Laparoscopy
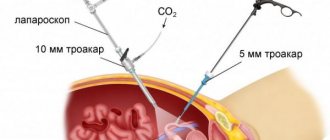
This term is defined as a new method of surgery using small incisions or holes of only one and a half centimeters to perform surgery on internal organs. The instrument used to carry out such actions is called a laparoscope. It is a telescopic tube with lenses and a video camera attached to it. Laparoscopes in the modern world have digital matrices that allow you to display images with great clarity.
An optical cable equipped with “cold” light also leads to the tube. Carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to form an operative space, that is, the abdomen is inflated, the abdominal wall rises above the internal organs. The surgical range of laparoscopy is very large and varied. But such operations have some consequences.
Reasons for appearance
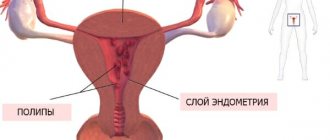
Basically, the nature of the appearance of adhesions is the inflammatory process after surgery, as well as during infections and any injuries. They are found between internal organs, most often between the fallopian tubes, ovaries, in the intestines, heart and bladder.
Adhesions after laparoscopy are whitish stripes that contradict the human anatomy and prevent the body from working in its usual rhythm. Lead to health problems. Adhesions after tubal laparoscopy may prevent a woman from becoming pregnant. But in the abdominal area they cause intestinal obstruction.
According to statistics, about 30 percent of patients after surgery suffer from the formation of adhesions. However, this is influenced by indicators that do not apply to everyone.
There is an approximate list of factors that influence and increase the percentage of adhesions after laparoscopy:
- Elderly people and people with diabetes are among the first to be at risk. This is due to the fact that this category of the population has low tissue regenerative function.
- Also, the environment in which the operation is performed can become such a negative factor. The air and gas composition leads to dryness of the abdominal cavity, which contributes to the formation of adhesions.
- These conditions include infection. Most often, this process occurs during surgical intervention in the pelvic organs, since infectious pathogens accumulate precisely at the site of endoscopy. They penetrate into a suitable environment for their reproduction, slowing down regeneration, as a result of which compactions are formed, that is, those same adhesions.
Symptoms
The manifestation of any signs that an adhesive process is forming in the pelvic organs may be completely absent. As the scar of the postoperative intervention increases, nagging pain appears at the site where the intervention was performed, which may intensify with movements and during sexual intercourse. The list of exacerbation of pathologies looks like this:
- the occurrence of intestinal obstruction;
- disturbance in the functioning of internal organs;
- the appearance of pain in the pelvic area;
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- development of infertility;
- bleeding, with an unpleasant odor.
Complications and consequences
Despite treatment and the possibility of diagnosis, doctors and women are frightened by the thought of the possible development of complications that lead to adverse consequences for the body.
The risk of developing complications and a woman’s attitude towards them largely depends on the age and performance of the patient’s reproductive function, and the desire to have children in the future:
- If the patient does not plan pregnancies in the future , if her reproductive function is completed and her age is approaching menopause, with a mild course of the pathological process, the prognosis is relatively favorable. In this case, discomfort in the lower abdomen may only occasionally appear, but there are no significant complications.
- If a woman is in active reproductive age after the development of adhesions in the ovaries and plans a pregnancy, then the most serious complication is the development of infertility, which can become irreversible. In addition, adhesions in the ovaries lead to the development of cysts, leading to the risk of their rupture.
- In severe inflammatory processes, the formation of a large number of adhesions leads to the formation of persistent pain and the most dangerous complication is intestinal obstruction when the intestines are involved in the adhesive process.
Diagnosis of adhesions
If signs of this process appear, the following procedures must be carried out:
- The first of them is a medical examination with palpation, identifying a list of symptoms that bother the person, with the help of which the doctor prescribes further examination.
- Ultrasound of the organs of the area where it is possible to see the appearance of adhesions.
- X-rays are taken on an empty stomach.
- Laparoscopic examination: a video camera is inserted through a small hole to visually detect the adhesive process.
However, the fact that the clinical manifestations of compactions are too diverse makes it difficult to diagnose them. When examined by a gynecologist, it is possible to determine the formation of adhesions after ovarian laparoscopy if they are painful.
If this process was facilitated by infection, a vaginal smear will show changes. In a general blood test, signs of inflammation will be visible.
Often used methods such as hysterosalpingography, in which the uterus and tubes are filled with a contrast agent and examined using X-rays; Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging is the acquisition of images showing the condition of a particular area of the body.
The most popular is laparoscopy.
There are several stages of the formation of adhesions after laparoscopy:
- The first is that seals in the area of the pelvic organs, or rather the fallopian tubes and ovaries, do not affect the penetration of the egg into the tube.
- The second is that the adhesions are located between these organs and represent an obstacle to the capture of the egg.
- Third, the pipe can be completely twisted by the seals or pinched by them, which indicates that there is no passability.
Treatment
In the fight against adhesions after laparoscopy of a cyst, tubes or ovaries, there are two ways:
- Surgical removal.
- In the early stages of compaction formation, conservative therapy is possible if there are any contraindications for the former.
Adhesions after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts are removed through a small incision during surgery. In most cases, techniques are used that allow the preservation of all healthy tissues of internal organs. During laparoscopy, the ability of eggs to penetrate into the uterus is restored.
Treatment of compactions in the pelvic organs is possible with the use of ultrasound, currents that have a high frequency. Ionopheresis with enzymes is also included in the methods of combating the problem of adhesions after laparoscopy. Mud therapy belongs to the same list of actions against seals. But it is worth noting that all procedures are most often good in combination. Carrying out one of the actions is often not entirely effective.
In acute forms, there is no way to avoid surgical intervention.
The ovary is fused to the uterus
Adhesions on the uterus and fallopian tubes occur less frequently, but they prevent a woman from realizing her reproductive function , so treatment must be carried out.
This type of disease causes infertility.
There are many reasons for its development: abortion, inflammatory processes, sexually transmitted diseases, unsuccessful use of contraception.
In medicine, there are rare cases where adhesions are formed due to a congenital anomaly. Then it is worth talking about the underdevelopment of the fallopian tubes or their absence.
Diagnosing the problem at home is quite difficult. This will require examination using special devices and tests. Sometimes adhesions in the uterus do not make themselves felt, but there are still some signs:
- acute pain in the area of commissures;
- temperature increase;
- heart rate increases;
- the patient's general condition is deteriorating;
- constipation
Sometimes, when new adhesions form, the woman suffers from a headache. You should pay attention to this symptom and consult a specialist.
Prevention
Preventive measures are actions that need to be taken in order to prevent the reappearance of adhesions without fail. Study these measures carefully and follow your doctor's instructions. To avoid adhesions after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts and other internal organs, the following preventive measures are taken:
- Various physical procedures.
- Treatment with medications.
- Massage.
- Following a strict diet.
- Having regular check-ups with a doctor.
The most common method for preventing symptoms of adhesions after laparoscopy is medication. It includes the prescription of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as medications that destroy a substance such as fibrin, which is one of the elements for building seals. The duration of such measures varies from several weeks to a month and a half.
There is a method that is aimed at separating internal organs by introducing a special liquid into a particular area.
After the operation, one of the effective actions is physical procedures, or rather active effects on the body: electrophoresis, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, paraffin baths, laser therapy.
Therapeutic massage is used as a concomitant aid in the prevention of treatment of adhesions after laparoscopy.
Following a special diet is one of the important areas in preventing the appearance of seals.
Physical exercise
Physical exercises after laparoscopy should be discussed with your doctor. Typically, heavy exercise is allowed after 4 months. This time is enough for the body to fully recover.
It is necessary to maintain intra-abdominal pressure at the same level for a month. Otherwise, an abdominal hernia may develop. At this time, it is necessary to avoid lifting heavy objects, exclude exercise in the gym, or at home.
However, this does not mean that the patient needs to lie on the couch all the time. Reasonable physical activity contributes to a beneficial effect on the rehabilitation period. You can strengthen your abdominal muscles and respiratory system by walking. The duration is discussed with the attending physician. The duration of walks is gradually increased.
Exercises included in the exercise therapy group are beneficial for restoring the body. With their help, it is possible to strengthen the musculoskeletal system. Most often, you are allowed to start playing sports after a month. However, you need to monitor the amount of exercise. It is necessary to increase the load gradually. Your doctor will help you choose the most optimal load.
Classes begin with breathing exercises, then include exercises for the legs in the form of sliding your heels along the floor or sofa. Side turns are allowed. Moreover, all sports activities should be carried out in a horizontal position. After 5 days you can start walking in a straight line. After 4 weeks, swimming in the pool is allowed. When playing sports, you need to listen to your own body so as not to overload it and worsen your well-being.
Traditional methods
Modern medicine is strong in the treatment of adhesions, but we should not forget what people used when there were no innovations such as laparoscopy and antibiotics.
The following folk methods come to help:
- Aloe. The recipe is easy to prepare and does not require any expenses. The plant should be no more than 3 years old; you should not water the aloe for several weeks, then tear off the leaves and put them in the refrigerator for 3 days. Then chop it into small pieces and add 1:6 milk and honey. You need to take this remedy 2 times a day for 2 months.
- Milk thistle can also be treated if adhesions have formed after laparoscopy. To do this, you will need to infuse its seeds: 1 tablespoon of them is poured into 200 milliliters of boiling water, boiled and filtered. Use for one month.
- Plantain seeds are also poured with boiling water and infused in the same proportions as milk thistle. You need to drink it for 2 months, 30 minutes before meals, at least 3 times a day.
- St. John's wort. If adhesions appear after tubal laparoscopy, then treatment with this plant will come in handy. 1 tablespoon of dried St. John's wort is poured with boiling water, then boiled and filtered. The decoction should be drunk once a day, 1/4 cup, for one to three months.
Basics of rehabilitation
Usually the recovery period lasts for 6 months. It includes not only physical well-being, but also a psychological component. Of course, during this time the person will begin to live a full life and work. But this time period is necessary for the accumulation of body reserves, which are necessary to endure stress without causing harm to health. Optimal health usually returns after 1.5–2 weeks.
However, in order for the rehabilitation period to pass as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- if no other recommendation is given, then you should abstain from sexual intercourse for 2 weeks;
- adhere to the recommended diet. If you have had surgery to remove the gallbladder, you must follow diet No. 5 for a month;
- avoid constipation;
- It is allowed to start playing sports after a month. You should start by lifting weights of no more than 3 kg for 3 months. Then, five-kilogram loads are allowed for six months;
- after a month, physical therapy is recommended;
- taking multivitamin preparations that strengthen the body.