Many people know that the determination of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the blood is used for early diagnosis of pregnancy, when the test strip is not yet able to determine the result. But, in addition, the hCG test is used in the diagnosis and monitoring of gestational trophoblastic disease and germ cell tumors. This article will discuss when a doctor can prescribe this test and how to interpret the results.
Other names for the test: quantitative hCG, β-hCG, total hCG, total β-hCG, intact hCG (English: Beta hCG, Total hCG, Total beta hCG).
HCG is
a protein hormone produced in huge quantities during pregnancy and in minimal amounts by the pituitary gland (part of the brain) in non-pregnant women and men. Consists of 2 subunits - alpha and beta. The alpha subunit is the same for FSH and TSH, but the beta subunit .
Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by some tumors, and its elevated level in the blood is an indicator of malignancy and the ability to spread to other organs (metastasize).
Tumor marker
- a substance that malignant cells or the body produce in response to the presence of a tumor. Read more about various tumor markers here. Learn how to prepare for a blood test for tumor markers here.
How to take hCG for tumor markers
To test for hCG tumor markers, a blood or urine test is prescribed. For the initial study, blood is often taken from a vein, because the concentration of the substance is higher in it. A urine test may be performed for follow-up purposes.
To obtain reliable results, the test must be taken on an empty stomach. 6-8 hours before the procedure, it is important not to eat food; you can only drink a small amount of clean water. Smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs is prohibited 2 days before the test.
Before a urine test, it is recommended not to use oral or vaginal contraceptives, or to have unprotected sexual intercourse.
In rare cases, the hCG tumor marker test is used to diagnose and monitor cancer pathologies other than germ cell tumors and trophoblastic disease.
Important information: What is the normal level of the hormone prolactin during menopause in women?
Features of the analysis
As a tumor marker, it is better to use beta-hCG analysis rather than total hCG since the test systems cross-react with the alpha subunit common to three other hormones (TSH, LH and FSH). In addition, as a tumor marker, hCG is tested in the blood; in urine its sensitivity is much lower.
Preparation for donating blood is standard - fasting for 8-10 hours before visiting the laboratory, you can drink still water. Medicines do not affect the level of hCG in the blood, so they are not canceled, but only reported to the doctor about taking them.
Indications
Your doctor may order a total beta-hCG test in the following situations:
- suspicion of a germ cell tumor (the test is prescribed simultaneously with determining the level of alpha-fetoprotein);
- assessment of the prognosis of progression of oncological pathologies;
- monitoring the condition of patients during therapy for tumor diseases.
The material for research can be blood serum, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, pleural fluid, ascitic fluid. The acceptable level of hCG concentration in any biological fluids is the range from 0 to 5 mU/ml.
Trophoblast tumors
Trophoblast -
the name of a special group of cells from which the membranes of the embryo develop - chorionic villi and subsequently the placenta. Normal trophoblast for full maturation of the fetus reduces the reactivity of the immune system by producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). During pregnancy, increased or decreased levels of hCG indicate diseases in the fetus - Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, frozen pregnancy, placental insufficiency.
For trophoblast tumors (trophoblastic disease)
its cells divide very actively and uncontrollably, which disrupts the course of pregnancy and the formation of the fetus. Several diseases are included in the group of trophoblast tumors.
Types of trophoblast tumors
- Hydatidiform mole (complete or partial)
- an abnormal development of pregnancy, when after fertilization the embryo does not grow, but only the mass of chorionic villi (from which the placenta should later appear) increases in the form of bunches of grapes filled with fluid, can transform into choriocarcinoma - invasive hydatidiform mole - this type of cancer grows into the muscular layer of the uterus and metastasizes
- chorionic carcinoma (chorionepithelioma) - malignant cancer from cells of the same hydatidiform mole, appears after hydatidiform mole, normal abortion and childbirth
- chorionic carcinoma in combination with teratoma or embryonal cancer - occurs in both women and men
- malignant trophoblastic teratoma
- trophoblastic tumor of the placental site - a benign tumor, occurs in non-pregnant women, the level of prolactin is higher than human chorionic gonadotropin
When should the analysis be carried out?
- menstrual irregularities, non-cyclic bleeding, uterine bleeding
- after a normal abortion - have all the masses been removed from the uterine cavity?
- during pregnancy - the size of the uterus does not correspond to (exceeds) the gestational age, suspicious findings on ultrasound of the uterus (“snow storm”), pain in the pelvis, bleeding from the genitals during pregnancy, after childbirth
- outside of pregnancy - neoplasm in the ovarian area
- in men - an increase in testicular size, palpable enlargement in the testicular area, enlargement of the groin lymph nodes
When is the study scheduled?
A quantitative hCG test may be ordered if gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) or germ cell tumor is suspected.
Signs and symptoms of TTH may include:
- Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.
- Fatigue associated with anemia (if blood loss is significant).
- Abdominal enlargement does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia in early pregnancy.
- Nausea or vomiting, the severity of which does not correspond to a normal pregnancy.
- A positive pregnancy test (high-quality hCG), but the fetus is not detected on ultrasound.
- A uterus that remains enlarged after childbirth.
The clinical manifestations of germ cell tumors in women and men are similar to those of ovarian and testicular cancer, respectively. If one of these cancers is diagnosed and hCG is initially elevated, it will be measured in the blood at regular intervals to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect relapse.
Normal hCG level in blood
The hCG norm as a tumor marker differs significantly from the norm during pregnancy:
- men - 0-5 (sometimes up to 10) IU/l
- non-pregnant women - 0-5 (sometimes up to 10) IU/l
- gray zone - 10-20 IU/l - for some manufacturers of laboratory test systems, the analysis should be repeated after 4 weeks
Remember that each laboratory, or rather laboratory equipment and reagents, has its own standards. In the laboratory test form they appear in the column - reference values or norm.
HCG analysis, what it can show
- 1 HCG, role in the body and the essence of the analysis
- 2, pregnancy test, Live Healthy program
- 3 Urine test for β-hCG, home pregnancy test
- 4, 1 - 37 weeks of pregnancy
- 5 Blood test for β-hCG in early pregnancy
- 6 What can an ultrasound show during pregnancy?
- 7 β-hCG analysis, indicators by week of pregnancy, normal
- 8, first trimester of pregnancy
- 9 Norm β-hCG in non-pregnant women and men
- 10 reasons why a man needs a pregnancy test, Live healthy
- 11 Reasons for increased β-hCG in non-pregnant women and men
- 12 Reasons for increased levels of β-hCG in the blood in pregnant women
- 13 Decrease in β-hCG levels in pregnant women
- 14 Dangerous decrease in the level of β-hCG in the blood in pregnant women
- 15 False-negative β-hCG test results
- 16, ectopic pregnancy, dangerous symptoms, Live healthy
- 17 Use of β-hCG as a marker
- 18 Indications for β-hCG control marker
- 19 Procedure for donating blood for β-hCG analysis
- 20 Site navigator
The hCG test determines the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood serum or urine. The hCG hormone regulates hormonal processes in a woman’s body during pregnancy. And a blood test for hCG is used in oncology as a marker of tumor processes for diagnosis. It is prescribed not only to women, but also to men.
HCG, role in the body and the essence of the analysis
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG and β-hCG) is a specific pregnancy hormone.
- Produced in a woman's body during pregnancy.
- The hormone accelerates the production of progesterone and estrogen in a woman in the first weeks of pregnancy, stimulates the development of the placenta, and prepares the mother’s immunity to accept the fetus.
- In the fetus, it affects the functioning of the gonads and adrenal glands, stimulates the cells that produce testosterone in male embryos.
- The dynamics of growth in the concentration of β-hCG in the blood during pregnancy reveals important features of the development of the fetus and the condition of the mother.
- But it is important to know that human chorionic gonadotropin is produced in the body during cancer, both in women and men.
- Therefore, a blood test for β-hCG is used to diagnose some cancers, as a tumor marker.
Urine test for β-hCG, home pregnancy test
According to statistics, more than 70% of women find out about their pregnancy by undergoing a rapid β-hCG test.
- It determines a significant increase in the level of this hormone in the urine.
- This allows you to diagnose pregnancy already on the 1st–2nd day of missed menstruation.
- But due to individual differences in the rate of β-hCG synthesis in women, it is better to conduct the study no earlier than a 3-5 day delay in menstruation, in order to avoid false positive results.
- If in doubt, the test should be repeated twice at intervals of 2-3 days.
- Around the fourth to fifth weeks of pregnancy, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin reaches such values that make it possible to diagnose it in urine in a qualitative way.
- The concentration of β-hCG in urine, which is determined by home pregnancy tests, reaches diagnostic levels 1-2 days later than in serum.
Blood test for β-hCG in early pregnancy
- For a more accurate diagnosis, doctors recommend a blood test for β-hCG.
- The level of β-hCG in the blood already on the 6th–8th day after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy.
- Blood test values for β-hCG on days 7–10 after conception will exceed 25 U/ml.
- Every 2 days the volume of this hormone increases 2 times.
- A β-hCG blood test can confirm pregnancy.
- Check the gestational age.
- Or the analysis will show the absence of pregnancy.
What can an ultrasound show during pregnancy?
- A positive blood test for β-hCG does not always mean pregnancy.
- Therefore, it is also necessary to do an ultrasound examination, ultrasound, in order to:
- confirm pregnancy
- see the location of the fetus,
- determine multiple births,
- exclude ectopic pregnancy.
- If an ultrasound shows no pregnancy, but the blood test for β-hCG continues to rise, this is an alarming symptom that indicates the development of a tumor of the ovaries, liver or some other formations.
- In this case, an oncology examination is required.
β-hCG analysis, indicators by week of pregnancy, normal
- The range of human chorionic gonadotropin levels depends on the week of pregnancy.
The result of a blood test for β-hCG is considered normal if, during the pregnancy period from conception, by week, the following data are present:
- in the second week – 50-300 U/l;
- in the third week – 1500-5000 U/l;
- in the fourth week – 10,000-30,000 U/l;
- at weeks 6-11 – 20,000 – more than 225,000 U/l.
- at the 12th week – 19,000-135,000 U/l.
- at the 13th week – 18,000-110,000 U/l.
- at the 14th week – 14,000-80,000 U/l.
- at the 15th week – 12,000-68,000 U/l.
- at the 16th week – 10,000-58,000 U/l.
- at the 17-18th week – 8,000-57,000 U/l.
- at the 19th week – 7000-49,000 U/l.
- at 20-28 weeks – 1600-49 000 U/l.
Values from 5 to 25 U/l. do not allow you to confirm or refute pregnancy and require re-examination after 2 days.
Norm β-hCG in non-pregnant women and men
- Minor levels of the hCG hormone are present in the blood of men and non-pregnant women.
- Normally it is less than 5 U/ml.
- To determine the completeness of the abortion, a β-hCG test is performed 1-2 days after surgery to exclude a false positive result.
Reasons for increased β-hCG in non-pregnant women and men
An increase in blood test values for β-hCG of more than 5 U/ml. may occur in both men and non-pregnant women. In women, in case of abortion, a blood test should be carried out within 4-5 days after the abortion. The reasons for increased levels of β-hCG in the blood may be:
- Neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract, including colon and rectal cancer.
- Neoplasms of the lungs, kidneys, uterus, etc.
- Taking hCG drugs.
- Hydatidiform mole, relapse of hydatidiform mole.
- Seminoma.
- Testicular teratoma.
- Chorionic carcinoma, recurrence of chorionic carcinoma.
- The results of analysis for β-hCG, as a marker of tumor processes, should be taken with caution.
- Be sure to compare it with the results of other types of examination.
- The data can in no way be considered as absolute evidence of the presence or absence of diseases.
Reasons for increased levels of β-hCG in the blood in pregnant women
The cause of increased β-hCG levels may be:
- Multiple pregnancy. Indicators increase in proportion to the number of fruits.
- Discrepancy between the actual and established gestational age.
- Taking synthetic gestagens.
- Prolonged pregnancy.
- Early toxicosis of pregnant women, gestosis.
- Diabetes mellitus in the mother.
- Chromosomal pathology of the fetus. Most often with Down syndrome, multiple fetal malformations, etc.
Decrease in β-hCG levels in pregnant women
- Alarming decreases in β-hCG hormone levels if:
- Inconsistency with the gestational age.
- An extremely slow increase or no increase in hormone concentration.
Dangerous decrease in the level of β-hCG in the blood in pregnant women
A dangerous decrease in the concentration of the hormone β-hCG by more than 50% of normal:
- with ectopic pregnancy,
- prenatal fetal death in 2-3 trimesters,
- true post-term pregnancy,
- non-developing pregnancy,
- threat of miscarriage,
- chronic placental insufficiency.
False-negative β-hCG test results
In case of pregnancy confirmed by other methods, false negative results of a blood test for β-hCG can be:
- if the test is done too early,
- with an ectopic pregnancy!
Use of β-hCG as a marker
In perinatal diagnosis, the β-hCG hormone marker is used:
- during prenatal control of the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy to assess the risk of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) and trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome).
Indications for β-hCG control marker
During pregnancy:
- Prenatal control of the 1st trimester of pregnancy to detect chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus in combination with the determination of PAPP-A at 8-14 weeks of pregnancy.
- Antenatal control of the 2nd trimester in combination with AFP and free estradiol between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- A special indication for the study is the age of a woman over 35 years old.
- The presence in the family of a child or a history of a fetus of an interrupted pregnancy, with genetically confirmed Down syndrome, other chromosomal diseases and congenital malformations.
- Hereditary diseases in close relatives.
- Radiation exposure or other harmful effects on one spouse before conception.
Procedure for donating blood for β-hCG analysis
- To determine the level of the hormone in laboratory conditions, venous blood is taken.
- Preparation for a blood test for beta-hCG is as follows:
- take in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- Avoid taking hormonal medications and dietary supplements, or inform your doctor before the test;
- do not exercise, do not smoke or drink alcohol the day before donating blood;
- Be sure to clarify when you need to take the test.
Decoding
Reasons for increased hCG in tumor diseases
- hydatidiform mole
- embryonal carcinoma
- polyembryoma
- dysgerminoma
- mixed germinal tumors
- testicular tumors in men - non-seminoma germinal testicular tumors 50-85%, seminomas 10-20%
- teratoma and teratoblastoma
- other types of tumors - liver cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer, intestinal cancer - hCG analysis for them has no independent diagnostic value
- cancer recurrence after treatment
Increased hCG in other diseases
- uterine fibroids - a benign tumor of the muscular layer of the uterus
- ovarian cyst - a round formation in the ovary filled with fluid
A negative hCG test result is NOT proof of the absence of cancer.
What do the results mean?
In men and non-pregnant women, hCG is usually not detected or is detected in very small quantities.
When the test is used as a tumor marker, an elevated level indicates the presence of a germ cell tumor (germ cell tumor) or gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD).
High levels occur in both GTB and normal pregnancy. However, at the beginning of a normal pregnancy, hCG increases at a constant and predictable rate, doubling approximately every 36-48 hours, and GTB is characterized by an unpredictability of its growth rate, which, in combination with ultrasound, indicates a pathological course of pregnancy, requiring intervention. HCG levels may be “excessively” high in normal pregnancies and may not show the expected decline after pregnancy or abortion.
During treatment for GTB or germ cell tumor, a drop in levels usually indicates that the disease is responding to therapy (50% decrease every 1.5 days). In turn, constant or increasing levels indicate that the pathological condition is progressing. Elevated hCG after treatment may indicate relapse of the disease.
Data
- HCG is normally produced by the germ cells of the human embryo, i.e. outside of pregnancy there is practically no hCG in the body
- the very first tumor marker, discovered in the 30s of the last century
- half-life 36 hours - rapidly decreases with successful treatment and at the same time actively increases with metastasis
- almost ideal tumor marker for choriocarcinoma - positive in 100% of cases
- During pregnancy, hCG protects the fetus from rejection by the mother's immune system
HCG tumor marker - indications, norm and interpretation was last modified: December 12th, 2020 by Maria Bodyan
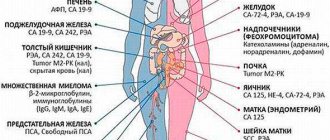
HCG tumor marker: indicators for oncology, beta, for cancer
This substance is a glycoprotein that is produced by ovarian tumor cells.
A study on the level of concentration of the tumor marker CA 125 in most cases serves as a tool for early diagnosis of a disease such as ovarian cancer, and is most effective for women in the menopausal stage.
A blood test for this tumor marker for young women is not as effective and is characterized by low sensitivity and specificity.
The analysis can also be prescribed to check the effectiveness of treatment for various types of ovarian cancer (serous, endometrial, clear cell), allows you to determine the formation of metastases or predict relapse several months in advance. The study can serve as an auxiliary tool for diagnosing breast, uterine, and pancreatic cancer.
Promotion
Under conditions of normal functioning of the human body, chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the trophoblast during pregnancy; early diagnosis of pregnancy and detection of pathologies as it develops are based on the determination of this substance.
Before talking about which tumors produce hCG, we should focus on benign pathologies, in which a slight increase in the concentration of the hormone is also possible. These conditions include:
- early puberty;
- ulcerative formations in the organs of the digestive system;
- inflammatory bowel pathologies;
- cirrhosis.
Malignant tumors that produce hCG are presented below:
- germ cell (chorionic carcinoma, ovarian cancer, testicular cancer);
- breast tumors;
- tumors of the stomach and intestines;
- liver tumors;
- pancreatic tumors;
- kidney tumors;
- small cell lung tumors.
Another dangerous condition in which the hCG tumor marker is detected in women is hydatidiform mole (molar pregnancy). It manifests itself as the degeneration of chorionic villi into vesicular structures that resemble grape bunches in appearance.
Hydatidiform mole can be complete or incomplete. A complete pregnancy occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg that does not have a nucleus. The paternal set of chromosomes doubles, but the formed zygote turns out to be non-viable, and the formation of an embryo does not occur.
An incomplete pregnancy occurs when two sperm penetrate a normal egg at the same time. The presence of three sets of chromosomes leads to the non-viability of the developing embryo.
With hydatidiform mole, the concentration of hCG increases five times compared to acceptable values. Detection of this dangerous pathology requires surgical intervention.
Analysis of CA 19-9
Testing for the substance CA 19-9 is used in most cases for the effective diagnosis of formations of the gastrointestinal tract.
As a rule, an analysis for tumor markers CA 19-9 is prescribed in combination with studies for CEA and CA 72-4, and is characterized by high sensitivity.
The concentration level of this marker must be examined if the doctor suspects the patient has diseases such as cancer of the stomach, pancreas, rectum, colon, or gall bladder.
In addition, the normal concentration of this tumor marker in the blood is checked as part of assessing the effectiveness of treatment and early diagnosis of metastases.
When is the study scheduled?
A quantitative hCG test may be ordered if gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) or germ cell tumor is suspected.
Signs and symptoms of TTH may include:
- Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.
- Fatigue associated with anemia (if blood loss is significant).
- Abdominal enlargement does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia in early pregnancy.
- Nausea or vomiting, the severity of which does not correspond to a normal pregnancy.
- A positive pregnancy test (high-quality hCG), but the fetus is not detected on ultrasound.
- A uterus that remains enlarged after childbirth.
The clinical manifestations of germ cell tumors in women and men are similar to those of ovarian and testicular cancer, respectively. If one of these cancers is diagnosed and hCG is initially elevated, it will be measured in the blood at regular intervals to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect relapse.
CA15-3 assay
The substance CA 15-3 is a specific breast tumor marker, the concentration of which in the blood increases in patients with breast cancer. The sensitivity of the study is directly determined by the stage at which the cancer is located.
The CA 15-3 assay is not as effective for early detection of breast cancer due to low sensitivity (approximately 20%).
Whereas at a later stage, the sensitivity of the study rises to 84%, which allows it to be used as a tool for monitoring breast cancer treatment and early detection of relapses.
Level up
When the level of the hCG hormone is elevated, it is quite dangerous for the condition and health of a person as a whole. A sharp change in hCG in the blood indicates the presence of cancer.
A similar phenomenon is also possible in the presence of germ cell tumors. It must be remembered that a test that was taken on time allows you to start treatment as quickly as possible.
This helps achieve higher efficiency in eliminating the disease.
Thus, quite often gonadotropin-based drugs are used to treat men. They are necessary to improve the stimulation of the gonadotropic effect. They are obtained by extraction from the urine of women. The use of therapy can achieve positive results for the following problems:
- Infertility.
- Secondary hypogonadism.
- Testicular underdevelopment.
- Undescended testicle.
When using such drugs, a man is required to undergo a special examination once a month and consult a doctor at the end of the course. Taking into account the obtained result, further dosage and the optimal course of treatment are selected.
Decreased hormone levels - negative hCG levels in men are normal. Thus, a low level of this indicator does not pose a danger.
CA 242 Analysis
The study plays a supporting role; its use in combination with the CA 19-9 test and other types of examination makes it possible to detect pancreatic, rectal and colon cancer in the early stages. Also, the results of testing the level of concentration of this substance in the patient’s body suggest a relapse within a few months.
The price of tests for tumor markers and the timing of the study depend on the specific laboratory. The transcript of the SEA study should definitely be shown to the attending physician.
Source: https://MedikTest.ru/analizy/nse-onkomarker-chto-eto-takoe.html
What diseases does it detect?
The hCG tumor marker is a specific organic substance produced by mutated cells or healthy tissues. In the latter case, it is considered the body’s response to damage to cancerous structures of the reproductive organs, digestive tract and lungs, the growth of benign tumors or certain inflammatory processes.
Oncologists are often asked about the purpose of prescribing the study of this specific substance to representatives of different sexes. In men, determination of the concentration level of the hCG marker is most often carried out in conjunction with the identification of the quantitative content of the AFP antigen. Such a study is required when signs of malignant testicular tumors appear in males.
What does the hCG tumor marker show in women? In pregnant women, a high level of this specific substance may indicate the development of a malignant tumor of the ovary, main reproductive gland, or uterus, and during pregnancy, chorionic gonadotropin helps to promptly detect fetal death, detect pathologies in its development, and assess the risk of spontaneous abortion.