What are tumor markers
Tumor markers, or tumor markers as they are also called, are specific molecules produced in the human body during the growth of cancer cells and several other conditions.
Using tumor markers, it is possible to detect cancer in the early stages of its development, which makes it possible to stop the disease and prevent its progression. Increased levels of these molecules after treatment indicate that the cancer process is ongoing and more radical measures should be taken to combat the cancer.
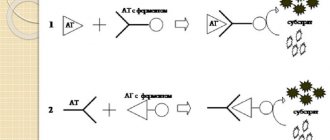
Oncological markers for cervical cancer are determined in blood samples taken from a sick woman, to which antibodies are added, forming certain complexes that are detected through laboratory tests. Specific molecules not associated with proteins, called free markers, are detected in the body using other versions of this test.
The results must be assessed judiciously and the diagnosis confirmed using other research methods.
Video: What are tumor markers
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8tBwErm9PoI
What does the SCC tumor marker determine?
If the concentration of tumor marker in the blood is high, squamous cell carcinoma is suspected in the nasopharynx, ears, vagina and uterine cervix, esophagus and other areas.
Some inflammatory diseases: respiratory organs, acute respiratory infections, chronic tuberculosis, renal and liver failure, skin diseases such as lichen planus, psoriasis, neurodermatitis can give a false positive result.
To diagnose skin melanoma, a tumor marker for the S100 protein is used, the explanation of which is given in the article on our portal.
Important. Slight increases in tumor marker levels will occur in the presence of benign and inflammatory diseases and physiological conditions. To confirm the diagnosis, the examination is continued.
Tumor markers
We also recommend studying this topic:
Ovarian tumor markers HE-4 and CA-125 using the Roma method
Cervical tumors
1. squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix – begins in the thin cells that line the fundus of the uterus, they are flat in shape, which gives it its name, the most common form of cervical cancer
2. adenocarcinoma (glandular cancer) – comes from the cells that cover the cervical canal itself
Diagnostics
A cancerous tumor is an accumulation in some organ of immature cells that are not characteristic of this organ. They increase in number, growing into healthy tissues and disrupting their functioning. At the beginning of the disease, a person does not feel any symptoms, but during this period it can be successfully treated with conservative methods. Testing for tumor markers helps here.
Often such examinations are carried out for preventive purposes for risk groups and are included in the program of medical examination of the population. What is a tumor marker? Tumor cells are immature, and the protein they produce is also defective and different from normal. Each type of tumor has its own type of protein, which can be detected in the blood serum, so the tumor seems to leave its own pattern in the human blood. This imprint can be identified by donating blood for a tumor marker.
The importance of timely diagnosis of malignant tumors of the cervix
Conducting studies for the presence of tumor markers is important for the following reasons:
- Oncological diseases of the female reproductive system reduce fertility.
- This study makes it possible to identify women at risk and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
At the third stage of the disease, the number of antigens exceeds the norm three times. As additional tests, the doctor prescribes a computed tomography scan, as well as urine and blood tests.
In case of somatic pathology, there is also a high probability that tumor markers of SCC squamous cell carcinoma will be detected. In such cases, it is necessary to study the dynamics, and for this, in addition to the standard analysis for tumor markers, a histological examination of the damaged tissues of the diseased organ is carried out.
The number of tumor markers changes in the event of metastases. Their number is also affected by the size of the tumor, its location and the degree of tissue damage by cancer cells.
Clinical utility of tumor markers
The usefulness of a tumor marker lies in its sensitivity and specificity, as well as its influence on patient treatment decisions. Because the pathological diagnosis of ovarian carcinoma is difficult to make without laparotomy, markers such as CA-125, in addition to diagnostic imaging, are useful in the preoperative evaluation of ovarian carcinoma in women.
To date, there are no tumor markers with high sensitivity and high specificity for endometrial cancer, although CA-125 is often used in clinical practice. The researchers note that elevated levels of CA-125 are able to predict a cancer diagnosis in women if they have:
- Ectopic disease;
- The tumor is larger than 2 cm;
- Penetration into the lymphovascular space and deep layers of the myometrium;
- Involvement of the cervix and adnexa;
- Positive cytology;
- Metastasis to the lymph node;
- The need for chemotherapy.
In addition, CA-15-3 and CA-19-9 are significantly higher in patients who required adjuvant therapy (chemotherapy), and CA-19-9 levels are useful in predicting penetration into the deep layers of the myometrium, into the cervix. CEA and AFP antigens were unable to predict any of the parameters assessed and prognostic requirements for chemotherapy.
SCC antigen is a useful tumor marker in the clinical treatment of cervical cancer. Beta-hCG and alpha-fetoprotein have been shown to be useful tumor markers for ovarian and germ cell tumors. In addition, beta-hCG serves as an ideal tumor marker for monitoring gestational trophoblastic disease and has established the standard against which other assays should be compared.
Research aimed at improving the detection of epithelial ovarian carcinoma, especially at an early stage, has identified several new candidate tumor markers. These include lysophosphatidic acid (a lipid found in blood serum and ascitic fluid), mesothelin, HE4, osteopontin, VEGF, IL-8, M-CSF, as well as various kallikreins.
Among these potential markers, HE4 has a sensitivity similar to CA-125 in detecting advanced disease and greater specificity than CA-125 in detecting early-stage ovarian carcinoma. Validation of HE4 as a diagnostic biotumor marker for women with early-stage ovarian cancer is ongoing.
Beta hCG
The beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) is usually produced by the placenta. Elevated levels are most often associated with pregnancy; False-positive elevations occur in hypogonadal conditions and with marijuana use. Elevations of beta-hCG are also found in patients with uterine choriocarcinoma, embryonal carcinomas, polyembryomas, mixed cell tumors, and, less commonly, dysgerminomas.
Beta-hCG and human placental lactogen (hPL) are the most useful tumor markers for trophoblastic diseases. The use of beta-hCG is not limited to trophoblastic diseases; it has been found in many gynecological neoplasms.
Decoding
Decryption is performed by specialists. Typically, testing for uterine cancer markers takes three days. As a result, the patient receives a table of results. But only a doctor can interpret them. Conditional standards for indicators are given below.
Interpretation of the study on tumor markers
| Name | Norm | Increased | Reduced |
| SCCA | 0-1,5 | Oncology | — |
| CA125 | 11-13 | Oncology, pregnancy (sometimes) | Hormonal imbalances |
| βhCG | 0-2,5 | Oncology, pregnancy | — |
| REA | Less than 2.5 for non-smokers, Less than 5.0 for smokers | Oncology, pregnancy | — |
| SA 27-29 | Less than 38-40 | Oncology, endometriosis | — |
There are a number of exceptions, so you shouldn’t despair immediately after a deviation is discovered. Often this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body of one type or another. Only a specialist can competently answer the question of whether cancer exists, and then only after additional research.
Indications
In medical practice, the SCC tumor marker is usually used for the following indications:
- diagnosis of epithelial malignant tumors of various localizations (neoplasia of the skin, cervix, esophagus, oral cavity, anus, respiratory system), but exclusively in combination with other tumor markers;
- monitoring the effectiveness of antitumor therapy (serial testing);
- monitoring for possible recurrence of carcinoma;
- diagnosis of secondary foci of epithelial neoplasia.
Unlike some tumor markers (for example, CA 19-9), analysis for SCC allows you to more accurately plan treatment tactics and predict its outcome.
- comprehensive diagnosis of tumors from squamous epithelium of various locations - cervix, lungs, head and neck, etc.
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment - before and after surgical treatment, chemotherapy
- planning further treatment
- detection of tumor recurrence during long-term monitoring
- predicting treatment success
The analysis is not carried out for screening or during primary research, therefore it is actively used by doctors to monitor the development of an already formed disease.
Noted in non-invasive cancer, an increase in level is found in 5-10% of women. While in patients with stage 3 it is increased in 70%.
The resulting substance makes it possible to identify cancer cells and establish the multiplicity of tumor forms.
To make an accurate diagnosis, oncologists in most cases prescribe an analysis in combination with other methods.
A tumor marker allows you to monitor the progression of the disease and control its development. Sometimes it is tested in people at risk. However, with tuberculosis, ARVI, bronchitis, the results may be unreliable.
What does a tumor marker blood test show and how much can you trust it? Of course, this analysis will not show the complete picture of the disease, but an increased level of tumor markers gives reason to suspect the development of pathology in the body and prescribe specialized types of tests, as well as the necessary examination (ultrasound, MRI and others).
If the level of tumor markers is elevated in a blood test taken during a medical examination, what does this mean? The presence of a cancerous tumor is not at all necessary; an increase can occur with a benign neoplasm, with some pathological processes in the pancreas and liver. There are other situations when the analysis shows a good tumor marker, but cancer develops in the body.
Content:
- What does the SCC tumor marker determine?
- Tumor marker indicators
- Indications for blood tests
- How to prepare for research
- How often to conduct research
← Blood test for tumor marker S-100 of skin melanoma
Tumor marker CEA - what does it show in the blood? →
An SCC tumor marker is a substance produced by malignant cells or the body in response to the presence of a tumor. The SCC tumor marker is a glycoprotein that inhibits serine proteases. Molecular weight - 45–55 kDa. Healthy epithelial tissues synthesize minimal amounts of SCC without entering the systemic circulation. Scientists have not yet figured out the biological role of SCC.
SCC tumor marker is synthesized by epithelial cells of the cervix, anus, skin, esophagus and bronchi
Purpose of the study
A specific antigen, known as the cancer marker SCC, Squamous cellcarcinoma antigen, Scc-ag or squamous epithelial tumor marker, appears in the human body as a result of its production by epithelial cells. Healthy cells produce negligible amounts of this substance. The altered (cancerous) cells produce the SCC antigen in large quantities, and this is reflected in the results of the blood test.
The cancer marker is used in the following studies:
- Determining the method of therapeutic treatment of the patient.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment (antigen concentration should decrease).
- Obtaining information and making a prognosis about possible carcinoma metastases.
- Monitoring the patient's condition after surgical removal of the tumor.
Tumor marker value
The structure of the SCC tumor marker resembles a protein consisting of two components. The marker is a glycoprotein and belongs to the group of protease inhibitors. Cells penetrate the membrane and change their structure. In a healthy person, the element is absent and manifests itself with the development of pathologies. The concentration of the substance can increase significantly when neoplastic processes occur. The antigen is found in all body fluids. In medical practice, tumor markers are used for blood tests. The marker has different names:
- squamous cell antigens;
- squamous cell carcinoma marker;
- SCCA;
- SCC-ag;
- TA-4 (tumor-associated antigen-4).
Experts note that the component is able to regulate the differentiation of healthy epithelial tissues and provokes the formation of malignant growths as a result of apoptosis dysfunction. The effect of this protein on the appearance of cancer has not been fully studied. The presence of a tumor marker is not considered 100% proof of the presence of the disease and is assessed together with a number of other diagnostic methods. The purpose of the test is to monitor the epithelium and cell functioning of the patient after treatment and during remission.
Why does antigen level increase in carcinoma?
An upward deviation from the norm of the SCC antigen indicates the progression of the tumor, the spread of metastases to the lymph nodes and other neighboring organs and tissues. In addition, the amount of antigen in the blood may be increased if:
- ineffectiveness of the therapy, when there is a high probability of subsequent relapses;
- development of benign pathology, or psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus, non-tumor diseases in the lungs: tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, exudative pleurisy or renal, liver failure.
The antigen for squamous cell carcinoma scca is also present in the body of a healthy person, but should not exceed 2.5 mg/l. As the tumor grows, the number of tumor markers will steadily increase. Carcinoma is fraught with relapses already at stages 1-2, so only regular determination of the antigen in the blood every 2-3 months will allow doctors to predict the course of the tumor and prevent relapses when primary clinical manifestations appear.
Exceeding the level indicates the development of oncological processes, as well as the release of glycoproteins from the epithelial layer of the cervix during the development of carcinoma.
The scc antigen is a tumor marker or detector for a squamous cell tumor, as it develops, the level of antigen in the blood increases sharply or when a protein is released - a protein from the epithelial layer of the cervix. At the same time, the level of ESR in the blood increases. Although it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using the SCC test alone. SCC level increases when:
- psoriasis;
- renal failure;
- gynecological diseases.
The squamous cell carcinoma antigen may indicate cervical cancer or other types of cancer.
SCC tumor marker is a tumor marker that is a kind of detector of cancer or squamous cell oncology that has a tendency to grow invasively. During this process, the tumor invades surrounding tissues and regional lymph nodes. The SCC tumor marker is also present in a healthy human body, only in small quantities. Its level increases with the development of cancer.
Experts say that thanks to the antigen of squamous cell carcinoma, it is possible to establish the development of neoplasms of the cervix, ear, esophagus, nasopharynx, lungs, etc.
Normal levels are up to 2-2.5 ng/ml; according to some data, even below 1.5 ng/ml
It should be noted, however, that this is the standard range of values accepted by most researchers. Adopting strict standards is not possible because some patients with squamous cell carcinoma have low blood antigen concentrations (below the acceptable upper limit of normal) even as the disease progresses. And vice versa - not every patient who shows an increase in antigen levels above the standards reveals the presence of oncological pathology.
Type of tumor markers
Each type of tumor produces its own unique marker, which is used to determine the type of oncology:
- SCC is used to track the outcome of treatment for carcinoma of the cervix, ear, and throat;
- CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) – increases its performance in colorectal carcinoma in combination with SCC in cervical carcinoma;
- Alpha-fetoprotein is used in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma;
- Gastric cancer antigen is used to monitor the treatment of gastric carcinoma;
- Mucin-like glycoprotein, a tumor marker of Tps, is used in monitoring the outcome of breast cancer treatment;
- CA 19-9 – cancer marker for determining pancreatic carcinoma;
- CA 125 is used in the control of testicular carcinoma disease;
- NSE – monitors the effectiveness of treatment for lung carcinoma;
- The cytocreatine-19 fragment is used in lung carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung;
- Ccc – monitors the development of colon cancer;
- Ubc – tracks the development of bladder cancer
- Ssk - used in the control of esophageal cancer.
Do you want to know the cost of cancer treatment abroad?
* Having received data about the patient’s disease, the clinic representative will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
Increased rate
The SCC norm for a completely healthy person is “0” in any units of measurement. The complete absence of this substance in the human body indicates the absence of pathologies. However, during the production of SCC by the cellular epithelium, a small amount of it can enter the blood. In these cases, the tumor marker concentration can be 1.5-2.5 ng/ml.
Exceeding the permissible level in women sometimes occurs naturally in the second trimester of pregnancy. A normal antigen level after appropriate treatment against squamous cell carcinoma indicates positive dynamics.
If the transcript shows that the SCC is indeed elevated as a result of the development of squamous cell carcinoma, additional studies must be performed to establish a diagnosis. More precise methods are used to determine the presence of cancer cells. A biopsy is considered the most reliable. Testing for tumor markers is carried out regularly after successful treatment of carcinoma:
- In the first year after surgery, an SCC test is performed every month.
- From the second year after successful treatment of carcinoma, blood is tested once every 2 months.
- In the third year, one blood test is performed.
- Starting from the fourth and subsequent years, tests for carcinoma (SCC marker) are carried out annually.
Even after successful treatment of squamous cell carcinoma and the risk of disease recurrence, the cancer marker SCC is not a clear indication of the growth of cancer cells. A tumor marker is used as an indicator of abnormalities in the body. More accurate methods are used to further study the health status.
normal tumor marker SCC in the blood – up to 1.5
Remember that each laboratory, or rather laboratory equipment and reagents, has its own standards. In the laboratory test form they appear in the column - reference values or norm.
The SCC tumor marker norm for women and men is the same.
When should I get tested for SCC?
In case of cancer, tests for cancer antigens must be taken regularly in order to dynamically monitor the condition of patients. In the first year after diagnosis, it is necessary to donate blood monthly along with other cancer markers, general and biochemical blood tests.
In the second year of the disease, the test must be taken every two months, then, judging by the patient’s condition, the doctor prescribes screening 1-2 times a year. If the indicator is elevated, examinations are prescribed every three months.
After taking cytostatics, radiation therapy or surgery, tumor marker tests should be carried out once a month throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
Pathologies indicating an increase in test value
The list of diseases that reflect SCC tumor markers includes not only tumor diseases, such as squamous cell cancer of the esophagus, oral cavity and nose, larynx, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, lungs, hearing organ, genital organs (uterine cancer, neoplasms of the external genitalia, cervix uterus), anus, adenocarcinoma of the gastrointestinal tract.
Somatic pathologies and conditions lead to changes in antigen concentration, including:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- renal failure;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and acute inflammatory processes in the bronchopulmonary system;
- skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis, pemphigus vulgaris);
- pregnancy, starting from the second trimester.
In non-tumor pathologies, the SCC tumor marker changes by no more than 50% of normal.
Oncology and women's health
Unfortunately, in our time, women not only after 40 years are susceptible to cancer. Increasingly, an increase in squamous cell carcinoma antigen is observed in young girls under 30 years of age.
The test for SCC tumor marker shows the norm in women if the antigen concentration level does not exceed 2.5 ng/mg. It is known that cervical cancer is a difficult disease. Therefore, the sooner it is possible to determine its presence, the more likely the most positive prognosis for recovery is. The SCC tumor marker, which shows a greater amount of antigen than normal, indicates the presence of cancer. Deciphering the tumor marker will enable the doctor to prescribe the correct treatment and monitor the development of the disease.
How to prepare for the test
Obtaining accurate test results for cancer markers depends on many factors. The attending physician is obliged to decide on the determination of SCC markers in the patient’s blood individually for each patient.
If a malignant tumor is diagnosed in a timely manner, it is possible to slow down the process and prevent the occurrence of complications. Studies are carried out in men over forty years of age if there is a suspicion of the development of oncology or its metastasis. For diagnosis, blood is taken from the patient’s vein in the morning. The analysis is given on an empty stomach.
A couple of days before the test, the patient should exclude hot, spicy and salty foods from food, and it is also necessary to avoid stressful situations.
It’s no secret that before any analysis you need to prepare
To obtain a reliable result, you need to take into account many factors. The specialist knows what affects the SCCA tumor marker indicators and takes this into account when conducting the analysis
Including possible ongoing inflammatory processes.
Before taking the tests, you should consider certain preparation rules
In any case, the patient must initially visit a general practitioner and oncologist, who individually decide when it is best to conduct this analysis and whether it is needed at all.
Blood donation for SCC tumor marker occurs in the morning. The patient should not eat before the test. Also, the day before the test, it is advisable not to eat fatty, spicy or fried foods. To ensure reliable results, smoking is prohibited at least half an hour before blood sampling. Drinking tea or coffee is also undesirable.
To conduct the study, only 5 milliliters of blood is sufficient, which is taken from a vein. This SCCA test is not recommended for mass screening of women, but is necessary for timely and precise control over the treatment.
After analysis for the SCC tumor marker, it is necessary to correctly interpret the results obtained. Since not everyone has a special education for this, it is better that the SCC tumor marker is deciphered by a qualified worker. And under no circumstances should you try to prescribe treatment yourself after decoding yourself.
Important! Everyone should know why the SCC tumor marker increases and what to do about it. The level of antigen concentration may increase if the body has recently suffered inflammatory processes
In this case, you need to repeat this study after three weeks.
The isolated SCC antigen, which shows a high level of concentration, allows the specialist to separate patients for surgery or radiation therapy. This also helps to correctly adjust the prescribed treatment if the patient’s condition worsens or there is no result.
The SCC tumor marker test, which indicates the presence of the disease, has fairly reliable results. At the same time, it can be used to determine what the indicators indicate.
- For tumors:
- For non-tumor diseases, the increase in rates is up to 50 percent due to:
- pancreatitis and renal failure;
- liver cirrhosis;
- endometriosis and other gynecological diseases;
- chronic lung disease (about 37% of patients);
- pemphigus, psoriasis, eczema.
If you take care of diagnosing a malignant tumor in time, you can slow down the process and prevent complications.
The study is performed in men over 40 years of age if the development of cancer or metastases is suspected. Only blood from the patient’s vein is suitable for testing. The procedure is performed by a specialist - a trained nurse - in the morning. The test must be taken on an empty stomach, 4 hours after eating. It should be remembered that a study to determine SCC tumor markers allows one to establish the specific location of the tumor, but the patient should also undergo some procedures by an oncologist.
A few days before the test, the patient must exclude spicy, salty, and spicy foods from the diet, avoid stressful situations, and limit smoking.
The patient should pay great attention to the analysis of the data obtained during the study
Rules for preparing for research
Before donating blood for the SCC tumor marker, you should not drink drinks such as coffee and tea, or take any food or medications for several hours. If it is not possible to exclude taking medications, this must be reported to the laboratory assistant who will decipher the indicators. Before donating blood for the presence of SCC squamous cell carcinoma antigen, you should not overexert yourself physically and emotionally. Blood sampling is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning, when the level of tumor markers due to the presence of cancer cells in the body increases the most.
Similar
| Brief results of the latest study on the topic “The Future of Quality” and about the book “Economic Benefits Study: International Case Studies” | Cuvette compartment, allowing the use of various types of cuvettes, including: round, dry, flow, etc. Allows you to study substrates, enzymes, electrolytes, hematological parameters. The photometer is an open system and can... |
| How American companies manage talent. Key Elements Half of American organizations cite talent management as a top priority. This is evidenced by research data... | Order No. 321 of the city of Nadym “On the organization and conduct of a district monitoring study of the readiness of first-graders to study at school in municipal... |
| The device is intended for binocular stereoscopic non-reflex examination of the fundus of the eye using the reverse ophthalmoscopy method when illuminated with white, blue and blue-green “red-free” light. The ability to operate the device from an autonomous power supply allows you to increase the productivity of medical personnel and carry out… | Documents1. /Basic principles of research/referat-online.at.ua.doc2. /Basic… |
| International scientific and practical conference “Social sciences: history, current state and research prospects” The organizer of the scientific and practical conference “Social sciences: history, current state and research prospects” is… | V. I. Tyupa narratology as an analyst of narrative discourse (“Bishop” by A. P. Chekhov) Tver, 2001 (Series “Literary text. Problems and research methods.” Appendix “Lectures” Series “Literary text. Problems and research methods.” Appendix “ Lectures in Tver" |
| Formation of the initial cost of a construction project when performing construction and installation work in an economic way; formulation of the relevance and goals of the study; Formulation of the relevance and goals of the study. One of the ways to receive fixed assets is new construction or expansion,… | Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education "Voronezh State University" Voronezh Department of the Russian Geographical Society Faculty of Geography, Geoecology and Tourism Voronezh Department of Argo All-Russian Interdepartmental Scientific and Practical Conference "Municipal Entities of the Regions of Russia: Research Problems, All-Russian Interdepartmental Scientific and Practical Conference "Municipal Entities of the Regions of Russia: Research Problems ,… |
| Exploring a function using its derivative |
Documents
Documents
Informative tumor markers for cervical cancer and methods for identifying tumors
Several metabolic products of atypical cells are detected in biological fluids when the cervix is affected. Tumor markers are informative:
- CA 125 is a tumor-associated antigen. The protein is present in the bronchi, pleura, pericardium, uterus, and endometrium. It can enter the plasma after an abortion or during menstruation. It has a high degree of significance in diagnosis. It increases only with neoplasms of internal organs. More often, the analysis is taken together with a test for another CEA marker (Cancer Embryonic Antigen). In combination, it is prescribed with a test for the HE-4 tumor marker. If it is elevated, a malignant tumor is suspected.
- SCCA is a glycoprotein that is completely absent in a healthy body. Prescribed for the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma. It is of high significance during the examination. The most informative analysis is at stages 3 and 4 of the disease. In the initial stages of pathology it is insensitive. False positive results are often obtained. There are other names: tumor marker for squamous cell carcinoma, SCC-Ag, TA-4. It is not specific, as it also shows benign formations.
- CEA (cancer embryonal or oncofetal antigen). It is of medium significance for detecting cervical cancer. In an adult, this antigen appears only during the development of pathologies (tumors, autoimmune diseases, severe inflammatory diseases). It is the most reliable for detecting relapse of the disease.
- Cytokeratins: TPA, Cyfra 21-1. Important for prognosis before starting therapy and monitoring the disease.
Tumor markers
Patients are prescribed tests for several markers simultaneously to ensure the reliability of the results. The analysis is carried out using ELISA and ICLA (immuno-chemiluminescent assay). When tumor markers are detected, additional examinations are indicated: x-ray methods, ultrasound, MRI, cytological examination of scrapings from the cervix.
SCC tumor marker of the cervix, normal, interpretation
In young patients, squamous cell carcinoma is quite common, and to correctly assess the radicality of surgical treatment, monitoring is carried out using SCC.
Studies depend on the size of the primary tumor and the degree of lymph node involvement. The antigen level in patients with squamous cell carcinoma increases significantly during exacerbations of concomitant pathologies: psoriasis, cholecystitis and acute respiratory infections.
If the SCC norm is significantly exceeded eight weeks after the end of primary therapy, then the specialist assumes that there is no effect from the treatment.
The tumor marker SCC, or squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA), is a tumor marker, that is, it is a substance that is present in the blood of cancer patients. SSC antigen may indicate cervical cancer and other types of cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a tumor marker that acts as a kind of detector for squamous cell carcinoma or a malignant tumor that tends to grow invasively. That is, it invades surrounding tissues and metastasizes to other organs, most often to nearby lymph nodes.
SCC tumor marker is present in a healthy human body in small quantities. Its levels only increase when cancer develops.
It is a glycoprotein and was first isolated from the epithelium of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix.
Disadvantages of the marker
Unfortunately, the tumor marker is not a specific tumor marker. This means that its levels are increased not only in tumors, but also in other diseases such as psoriasis.
Elevated SCC levels of twofold or more were found in 80% of patients with cervical cancer. Increased values may also be present in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the bronchi, tongue, esophagus or anus. Found in patients with chronic renal or liver failure. Slightly elevated values may be found in patients with other gynecological diseases.
It serves to early detect relapse, the presence of residual disease and monitor the effects of therapy.
Although the marker has approximately 90% specificity and 70–80% sensitivity for squamous cell carcinoma, it is not recommended for use as a screening marker to detect the primary tumor.
- used as a marker for second-line therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (following CYFRA 21-1)
The antigen is found in sweat, saliva and other bodily secretions. Thus, contamination of the test material with them (for example, saliva splashes) can cause a false reading of elevated values.
Information
Deciphering the tumor marker
Most often, the tumor marker SCC is found in quantities greater than normal in women with squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. The higher the score, the higher the stage of the pathology. If the cancer is non-invasive, then a positive result will be in five or ten percent of patients, with stage 1-A in thirty, if the cancer has reached the third stage, then the level of tumor marker will be high in seventy percent of patients, with the fourth stage of the disease - in ninety.
Sick women may also have normal indicators, so decoding should not serve as the only diagnostic measure.
Antigen test results
Cancer is the most insidious disease, because often in the early stages the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Determining SCC tumor markers helps to recognize the first manifestations of the disease and determine its presence. This antigen is a glycoprotein produced by squamous cell tissue. Normally, the antigen in the patient’s blood does not exceed 2.5 ng/ml, however, an increase in tumor markers is often detected in the following categories of people:
- pregnant women; patients suffering from bronchial asthma; patients with liver failure.
With an increase in SCC markers in patients suffering from stage 1A and 1B cervical cancer, a relapse of the disease occurs.
The antigen for squamous cell carcinoma scca is determined quite regularly, once every three months, because this study makes it possible to predict the formation of a tumor even before the development of the first symptoms.
In carcinoma of the ear or nasopharynx, the level of the SCC marker always increases. The antigen rate increases greatly with the development of benign neoplasms and is 10 ng/ml.
Features of the analysis
A study for the SCC tumor marker is not carried out if a person is diagnosed with diseases such as tuberculosis of the lungs or another organ, as well as dermatitis, psoriasis and any skin rashes, since in this case the level of the tumor marker may be increased. The analysis is done two weeks after therapy for these diseases has been completed. The presence of the SCC marker alone cannot indicate the presence of a cancerous tumor; it is necessary to examine the blood for other tumor markers:
- Cyfra 21-1 and TSP – lung cancer antigen;
- CA 125 – ovarian cancer antigen;
- HE-4 – antigen of neoplastic changes in the female gonads;
- CEA – carcinoembryonic antigen.
We recommend reading Why it is performed and what the CA 15-3 tumor marker shows
If necessary, additional diagnostic measures are carried out to determine the presence of carcinoma:
- Gynecological examination of the cervix using speculum;
- Ultrasound examination with a transvaginal sensor;
- Colcoscopy with smear collection;
- PAP smear test;
- Biopsy followed by histology;
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic organs.
As a rule, after cancer treatment, the SCC level increases only in the presence of metastases that led to relapse, if there are no other reasons influencing the result of the study, therefore, after treatment, this analysis, in combination with other diagnostic methods, allows us to identify newly emerging pathology at the earliest possible stages .
Analysis is NOT carried out
Tumor marker testing for squamous cell carcinoma is carried out using immunochemiluminescent techniques. The method is based on specific reactions that occur between an antigen and an antibody with the formation of a stable complex and its subsequent detection using UV. The advantage of the technique is its high sensitivity, which reaches 90%.
The biomaterial for diagnostics is venous blood. Recommendations for proper preparation for the study:
- Do not take alcoholic drinks, fatty or smoked foods for 1 day;
- You must donate blood on an empty stomach; you are allowed to drink unlimited amounts of still water;
- avoid physical and emotional stress within 30 minutes;
- Smoking is prohibited 30 minutes before.
It is important to strictly follow the rules for collecting biomaterial, since contamination with respiratory tract secretions, saliva or sweat can lead to false positive results. The list of laboratory tests necessary for each person, in addition to analysis for this glycopeptide, includes:
The list of laboratory tests necessary for each person, in addition to analysis for this glycopeptide, includes:
- SCC testing is NOT used to screen for cervical cancer - testing should not be done on all women
- A repeat SCC test is NOT performed if the first test was negative.
Indications for blood tests
The cervical tumor marker is determined to:
- Evaluate the treatment provided to patients whose diagnosis was established, as well as the initially elevated concentration.
- Determine the probability of spread of tumor metastases.
- To predict the survival of patients after complex oncology therapy.
- Monitor the course of the disease and prevent relapses.
An analysis for tumor markers of cervical cancer is examined before the start of complex therapy, in order to further compare and analyze the course of treatment and the course of the disease, and build new treatment regimens.
Important. After removal of the tumor, the control SCC tumor markers paired with CA 125 will be normal for the first 4 days. The next study is carried out after 2 months, then once every six months.
Norms
Laboratories use different methods for determining the level of tumor markers. To eliminate errors in the perception of results, laboratories conducting analyzes provide information about the normal values and the analysis method used. It is recommended to interpret the test results in the clinic where the tests were performed, and when re-determining tumor markers (screening studies and follow-up over time), it is also recommended to contact the laboratory or clinic that performed the initial tests.
| Tumor marker | Normal level of tumor markers | Study group | Note |
| SA-125 | Not more than 35 milliunits/milliliter of blood serum | Women | During pregnancy, levels up to 100 milliunits do not indicate a tumor |
| hCG | Not more than 6.15 mU/l B-subunit = 0.013 mIU/ml | Not pregnant women | |
| REA | 3 ng/ml | In some cases, the norm is within the range of 5-10 ng/ml. With alcohol and tobacco abuse, the level can vary between 7-20 ng/ml. |
Carrying out a test for tumor markers of cervical cancer
Biomaterial is given only on an empty stomach in the morning. It is not recommended to take the test immediately after returning from the cold. In winter, it is better to come to a medical facility in advance.
Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein. For a full study, 5 ml of biomaterial is required. During collection of material, it is necessary to strictly observe sterility, since the tests are very sensitive. Test results are provided after 2–10 days.
The information content of the study is affected by compliance with the rules for the preparation and storage of biomaterial:
- within one hour from the moment of blood collection, the serum is separated from the red blood cell mass;
- the biomaterial is poured into test tubes and frozen at -200C;
- repeated defrosting and freezing of the material is unacceptable;
- Hemolysis of red blood cells, which occurs due to improper collection and transportation of the material, is unacceptable.
If the indicators are high, it is recommended to do the test again after 4 weeks to exclude errors in the study or non-compliance with the rules for preparing the patient.
Deviations and their reasons
When the indicator increases to 10 ng/ml, a benign formation or somatic disease is diagnosed.
Reasons for increased tumor markers:
- colon ulcer;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- emphysema;
- pancreatitis;
- renal failure;
- cystic fibrosis;
- Crohn's syndrome;
- pneumonia and bronchitis;
- liver hemangioma;
- polyposis, fibroma, lipoma.
With a decrease in the amount of the substance shown, we can talk about progressive remission of the tumor, successful treatment and the disappearance of the source of inflammation.
If a high jump in the number is shown, this can only mean the presence of a cancerous tumor and metastasis.
The marker shows the result most accurately:
- For cancer of the rectum and colon, bronchopulmonary system, pleura.
- When metastases appear in the thyroid gland, stomach, esophagus, bladder.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in several ways.
What does a tumor marker indicate for cervical cancer?
A rapid decrease in the concentration of tumor markers after surgery or other forms of treatment indicates a successfully selected tactic. If the level of indicators does not decrease, therapy is adjusted. A long-term low level of indicators indicates a period of remission.
A gradual increase in tumor marker values from the baseline indicators tells the doctor about the onset of a relapse of the disease. Tests can warn of re-development of the disease 3 months or a year before relapse is confirmed by other means of examining the patient.
Types of tumor markers
A decrease in the level of markers after a period of their growth indicates the effectiveness of drugs after correction of therapy. An increase in the level of indicators after treatment indicates that the tumor is resistant to the prescribed drugs. A progressive increase in markers indicates an unfavorable prognosis.
Purpose of analysis
A test for the CA 125 marker is recommended for patients after the onset of menopause for the timely detection of oncological processes in the mammary gland and pelvic organs. An examination is required if there are space-occupying formations in the projection of the appendages.
With an increase in CEA, the progression of the disease is judged over time. A test is prescribed for the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant tumors. A slight increase indicates the presence of a benign formation. If the values periodically rise and fall, they speak of a wave-like course of the pathology with periods of relapses and remissions. The marker is also needed to evaluate neoadjuvant chemotherapy, which is administered before surgery.
SCCA is prescribed for the purpose of diagnosing cervical cancer, further monitoring the course of the disease and the effectiveness of therapy. It makes sense to prescribe the test to patients who are at risk for cancer. The test is performed to exclude tumor metastasis to other organs. The level of antigen depends on the stage of the disease. The test is most informative for detecting squamous cell carcinoma. In 10% of cases it may be positive for adenocarcinoma.
Indications for window marker analysis
Cancer tumor markers for various organs, including the uterus, are necessary for timely diagnosis, when effective treatment is possible, guaranteeing maximum restoration of health. They help determine whether uterine cancer is completely removed during surgery, to predict the results and adjust the prescribed treatment. The normal level of tumor markers may be an indicator of the absence of oncology of the reproductive system, but if there are clinical symptoms of the disease, you should not reassure yourself about the level of tumor markers. It is necessary to take other tests to establish a clear diagnosis.