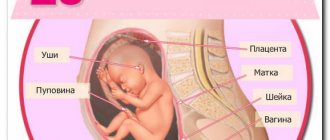
Technological progress is rushing forward at cosmic speed, affecting all areas of human activity. However, even today you can meet expectant mothers who believe that the 3D ultrasound procedure can be dangerous for the baby, like any radiation. At the same time, each of them wants to know how the baby feels, how he is developing, and whether everything is going right. A paradox that arose as a result of incorrect and narrow-minded ideas about the latest technologies in the field of ultrasound examination of the fetus, so-called myths, which we will try to dispel in this article.
How is it that Down syndrome is not visible on ultrasound?
The diagnosis of Down syndrome or other chromosomal disease in a fetus cannot be made using ultrasound. When conducting diagnostics, doctors assess the condition of the fetus according to a number of parameters in accordance with the approved research protocol. For example, the size of the fetal cervical fold is assessed.
Then a special computer program uses these parameters to calculate the probable risk that the child may be sick.
If the risk is higher than 1:360, it is considered high, in which case the woman is invited to a consultation at a medical genetic center to carry out a clarifying diagnosis.
Unfortunately, the body does not always respond to disease by changing certain signs. This is nature, the peculiarities of the development of the organism. Like with the flu - in the classic version there should always be a temperature, but in some cases there may not be one, and the person is sick.
Therefore, ultrasonic signs are called indirect. This is not a diagnosis yet, but an assumption that a woman has a certain risk of a chromosomal disease in the fetus.
Today , the probability that a pregnant woman with a fetus with Down syndrome will be at risk based on an ultrasound scan in the 1st trimester is about 70% . This does not depend on the specialist or ultrasound machine - this is how nature orders.
Requirements for conducting the study
In a normal pregnancy, it is recommended to do 3 ultrasound examinations of the fetus:
- at 11–14 weeks,
- at 15–20 weeks,
- at 30–36 weeks.
At any time, starting from the eleventh week, Down syndrome can be detected by ultrasound in the fetus. In the first trimester, this is indicated by indirect signs, in the second – indirect and objective. In the third trimester, the diagnosis is almost 100% reliable, but medical termination of pregnancy is not performed after the 22nd week. A woman has a choice: artificial childbirth or physiological.
The exact timing of the screening will be determined by your obstetrician-gynecologist. Since the method is absolutely harmless, ultrasound can be done as prescribed by a doctor an unlimited number of times.
To obtain reliable results and correct data, contact experienced specialists who use modern equipment.
To make the image of the fetus three-dimensional, 2D, 3D, 4D ultrasound is used. The better your research, the lower the risk of bias.
What about the blood test that women take at 12 weeks?
Biochemical analysis also helps doctors diagnose chromosomal disorders. The level of certain proteins is examined, which may change if the child is sick. But again, a diagnosis is not made, the probability of possible diseases is calculated.
It is important to understand that all these studies must be completed at 10–13 weeks of pregnancy. At a later stage, measurement of the cervical fold and biochemical markers of the 1st trimester are not very informative.
The studies we are talking about are part of the prenatal screening program, which has been carried out in our country since the 90s. All pregnant women undergo an ultrasound scan of the fetus three times during pregnancy; if any abnormalities in the development of the fetus are detected - a malformation or a risk for a chromosomal disease, a clarifying diagnosis is prescribed.
How to prepare for a 4D ultrasound
A pregnant woman does not need to prepare for a 4D ultrasound in any special way. Usually the doctor prescribes the same actions that are required to prepare the body for the classic type of ultrasound:
- a couple of days before the study, you need to avoid foods that cause increased gas formation, as this may interfere with examining the fetus;
- it is better not to have dinner the day before the ultrasound;
- Half an hour before the procedure, it is advisable to drink a couple of glasses of water so that the fetus is better visualized.
Don't forget to take with you:
- exchange card;
- a diaper - to lay on the couch;
- wet wipes - to later wipe off the gel applied to the skin.
A pregnant woman’s exchange card is the main document that you should always keep with you
If a woman is at risk, what should she do?
If the risk according to the results of ultrasound and biochemical studies is high, we suggest coming for a consultation with a geneticist.
According to the results of studies of the 1st trimester, an average of 4% of women are at risk.
We offer them invasive procedures, such as amniocentesis, where amniotic fluid is taken for examination. Thus, we obtain cells in which we examine the set of fetal chromosomes and can give an answer whether the child has a chromosomal disease or not.
Tests must be monitored in advance - blood and urine tests, a smear is taken, if there are contraindications, amniocentesis is not prescribed or is carried out after treatment and repeated control of tests. The procedure for collecting amniotic fluid is done under ultrasound guidance. After the procedure, the woman has the opportunity to lie down and relax.
Ultrasound during the perinatal period
Examination of a pregnant woman using ultrasound is one of the mandatory aspects of perinatal screening. If the process of bearing a child is uneventful, an ultrasound scan is performed once in each trimester. In case of complicated pregnancy, the doctor prescribes additional ultrasound procedures. Ultrasound waves are safe for the baby and mother, so the study has no restrictions on the frequency of sessions.
Diagnosis is carried out abdominally (externally), without causing any discomfort to the woman or fetus.
Types of ultrasound
Scanning can be done in several ways:
Can an ultrasound fail to see twins?
- 2-D ultrasound is a black and white image; only a medical specialist (ultrasound doctor) can decode a flat image;
- 3-D ultrasound – data received from the sensor is processed by a computer program, and a three-dimensional image of the embryo is projected onto the monitor;
- 4-D method - the child is displayed on the screen in a three-dimensional projection, while you can observe his movements in the womb.
In the last two options, the procedure takes a longer period of time. At the request of the parents, the doctor can print out a photo of the baby. In order to prevent serious health problems for the mother and child, it is strictly prohibited to ignore ultrasound examination during the perinatal period.
Diagnosis of the first trimester
During the first ultrasound, performed from 10 to 14 weeks, the doctor evaluates fetometry (the overall size of the child), its position in the womb and the nature of the pregnancy. To identify downism, certain markers (normative indicators) are used, with which the real picture of the study is compared.
The main defining markers include:
- TVP (thickness size of the collar space). The standard indicator for the amount of fluid under the skin of the embryo in the neck area should not exceed 2.7 mm. In Down syndrome, TVP is markedly increased;
- upper jaw size. An ultrasound clearly shows the baby’s shortened upper jaw, which is a characteristic sign of downism;
- anatomical structure of the outer part of the ears. Underdeveloped ears are grounds for suspicion of a genomic abnormality;
- HR (rhythm or heart rate);
- absence of the main nasal bone. Downs tend to have a flattened face shape. This sign indicates the presence of pathology.
The following indicators are considered normal for a child in the first trimester:
| age | beats/minute |
| 5 weeks | 100 |
| 10 weeks | 170 |
| 14 weeks | 155 |
Tachycardia (increased heart rate) is not one of the main signs of the syndrome, but may be indirect. An experienced doctor will not ignore this indicator. According to medical data, the accuracy of determining Down syndrome during the initial examination is about 90%.
Symptom of downism (absence of nasal bone) on a 2-D ultrasound image
Second trimester scan
Determination of downism in the second trimester of pregnancy is carried out according to the following indicators:
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the nasal bones. The nose is not visible on the monitor screen, since its size does not exceed 2.5–3 mm;
- heart disease. Children with autosomal syndrome suffer from heart pathologies in more than half of the cases;
- non-compliance with the normal size of the femur, ilium and humerus bones in length. In the image, these indicators are significantly underestimated.
In addition, the doctor may see a violation of the functionality and size of other internal organs. The genetic anomaly is characterized by changes in: brain structures (hypoplasia of the cerebellum, frontal lobes), bladder (increase in organ size).
Is it possible to detect Down syndrome with 100% certainty using ultrasound? Yes, it is possible, but only in the third trimester, when visual signs become absolute. The decision to terminate a pregnancy through induced labor or to give birth to an unhealthy child rests with the parents. The doctor can only give advice, but not insist on any position.
Many people are afraid of such procedures as fire. Why?
The risk of miscarriage after amniocentesis is believed to be about 1%, which is why many people are afraid to do this test. In fact, there is a risk of pregnancy loss for a variety of reasons in any pregnancy. Therefore , if the likelihood of the fetus having a genetic disease is high, we believe that this procedure is justified.
According to the results of amniocentesis, of those who fall into the risk group, the diagnosis is confirmed on average in one out of 9 women.
Sometimes couples refuse an invasive procedure - for various reasons. Of course, such parents are more likely to have children with genetic disorders.
What is 4D ultrasound and when is it prescribed during pregnancy?
With the classic type of ultrasound, a flat image is displayed on the monitor - a projection of the internal organs onto a plane. 3D ultrasound gives a three-dimensional image, and 4D ultrasound allows you to demonstrate a video - in real time you can see all the movements of the child, examine his facial features, and assess his condition.
4D ultrasound allows you to see not a flat image of the baby, but a three-dimensional video
Of course, parents are delighted with the opportunity to receive the first video recording of the child even before his birth. But not every ultrasound makes sense to conduct in this format. It is considered optimal to do a 4D ultrasound at a period of 20–27 weeks .
At earlier stages, the fetus has not yet formed subcutaneous fatty tissue that can “reflect” directional sound, so only bones and internal organs can be seen, which sharply reduces the information content of the study; in addition, this type of child can frighten the expectant mother.
And towards the end of pregnancy, the child is already too large to “fit” entirely into the monitor, in addition, his mobility is limited due to his size. Since this study is usually done for the sake of a beautiful picture and video, it is better to choose the time when the baby’s image will be the best and his movements will be freer.
Usually, expectant mothers go for a 4D ultrasound of their own free will, but sometimes this also happens on the direction of a doctor. Indications for which this type of study may be prescribed:
- multiple pregnancy;
- surrogacy;
- pregnancy as a result of artificial insemination;
- suspicion of complications in fetal development;
- risk of hereditary pathologies.
The reason why 4D ultrasound is more informative than its predecessors is simple - in real time you can examine the fetus from all sides, try to assess its condition by its facial expression, evaluate its motor activity, that is, obtain additional information.
However, doctors have still not come to a consensus regarding the benefits of such a study - many of them believe that a classic ultrasound is quite sufficient to assess the baby’s condition. Therefore, there is no unambiguous list of indications for which it is necessary to undergo a 4D ultrasound - the doctor can refer the patient to this procedure if he thinks that this type of study will provide more information .
4D ultrasound is a fairly new study that requires certain technical equipment in medical institutions and sufficient skills among doctors. Not all clinics are able to perform this procedure due to lack of necessary equipment. Another obstacle for young parents on the path to the desired result can be the price - its cost starts from 2 thousand.
Video: 4D ultrasound during pregnancy
Is it possible to do without collecting amniotic fluid?
For those who are afraid of amniocentesis, today there is a DOT test - a study of fetal DNA that is in the mother's bloodstream. This test is designed to detect several of the most common chromosomal diseases.
If the test determines that the fetus has an abnormality, it is usually suggested to confirm this result with an invasive procedure. If the test shows normal, the result is not rechecked.
We do not offer such tests, because they are not yet carried out in Belarus. If future parents want to undergo such a study, they themselves make a decision about this and contact a private center or laboratory.
Benefits of 3D Ultrasound
Three-dimensional sonography during pregnancy is characterized by the following undeniable advantages:
- The resulting three-dimensional image makes it possible to better examine some areas and structures that were inaccessible or difficult to access in two-dimensional mode. It is much easier for parents and doctors of other specializations to understand the image.
- Three-dimensional sonography during pregnancy provides valuable additional information that is indispensable for the diagnosis of external malformations. 3D research can dispel all doubts. The expectant mother and the doctor can count all the baby’s fingers and make sure there are no other external defects. Thanks to this type of ultrasound, doctors can evaluate different parts of the fetal body in three projections, which is important in terms of identifying developmental anomalies. The data obtained provide information for diagnosing defects of the spinal column and limbs.
- 3D scanning allows you to see the child’s facial expressions, so parents can understand whether he is upset or smiling. Bad emotions in the fetus can occur due to problems such as insufficient oxygen supply, improper development of internal organs, causing pain.
- The intensity, power, and frequency of the wave are within the same limits as in a normal study.
- 3D ultrasound examination during pregnancy helps to reconstruct the structure of the brain. This allows you to completely eliminate the development of abnormalities of the central nervous system.
- Volumetric sonography helps diagnose congenital heart defects in the fetus. Recently, it is considered a common intrauterine anomaly that can cause death in the newborn. With a standard study, such a diagnosis is very difficult and can only be carried out by a very highly qualified specialist. 3D diagnostics makes the result independent of the doctor’s training and skills, therefore it is an effective and reliable procedure.
- Three-dimensional scanning during pregnancy helps to exclude the presence of fetal facial anomalies, for example, “cleft lip”, “cleft palate”.
In what cases is it better to terminate a pregnancy?
We do not so much recommend terminating the pregnancy as we explain to the family why a particular disease is dangerous, how it manifests itself, what treatment options are available, and then the family makes their own decision.
If, for example, a heart defect is detected, the family can consult a cardiac surgeon and find out all possible treatment options.
Chromosomal diseases are almost always accompanied by mental retardation. Therefore, here the spouses must decide for themselves whether they are ready to make efforts to rehabilitate the child or whether this is unacceptable for them.
As a rule, if a child is diagnosed with a serious illness that has no effective treatment methods, the family decides to terminate the pregnancy.
The situation is the same with Down syndrome, although sometimes parents, despite the diagnosis, refuse to interrupt.
There have been cases when women even continued pregnancy with a fetus whose defects were incompatible with life.
It is important to make a decision before 22 weeks of pregnancy. Starting from 22 weeks, the child is already considered viable. It is impossible to induce artificial birth in such cases - not only will the child have a developmental defect, but he will also be severely premature.
Second trimester scan
From the 14th week the second trimester begins. Before the 20th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother must attend a second ultrasound to exclude signs of Down syndrome in the fetus. The doctor evaluates:
- compliance of the development of the skeleton and organs with the period;
- size and structure of internal organs.
At this time, you can see heart defects, bladder enlargement, brain abnormalities and other pathologies.
Doctors analyze 3 blood parameters:
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- alpha-fetoprotein;
- free estriol.
If there are deviations, the pregnant woman may be referred to a specialized center to clarify the diagnosis.
An ultrasound monitor shows a fetus with Down syndrome at 24 weeks:
Does it make sense for older parents to be examined in advance?
Conventionally, the threshold age for chromosomal diseases in women is considered to be 35 years, when the risk begins to increase relatively quickly. This does not mean that all women over 35 will necessarily have a child with a genetic disease, but the likelihood is higher.
Men also have their own risks due to genetic changes, usually we are talking about the age over 45-50 years.
However, there is no point in undergoing any tests before planning a pregnancy.
Most of the time the changes I'm talking about are random. They occur in the reproductive cell of one of the parents at the time of conception and are in no way related to lifestyle or heredity.
If there is any hereditary disease in the family, it is worth consulting a geneticist when planning a pregnancy to determine whether future parents need laboratory testing and whether additional testing will be needed during pregnancy.
Causes and consequences of deviations from the norm
The reasons for the deviation of fetal parameters from the norm can only be determined by a doctor. For this, the expectant mother is sent for additional examinations, because an increase or decrease in the value of any indicator can be either a characteristic feature of this child or a consequence of a long series of problems.
Deviations in biparental size:
- above normal: hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain;
- macrocephaly is a congenital disorder of skeletal development;
- diabetes mellitus in pregnancy;
- developmental disorder of the spine;
Deviations of fronto-occipital size:
- more than normal: volumetric formations of the brain or skull bones;
- cerebral hernias;
- hydrocephalus;
- underdevelopment or absence of anatomical structures of the brain.
Causes of insufficient nasal bone length:
- genetic abnormalities;
- toxic effects on the fetus in the early stages;
- infectious diseases;
- physical injuries to the abdomen;
- heatstroke.
Possible consequences of insufficient amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios):
- fetal hypoxia;
- fusion of tissues of the developing fetus and membranes;
- abnormal development of fetal limbs.
Possible consequences of excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios):
- dysfunction of the placenta;
- disruption of the development of the nervous and digestive systems of the fetus;
- infectious diseases;
- premature birth.
Why is everyone afraid of Down syndrome?
Down syndrome remains the most common chromosomal disorder in humans. If diagnosis is not made during pregnancy, the incidence of such children is 1 in 800, 1 in 1000 births.
The disorder is caused by additional material on chromosome 21. There are other chromosomal diseases caused by changes in 13, 18 and other chromosomes, but they are much less common.
After birth, all children in Belarus also undergo a genetic test to exclude phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism. These are also serious genetic diseases, but if you start treating them on time, there will be practically no manifestations.
https://rebenok.by/
Approximate cost of ultrasound examination
How much does a 3D ultrasound cost? The price for a three-dimensional examination depends on factors such as the level of qualification of the gynecologist, the purpose of the examination, the quality of the equipment, and the urgency of the procedure. This all forms the final cost of diagnosis. Most modern medical centers conduct three-dimensional ultrasound scanning using high-precision and modern expert-class equipment.
| Name of the clinic, Moscow | Cost of 3D ultrasound, rub. |
| Dr. Bormenthal | 3500 |
| Enel clinic | 3500 |
| Dobromed | 3600 |
| First Doctor | 2600 |
| Euromed | 3500 |
Note: The data presented were obtained by random analysis of prices of medical centers in Moscow. The information is provided for informational purposes only and is not of an advertising nature. The data may be out of date at the time of viewing.
What is the difference between ultrasound and 3D ultrasound?
Three-dimensional diagnostics, like conventional research, uses the ability of ultrasonic waves to penetrate body tissues that have different structures and densities. The two-dimensional image is understandable to the doctor, without being of particular interest to the parents.
The term "3D" refers to the number of dimensions in which an image is transmitted - depth, width, height. A three-dimensional study allows you to see a three-dimensional image of a child in color by examining a tiny face. The photograph of the examination will remain as a keepsake as evidence of the first meeting with the baby. The method will not replace conventional ultrasound diagnostics. Volumetric scanning determines the external structure of the fetus, while internal pathologies are determined by the usual method.
What three-dimensional diagnostics shows, features of the method
It must be said that the three-dimensional method of examining a baby makes it possible to see all the existing pathologies that ultrasound can detect. If an ultrasound is done at the tenth week, it is possible to determine the heartbeat, assess the formation of vital organs, and see developmental problems that require medical termination of pregnancy.
For a period of twenty weeks or more, it is the 3D ultrasound that describes pregnancy as informatively as possible, determines all sorts of problems and developmental features, as well as the gender of the unborn child (if he has not turned his back outward). In addition, at the same time, amniotic fluid is assessed and the cervix is examined. If a woman undergoes an examination at the thirty-second week, then the scan provides the most complete information about the presentation of the fetus, whether there are any infections, and about the general condition of the child.
As for the diagnostic features, you need to keep in mind that in terms of information content and quality of examination for the doctor, there is practically no difference between a conventional ultrasound and 3D. The modern improved examination is better only in the number of available image planes and the clarity of the resulting images to the baby’s parents. In addition, this examination is noticeably more expensive than a conventional ultrasound and costs about three thousand rubles. In addition, you will have to pay for recording the received images on any media or printing them.
How often is it done, is it harmful to the fetus?
No negative effects of three-dimensional ultrasound examination were found.
The only thing that experts warn about is that any external impact on the fetus in the womb may have consequences in the future. No one can give a 100% guarantee that ultrasound is safe, because there have been no experiments on people. During the procedure, slight heating of the tissue occurs, which does not affect the condition of the expectant mother and fetus. The number of necessary appointments is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the course of pregnancy and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
A huge advantage of 3D ultrasound in the second trimester is that you can thoroughly examine the internal organs of the child and prevent or identify possible deviations, draw up a treatment plan, and determine the process of childbirth.
How is the diagnosis done?
In general, the examination is carried out in exactly the same way as a traditional ultrasound. The only difference is the time required to obtain all the data. With the usual method, all actions take an average of half an hour. 3D diagnostics can take about an hour, or even more . At the same time, the risks of negative effects on the baby do not increase, because the time increases due to the processing of the received acoustic information and its visualization, and not due to the impact on the pregnant woman.
The quality of the information obtained depends on the position of the baby, the amount of water, whether the mother has scars or morphological defects in the pelvic area, and the volume of the woman’s fat layer. All this makes it difficult for ultrasound to access the child.
The examination process is quite familiar: a woman lies down on a couch, the doctor applies a special conductive composition to her stomach and uses a sensor to carry out the procedure, and then removes the remaining gel from the skin. Future parents can ask the doctor to write down the pictures taken for them or print them out on paper.
How much does it cost and where is it made?
4D ultrasound is rarely prescribed in clinics; the initiative to undergo such a procedure most often belongs to parents and is currently available only in large cities of our country. Perinatal and diagnostic regional centers, as well as large private clinics, provide the service of four-dimensional computer ultrasound for 3500-5000 rubles.
Most commercial medical institutions additionally offer:
- video disc;
- printout of the baby's photo;
- a plaster cast of the baby’s face according to the parameters from the monitor.
Contraindications and harm
The radiation indicators of ultrasonic waves are always the same for any ultrasound. Conducting a 3D scan is harmless and harmless to the fetus. In medical practice, there have been no cases in which there was a negative effect of ultrasound on intrauterine development or the condition of the unborn child.
Approximately 1.5% of ultrasound examination time is spent on diagnostics in three dimensions. The rest of the time is spent processing incoming information.
An ultrasound is performed according to indications, often within the period specified by the gynecologist. It is believed that a pregnant woman undergoes three screenings as planned.