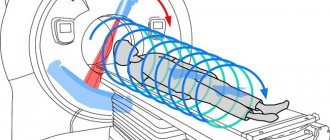
MRI of the abdominal cavity is one of the safest and most informative methods of examination using imaging. This examination does not imply the use of ionizing radiation, which has a detrimental effect on human health.
Magnetic resonance imaging can give an accurate result without the use of many complex and traumatic manipulations, using the influence of a magnetic field and radio frequency pulses.
What internal organs are examined using MRI?
The following are organs that can be examined using magnetic resonance imaging:
liver, gallbladder, condition of the bile ducts; pancreas; kidneys and adrenal glands; vessels and lymph nodes; spleen; gastrointestinal tract; ureter.
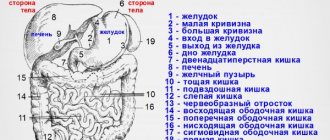
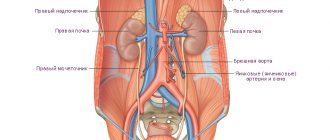
Anatomical projections of the abdominal organs
What is MRI and what is the diagnosis based on?
Most patients learned about what an MRI is and how it differs from the same ultrasound of the abdominal cavity relatively recently, about 15 years ago. This diagnostic method is a study using a powerful magnetic field created inside a closed loop. With its help you can see everything that is inside the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostic and control examination of the abdominal cavity MRI is carried out by exposing tissue to magnetic fields and radio pulses of a certain frequency. That is why the method got its name - MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging.
Obtaining 100% accurate results was made possible thanks to the influence of magnetic fields on hydrogen, which is a structural component of protein cells, DNA molecules, and bone tissue. During an MRI procedure of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, the atoms are magnetized and then begin to emit residual energy, which is captured by sensors. If there are pathological changes inside the abdomen, the characteristics of the return radiation deviate from the norm. It is these changes that are taken into account when interpreting the results of the study.
As a result of the diagnostic procedure, the doctor receives images of the organs and structures being examined, as well as the tissues and organs surrounding them in various projections (3D format) or in the form of layer-by-layer sections with different axes. In this case, the doctor can visualize pathologies of internal organs and structures, the location of stones and foreign objects, as well as surgical instruments (if magnetic resonance imaging is used for monitoring during minimally invasive procedures). The diagnostic result may look like a set of images in 2D format, or in the form of a three-dimensional model.
The key advantage of MRI over other methods is the identification of physiological processes in the examined area. If necessary, it can take place in real time.
What is revealed during an abdominal MRI examination?
An MRI can reveal:
Tumor growth processes (malignant and benign), cysts, metastases. The pathological nature of the development of organs, congenital in nature. Presence of foreign bodies or stones (for example, in the bile ducts). Various pathological changes in internal organs after injuries, as well as scars. Accumulation of pathological fluids. Hidden bleeding. Pathological processes in blood vessels, such as aneurysm or thrombosis. Ischemic processes. Fatty degeneration, pancreatitis, cirrhosis of the liver.
Types of aneurysms
What diseases affect the abdominal cavity?
When a bacterial infection enters the body, appendicitis can develop. Treatment is carried out using a surgical method, that is, the appendix is removed. Organ prolapse is often diagnosed. The stomach usually goes down first. Therapy includes proper nutrition prescribed by a nutritionist, exercise therapy and wearing a special belt - a bandage.
If intestinal obstruction develops or adhesions appear, surgery is performed. If adhesions cause obstruction, they are removed, but only for health reasons. In such cases, relapses are possible. For frequent exacerbations of obstruction, doctors recommend a slag-free diet.
If you have inflammation of the stomach, it is not necessary to see a doctor if the symptoms go away within a couple of days. It is important to drink more fluids to avoid dehydration. If the patient does not feel better on the third day, it is necessary to go to the clinic. Doctors will prescribe the necessary tests and comprehensive treatment. In most cases these are medications.
The most common disease in the retroperitoneal space is hemorrhoids. Pathology brings a lot of unpleasant sensations. In cases of unbearable pain, doctors perform surgical treatment. If the progression of the disease is moderate, therapy is carried out with medications, lotions, compresses and baths using herbal preparations.
An abdominal hernia is a congenital or acquired disease, as a result of which the large or small intestine protrudes through an opening in the abdominal cavity. Occurs during pregnancy, obesity or heavy physical exertion due to constant pressure on a certain point in the peritoneum. Another reason is strong pressure on the lining of the internal organs. The pathology is treated through surgery.
Contraindications for MRI
Along with numerous advantages, MRI has a certain list of contraindications:
the presence of electronic systems in the patient’s body, for example, a pacemaker; the presence of fragments or bullets in the organs; first half of pregnancy and breastfeeding; the presence of ferroalloy metals in the patient’s body; a state of fear and panic in a closed space (but if you warn a specialist about this in advance, you can find an acceptable way out); high sensitivity to contrast agent (in case of renal failure, contrast agent is not administered); some mental disorders (during the examination the patient exhibits violent behavior).
Possible risks
According to statistics, only 4% of patients are allergic to the components of the contrast agent. This is usually clarified during the preparatory stage. If an atypical reaction of the body begins during the scan, the doctor takes appropriate measures and provides emergency assistance. Everything you need for this is available in the X-ray room.
Another danger is associated with radiation exposure to the body. Since the radiation dose from CT is significantly lower than from conventional radiography, there is no point in fearing serious pathologies. However, to avoid risk, it is recommended to refrain from frequent scanning in this way. If it is necessary to conduct multiple checks, it is better to choose non-radiation diagnostic tools. For example, MRI or ultrasound.
Preparation for MRI of internal organs
An examination such as MRI of internal organs is carried out without specific preparation. The most important thing before an MRI procedure is to follow a diet. This diet begins one day before the scheduled procedure and includes avoiding the following foods: raw and cooked vegetables, various fruits, black bread, various carbonated drinks, kefir, cottage cheese.
For people who suffer from constipation or gas formation, it is recommended to give a cleansing enema or take a laxative. In order to prepare for high-quality MRI images, it is necessary to take activated charcoal immediately before the procedure, at the rate of one tablet per 10 kg of body weight, or the anti-flatulence drug Espumisan.
Half an hour before an MRI of the abdominal organs, the patient needs to take No-shpa; one or two tablets are enough. Also, preparation excludes the intake of any food for a period of 6-8 hours before the MRI examination.
Preparatory activities for diagnosis
Some types of ultrasound examination of internal organs require preliminary preparation. This is done in order to optimize the examination results as much as possible. Preparatory measures are usually not particularly difficult for the patient. The most unpretentious, in this regard, is the study of the thyroid gland, for which special preparation of the body is not required.
Before echocardiography, it is necessary to stop smoking, drink coffee and energy drinks, and limit physical activity. The longest preparatory measures are provided before a general ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys. In order not to distort the final results, three days before the ultrasound scan you need to change your eating behavior and start taking medications.
All foods that cause intense gas formation are excluded from the diet:
Transabdominal pelvic ultrasound
- cabbage;
- beans, lentils, peas and other legumes, and dishes made from them;
- fresh milk;
- baked goods and brown bread;
- pears, apples, grapes, radishes, radishes, cucumbers, tomatoes;
- sweet desserts.
Dietary nutrition involves foods that will be easily absorbed by the body. Portions should not be voluminous, maximum 350 g, every 3-4 hours. To the frequently asked question, is it possible to eat before an ultrasound, the answer is categorically negative. Residues of food will not allow the doctor to examine the organs, or the data will be interpreted incorrectly. Ultrasound is always performed on an empty stomach. Drinking regime before the procedure plays an important role.
The volume of fluid consumed per day should be 1.5 liters. You can drink water, juices and fruit drinks. Green and herbal teas are recommended. Soda and kvass are prohibited, they cause excess gas. The medicinal component of preparation for ultrasound diagnostics consists of taking carminatives (Espumizan, activated carbon) for three days. This is done in order to eliminate excess gases. On the eve of the examination, it is recommended to cleanse the intestines with laxatives (Lavacol, Forlax).
Before any study, drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
What can be seen with an MRI scan of the abdomen?
Using MRI, examinations of the abdominal organs, which are vital for the human body, reveal deviations that arise from certain diseases, the presence of malignant and benign tumors, various injuries to internal organs, as well as pathological deviations in size with an accuracy of 2-3 mm from norms.
An MRI scan shows disturbances in the functioning of each organ individually at the very initial stage. This makes it possible to study the nature of the disease before the first symptoms appear.
MRI of the pancreas
MRI of internal organs makes it possible to determine the course of the tumor and its exact location in the liver, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys using dynamic contrast, this is very valuable for diagnosing in oncology. This examination will help avoid a painful liver biopsy and laparoscopy procedure.
An MRI of the abdomen shows the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts. For this purpose, non-contrast cholangiography is used, which makes it possible to detect the presence of stones from one millimeter in the ducts. In order to assess the functioning of the urinary tract, non-contrast urography is used.
Non-contrast cholangiography
Also, the MRI examination includes viewing the pathological processes of the stomach and intestines, but this study of these organs is used as an auxiliary method, during which the localization of the tumor, the occurrence and spread of metastases, and changes in the lymph nodes are determined.
Colon cleansing before abdominal ultrasound
To obtain reliable ultrasound results, doctors often recommend bowel cleansing on the eve of the procedure.
This procedure can be carried out using an enema, but recently most people prefer an alternative method of cleansing the intestines - taking laxative medications: Senade, Senadexin or the drug Fortrans, which must be taken depending on body weight.
1 tablet or one sachet of laxative is designed for 20 kg of human body weight. As a laxative, you can also take drugs such as: “Normaze”, “Dufalak”, “Prelaxan”.
Before using any laxative, you should read the instructions for use or consult your doctor.
Progress of this study
In order to improve the quality and clarity of the image of the internal organs and tissues of the patient being examined, a contrast agent is used. The contrast agent is a specific medical solution containing gadolinium (a heavy metal that enhances image signals).
The contrast agent is a completely safe agent, does not affect the body, and this solution is administered intravenously, which takes about one to two minutes. Such a substance enters only those parts of the body where pathological processes occur and deviations from the norm are present. In this case, the properties of the pericellular fluid are not disturbed. The contrast is localized in the tumor, this gives a complete picture of the tumor with clear contours and boundaries.
Contrast agent
After an MRI examination, it is recommended to drink a large amount of fluid, this will facilitate the rapid removal of the solution from the human body.
Anatomical structure of the abdominal organs
The science of anatomy studies the structure and location of the internal organs in the human body. Thanks to it, people can find out the location of the insides and understand what hurts them.
A cavity consisting of muscles that performs storage, mixing and digestion of food. In people with food addictions, the stomach is enlarged. Located between the esophagus and duodenum. Thanks to pulsating contractions, which is part of the motor activity of the organ, it removes chemicals, poisons and other harmful substances from the body. This ensures a protective (immune) function.
In the gastric pouch, proteins are broken down and water is absorbed. All incoming food products are mixed and passed into the intestines. The quality and speed of food digestion depends on the gender and age of the person, the presence or absence of diseases, capacity, and efficiency of the stomach.
The stomach is pear-shaped. Normally, its capacity does not exceed one liter. If you overeat or absorb a large amount of liquid, it increases to 4 liters. This changes its location. An overfilled organ can sink down to the level of the navel.
Stomach diseases can be very painful, so you need to be attentive to any unpleasant symptoms that arise in it.
Gallbladder
Serves as a cavity for the accumulation of bile excreted by the liver. Therefore, it is located next to her, in a special hole. Its structure consists of a body, bottom and neck. The walls of the organ include several membranes. These are sulfur, mucosa, muscle and submucosa.
It is an important digestive gland for the functioning of the body. The weight of the organ in an adult often reaches one and a half kilograms. It is able to eliminate poisons and toxins. Participates in many metabolic processes. It deals with hematopoiesis in the unborn baby during the period of pregnancy by the mother, the absorption of glucose and cholesterol, and the maintenance of normal lipid levels.
The liver has an amazing ability to regenerate, but advanced diseases can seriously undermine a person's health.
Parenchymal lymphoid organ located behind the stomach, under the diaphragm. This is the upper part of the peritoneum. It consists of the diaphragmatic and vesceral surfaces with an anterior and posterior pole. The organ is a capsule filled with red and white pulp inside. It protects the body from harmful microorganisms, creates blood flow in the unborn baby in the womb and in an adult. Has the ability to renew the membranes of red blood cells and platelets. It is the main source of lymphocyte production. Capable of capturing and purifying microbes.
Pancreas
An organ of the digestive system, second in size only to the liver. Its location is the retroperitoneal space, slightly behind the stomach. The weight reaches 100 grams, and the length is 20 centimeters. The structure of the organ looks like this:
The pancreas has the ability to produce a hormone called insulin. It regulates blood glucose levels. The main function of the organ is the production of gastric juice, without which food cannot be digested.
A person cannot live without the pancreas, so you should know which foods are most harmful to this organ.
Small intestine
There is no longer organ in the digestive system. It resembles a tangled tube. Connects the stomach and large intestine. For men it reaches seven meters, for women – 5 meters. The tube consists of two sections: the duodenum, as well as the ileum and jejunum. The structure of the first department is as follows:
The second two sections are called the mesenteric part of the organ. The jejunum is located at the top on the left side, the ileum at the bottom in the right region of the peritoneum.
Colon
The organ reaches one and a half meters in length. Connects the small intestine to the anus. Consists of several departments. Feces accumulate in the rectum, from where they are removed from the body through the anus.
What does not enter the digestive system
All other organs “living” in the peritoneal area belong to the genitourinary system. These are the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, and also the ureters, female and male genital organs.
The buds are shaped like beans. Located in the lumbar area. The right organ is comparatively smaller than the left. The paired organs perform the cleansing and secretory function of urine. Regulate chemical processes. The adrenal glands produce a number of hormones:
- norepinephrine;
- adrenalin;
- corticosteroids;
- androgens;
- cortisone and cortisol.
From the name you can understand the location of the glands in the body - above the kidneys. Organs help people adapt to different living conditions.
Important! Thanks to the adrenal glands, a person remains resilient in stressful situations, which protects the central nervous system from negative influences.
The appendix is a small organ of the peritoneum, an appendage of the cecum. Its diameter is no more than one centimeter and its length reaches twelve millimeters. Protects the gastrointestinal tract from the development of diseases.
How is this procedure done?
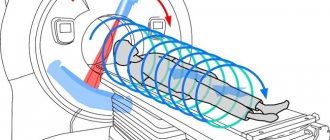
An MRI examination is a rather long process, which takes from half an hour to two hours. The examination itself is carried out by a doctor who specializes in tomography, and a radiologist interprets the results.
Preparation for the procedure includes the need to remove all jewelry (chain, earrings, etc.). It is forbidden for any metal parts to be present on clothing, so it is necessary to remove everything from pockets that could interfere with the examination, for example, a telephone, keys, coins.
The patient is placed in a special scanner in which he will be able to feel air movement and hear sounds. The procedure is performed with the patient lying on his back. During the examination, you should not make any movements, otherwise the image may turn out blurry.
MRI examination
Before an MRI, some patients may be restrained with straps to prevent involuntary movements. The specialist conducting the examination, if necessary, may ask you to hold your breath.
For the comfort of patients, some MRI machines have built-in televisions; also, if the patient feels chilly, he can be covered with a blanket, this will not affect the image in any way.
Procedure
An MRI is a procedure that can take anywhere from half an hour to two hours. The doctor conducting the examination must determine how long the procedure will take, taking into account which abdominal organs will be examined. In the future, the results obtained need to be deciphered and this will be done by an experienced radiologist.
The procedure should be carried out only after the patient has completed all the necessary recommendations and has also removed metal jewelry. It is strictly forbidden to begin the study if there are metal products in the patient’s clothing or on the body.
Subsequently, the patient is placed on a horizontal surface that enters the scanner. The person being examined will feel the movement of the air mass and sounds, so from a psychological point of view, the person will be quite comfortable. Throughout the entire study, the person lies horizontally and, preferably, motionless. If you neglect these requirements, the image will turn out blurry.
Before the CT scan, some patients are secured with special straps to avoid various movements. Experts also ask you to hold your breath. For a comfortable procedure, modern MRI machines have mounted TVs and headphones for listening to music. To increase comfort, some patients are offered blankets.
When preparing for an MRI examination, it is advisable to adhere to a carbohydrate-free diet for 24 hours.
Decoding the results
Deciphering the results of an MRI of internal organs takes about two to three hours after the examination, but can take a couple of days. It happens that immediately after the end of the procedure, the specialist can tell you about the preliminary results. Sometimes MRI images show some abnormalities in tissues and organs that are examined for the first time and in appearance and size are in a normal, healthy state.
MRI images of the abdomen
Decoding results
Indicators of ultrasound examination of organs have certain standards. The doctor examines the data obtained during the examination, compares them with the norm, and assesses possible inflammatory and other pathological processes. Each area of research has its own digital indicators:
- length and width dimensions;
- fabric density;
- echogenicity;
- Wall thickness.
The shape of the organ is assessed and must be anatomically correct. The ideal outline is a clear and even contour, the structure is homogeneous (homogeneous). The location of the organ in the body must correspond to the standard anatomical one. The final protocol reflects all existing changes. You should not self-diagnose. Only a doctor should decode the ultrasound results.
Deciphering the results by a qualified specialist does not take much time. After about an hour, the patient has an idea of the state of his health
Ultrasound is an informative technique that gives a complete picture of the condition of the soft tissues of organs. However, there are situations when the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis. In this case, the best option would be to undergo an additional examination with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
What are normal indicators on MRI?
Normal indicators:
there are no signs of infectious or inflammatory processes; the size of the abdominal organs must be within normal limits and have the correct location; proper functioning of blood vessels, without any deviations; absence of tumor formations; absence of blockages in the ureters; ducts of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder without plugs; absence of bleeding, accumulation of abnormal fluid; absence of blood flow obstructions and vascular aneurysms.
Deviations from normal indicators are the following:
The internal organ of the abdominal cavity that is being examined is too enlarged or has a much smaller size than normal, its location is disturbed. Various scars or injuries may be present; the presence of a tumor formation, both malignant and benign. It is possible to detect various signs of infectious processes; the presence of fluid that should not be there, this may indicate internal bleeding and infections; the presence of an aneurysm on the vascular walls; if the blood vessels are clogged, narrowed; if the bile ducts have plugs (they are provoked by gallstones, neoplasms, inflammation and infectious processes; if blockages are visible in the ureters (tumor formations, the presence of kidney stones, infections contribute to this).
In most cases, before an MRI, an examination using ultrasound and CT is prescribed. Further examination after MRI includes ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, which will help in prescribing treatment for pathological processes of internal organs).
What does the study show?
Diseases that ultrasound helps reveal are collected in the table:
| Organ | What can you see |
| Pancreas | The study allows you to detect compaction and swelling of the gland tissue - a direct sign of pancreatitis . In addition, it is quite easy for a doctor to notice space-occupying formations: cysts, tumors. Sometimes fatty infiltration is found. |
| Liver | Using ultrasound, the doctor sees diffuse structural changes, which are a sign of hepatitis or cirrhosis . The color rendering function allows you to highlight individual areas of tissue necrosis and parasitic infestation (echinococcosis). There are criteria for diagnosing portal vein hypertension, which is a sign of liver failure . In patients with excessive body weight, fat deposits are found. |
| Gallbladder and bile ducts | Ultrasound makes it possible to detect stones (calculi) in the bladder or ducts. Hardening of the gallbladder wall indicates chronic cholecystitis . An experienced physician will notice areas of bile stagnation, which is a sign of cholestasis and bile duct dyskinesia. |
| Spleen | With an increase in the size of the organ, splenomegaly - a symptom of many somatic diseases. Also pay attention to the presence of additional shares. |
| Stomach | Ultrasound makes it possible to detect abnormalities in the development of the stomach (which is especially important in infants), chronic inflammatory processes ( gastritis ), and defects of the mucous membrane ( peptic ulcer ). |
| Intestines | During the examination, the doctor examines intestinal permeability and the presence of feces ( coprostasis ). Changes in wall thickness or unevenness can be symptoms of inflammatory diseases ( ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, appendicitis ). Using Doppler ultrasound, the patency of the mesenteric vessels is monitored. |
| Large vessels (aorta, inferior genital vein) | Dilatation of the inferior pudendal vein is one of the signs of right ventricular heart failure . The longitudinal dimensions of the aorta are measured to detect an aneurysm of its abdominal section . |
What organs does ultrasound examine?
What does an ultrasound of the human body show? The condition of the organ (its size, wall thickness, tissue structure), its location, the presence of pathological inclusions, and characteristic signs of inflammatory processes, developmental abnormalities, etc.
What organs and systems can be examined? In the ultrasound diagnostic technique, independent categories of examined organs and systems are identified. This is done for the convenience of the doctor and the patient, because... Some organs are usually examined together.
The study of the hepatobiliary system, spleen, and pancreas is classified as ultrasound of the abdominal organs (AUS). Examination of the gallbladder and ducts can be performed separately as monitoring of the course of cholelithiasis. A number of clinics and medical centers perform ultrasound examinations of the stomach, esophagus and intestines. Such an ultrasound is informative only for identifying individual pathological processes, such as tumors, diverticula, etc.
Some clinics offer ultrasound examinations of the stomach, esophagus and intestines. It is especially successful in identifying various neoplasms and assessing their location in order to prepare for surgery.
A separate category is ultrasound of the retroperitoneal organs. This category includes: study of the condition of the kidneys, adrenal glands and ureters. If the Doppler scanning function is available, the condition of the arteries and veins of the renal vasculature can also be studied.
The category of pelvic ultrasound includes the diagnosis of a woman’s reproductive organs (uterus, ovaries), prostate gland (men), bladder, as well as lymph nodes and the vascular system that provides blood supply to these areas. Ultrasound examinations occupy one of the leading places in research:
myocardium; great vessels; large joints; lymph nodes; lungs and pleura (to identify certain types of pathology).
Diagnosis of the mammary and thyroid glands is also actively carried out using the ultrasound method. Despite the fact that these organs are not considered truly “internal”.
How to check internal organs?1
With the help of such an examination, you can examine the liver, gall bladder, pancreas and spleen, bile ducts, kidneys, and prostate in men. If you are concerned about pain in the upper abdomen or a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth, increased gas formation in the intestines, then you need to consult a therapist or gastroenterologist, who in turn will refer you to an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. It is advisable to do this ultrasound examination every year for the timely detection of serious disorders in the functioning of internal organs. During ultrasound, the size of the liver, its position, shape, ability to transmit ultrasonic waves, structure, condition of the vessels and bile ducts, the presence of foreign formations (for example, stones), shape, condition of the walls, size of the gallbladder, its position, condition of bile, presence of foreign formations, structure, shape, position, ability to transmit ultrasonic waves, condition of the pancreatic duct, study the condition of the bile ducts (measuring their lumen). The same scheme is used to evaluate the pancreas, spleen, and kidneys. At the end of the study, the general condition of the upper abdominal cavity is assessed.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder serves to store bile and release it into the lumen of the duodenum after eating. The study evaluates the size and shape of the gallbladder, the thickness and condition of its walls, and contents. Deformations of this organ in the form of kinks and septa are often encountered. They refer to abnormalities in the development of the gallbladder that are inherited. In themselves, such deformations are not a pathology, but they predispose to the development of various diseases of the gallbladder: dyskinesia - a violation of the contractile (motor) function of the gallbladder of the biliary tract, cholecystitis (acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder), cholelithiasis (formation of stones). in the gallbladder and bile ducts). Note that stones can be an accidental discovery, that is, they can be detected even if the person being examined has no complaints.
Pancreas
The pancreas produces enzymes that, when released into the intestines, ensure the digestion of food. The pancreas also produces the hormone insulin, which is necessary for the absorption of glucose. During the study, the size and internal structure of the pancreas is assessed. This organ is very sensitive and “delicate”, therefore it reacts to many changes occurring in the body: allergic manifestations (bronchial asthma, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, dermatitis), viral infections (ARVI, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, herpes and other infections) and parasitic infestations . These are so-called secondary changes in the pancreas. But there are changes that are associated with dysfunction of the pancreas itself. This is inflammation of the pancreas, cysts, abscesses of the gland. Diseases such as diabetes, obesity and various metabolic changes also lead to changes in the structure of this organ.
Spleen
The spleen is involved in the production of blood cells, utilizes used red blood cells, and participates in the production of antibodies. The study evaluates the size of the spleen and its internal structure. The spleen is an organ directly involved in all immune responses, so it responds by increasing its size to viral diseases of the body (intracellular infections, parasitic infestations). In addition, cysts (in particular, hydatid cysts), abscesses and tumors can be detected. Due to the characteristics of its structure (thin capsule, loose, spongy structure), the spleen most often suffers from injuries to the abdominal cavity.
Liver
The liver is a very important organ; it is called the biochemical laboratory of the body. The liver is involved in all types of metabolism (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), all blood proteins are formed in it, and it also ensures the removal of harmful substances and metabolic products from the body. The liver is also involved in the processes of hematopoiesis.
When examining the liver, calculi (stones), hemangiomas (vascular tumors), enlarged lymph nodes, which are more common in various viral infections (hepatitis), echinococcal cysts (bubbles filled with liquid in which the larva of the echinococcus parasite develops and which are not detected) can be detected during a routine examination by a doctor and are not felt by the patient), as well as various other liver diseases.
Stomach and duodenum
The stomach and duodenum are also examined using ultrasound. After food passes into the mouth and esophagus, it enters the stomach and then the duodenum. In the stomach, it is mixed, exposed to hydrochloric acid, and in the duodenum, food is exposed to pancreatic enzymes, since the pancreatic duct opens into this section of the digestive tract.
The study evaluates the thickness of the stomach walls, the presence or absence of secretions in them. Signs of hypersecretion (increased production of digestive juices, the presence of fluid in the stomach cavity even on an empty stomach) are indirect ultrasound symptoms of gastritis.
Ultrasound is performed with the patient lying on his back. Sometimes, to get a better picture, the doctor asks the patient to turn on his right or left side, take a deep breath, and hold his breath. Some patients with individual characteristics (for example, with a high position of the spleen) have to be examined while sitting or even standing. A transparent gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen, which does not cause allergic or other unpleasant reactions. The gel is applied to fill the air gap between the patient's skin and the ultrasound transducer, which otherwise does not allow ultrasound waves to penetrate deep into the tissue. After this, the doctor conducts a study. To improve visibility, it is often necessary to take a deep breath and hold it. Ultrasound is performed in real time, so the result becomes obvious by the end of the study.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor writes a research protocol with a conclusion.
Preparing for the study
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs can be performed both in the morning on an empty stomach and after 12:00. If the study is carried out after 12:00, then you can have breakfast at 7–8 in the morning, after which you should not eat food. You can drink water. 1-2 days before the test, it is advisable to exclude gas-forming foods from the diet - raw vegetables, dairy products, brown bread, legumes. Otherwise, many organs may be “covered” by swollen intestinal loops, and their examination will become impossible. If the patient has diabetes, a light breakfast (warm tea, crackers) is acceptable. Before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, it is not recommended to chew gum or suck hard candies. Smoking is also undesirable, as this can lead to stomach spasms and ultimately to an incorrect diagnosis. If the patient takes medications regularly, then they should not be discontinued, but the doctor must be notified about this. If the patient is prone to gas formation and is overweight, it is recommended to take activated carbon (2 tablets 3-4 times a day) 2-3 days before the test.
You can sign up for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs at the Latgale Medical Center in Daugavpils, st. Rigas, 20, or by phone 25251010.
We will be happy to help you quickly, efficiently and confidentially!
IMPORTANT!
Before a planned pregnancy, along with a consultation with a therapist and gynecologist, it is especially important to visit an ultrasound diagnostic room: during the examination, “accidental findings” are possible, which must be eliminated before pregnancy. Firstly, during pregnancy, increased demands are placed on the mother’s body, which can lead to the manifestation and exacerbation of various diseases. Secondly, the possibilities of drug treatment during pregnancy are limited due to the likelihood of negative effects of drugs on the fetus.
Hepatobiliary system: norm and pathology
The liver, when examined by ultrasound, should be clearly visible and have a high-density, uniform structure. With clear visualization of the lobes and the large vessels supplying them.
The liver is very clearly visible on ultrasound due to its dense structure. In addition, ultrasound shows the vascular system of the organ and allows you to evaluate its characteristics
An ultrasound scan of the liver can reveal echo signs of inflammation (hepatitis), cirrhosis, primary neoplasms and metastatic tumors. Signs of parasitic liver damage (schistosomiasis, echinocococosis), cysts with serous and purulent contents, and hematomas can also be detected.
Normally, the gallbladder is located under the liver, low echogenic, and pear-shaped. The wall thickness does not exceed 3 mm, the width of the lumen does not exceed 4 cm.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system can reveal changes in the localization of the organ, developmental abnormalities, spastic conditions of the gallbladder and its ducts, changes in size and shape due to congestive or inflammatory processes. Diagnostics shows the presence of foreign inclusions (concriments, cystic formations, tumor processes and abscesses), as well as pathological compression by the tumor in adjacent tissues.
Ultrasound data of the spleen and pancreas
In the absence of a pathological process, the spleen on ultrasound is moderately echogenic, has clear contours, a crescent shape and is located towards the top of the abdominal cavity on the left. The main vessels and their places of entry into the organ are clearly visualized.
During the examination, echo signs of an increase in the size of the spleen may be detected, which is a sign of severe anemia, liver pathology or an infectious process. The following pathologies can also be identified: oncological processes of varying quality and degree of development, cystic formations with serous and purulent contents, parasitic lesions, abscesses.
In a healthy state, the pancreas has a homogeneous structure; ultrasound standards of the pancreas are: 2.8 cm - head, 2.5 cm - tail, 2 cm - body. Atrophy, a number of tumors and senile changes lead to a decrease in the size of the spleen. Ultrasound also allows you to identify echo signs of inflammatory processes and neoplasms (enlarged spleen, nodes) and cystic lesions of the spleen, abscesses.
Research technique
Before starting the ultrasound procedure, the examinee removes metal jewelry. He is placed on the couch in a supine position. During the process, the doctor will ask the patient to change position, turning over to the left or right side.
The examination is carried out abdominally, that is, through the anterior wall of the abdomen. A special conductive gel is applied to the abdomen, which improves the glide of the sensor over the body and helps reduce interference in the image.
The procedure is completely painless and takes no more than 20-30 minutes.
The examination algorithm involves performing an ultrasound of larger organs first. For example, a physician might start with the liver. It evaluates and records the size of the liver, its location and shape, structural features and ability to transmit ultrasonic waves, as well as the condition of the blood vessels.
Next, the doctor proceeds to examine the gallbladder and bile ducts:
- their forms;
- structure and condition of the walls;
- presence or absence of foreign inclusions;
- bile conditions.
The diagnostician checks the position of the pancreatic duct, the lumen of the biliary tract, the portal, inferior and splenic veins. Next, he evaluates the condition of the spleen, pancreas and kidneys according to a similar scheme. At the same time, the doctor must remember that examining the pancreas is often difficult due to the peculiarities of its anatomical location - it is partially overlapped by the intestines and stomach.
To visualize the spleen, the patient is placed on the right side. Access to it is also a little difficult, since it is surrounded by ribs and lungs.
In some cases, during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the bladder is also examined.
Norm and pathology in ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
Normally, the intestine is moderately echogenic and has uneven edges of the mucosa. The abdominal cavity has no fluid inclusions, the walls of the stomach are not thickened or ulcerated. As a result of an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract, the following can be detected: ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines, intestinal obstruction, diverticulosis, oncopathology, cystic formations of the esophagus, abscesses of the stomach or intestines. As well as echo signs of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity as a result of injury to a section of the intestine, rupture of the appendix, urinary or gallbladder, etc.
Diagnostic results
For professional doctors, decoding an MRI of the abdominal cavity is not difficult, but it still takes from several hours (if necessary, to make an accurate diagnosis in a short time) to 3 days. The patient receives a doctor's report, which cannot be considered a diagnosis. It will be diagnosed by the attending physician based on the facts stated by the specialist.
MRI interpretation is prepared in the form of a package of documents, which includes:
- photographs (sections) of the examined organs and systems in printed form or on electronic media;
- forms with explanations from a specialist regarding recorded changes in the structure, position of internal organs, the presence of neoplasms in them, and so on.
The listed materials must be given to the attending physician, who recommended an MRI.
Ultrasound signs of pathology of the genitourinary system
Normally, the kidneys on ultrasound are paired organs, located on both sides of the spinal column, have a homogeneous structure, the pelvis does not contain foreign inclusions (sand and stones). The kidney dimensions are approximately 10*6*4 cm (length*width*thickness).
The ultrasound method allows us to detect the absence of one of the paired organs, echo signs of inflammatory processes, hematomas, neoplasms, abscesses. Stones and sand in the kidneys are also well located.
The diagnostician can easily see the inflammatory process in the kidneys and determine the presence of stones - one of the most common abnormalities in the functioning of the excretory system
In its normal state, the bladder is an ovoid, tapering towards the top. Its volume is 0.35-0.75 liters for men and 0.25-0.55 liters for women. Wall thickness is up to 4 mm, the walls are smooth.
Ultrasound of the urinary system allows you to diagnose urolithiasis, hypertrophy of the walls of the bladder, as a sign of inflammation, and determine the echo signs of an oncological process affecting the walls of the organ.
Features of abdominal ultrasound in children
Ultrasound in infants is of particular interest, since in children one year and older, ultrasound is virtually no different from that in adults. Young children are referred for an abdominal ultrasound if:
- the presence of congenital pathologies;
- abdominal injuries;
- abdominal pain and fever of unknown origin;
- routine screening, which is mandatory during the neonatal period.
Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the digestive and excretory systems, namely: liver, bladder and ureters, kidneys, gall bladder, pancreas, stomach, intestines. The retroperitoneal space, adrenal glands, arteries, veins and nerve plexuses must be examined.
The procedure is carried out according to the same principle as the examination of an adult, but in the presence of one of the parents, who helps to hold the baby.
This study is necessary to exclude (or confirm) congenital pathologies, confirm the normal condition and functioning of organs according to age standards.
Ultrasound examination of the reproductive system organs
Ultrasound of internal organs also includes examination of the scrotum. The testicle of an adult healthy man measures 5*3 cm. The epididymis are visualized nearby. Ultrasound scanning reveals the following pathologies: neoplasms and inflammatory lesions, traumatic lesions, hydrocele, inguinal hernia, varicocele, pathological twisting of the spermatic cord
The digital characteristics of the condition of the female genital organs are influenced by whether the woman has given birth or not, the day of the cycle, and age. The only thing that remains constant is the location of the pelvic organs in women. The body of the uterus is tilted anteriorly; as a variant of the norm, the bend of the uterus towards the rectum can be considered. The ovaries are located on the sides.
The ultrasound examination method allows us to identify developmental abnormalities, inflammatory processes and neoplasms affecting the fallopian tubes, ovaries and the uterus itself. An ectopic pregnancy and varicose veins of the small pelvis can be diagnosed.
Ultrasound of the uterus and other organs of the woman’s reproductive system is done not only during pregnancy. The study allows, among other things, to identify the causes of pain, neoplasms, and organ development abnormalities
How they do it and how much it costs
The procedure is almost always performed externally; in exceptional cases, the ultrasound receptor sensor must be placed inside the vagina (in women) or rectum (in men). Otherwise, this is the least invasive technique, which is especially important when examining children.
To study the condition of blood vessels and the nature of blood flow in the abdominal cavity, a relatively new form of ultrasound is prescribed - Dopplerography. The sensitive sensor is capable of measuring the length of the ultrasonic wave reflected from a dynamic object.
In private clinics, the lower price limit for ultrasound of internal organs is 500 rubles, the average range is from 1 to 2 thousand rubles. As a rule, subjects do not have to buy the gel themselves; for reference, its price is in the range of 100-200 rubles per liter (varies based on viscosity, delivery conditions and the presence of additional components, such as hypoallergenic aloe vera extract). Ultrasound also includes negligible trivial expenses - wipes to remove gel from the skin, shoe covers, and so on.
For children
Ultrasound screening is recommended to be done at a very early age in order to identify deviations from the norm - it examines the internal organs (including brain structures) of the child, its tissues, cartilage and joints. The preparatory measures are always the same: the child is placed on his back or side, a sound-conducting gel is applied to the skin in the area under study and sensors are placed, after which the procedure begins.
When analyzing the condition of the joints, they scan in several phases, changing the position of the limbs (in a bent and unbent state, moving the leg and arm to the side) in order to collect a comprehensive picture.
For adults
For adults, the situation is little different: the patient lies on his back or side, a gel is applied to the skin, a sensor is applied, and scanning begins. It is not accompanied by vibrations, tingling or other unpleasant sensations (except in possible cases in the presence of irritation or injury - but this is no longer the fault of the equipment). Periodically, you may need to hold your breath for a few seconds to improve visibility.
The average duration of an ultrasound is 10-20 minutes.
How often can an ultrasound of internal organs be done?
Given the extremely weak effect of ultrasound on cells and tissues - at least in the context of clinical settings, when the intensity of the sound waves is low - ultrasound cannot directly generate any side effects, and there is no “ceiling” on the number of times a complex ECHO can be done internal organs. On the other hand, frequent repeated preparation - restricting the diet, measures to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract and others - sooner or later can lead to exhaustion, imbalance and deficiency of substances in the body, so you should carefully schedule a visit to the doctor. For preventive purposes, the norm for ultrasound is no more than once a year (provided there are no chronic conditions that require more frequent screening).