, and the Mongoloid race have lower levels.
- The presence of endocrine diseases is taken into account, for example, diabetes mellitus, biotin intake, viral diseases that occurred in the recent past.
- Small changes in values are found in multiple pregnancies.
- If a woman does not wait for the baby to be born, the level will change due to hepatitis, kidney failure or hepatitis.
- A level that is too low in combination with other indicators that are outside the normal range indicates a high risk of having a baby with Down syndrome. Among the reasons are also the placement of the placenta too low.
Preparation and procedure for analysis
To determine the level of the tumor marker AFP, blood from a vein is required. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning within 2-3 hours after a night's sleep. The result of the study depends on the accuracy of following the recommendations of the attending physician. Preparatory activities play an important role in the accuracy of the analysis.
The patient is advised to follow special rules before donating blood:
- For 2-3 days, you need to eliminate fatty, fried, canned and pickled foods from your diet, which cause a heavy load on the liver, which will affect the test results.
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages for 1-2 days before blood sampling.
- Dinner before the test should consist of light nutritious dishes - porridge with milk, vegetable casserole or cottage cheese with fruit.
- Physical activity is prohibited 2-3 days before the procedure.
- 14 days before the event, it is not recommended to take medications - if it is not possible to exclude medications, then you need to inform the laboratory assistant about the type and schedule and dosage of the intake.
- People with type 1 diabetes are given a special note on the diagnostic sheet; the nurse should be informed of this fact.
- In the morning before the procedure, doctors do not advise brushing your teeth or smoking - this will affect the results.
- During pregnancy, a woman also informs the laboratory assistant about the duration of pregnancy, the types of medications taken for 14 days and the exact daily dosage, including vitamins.
- The morning before the event you should not eat or drink water.
The result depends on the correct preparation and implementation of the required measures. Violation of the diet schedule or refusal to inform the laboratory assistant about taking the drug and other restrictive points leads to an erroneous diagnosis.
The analysis is deciphered by the oncologist after the necessary manipulations by the laboratory assistant. The research time required is 3-4 days. It all depends on the equipment and the availability of an experienced doctor.
It is possible to donate blood to study alpha-fetoprotein in a public clinic or in a private clinic that has an oncologist on staff. The price of the procedure starts from 300 rubles.
There is no point in trying to check your AFP marker level on your own. Only a doctor competent in the matter with the necessary knowledge can decipher the result. Including preparatory rules will be violated, which will affect the outcome of the procedure. Distortion of data will lead to an erroneous diagnosis and the initiation of incorrect treatment. This development of events can provoke the formation of severe complications and deterioration in well-being.
How to prepare for this test
Blood for testing is taken from a vein. In order for the result to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary to take the right approach to testing for the AFP tumor marker:
- donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach;
- one day before blood sampling, you should give up fatty, smoked and seasoned foods, and eight hours before the test - from food in general;
- on the eve of the study, you should not overwork yourself physically and emotionally;
- It is forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages several days before the test;
- It is better not to smoke for several hours before testing for AFP and not to take medications (if it is impossible to exclude taking medications, you must inform the laboratory assistant about the time, dose and name of the medication taken);
- Water can be drunk in unlimited quantities before analysis.
We recommend reading: What does the CA 242 tumor marker mean, its meaning and normality?
As you can see, there are no serious restrictions, and compliance with the rules described above will allow the results to be correct.