Doctors often prescribe tests and various research methods, but do not always clearly explain their results. Or the girl decided to do the analysis herself, and there was no one to explain the results. If you have a similar situation with femoflor 16, this article will help you understand the unclear columns and rows.
This is the best method for diagnosing bacterial diseases of the vaginal flora. Femoflor 16 quickly and qualitatively determines the components of the biocenosis of the urogenital tract in a woman, finds bacteria that disrupt the normal functioning of the flora and the functioning of the adequate functioning of the vagina.
Femoflor screening – what is it?
As mentioned above, femoflora screening is based on the PCR method. This is a fairly effective diagnostic procedure that can detect traces of pathogenic agents from just a few molecules of their DNA left behind in the microflora.
Depending on what exactly the procedure was assigned for, it is assigned a specific number (for example, 13 or 16). One of the most common methods is the Femoflor 16 test. The prefix in the form of a number indicates the number of microorganisms that the doctor will look for during decoding. In addition to anaerobic bacteria, these include:
- Mycoplasmas.
- Fungi of the genus Candida.
- Ureaplasma.
- Trichomonas.
- Cytomegalovirus, etc.
The higher the number, the greater the number of bacteria, viruses and fungi that will be tested. At the same time, specialists receive not just confirmation of their availability, but also the most accurate quantity. Based on this, the analysis helps to record even minute deviations from the norm, indicating the presence of pathology.
Femoflor screen in gynecology has a very important role, because the doctor receives data on the distribution of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria, namely the number of lactobacilli, which are considered one of the most important for maintaining women's health. When their numbers are low, opportunistic bacteria and fungi will gain the ability to actively reproduce and lead to various inflammatory diseases.
Why is the effectiveness of the method better?
Femoflor 16 has long lived up to its expectations and surpassed other research methods.
This analysis is done in real time, then the doctor and the patient can receive the result within a few hours. In comparison, seeding the vaginal flora takes about a week. This time is necessary for the growth of pathogenic flora and the detection of colonies of microorganisms.
Femoflor 16 is produced by PCR (polymerase chain reaction), which is particularly sensitive and specific.
The polymerase chain reaction method is carried out faster and better due to its principle of action and detection of microorganisms. The polymerase chain reaction contains antigens to certain microorganisms, viruses and other bacteria, which are developed by bacteriologists and virologists. This analysis contains antigens of 16 bacteria, the list of which is given below. This test looks for the native DNA of the organism in a scraping taken from the vagina. Even the smallest number of bacteria, down to 1, will not be able to escape the polymerase chain reaction. The analysis will quickly determine the amount of bacteria contained. Therefore, it is distinguished by quality and specificity, unlike other methods that require a minimum content, much more than 1 microorganism, to determine the presence, and not just the quantity.
The analysis is taken without special preparation. The only rule for proper preparation for analysis so that it shows the correct value is personal hygiene. Before going to the doctor, it is necessary to toilet the external genitalia, since overnight accumulation in the natural skin folds of the external labia can lead to false results and incorrect calculation of the number of opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms.
It is not recommended to carry out analysis during menstruation. Since blood is the best habitat and opportunity for the reproduction of pathogenic flora and simply attracts bad rods and cocci.
Femoflor 16 serves as an excellent method for determining the effectiveness of treatment.
Decoding and norm of femoflor 16 in women
Deciphering femoflora 16 in women (establishing a final conclusion) is carried out in a laboratory, based on data from special tables.
Correct decoding depends on many criteria:
- How accurately was the biomaterial collected for the study?
- Total number of bacteria.
- The presence of bacteria from the normal vaginal microflora.
- Quantitative composition of pathogenic flora.
- The number of pathogenic bacteria in the examined biomaterial.
The quality of biomaterial collection is assessed based on the number of epithelial cells obtained in one sample. If the flora is collected correctly, epithelial cells are found in quantities of less than 1000.
The total mass of microorganisms must also be within certain parameters. The lower acceptable limit for the number of bacteria is 1,000,000 rods and cocci.
Normally, the interpretation of the results of femoflor screen 16 should show the normal composition of the vaginal flora, in which lactobacilli are superior. This is a kind of “ruling population”. In a healthy woman, lactobacilli should outnumber all other microorganisms. In general terms, their level should reach 90% of the total flora.
Conditionally pathogenic flora is also acceptable in normal smears, but only within certain limits. As its amount increases, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs develop.
Indications for analysis
In general, there are no restrictions on prescribing a vaginal smear examination.
But most often Femoflor is prescribed for:
- 1Identification of the pathogen during the infectious process (the appearance of pathological leucorrhoea, its unpleasant odor) and the appointment of adequate etiotropic therapy.
- 2Studying the composition of the vaginal flora, its qualitative and quantitative components.
- 3 Making a diagnosis when there is a discrepancy between clinical and laboratory data.
- 4Screening during pregnancy (in all trimesters).
- 5Screening during preconception preparation.
- 6As a supplement to microscopic examination to assess the state of the biocenosis of healthy women.
- 7 Confirmation of the diagnosis of “bacterial vaginosis” with identification of facultative flora with a pathological growth pattern.
- 8 Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
- 9Monitoring the restoration of normal flora.
There are no contraindications to the analysis. The only condition is the correct collection and transportation of the test material.
To clarify the etiology of gynecological diseases, it is sometimes necessary to additionally analyze the presence of absolute pathogens (chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas) using the PCR method.
The presence of these microorganisms is examined in the format of Femoflor Screen reagents, which additionally includes the determination of:
- 1Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- 2Herpesvirus 1
- 3Chlamydia trachomatis
- 4Trichomonas vaginalis
- 5Citomegalovirus
- 6Herpesvirus 2
When and which Femoflor is prescribed, we will consider below.
9.1. Femoflor 4
An assessment of the general condition of the biocenosis is carried out. It is advisable to use for symptom complexes of vulvovaginal candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, or to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy.
9.2. Femoflor 8 (Femoflor 9)
A more extensive assessment of the state of the biocenosis is being carried out. Also used for symptoms of candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, as well as for the purpose of assessing the quality of treatment measures, nonspecific vaginitis.
9.3. Femoflor 16 (Femoflor 17)
The composition of the flora is analyzed in detail. Prescribed for chronic recurrent infectious processes, during preconception preparation, preparation for operations, hysteroscopy, IVF, insertion of an IUD, as well as for assessing the quality of therapy.
9.4. Femoflor Screen
Additionally, the presence of specific infections and viruses is analyzed. Prescribed for specific infections (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis), genital herpes, secondary infertility, the presence of adhesions in the pelvis, pregnancy pathology, pre-conception preparation, chronic colpitis and cervicitis.
Femoflor 8
A smear for femoflor 8 is indicated for assessing the state of the vaginal microflora in women using the PCR technique. As a result, doctors receive a comprehensive picture of the composition of the vaginal flora. Also, it allows you to assess the biocenosis of the vagina as a whole, and establish the exact cause of the infectious process.
Read further: What tumor markers should I take for prevention? What can be determined from the results of a blood test?
What can cause disturbances in the microflora of the urogenital tract?
Dysbiosis in women can be practically asymptomatic. However, it often leads to the development of serious problems in the functioning of the reproductive system and a decrease in the patient’s quality of life.
To avoid the occurrence of pathologies associated with an imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria, it is necessary to carefully monitor the health of the entire genitourinary system. Pay special attention to the presence of factors that potentially pose a threat to women’s health:
- hormonal changes caused by irregular sex life, pregnancy, childbirth, abortion, menopause, and the use of hormonal contraceptives;
- maintaining an antisocial lifestyle, frequent changes of sexual partners;
- untimely treatment of STDs;
- long-term therapy with antibiotics;
- chronic intestinal diseases and dysbiosis;
- violation or incorrect adherence to personal hygiene rules;
- stressful situations;
- change of climate zone.
What does femoflora analysis 8 find?
- Control of material intake.
- Total number of bacteria.
- Lactobacilli.
- Enterobacteriaceae.
- Streptococci.
- Eubacteria.
- Gardnarellas.
- Mycoplasmas.
- Fungi of the genus Candida.
Femoflor 8, the decoding of which is recorded in a specially created table, reveals the level of bacteria in various indicators. The total number of detected DNA (absolute) is entered in column 1, and the number of bacteria found from the total mass of the flora (relative) is indicated in column 2.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for patients of different sexes is almost always favorable. Complications develop only in exceptional cases. Typically, after 2 weeks of active treatment, all symptoms disappear. Sometimes therapy lasts up to 3-4 weeks.
Complications rarely develop. If left untreated, eubacteria penetrate the bladder and kidneys, and inflammation and a purulent process develop. In women, the likelihood of developing symptoms of advanced colpitis and even endometritis increases.
Only in some cases, when the purulent process is advanced, bacteria penetrate into the blood, which leads to its infection and deterioration of the general condition.
Eubacterium spp in a smear is a fairly common occurrence among patients of all ages. In women and men, the symptoms of the disease are almost the same, and the treatment regimen is selected individually in each case.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Femoflor 9
An analysis to perform a comprehensive assessment of microbiocenosis in a woman’s genitourinary system, carried out by comparing the concentration of bacteria from beneficial and opportunistic flora in the entire bacterial mass. Like all others, femoflor 9 is performed using PCR.
Defined indicators:
- Control of material intake.
- Bacterial mass.
- Mycoplasmas.
- Yeast mushrooms.
- Lactobacilli.
- Enterobacteriaceae.
- Streptococci.
- Gardnarellas.
- Eubacteria.
- Mycoplasmas.
Who should undergo analysis to determine the qualitative composition of microflora?
Obvious signs of a violation of the bacterial background in the patient’s urogenital tract may be:
- burning sensation;
- constant itching of the outer labia and vagina;
- changes in the intensity and abundance of natural female discharge;
- discomfort in the genital area.
If at least one of the above symptoms appears after long-term antibiotic or hormonal therapy, femofloral screening is especially important. What it is, how the analysis is carried out, as well as how to carefully prepare for it, women who:
- planning pregnancy;
- preparing for in vitro fertilization;
- will undergo surgery on the pelvic organs in the near future;
- undergo comprehensive diagnostics to identify diseases in the presence of the above symptoms;
- suffer from rapid progression of dysbiotic processes;
- underwent a course of ineffective treatment.
Femoflor 12
Analysis to determine the quantitative composition of the microflora in the patient’s vagina. It includes: Lactobacilli, Gardnarella, quantitative assessment of the level of Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma, Candida fungi.
Also, analysis of femofloras for women (12) allows the gynecologist to find 7 unconditional pathogens that most often cause pathologies of the urogenital tract in women: Mycoplasma, Trichomonas, Neisseria, Chlamydia, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes type 1 and 2.
Read further: What to do with high hemoglobin in women
Femoflor: what infection can be detected
The results of the study can give the doctor as much necessary information as possible.
A detailed analysis allows you to determine the composition of the microflora and the number of microorganisms. Thus, with the help of analysis it is possible to identify the presence of not only natural urogenital flora. But also sexually transmitted infections: chlamydial, cytomegalovirus, herpetic, trichomonas, mycoplasma, fungal, ureaplasma, gardnerella.
Even the most minor changes in the composition of the microflora make it possible to understand the cause of the imbalance in microbial balance.
Decoding femoflora 13
Test reference values will vary depending on the type of microorganism being calculated. Femoflor 13 interpretation of the analysis is carried out using absolute and relative units. The conclusion of the test includes:
- Evaluation of the smear, based on the results of which material with indicators of 104 GE should be collected. If it is too low, you will have to do another scraping.
- General contamination, indicating the mass of microorganisms in the genitourinary system. Its norm should be at least 105.5 - 109. If this figure is less than 106, it indicates drug treatment, so the test will need to be repeated (about 1-2 weeks after the end of the therapeutic course).
- The total level of lactobacilli, which indicates the norm. If the amount of beneficial flora is more than 80%, there is no pathology. If its level fluctuates between 20-80%, a conclusion is made of a moderate imbalance, and less than 20% is already a diagnosis of dysbiosis.
- Counting the amount of pathogenic flora. It is carried out in the presence of characteristic clinical signs. Up to 1% (normal), from 1 to 10% (moderate infection), more than 10% - excessive contamination.
- When a gynecologist reveals a clinical picture of thrush during an examination, it is necessary to calculate the causative agent, including mycoplasma. Its conditional norm should be within 105 GE, and for Candida mushrooms - 104 GE.
Femoflora analysis for women should be assessed and interpreted test results only by the attending physician. This test is only an additional diagnostic method. Independent use of the obtained data is not allowed, as is taking medications based on their results.
How is screening carried out?
The quality of the material taken plays a fundamental role in the analysis. An indispensable condition for the success of this type of diagnosis is the correct technique for collecting biological material, for which scrapings are taken from:
- urethra;
- cervical canal;
- vagina.
The material required for screening is usually obtained using a sterile, disposable instrument such as a cytobrush. The clinical sample is then placed in a prepared Eppendorf tube. Its feature is considered to be the presence of a medium suitable for transportation. After placing the clinical material inside, the tube is labeled with the patient's data, date and name of the test.
Femoflor 17
One of the types of vaginal flora analysis, which is prescribed to women if pathologies in the urinary and reproductive systems are suspected. The referral is issued by a gynecologist. For the test, the patient must have certain indications:
- Feeling of burning or itching in the vaginal area.
- Discharge with a foul odor or an unnatural color.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Rash on the genitals or the skin around them.
- Dysmenorrhea.
- Pain during sex.
- Pregnancy or early planning.
- Tumors and other types of formations in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Rules for collection and transportation of material
To analyze the microbiota using the Femoflor Screen/4/8/16 method, scrapings can be taken from:
- posterolateral vaginal vault;
- cervical canal of the cervix;
- urethra.
The techniques for collecting secretions, as well as the requirements for its transportation, differ for each of these methods. Let's take a closer look at these options.
Posterolateral fornix fence
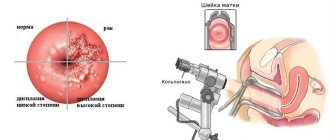
The material for research is a certain amount of epithelial cells necessary for the analysis of vaginal microflora. The sampling is carried out during a preventive examination using gynecological mirrors strictly before performing a manual examination. An important condition is the absence of pathological mucus and blood in the area of the smear, which, if necessary, are removed mechanically using a cotton swab.
A smear on the flora is obtained with a special disposable probe. Subsequently, the material is transferred to a labeled microtube with a nutrient medium, tightly closed with a lid. As a rule, products from the German manufacturer Eppendorf are used. The probe is discarded.
Collection from the cervical canal
Material from the cervical canal of the cervix is taken if an inflammatory process (cervicitis) and other pathologies in this area are suspected.
If the source of inflammation is reflected in the gynecological speculum, scraping is performed in the affected area. If visibility is insufficient, a special probe is inserted into the cervical canal no deeper than 1.5 cm. Then, a circular movement is described with this instrument in order to obtain material around the perimeter, after which it is carefully removed. It is important not to touch the vaginal walls, since the information content of such an analysis will be questionable.
If there are foreign impurities and mucus in the area where the smear is performed, it is cleaned with a sterile cotton swab, treated with sodium chloride solution (concentration - 0.9%), after which the procedure begins.
Storage occurs in the same way as when obtaining epithelium from the posterolateral fornix.
Collection of the separated urethra
Before collecting material from the urethra, the external opening is treated with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. After preparatory manipulations, a probe is inserted with a clear movement to a depth of 1-1.5 cm, and then removed in the same way.
If the patient has mucous or purulent discharge, there is no point in observing a two-hour interval between the last urination and the start of the procedure.
The scraping is placed in a tube, labeled and transported by a suitably qualified laboratory technician. It is allowed to store the analyzed object at a temperature of -20°C for no more than one month.
What does femoflora 17 analysis find?
When taking the femoflor 17 test, you need to know which infections are included in its search range:
- The total number of all microorganisms.
- Lactobacilli.
- Enterobacteriaceae.
- Streptococci.
- Staphylococci.
- Gardnarellas.
- Eubacteria.
- Leptotrichia.
- Veillonella.
- Clostridia.
- Corynebacteria.
- Peptostreptococci.
- Vaginal atopobium.
- Mycoplasma genitalium.
- Mycoplasma hominis.
- Ureaplasma.
- Fungi of the genus Candida.
general characteristics
Bacterial vaginosis
(BV) is an infectious non-inflammatory syndrome, which is characterized by a high concentration of obligate and facultative anaerobic opportunistic microorganisms with a decrease/absence of lactic acid, primarily peroxide-producing, bacteria in the vaginal discharge. The pathogenesis of the development of bacterial vaginosis is caused by two interrelated and interdependent processes: alkalization vaginal contents and a decrease in the concentration of lactobacilli.
Decoding femoflora 17
Analysis of femoflora 17 decoding in women is carried out by the attending physician, and consists of taking into account many criteria:
- The quality of the smear is normal, at least 104 GE. If this figure is less, one can argue that there is insufficient material for the examination. For this reason, the final result obtained will most likely be incorrect.
- Total number of bacteria - shows all vaginal bacteria (normally 106-108 units in one sample).
- Normal flora – shows the level of lactobacilli. The norm is 80-100%, if the amount is within 20-60%, this is moderate dysbiosis, 20% or less is severe dysbiosis.
- Conditionally pathogenic flora - normally less than 1%, from 1% to 10% - moderate dysbiosis, more than 10% - pronounced.
- In normal tests, bacteria such as ureaplasma, mycoplasma and Candida fungi should be absent. Their trail indicates an infection that can provoke dysbiosis.
Norms of indicators
Each age group of patients is characterized by the presence of a certain number of eubacteria. In children, they are present only in the intestines and do not penetrate other organs. In adults, the number of microorganisms in the vagina and urethral secretion (in men) increases sharply.
Among women
The norm of eubacteria in a woman’s vaginal secretion is 10-15 CFU/ml. When the indicator increases, we can talk about the development of inflammatory and non-inflammatory pathologies.
It is worth noting that the definition of this indicator is not considered basic. Additionally, the specialist identifies the number of lactobacilli, or Doderlein bacilli.
In men
Due to the anatomical features of the male urethra, the number of eubacteria in the urethral secretion should not normally exceed 10 CFU/ml. This is explained by the large distance between the urethral opening and the anus.
How to prepare for femoflor screen
When a woman receives a referral for a diagnostic test to identify several biotypes, each of which is produced with a new set of materials (test tubes, probes, etc.). Just like with any other gynecological examination, without certain preparation, it will not be possible to perform high-quality femoflor screening. Preparation for the procedure on the part of the woman should be carried out on the eve of the examination date and consist of the following actions:
- Before a smear, a woman should not use soap or douche.
- For 7 days you need to stop taking any antibiotics and certain groups of drugs (check with your doctor).
- The study is not carried out during menstruation, and within 5 days after its end.
- 3 days before the test, you need to stop taking contraceptive medications in any form.
- In about 3-4 days, you need to give up sex.
- Several hours before taking a smear, you should refrain from going to the toilet.
- It is prohibited to collect materials for PCR after a recent colposcopy.
Vaginal microflora
The urogenital tract is a sensitive environment, in which changes in the normal composition of the microbiota can be influenced by various factors:
- age;
- lifestyle, nutrition system;
- presence of a permanent sexual partner, his change;
- contraceptive method used;
- taking antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- general hormonal and immune status;
- general and special gynecological anamnesis;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- diseases of other organs and systems.
All of the above facts can have an impact on the state of the vaginal flora: both relatively harmless and negative, up to the development of diseases. Moreover, it is not so much the qualitative characteristics that play a role as the quantitative ratio of microorganisms.
During pregnancy
Normal biocenosis is an important condition for a woman’s health. But its observance becomes even more important for the full implementation of the reproductive function.
Dysbiotic disorders and the spread of infections in the body of a pregnant patient lead to intrauterine infection, the occurrence of pathologies in the fetus, provoke miscarriages, premature birth, and other deviations in the normal course of the process of bearing a child.