Definition
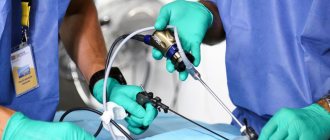
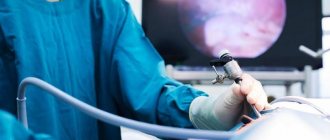
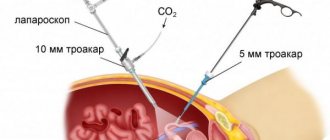
Laparoscopic intervention is a surgical method that involves performing an operation through small punctures. Their number does not exceed 5-6 pieces, and their sizes are minimal (5-10 mm). To monitor the movements of medical instruments, mini-video cameras are used that are inserted into the body. To create space, a portion of carbon dioxide is injected into the operated area. It expands the walls and allows free movement of instruments.
Today, cameras of the latest generations are used in medicine. They allow you to enlarge the image tens of times. The image is output to the computer in HD format.
Similar operations are performed on different organs, but the most common is renal laparoscopy.
Possible consequences
The risk of potential complications after removal of a diseased kidney always exists, but it is small - only 3-10%. Much, if not everything, depends on the qualifications of the surgeon, his experience, and assistants. Consequences are rare, but they can occur both after abdominal surgery and after laparoscopic intervention.
Open nephrectomy can provoke:
- respiratory failure;
- bleeding, sepsis;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- intestinal obstruction;
- heart failure;
- injury to the pancreas, spleen;
- thrombus formation.
When one kidney is removed using a laparoscope, the following consequences are possible:
- hernias that form at the trocar entry site;
- blockage of arteries in the lungs;
- pneumonia;
- damage to nerve endings.
Removing a diseased kidney affected by cancer provokes its relapse. This consequence is being combated with new targeted drugs that target certain proteins of the cancer cell.
Operations in the 90s
The kidneys perform many functions in the body, the main ones being cleansing the body of harmful substances and excess water. This is a paired organ with an oval shape. The kidneys are located below the ribs, closer to the spine area.
It is because of this location that for a long time operations were performed with an incision in the lumbar region. There are many intertwined muscles in this area. Their incision increased the complexity of the operation and the duration of the recovery period. Renal laparoscopy was first performed only in the 90s.
Resection
Kidney resection is a surgical intervention that is based on the removal (excision) of the affected area of the organ. The procedure can be performed through a skin incision with wide access to the pathological area or laparoscopically.
The operation carries a risk of bleeding due to the direct removal of part of the affected organ. The use of laparoscopy helps to minimize the patient's traumatization and improves the patient's well-being during the rehabilitation period.
Advantages of laparoscopy
Before the advent of this method, a complete opening of the cavity was performed. The incisions could reach 20 cm. The operation was accompanied by a long period of rehabilitation, large blood losses, and a stain remained on the body for life as a memory. Thus, the following advantages of laparoscopic operations can be identified:
1. Renal laparoscopy is accompanied by less pain and does not require the use of strong painkillers. The doses of analgesics prescribed are minimal, and the pain goes away faster.
2. The rehabilitation period takes little time. As a rule, 7-10 days are enough. Compared to open surgery, the period is minimal. With abdominal surgery, rehabilitation took from several weeks to a month.
3. Laparoscopic intervention leaves minimal traces behind. These are small puncture points. Very often they heal completely. Sometimes even a professional cannot detect them.
4. The likelihood of adhesions forming is minimal. Very often, the appearance of adhesions causes pain and intestinal obstruction.
5. The risk of ventral hernias is minimal.
6. The operation rarely has consequences such as infection.
Possible complications
Usually, kidney diseases are eliminated fairly quickly using laparoscopy, and the risk of undesirable consequences of the operation remains minimal. However, there is a possibility that a variety of problems will arise after surgery.
All possible complications after laparoscopy are divided into general and specific. Common ones include:
- bleeding from surgical wounds;
- elevated temperature after surgery (low-grade fever is recorded on the first day);
- pain and swelling of the external sutures;
- dizziness, confusion, runny nose or sore throat due to the use of general anesthesia.
The listed phenomena are considered normal and, with careful care of the patient, go away on their own.
Important! If unpleasant symptoms persist for more than 2-3 days and tend to intensify, there is a possibility of dangerous complications, including the development of infection.
Both laparoscopic nephrectomy and smaller interventions can result in specific complications. The most common complications are the formation of adhesions and relapse of the disease. They require repeated examination and examination by a urologist. Such consequences can be eliminated only through repeated surgical intervention.
Disadvantages of the method
Despite the abundance of advantages, an operation such as renal laparoscopy also has its disadvantages in comparison with open surgery:
1. High cost of the operation. Due to the use of expensive equipment, the price of the operation may seem high. However, we should not forget about the long recovery period after open surgery, which requires the use of painkillers and often wearing a corset.
2. High professionalism of the surgeon and medical staff. The operation of kidney laparoscopy implies that the hospital staff has all the necessary skills to carry out such manipulations.
Application of the method in practice
For renal diseases, the laparoscopic method has proven itself only from the best side, despite such a short period of existence. The main pathologies for which laparoscopy is used:
- Urolithiasis.
- Cystic formations.
- Tumors of varying quality.
- Urethroplasty.
- Kidney prolapse.
Manipulative actions are aimed at removing coral stones in the renal pelvis, which is effective and less traumatic for the patient. Additionally, stones in the ureters and bladder can be removed.
The method is especially effective when the cyst is localized on the kidney parenchyma. A special feature of the procedure is the ability to preserve the entire internal organ by eliminating only the neoplasm without damaging adjacent tissues and organs.
Such formations require either complete removal of the kidney or partial removal. Nephrectomy can be successfully performed by laparoscopy. In this case, organ resection will be less traumatic for the patient.
Prolonged presence of stones in the ureter causes injury and narrowing of ureteral strictures, proliferation of connective tissue with subsequent scarring. Laparoscopy can effectively cope with this pathology, even in inaccessible places (pyelo-ureteral segment).
The procedure, which is called laparoscopic nephropexy, involves manipulations to lift and fix the kidney with a special mesh.
Laparoscopy of a cyst in the kidney
Kidney cysts are a common occurrence. A cyst is a growth on a certain organ, round in shape, filled with fluid. When such a disease appears, it remains asymptomatic for a long time. The first symptoms manifest as pain and lead to complete atrophy of the organ. Treatment of such a problem is only possible through surgery.
When is a kidney removed?
Laparoscopic nephrectomy is a complex operation that can be performed by a highly qualified surgeon. Removing a kidney is a last resort measure , after which the patient’s lifestyle radically changes.
Indications for kidney removal are:
- Organ cancer no later than stage 2.
- Gunshot wound to the kidney.
- Acute renal failure, in which complete organ damage occurs.
- Kidney stones that cause suppuration or death of the organ.
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Hydronephrosis, in which the kidney tissue atrophies.
Read what hydronephrosis is here.
It is often necessary to remove a kidney from elderly patients due to age-related changes that provoke loss of organ function .
Contraindications to surgery are:
- Metastatic cancer stage 3. In this case, there is a risk of even greater spread of metastases, and removal will not lead to a cure. Such patients are usually prescribed palliative treatment.
- Severe cardiovascular diseases for which anesthesia is contraindicated.
- Blood diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.
- Allergy to anesthetic drugs.
- Overweight.
- Infectious diseases.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Peritonitis.
- Bronchial asthma in the acute stage.
Indications for surgery to remove a cyst in the kidney
If a number of symptoms appear, surgery to remove the tumor is recommended:
1. Sharp or aching pain in the kidney area.
2. Large size of the tumor (up to 10 cm).
3. Problems with urination. The cyst can compress the urethra and impede the natural process.
4. Beginning of the inflammatory process.
5. Burst cyst.
6. Detection of blood clots during urination.
7. Detection of cancer cells in a neoplasm.
The essence and advantages of laparoscopy
Laparoscopic surgery involves a step-by-step procedure aimed at removing the cause of kidney disease. All manipulations are performed under general anesthesia through 3-4 percutaneous punctures. Using special instruments that are inserted into the patient's abdominal cavity, the doctor gains access to the retroperitoneal space. Additionally, the camera is adjusted to obtain visual control, while the maximum enlarged image of the internal organs is displayed on the monitor.
The operation is considered quite complex, and therefore requires the full dedication and professionalism of the doctor, since it is necessary to manipulate instruments whose diameter does not exceed 10 mm. Thanks to the endoscopic video device, the risk of damage to neighboring organs and tissues is reduced, and hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity can be prevented.
The main advantages of renal laparoscopy include:
- minimal injury;
- absence of extensive scars and adhesions;
- reduction of rehabilitation time;
- there is practically no pain;
- the likelihood of postoperative hernia formation is significantly reduced;
- the use of painkillers is limited;
- the risk of an infectious process is reduced due to minimal intervention.
Contraindications to the procedure
Surgical intervention in the kidney area is not performed in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Absolute contraindications are colds, coughs and high body temperatures. With such violations, there is a need for correction. Only after the inflammation has been eliminated is it possible to perform laparoscopy. Among the absolute contraindications, the following should be highlighted:
- excess weight (obesity in the final stages) complicates manipulations;
- the presence of infectious processes requires preliminary treatment;
- persistent high blood pressure;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and pulmonary nature;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- blood clotting disorders;
- states of shock;
- purulent peritonitis.
Preparation period
Before surgery, you need to follow some recommendations:
1. Don't get too cold. Any weakening of the immune system is undesirable.
2. Avoid using blood thinners.
3. Take the necessary tests: blood, urine, presence of infections. Do an ultrasound and ECG.
4. A few days before the appointed date, you need to adhere to a certain diet. Eliminate fatty and fried foods, baked goods, vegetables and fruits from your diet.
5. On the eve of the operation, a bowel cleansing procedure is performed. Food and water are excluded 8 hours before surgery.
6. It is necessary to remove hair from the pubic area and abdominal area. You can simply cut them short.
7. If you have venous diseases, it is better to purchase compression stockings, which are worn during the operation. Sometimes it is possible to continue wearing it according to the doctor's indications.
Types of operations
There are several ways to carry out the procedure for removing a tumor in the kidney when laparoscopy is performed. Kidney removal is performed exclusively during open surgery. In this case, the entire organ is removed. This method is used extremely rarely today.
When performing a laparoscopic operation, either the walls of the cyst are glued together, or it is sutured to the wound.
Kinds:
1. Insertion of the endoscope into the urethra.
2. Performing a puncture in the back or abdominal area.
The first version of the operation is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure involves connecting the tissues of the cyst with the tissues of neighboring organs. The cyst should heal and leave no traces behind. After the operation there are not even any scars left. This method has not gained popularity due to the possible occurrence of negative consequences.
The second type of surgical intervention is used quite often because it is the most gentle. The contents of the cyst are removed. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
After the operation, a repeat ultrasound is performed to evaluate the results of the surgical intervention. Laparoscopy of a kidney cyst usually has favorable consequences. Initially, a small amount of fluid remains in the tumor. Gradually it resolves on its own. Otherwise, it may be refilled, which will cause another operation.
Indications and contraindications
Surgery is used when conservative therapy is ineffective. The key difference is the aggressiveness of implementation into the functioning of the body with the help of specialized instruments for radical treatment of the patient.
Indications for kidney surgery:
- Urolithiasis with the formation of large stones that interfere with the normal flow of urine.
- Anomalies of kidney development.
- Strictures are narrowings of the urinary tract.
- Purulent kidney lesions with the formation of abscesses requiring removal.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms in organs.
- Renal failure requiring a kidney transplant.
- Injuries with damage to the organ structure.
Contraindications:
- The patient's state of shock.
- Heart failure that does not allow surgery.
- Sepsis.
In each specific case, the doctor decides what type of intervention to use to eliminate the problem. The types of kidney operations used in practice will be described below.
Removal of a kidney cyst (laparoscopy): postoperative period
The recovery period depends on the type of surgery, but generally does not take more than one month. The first days the patient is not allowed to get up. On the 2-3rd day, you are usually allowed to get up and walk slowly. If laparoscopy is performed, you can go home on the third day. With an open operation - in a week.
Kidney laparoscopy surgery, the postoperative recovery period of which does not take much time, is quite common. Despite this, the patient cannot avoid using painkillers.
Diet after surgery
After surgery (laparoscopy of a kidney cyst), the diet must be followed. You need to follow these rules:
1. Over-salted foods, fried, fatty, spicy, coffee and chocolate are excluded from the diet.
2. The consumption of protein foods should be sufficient and not excessive. Such restrictions are associated with reducing the load on the body and ridding it of toxic products.
3. You will have to control the amount of liquid you drink per day. Similar recommendations are relevant for patients with a tendency to edema and problems with cardiac activity.
4. The consumption of salty foods can be minimized or eliminated altogether. This is relevant for those who have a cyst that can cause kidney problems.