At 30 weeks of pregnancy, a woman already fully feels her position. The uterus has reached a large size and is pushing the stomach and diaphragm and lungs upward. As a result, the pregnant woman experiences heartburn and shortness of breath. Now it becomes difficult for a woman to do even ordinary household chores. And it’s not for nothing that she has been granted maternity leave since this period. She will soon be scheduled for a routine ultrasound examination in the third trimester. Let's figure out what a 30-week ultrasound can tell you.
Target ultrasound at 30-31
An ultrasound scan in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is a mandatory examination for all pregnant women. It is part of the 3rd trimester screening. During a normal period of gestation, this is the last study. It sums up all three screenings. Based on the results of this ultrasound examination, a conclusion is formed about the condition and development of the fetus for childbirth, and delivery tactics are determined. A woman may refuse to undergo the examination, but she must be warned of all the consequences of her decision.
The third planned ultrasound examination is carried out at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy. The objectives of this study are:
- Detection of anomalies and features of fetal development that were not identified during the first two screenings. These may be pathologies that can only be determined at a later stage, or the detection of developmental anomalies occurred with questionable or good results from past studies.
- Identification of complications during pregnancy, both in the presence of complaints in the pregnant woman and in their absence.
- Carrying out Doppler measurements as indicated. An assessment of uteroplacental blood flow is necessary only if the doctor suspects a disturbance in it.
- Assessment of the characteristics of the fetus and maternal reproductive organs in order to determine delivery tactics. The parameters that influence this choice are the size of the baby, the condition of the postoperative scar on the uterus, the position of the fetus, and others.
Height and weight standards
As already mentioned, it is by the seventh month of pregnancy that data on the baby’s height and weight become indicative. It is impossible to track them until the eighth week, so doctors do not undertake to make any predictions. As you know, they are registered after the 12th week, having recorded the first ultrasound readings. But this moment is already far behind us. Now your baby is very big, based on the results of the third ultrasound, doctors make a diagnosis: “30 weeks of pregnancy.” The weight of the fetus at this time is usually about 1300 g. This is an average figure, and if the doctor does not see anything wrong with minor deviations, then you should not worry. The baby’s height is already more than thirty centimeters, that is, over the last two months he will have to not only gain two kilograms, but also grow by 10-15 cm. The task is not an easy one.
What is an ultrasound at 30-34
In the third trimester of pregnancy, ultrasound is performed transabdominally. The woman lies on her back. A sensor using a special gel moves across the abdomen. Ultrasound passes through the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall to the fetus and reproductive organs of the mother and is partially reflected from them. As a result, on the monitor screen the doctor sees the black and white image necessary for the assessment. In case of severe inferior vena cava syndrome, when, due to compression of large vessels by the uterus, while on her back, the pregnant woman becomes ill and loses consciousness, the examination is allowed in the lateral position.
To make the ultrasound diagnostic procedure easier, a woman can empty her bladder. No special preparation is required for the study. However, if it is necessary to measure the thickness of the postoperative scar on the uterus, the bladder must be filled. To do this, you need to drink 0.5-1 liter of liquid in 30-60 minutes.
Training contractions: what are they?
The 30th week of pregnancy is a fairly long period during which a woman has already become familiar with the so-called false contractions. Now the fetus has already dropped and the body is actively preparing for the birth process. False or training contractions, as a rule, do not pose a threat to the mother and fetus. They differ from the true ones in the absence of an increase in intensity and regularity.
If a girl feels cramping pain, she should accurately calculate the interval between them. With false contractions, the painful sensations go away on their own. If the pain increases and the interval between them decreases, the woman should immediately go to the hospital.
Read more about false and true contractions in our article.
Evaluation indicators
When performing an ultrasound examination, the motor activity and heart rate of the baby are assessed. Normally, the fetal heart beats 120-160 times per minute. A significant increase or decrease in heart rate is a poor prognostic sign and requires urgent hospitalization and a decision on delivery.
The dimensions of the fetus obtained by ultrasound at 30 weeks of gestation must correspond to the following values:
- biparietal head size –71-85 mm;
- fronto-occipital head size – 89-105 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 239-290 mm;
- head circumference – 265-305 mm;
- thigh length – 52-62 mm.
The weight of the fetus according to ultrasound at 30 weeks is about 1300 grams.
Ultrasound norms 31 weeks of pregnancy:
- biparietal head size – 73-87 mm;
- fronto-occipital size of the head – 93-109 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 247-301 mm;
- head circumference –273-315 mm;
- thigh length –54-64 mm.
When performing an ultrasound at 31 weeks of pregnancy, the approximate weight of the fetus is calculated as 1500 grams.
The obtained fetal size values are compared with standard values. They must correspond to the duration of pregnancy. However, these values are very variable. The assessment must be made taking into account the constitutional characteristics of the baby’s parents.
When the size of the fetus decreases by 2 weeks or more, they speak of intrauterine growth restriction. At 30-31 weeks it is most often asymmetrical, i.e. there is a lag only in the size of the abdominal circumference. This is often due to the existence of fetoplacental insufficiency. At an earlier age, a symmetrical form of fetal growth restriction begins to develop, the causes of which are most often chromosomal abnormalities and intrauterine infections.
Number of movements
It is important at this time to count the baby’s movements during his period of activity. It is better to learn from your doctor how to calculate correctly. If the movements are rare or disturbing to the pregnant woman, then you should immediately inform your gynecologist about this.
What complications can be identified?
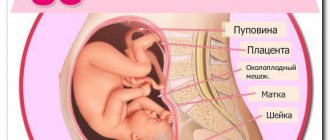
Using ultrasound of the placenta, the location of the placenta, its thickness and features are determined. Low placentation and placenta previa are fraught with an increased risk of placental abruption with the development of life-threatening bleeding. Thickening of the placenta occurs with Rh conflict, intrauterine infection and other reasons. Hyperechoic inclusions are often detected on ultrasound. They represent areas of calcification in the placenta and are signs of natural degenerative processes. However, their detection before 34 weeks should be the reason for Doppler testing to assess uteroplacental blood flow.
Describe the course of the umbilical cord and its structure. Normally, it contains three vessels: two arteries and one vein. If a single umbilical cord artery or entanglement of the umbilical cord is detected, additional Doppler examination is necessary.
The amount of amniotic fluid is determined. Oligohydramnios occurs when renal function is impaired, placental insufficiency, or premature rupture of amniotic fluid. Polyhydramnios occurs with infection, gestosis, and diabetes.
Child development during this period
By this time the baby’s height reaches 40 cm, and he should weigh from 1.5 to 1.8 kg. The body is still thin, fragile, and subcutaneous fat is forming. A protective lubricant forms on it, and the original fluff - lanugo - begins to gradually disappear. By birth, most babies no longer have it, but some children completely lose it only by the second month of life.
The genitals of the fetus are already fully formed, so by this time the future parents already know the sex of the child.
The baby's heart beats rhythmically and quickly: the heart rate ranges from 120 to 170 beats per minute. Surfactant begins to form in the lungs - a mixture of surfactants that lines the alveoli and prevents them from sticking together.
The brain grows and actively develops, new grooves and convolutions are continuously formed in it. The digestive system also works: the stomach digests amniotic fluid, the intestines already contain original feces - meconium. The liver accumulates iron in preparation for independent work outside the womb.
Mandatory tests and examinations
At this time, the woman must undergo general blood and urine tests. The latter allows you to timely detect an inflammatory process in the urinary tract or genital organs - it will be indicated by the presence of epithelial cells.
In addition, it is required to donate blood for biochemistry, which will allow the doctor to evaluate the functioning of the internal organs and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
During the same period, a coagulogram is once again performed - a blood test for clotting.
It is necessary to repeat tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C. The incubation period of these diseases lasts six months, therefore, if a woman became infected with them at the beginning of pregnancy, the test will be positive. In the later stages, the question of interruption is not raised - the doctor simply prescribes adequate treatment.
Another mandatory test is a gynecological smear for flora. It is needed to promptly detect an infection in the vagina and prevent infection of the fetus as it passes through the birth canal.
At 30 weeks, a woman, as at the beginning of pregnancy, is examined by specialized specialists: a cardiologist, a dentist and an ophthalmologist.
What position should the fetus be in?
At gestational age 30-31 weeks, the fetus in most cases is in a longitudinal position. With polyhydramnios, in women who have given birth many times, and in other cases, the baby may be positioned transversely or obliquely. The correct position is longitudinal, the presenting part should be the head. Sometimes the buttocks or legs of the fetus are located above the entrance to the small pelvis, then they talk about breech presentation. Until the 34th week of pregnancy, it is believed that the baby has enough space in the uterus, and he can still roll over and take the correct position. To promote this, you can do special gymnastics.
Mother's condition and how the fetus develops?
This stage of pregnancy is quite difficult for many women to endure, as they experience dizziness, may faint and feel a lack of oxygen. This condition can be alleviated by walking in the fresh air, but heavy physical exertion should be avoided.
Meanwhile, the baby is active. It is already very well developed and in case of premature birth it can survive and exist normally with a very high probability. His torso looks proportional, but still thin.
In what cases is it necessary
Doppler testing is not performed on all pregnant women. It is prescribed according to maternal or fetal indications. Reasons for prescribing Doppler ultrasound are:
- maternal diseases (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, antiphospholipid syndrome, thrombophilia, etc.);
- stillbirth, gestosis, placental insufficiency in previous pregnancies;
- gestosis;
- oligohydramnios;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- single umbilical cord artery;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck;
- Rhesus conflict;
- multiple pregnancy;
- post-term pregnancy, etc.
Woman's feelings
As the baby becomes heavier day by day, his movements become more and more noticeable to the mother. Sometimes they can already cause discomfort, but as soon as the baby falls asleep, the mother begins to miss his games. Enjoy these moments, they may never happen again. At this time, it can be very interesting to study the literature that describes the features of intrauterine development. This way you will not only know what height and weight your baby is, but also what is happening in his body now, what he is doing there. It is this kind of knowledge that helps make your state more harmonious.
Significant changes in the fetus from 30 weeks
With this period, the following changes are noted inside the child’s body:
- Active blinking is observed;
- The recruitment of white adipose tissue is very active;
- The lungs are in the process of development. During this period, they are still unable to function independently;
- There is an increase in the child's activity. All the time free from sleep, the fetus vigorously moves its limbs. And during sleep, he clenches his fists, frowns, shrugs his shoulders;
- The baby has a gradual disappearance of vellus hair;
- In the convolutions of the brain there is an increase in their number and depth;
- The liver rapidly accumulates iron (for hemoglobin).