Reduced performance
In diseases that provoke an incorrect reaction in hemoglobin synthesis, mchc levels decrease, last of all, when all other functional reactions of the body have already been exhausted.
The approximate concentration of hemoglobin never depends on the cellular volume. Therefore, this parameter serves as an indicator of all pathologies of hemoglobin synthesis. MCHC and MCH blood tests help determine the type of anemia. Mch blood value is recorded in picograms (pg or pg). Blood test mchc and mch normal within 25-36 pg. Based on these data, all anemias can be divided into normochromic (color index 0.85-1.05), hypochromic (color index below 0.8) and hyperchromic (color index above 1.05)
Reasons when mchc and mch blood tests are low:
- megaloblastic anemia - the volume of red blood cells is greater than the saturation with hemoglobin;
- hemoglobinopathy - pathologies of hemoglobin synthesis;
- increased levels of high-osmotic compounds glucose and sodium in the blood;
- Thalassemia is a genetic disease;
- Hypochromic anemia - appears with iron deficiency anemia, hypothyroidism...
Treatment of all types of anemia, after a blood test for mch and mchc, as well as the prescription of medications and regular monitoring, is carried out only by the attending physician!
Normal and discolored red blood cells
Preparing for analysis
A blood test to determine erythrocyte indices must be taken on an empty stomach. Before conducting the study, it is recommended:
- eliminate alcohol consumption;
- do not smoke or limit smoking;
- do not drink strong coffee, tea;
- reduce the amount of fried, fatty foods in your diet.
Doctors do not advise exposing the body to physical overload, overheating or hypothermia before taking a blood test.
If on the eve of a blood test it is planned to undergo an x-ray, massage or physiotherapeutic procedure, then it is better to postpone the blood test for 3 days.
When going to the laboratory to conduct research, do not rush or worry. It is best to climb the stairs by walking, or even better - use the elevator.
In front of the office, it is advisable to sit quietly on the couch for 10 minutes, calm down, and only then go into the treatment room.
Decoding increased indicators
The results of each blood test are presented in the conclusion of the analysis. But to understand these terms, you need a professional interpretation.
A sign of pathology can be considered indicators that are higher or lower than the accepted norm. Based on the nature of the deviations, the causes that caused them are determined and, thus, the disease is diagnosed.
If the MCH index is elevated, then this condition is usually regarded as hyperchromia. This term refers to the pathological state of red blood cells, accompanied by an increase in hemoglobin content.
At the same time, a higher hemoglobin indicator does not mean that the pigment concentration has become higher, since most often the causes of pathology lie in an increase in the volume of red blood cells.
Hyperchromia is a general concept that implies several different types of anemia, which in itself is already a sign of pathology.
That is, the reasons that increase the amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells are related to the total volume of cells, and not to the concentration of pigment in a single blood cell.
The MCH may be increased due to:
- pronounced leukocytosis;
- cold agglutinins;
- destruction of red blood cells;
- monoclonal proteins in the blood;
- high concentration of heparin;
- increased content of fats in the blood.
Hyperchromic anemia is usually associated with excess hemoglobin, the level of which is increased in megaloblastic anemia. This disease is characterized by the appearance of megaloblasts.
The main causes of megaloblastic anemia are vitamin B12 deficiency, B9 deficiency, myelodysplastic syndrome, the effect of various medications prescribed for malignant tumors, rheumatic and autoimmune diseases, epilepsy, and HIV infection.
The MCH index may be elevated if liver disease, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, tumors, leukemia, or aplastic anemia are diagnosed.
Also, the hemoglobin level may be increased with hypothyroidism. Often the MCH index is elevated in people who have been taking contraceptives for a long time.
In some cases, incorrect calculations may occur during blood tests. Therefore, if the general conclusion of the analysis indicates that the MCH index is elevated, then this is not yet a reason to sound the alarm.
It is quite possible that the reasons for the anomaly lie in incorrect calculations.
How to normalize MCHC
The indicator returns to normal only after the cause of its increase is eliminated. The patient needs to quit smoking and stop drinking. If the average hemoglobin concentration is increased due to the use of pharmacological agents, then it is worth changing the treatment regimen, replacing hormonal or sedative drugs with similar effects.
If the cause is a deficiency of B vitamins, then treatment is easiest. To do this you need:
- adhere to a special diet, which contains: cottage cheese, green vegetables, meat, fish, sour cream, eggs, nuts, cereals, vegetable oils,
- give injections with group B drugs, with a gradual reduction in dosage after completion of the main course,
- use physical therapy.
In addition, you must adhere to simple rules:
- sleep at least 9 hours,
- to walk outside,
- reduce tea and coffee consumption,
- protect yourself from stress and mental overload.
It is impossible to completely get rid of erythremia; doctors only try to normalize hematocrit and hemoglobin levels so that secondary ailments do not develop against the background of pathology. Malignant tumors often develop against the background of erythremia. Medicines used for therapy:
- antitumor (Hydroxyurea, Busulfan, Myelosan),
- Interferon, Anagrelide to reduce platelet count,
- iron preparations Sorbifer Durules, Fenyuls, Ferrum Lek,
- agents that regulate uric acid levels - Sulfinpyrazone, Allopurinol.
Only a doctor can select medications, since side effects must be taken into account. You can regulate the level of red blood cells using bloodletting or using the erythrocytepheresis method. The latter refers to more modern methods, in which only red blood cells are extracted from the blood. The course of treatment is complemented by symptomatic therapy, including antihistamines, hepatoprotectors, anticoagulants, drugs to strengthen the heart muscle and other medications. Surgery to remove the spleen is contraindicated in 75% of patients, as there is a risk of death due to complications. With timely therapy showing good results, surgery takes place without complications.
Source: s-voi.ru
Sample considerations
Stability
The MCHC is unstable. It can either decrease (storage-associated RBC swelling, which increases the MCV) or increase if there is RBC lysis in vitro with storage.
Interferences
- Lipemia: Will falsely increase MCHC due to false increases in measured hemoglobin. It will have no effect on the CHCM.
- Hemolysis: In vivo intravascular hemolysis or in vitro (artifactual) hemolysis falsely increase the MCHC (measured hemoglobin is proportionally higher than HCT or PCV) and decrease the calculated hemoglobin and thus the CHCM (because there are fewer intact RBCs – this will be a false decrease with in vitro but not in vivo intravascular hemolysis).
- Icterus: No effect.
- Other: (many, particularly if large) may falsely increase the MCHC with less of an effect on the CHCM.
- Agglutination: Falsely increases the MCHC (measured hemoglobin is proportionally higher than HCT) with newer optical-based analyzer. The CHCM is more accurate in this setting.
- Excess EDTA: This dehydrates RBC, falsely increasing the MCHC and CHCM.
Why may the indicator be increased and what does this mean?
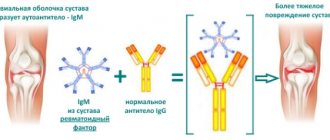
An increase in the concentration of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte is an indicator not only of an existing pathology in the body, but also in itself causes a dangerous condition - the deposition of clumps of hemoglobin pigment in the organs and tissues of the body, which leads to disruption of their function.
Important! If the general blood test indicators deviate slightly from the norm (less than 1.5 times), most likely the changes are temporary or the analysis technique was violated. It will need to be retaken. The presence of a sustained increase in MCHC during repeated testing may indicate the following diseases:
The presence of a sustained increase in MCHC during repeated testing may indicate the following diseases:
- Hyperchromic anemia (when the hemoglobin content in red blood cells is so elevated that their membrane is prematurely destroyed and life expectancy is shortened).
- Megaloblastic anemia (develops with a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. In this case, red blood cells are greatly increased in size (red blood cells are giants), but their number is very small and they cannot perform their function of transporting oxygen to tissues due to their irregular structure.
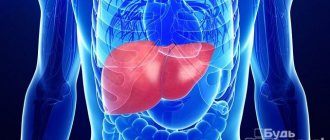
- Liver diseases (one of its most important functions is protein synthesis. In some diseases in the liver, the production of protein molecules increases several times, their quantity becomes pathological. In particular, hemoglobin synthesis increases excessively).
- Oncology (leukemia, erythremia) - in this case, bone marrow sprouts damaged by the tumor process produce a huge number of blood cells, but all of them are defective, unable to perform their functions and are quickly destroyed. A paradox arises - with a large number of blood cells, the patient constantly experiences oxygen starvation, chronic intoxication, and loses weight.
- Hypothyroidism (means underfunction of the thyroid gland when not enough thyroid hormones are produced, which plays an important role in the formation of new red blood cells).
- Genetic blood diseases (spherocytosis is a hereditary pathology in which the red blood cell has an irregular round shape. This reduces their ability to be saturated with hemoglobin and reduces life expectancy. Therefore, with a normal hemoglobin content of red blood cells, there is little and in the analysis its level is regarded as increased).
Also, MCHC can increase in general pathological conditions: diabetes mellitus, chronic heart and pulmonary failure, chronic alcoholism.
Why do level changes occur?
A shift from normal values of hemoglobin content can be observed in one or the other direction, that is, decrease or increase. The reasons that influence this indicator have a fairly wide range and are mostly pathological.
Increasing MCHC values
Many people know that a decrease in hemoglobin concentration is a consequence of the development of a large number of diseases - from fairly simple and easily curable to serious, difficult to treat. It is less often discussed when the Hb content in red blood cells is increased, but, nevertheless, such a deviation is also dangerous. Reasons that can increase the MCHC rate include the following.
Anemia
Among this series of pathologies, the first place is occupied by hyperchromic (saturated with hemoglobin) and megaloblastic (which received their name due to the formation of large red blood cells) anemia. With these diseases, disturbances in blood transportation occur (which is associated with an increase in the amount of hemoglobin), and the quality of blood supply to small vessels (capillaries) of internal organs decreases, leading to dysfunction of the latter.
An increase in the level of hemoglobin in these situations does not allow the body to use it fully, since the cells are defective and their biological cycle is short.
Liver pathologies
As is known, it is the liver that is responsible for the synthesis of most of the protein compounds, while their content can increase both in the organ itself and in its internal environment. This is especially evident with liver hypertrophy or the development of an oncological process (synthesis increases in cancer cells). As a result, the number of red blood cells increases, and at the same time they contain a lot of hemoglobin. It should be noted that this condition is much more common in men than in women.
Structural connections of hemoglobin
Oncological diseases
Significant deviations in the blood formula, and in particular the state of red blood cells, are caused by disturbances in the activity of the red bone marrow (responsible for their production), as well as the lungs and stomach. In adults and children suffering from leukemia (blood cancer), there is a significant increase in MCHC and MCH, and each of these coefficients can exceed the norm tens of times.
Hypothyroidism
A decrease in the function of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for the production of thyroid hormone, leads to a decrease in bone marrow activity. And due to the reduced level of thyroidin, the level of hemoglobin increases. According to experts, a slight increase in MCHC or MCH levels is not a life-threatening condition.
This fact indicates that the blood system copes with its function to one degree or another. But if, on the contrary, the hemoglobin concentration is reduced, then the situation will be regarded as more dangerous for patients. You can read more about the increase in MSHC in a blood test in this article.
Decrease in MCHC values
If deciphering the results of a general blood test showed that the coefficient of hemoglobin content in red blood cells is low, then the doctor will definitely insist on urgent additional diagnostics, since this blood condition can cause the development of many metabolic disorders.
Due to a decrease in MCHC parameters, which is directly related to a decrease in the average concentration of hemoglobin and oxygen in the blood, cell perfusion suffers. This leads to a deterioration in the condition of the tissues of internal organs, as a result of which their performance decreases.
Such blood changes are especially dangerous for children and pregnant women, since a lack of hemoglobin will cause oxygen starvation of the fetus, disrupting the natural processes of the formation of its tissues and organs. And in a growing child’s body, hemoglobin deficiency can cause various abnormalities. There are several main reasons why the MCHC indicator decreases.
Reduced iron content
The normal level of iron in the human body is approximately 5 mg. Its decline is observed with internal bleeding caused by diseases of the digestive system or an unbalanced diet. Due to a lack of iron in the blood, the synthesis of complete Hb cannot occur, resulting in the development of iron deficiency anemia.
This pathology is mainly observed in females, since due to their physiological characteristics there is a monthly loss of iron. Therefore, people with heavy periods should regularly monitor the content of this element and ensure sufficient intake of it in the body.
Hereditary blood pathologies
One such disease is thalassemia, and most of the cases affect children. The disease is characterized by a violation of the production of structural units of Hb - protein chains (mainly alpha type). Hemoglobin, which carries these compounds, is not able to sufficiently provide cells with oxygen. Such a pathology in a child can be detected already in the first years of life and appropriate measures can be taken in time.
Vitamin B6 deficiency
Vitamin B6, like all those included in this group, is involved in many metabolic processes. Its normal values are approximately 2 mg, but the concentration in the blood undergoes regular changes. The bone marrow is the most susceptible to such fluctuations - the place of formation of most of the blood cells, as well as hemoglobin.
When the B6 content decreases, the binding of hemoglobin polypeptide chains is disrupted, which causes a decrease in MCHC. In women, such deviations are observed much more often than in the stronger sex.
Main manifestations of anemia
All of the above reasons have a great impact on the functioning of the blood system, causing a decrease in the color index and hemoglobin content in red blood cells. To be able to prevent the occurrence of deviations, preventive measures should be carried out regularly.
Differential diagnosis of anemia
To a large extent, the diagnosis of anemia is facilitated by the correct interpretation of morphological changes in red blood cells:
| Index | Type of anemia | |||
| Iron-deficiency anemia | hemolytic anemia | hypoplastic anemia | B12 deficiency anemia | |
| Hemoglobin | reduced | significantly reduced | significantly reduced | sharply reduced |
| Red blood cells | reduced | reduced | reduced | sharply reduced |
| reduced | norm | norm | reduced | |
| Red blood cell diameter | reduced | reduced | elevated | significantly increased |
| norm | elevated | elevated | sharply increased | |
| reduced | elevated | elevated | sharply increased | |
| reduced | norm | reduced | reduced | |
| Reticulocytes | norm | sharply increased | sharply markedly reduced | reduced |
| Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example |
Normal average erythrocyte volumes depending on age
| Age | Women MCV, fl | Men MCV, fl |
| Umbilical cord blood 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-6 years 7-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 60-65 years old over 65 years old | 95-118 95-121 88-126 86-124 85-123 77-115 77-108 72-89 76-90 76-91 80-96 82-96 81-98 80-100 82-99 80-99 80-100 | 98-118 95-121 88-126 86-124 85-123 77-115 77-108 70-99 76-89 76-81 79-92 81-93 80-93 81-94 82-94 81-100 78-103 |
The average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell is normal depending on age
| Age | Women MCH, pg | Men MCH, pg |
| 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60-65 years over 65 years | 31-37 28-40 28-40 28-40 26-34 25-35 24,0-31,0 25,5-33,0 27,0-32,0 27,5-33,0 27,0-34,0 27,0-34,0 27,0-34,5 26,5-33,5 26,0-34,0 | 31-37 28-40 28-40 28-40 26-34 25-35 24,5-29,0 26,0-31,0 26,5-32,0 27,5-33,0 27,5-33,5 27,5-34,0 27,5-34,0 27,0-34,5 26,0-35,0 |
The average hemoglobin concentration in a red blood cell is normal depending on age
| Age | Women MCHC, g/dl | Men MCHC, g/dl |
| 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-6 years 7-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60- 65 years over 65 years | 29,0-37,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 29,0-37,0 30,0-36,0 33,0-33,6 32,4-36,8 32,2-36,8 32,4-36,8 32,6-35,6 32,6-35,8 32,4-35,8 32,2-35,8 32,2-35,8 31,8-36,8 | 29,0-37,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 29,0-37,0 30,0-36,0 32,2-36,6 32,2-36,2 32,0-37,0 32,2-36,4 32,8-36,2 32,6-36,2 32,6-36,4 32,6-36,2 32,2-36,9 32,0-36,4 |
ATTENTION! The information presented on the website DIABET-GIPERTONIA.RU is for reference only. The site administration is not responsible for possible negative consequences if you take any medications or procedures without a doctor’s prescription!
Normal values for different categories of patients
Like many parameters that are important for making a diagnosis, MSNS depends on the gender and age of the subject, therefore the coefficients accepted as the norm tend to differ. This indicator is measured in grams per liter.
Normal values for children
Up to 12 years of age, normal parameters for children do not differ. From birth to 3-5 years per week, this figure is approximately 280-350 g/l.
Then the MCHC coefficient increases slightly, reaching a value of 370 g/l, and should remain at this level until the age of 12.
Normal for teenagers
Once a child reaches 12 years of age, the MSHC coefficients begin to differ, this is due to the characteristics of puberty. Therefore, normal values for girls are considered to be up to 360 g/l, and for boys - not exceeding 380 g/l.
The lower coefficient in girls is due to hormonal changes and the onset of the menstrual cycle.
Norms for people 18-45 years old
In young and mature ages, the values of the described parameter gradually become equal, and as a result, the norm for women and men is 320-360 g/l. After 45-50 years, the norm for women and men is slightly reduced, since in older people, as a rule, all metabolic processes, and in particular the reproduction of blood cells, decrease.
Moreover, a decrease in hemoglobin concentration is most often observed in females.
What is MCHC?
Blood is responsible for feeding the cells in the human body.
Transported hemoglobin, which is found in red blood cells, is responsible for the transport of oxygen. For each organism there are normal hemoglobin levels, but if there are deviations from the norm, it is recommended to do more detailed tests. This analysis will be a test for MSHC, which shows the average level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. This indicator is important for diagnosing anemia of various etiologies and other diseases. MSHC depends on the ratio of the volume of leukocytes, platelets, red blood cells to the liquid components of blood.
This analysis cannot exceed acceptable limits. If during the examination the MSHC is higher, then this may be a mistake by the laboratory technician. The reason may be a poorly washed test tube or the use of expired chemical reagents. The laboratory technician's mistake may consist of incorrect setup of the analyzer. Exceeding MCHC occurs when red blood cells are damaged and subsequently released into the plasma. Visually damaged blood components become pink. In such a situation, doctors recommend retaking the test.
MCHC in blood test
If you have a condition in which there is morning weakness, heaviness in the head and confusion of thoughts, while a pale complexion is observed, then this is nothing more than anemia. In this condition, the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood is very low. The cause of anemia is insufficient levels of components such as folic acid and iron in the body. This, in turn, can be caused by poor diet, taking various medications and a number of other reasons.
Detection of anemia is possible by determining the MCHC content in a blood test - the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. This index is calculated during a general blood test. It is always prescribed before surgery or if any disease is suspected.
What is MCHC?
This is one of the blood indicators that is measured with a special device. Simply put, this is the erythrocyte index; it indicates the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. The indicator tells how much hemoglobin is saturated with red blood cells.
Decoding
The interpretation of the analysis according to the MCHC index is done by the attending physician. This indicator is informative only if there are few abnormal red blood cells in the blood, and better if they are completely absent. The volume of red blood cells is measured by a femtoliter, and its norm should be in the range of 80-100 fl.
The MCHC index characterizes the hemoglobin saturation of red blood cells, and it is considered the most informative and accurate. If there is even a slight change in hematocrit or hemoglobin in the blood, the MCHC will be higher than normal. If the indicator is underestimated, then it is likely that problems such as hemoglobinopathy, iron deficiency anemia, and thalassemia will develop in the body.
The index may differ, depending on the gender and age of the patient. If you notice symptoms of anemia, consult your doctor; he will definitely prescribe an MCHC test for you. You can study the transcript yourself and assess your condition, but it will be better if a specialist does this. Specialists from any medical clinic in Moscow recommend taking preventive measures to normalize your health and prevent anemia. But remember that prevention is always easier than long-term treatment.
Normal MCHC level in blood
The norm for this indicator is as follows:
· The norm for men is from 32.3 to 36.5 g/dl,
· The norm for women is from 32.2 to 35.5 g/dl.
With age, this figure may increase in both women and men.
Conclusion
Now you know what MCHC is and what it stands for. In order to prevent a decrease or increase in this index, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations and blood tests for preventive purposes.
Purpose of mchc measurement
As already mentioned, in the process of laboratory research, a specialist calculates the quantity and determines the qualitative composition of the main components of blood. Among them:
- red blood cells;
- leukocytes;
- platelets.
In fact, a test that determines blood mchc is very important. After all, the transfer of hemoglobin through tissues and organs is one of the most important functions of red blood cells. Consequently, the condition of the entire organism depends on how efficiently red blood cells work.
The mchc level can only be determined by taking blood for analysis. Decoding the results gives an idea of how much high-quality hemoglobin is contained in the patient’s circulatory system.
MCH blood test
The most important information about a person's health can be obtained from a blood test.
MSN blood test is an important part of any diagnosis. Modern medicine uses analyzers to study the resulting sample, this makes it possible to determine a large number of blood parameters, not only the MSN value
The analyzer itself calculates all indices automatically, which greatly simplifies the doctor’s work. Let's take a closer look at what the MCH index is and what it affects.
MCH Index
This indicator is calculated in picograms and reflects the average level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. The MCH index is also identified in the blood with a color indicator. But in the case when a study is carried out using an analyzer, there is no need to count the CPU. The analyzer itself will calculate the MCH index.
MSN norm
The normal average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes ranges from 24 to 34 pg. But this indicator depends on the age of the person. All this is taken into account by the specialist during the final decoding of the received data. It is worth noting that the MCH value is highest in newborns, and over the years it decreases.
Reasons for increasing MSN
If an increase in this indicator is detected, this may indicate the development of hypothyroidism, anemia, liver problems, or cancer. The index may be altered by taking certain medications, including anti-seizure medications and hormonal contraceptives.
Reasons for lowering MSN
The average hemoglobin content in red blood cells may be reduced for the following reasons:
1. Iron deficiency anemia,
2. Lead intoxication,
3. Failure in the synthesis of porphyrins,
4. Genetic diseases,
5. Lack of vitamin B6,
6. Chronic inflammation.
And all this can be discovered during a study, which can be carried out by any medical clinic in Moscow.
How is the analysis carried out?
This procedure does not take much time. The blood test is carried out early in the morning and always on an empty stomach. Everything must be carried out under sterile conditions. The pad of the 4th finger is treated with alcohol, then a puncture is made. The blood is collected in a test tube. When the blood collection is completed, an alcohol-containing cotton wool is applied to the puncture site to disinfect and stop bleeding. A blood test using an analyzer is carried out in a couple of minutes.
After this, the attending physician analyzes the data obtained. In this way, the exact health status of the patient is established. Based on the results of blood tests, various diseases are identified, and the doctor develops a treatment system.
Methodology and features
For the results to be reliable, the patient needs to prepare. Eliminate increasing and decreasing factors:
- taking medications;
- eating less than 8 hours before;
- hunger for more than 24 hours;
- exposure to alcohol, nicotine and drugs.
On a note!
Women during menstrual bleeding are not tested. The results will be significantly distorted.
It is recommended to postpone going to the laboratory immediately after serious diagnostic procedures. For example, x-rays distort results within one week. This applies to any general blood test.
It is not recommended to donate biomaterial immediately after surgery, even under local anesthesia, if the results are necessary not to monitor the current condition, but to diagnose other diseases.
The procedure itself is familiar to almost everyone. Blood is drawn from a finger. At the same time, the possibility of antiseptic getting into the samples is excluded, pressure is not applied, and blood is taken, which appears “by gravity.”
You can use any technology for obtaining materials. This can be either a standard puncture needle or an automatic device.
You won't have to wait long for tests. The analysis procedure takes on average 30 minutes, but can last up to two hours. The doctor’s task is to understand what the resulting number means and whether there are any deviations. But decryption is easy to do on your own. To do this, you can use the table of norms for adults:
| Age | The norm for a man | The norm for a woman |
| 15-20 years | from 27 to 32 | from 26 to 34 |
| 20-45 years | from 27 to 34 | from 27 to 34 |
| 45-65 years | from 27 to 35 | from 27 to 34 |
The indicator should not have a large spread. It is stable and practically does not change over the years. It is difficult to notice sharp fluctuations, so it is recommended to conduct surveys in stages, tracking the dynamics in the future. The most variable indicator will be in children. It gradually decreases with age, and peaks in the first months of life. For a child up to two weeks, the normal level will be 39 units, then until 9 weeks it decreases to 34 units. In the first year, the amount of hemoglobin reaches its minimum, only 22 points, and after that it begins to increase slightly. By the age of six, the norm increases to 31 units.
On a note!
Although the child's body needs an active supply of oxygen, excess hemoglobin is still dangerous. However, the dynamics of the results are monitored more frequently to make a diagnosis.
Standard tables
Among women
| Age (years) | Level in g/dl |
| 15-40 | 31-36 |
| 41-60 | 31-35 |
| Over 60 | 32-36 |
In men
| Age | MHCH norm in g/dl |
| 15-60 years | 32-35 |
| Over 60 years old | 31-36 |
In children
| Life period | Normal level in g/dl |
| Up to 14 days | 28-34 |
| Up to 30 days | 28-36 |
| 1-2 months | 28-35 |
| 2-4 months | 29-38 |
| Up to 1 year | 32-37 |
| 1-3 years | 32-38 |
| 4-15 years | 32-37 |
Further, starting from the age of 15, calculations are carried out based on adult calculations and the results are interpreted accordingly, taking into account differences by gender.
You won't be able to decipher the analysis yourself. Yes, laboratories indicate reference values, that is, normal values, directly in the protocol and conclusion. But the result itself will say little. A comprehensive assessment is needed.
What does the abbreviation MCH stand for in a blood test?
The average content of red blood pigment (hemoglobin - Hb, HGB) in red blood cells circulating in the bloodstream has no independent diagnostic value, however, this indicator acquires some significance in the differential diagnosis of anemia. In addition, the role of MCH in blood analysis increases in the “company” of other erythrocyte indices, with which the described laboratory criterion is compared. First of all, this is MCV (average erythrocyte volume), followed by MCHC (average concentration of Hb in Er) and color index (CI), which is calculated out of old habit, out of interest or due to the lack of an automatic device, since it (MCH), in principle, corresponds to the CPU (in this regard, there is no need to repeat).
Of course, MCH in a blood test correlates with the number of red blood cells (the content of red blood cells in 1 liter) and the content of hemoglobin itself, since it is calculated using a formula based on their numerical values:
MCH = Hemoglobin (g/100ml) x 10 : red blood cell count (million/microliter)
It is obvious that an automatic machine, before calculating the average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell, will have to count red blood cells and red pigment in the blood.
A similar indicator of the Hb content in an erythrocyte is SGE (the abbreviation stands for), which is calculated in the same way (hemoglobin values are divided by the number of red blood cells) - this calculation formula is used if the laboratory does not have a hematology analyzer.
In general, you can show the data in a table, it will be more visual and understandable:
| MCH (average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell) | Norm, pg |
| Children under one year old | 28 – 35 |
| Children (from one year old) and teenagers (up to 16 years old) | 28 – 32 |
| Adults | 27 — 31 |
As always, the reader may become prematurely worried if he himself donated blood for research, having previously “studied” laboratory reference books, and then saw his results somewhat beyond the given norm. Not worth it. You just need to find out the laboratory reference values. Perhaps everything is as it should be in a healthy body.
MCHC in a blood test, what is it, how is the indicator determined, and what affects it
One of the important indicators of a general blood test is hemoglobin
The concentration of this substance in red blood cells has important diagnostic value in identifying diseases of the hematopoietic organs. The average value of hemoglobin content in one red blood cell is indicated by MCHC in a blood test: what this indicator is and how it is calculated is known to few
What does MCHC mean in a blood test?
The abbreviation MCHC in blood test results refers to the average concentration of hemoglobin in a red blood cell. This substance in its structure is a protein compound that is present in human blood. Hemoglobin is able to combine with oxygen molecules and transport it to the tissues of the body. In addition to the concentration of hemoglobin in the bloodstream (Hb), indicators such as MCH and MCHC are also determined. The first parameter reflects the concentration of hemoglobin protein in a single red blood cell. Essentially, it is the ratio of total hemoglobin to the number of red blood cells.
Doctors are often interested in such a parameter as MCHC in a blood test: most patients have no idea what this parameter is. MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration) – the average volume of the so-called corpuscular, bound hemoglobin. It reflects the volume of iron component in red blood cells. This parameter is used to confirm the MCH result, since these two indicators are mutually dependent.
MCHC blood test - transcript
Having found out how MCHC stands for in a blood test, what kind of abbreviation it is, let’s pay attention to the peculiarities of interpreting the results. When identifying blood diseases, doctors always take into account erythrocyte indices - the norm of these parameters changes with the patient’s age and depends on gender
At birth in children, these indicators are less important. The increase in MCHC in the analysis occurs with age. Taking these features into account, only a doctor can carry out an objective assessment of the research results.
MCHC blood test - interpretation, normal in women
With the onset of puberty and the establishment of the menstrual cycle, the concentration of MCHC is established at the same level. Every month, healthy girls experience menstruation. During this physiological process, blood is released from the uterine cavity along with endometrial cells. If a woman experiences heavy and prolonged menstruation associated with hormonal fluctuations, this negatively affects the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin. How MHCH changes, the norm for women, can be found in the table below.
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at maintaining the MCHC indicator within the acceptable range are reduced to:
- optimization of physical activity;
- increasing the amount of time spent daily outdoors;
- minimizing the impact of adverse production factors (to the extent possible);
- compliance with the principles of a balanced diet (the menu is supplemented with foods rich in vitamins, iron, amino acids and other valuable components in the proportions required by the body);
- giving up bad habits, strict diets, fasting, taking multivitamins, medications not prescribed by a doctor;
- undergoing regular medical examinations (especially during pregnancy);
- organizing timely treatment of diseases of the circulatory system and other associated pathologies characterized by changes in blood composition.
To share this article or leave a comment, use the form below.