As you know, both magnetic resonance and computed tomography are very valuable diagnostic techniques that are prescribed to patients to identify a wide variety of pathologies. They are often used in cases where it is necessary to clarify the results of other studies. Often patients even undergo these procedures without a doctor's referral. In this case, the question often arises: what are the differences between MRI and CT, what to choose, and which method is better?
It must be said that the very formulation of this question is fundamentally incorrect. Despite the fact that both procedures are performed in a similar way and end with the production of images, their essence, results and indications for their use are in many ways different. Let's look at the differences between MRI and CT .
How are the methods different?
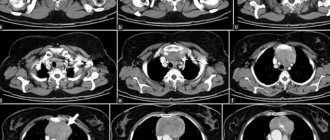
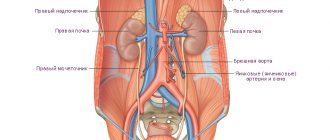
Computed tomography is a type of x-ray examination. Its main principle is the creation of layer-by-layer images of the organ under study, through which X-rays pass in a narrow beam.
Different tissues of the human body absorb these rays differently. As a result, the radiation is attenuated. This coefficient is recorded by special sensors, and the radiologist receives sections of any area of the human body. By processing the received data, it is possible to reconstruct the spatial image of the object on the monitor screen.
CT principle
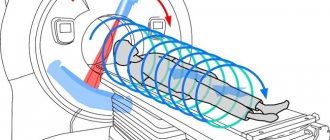
Magnetic resonance imaging is a slightly different study. It is based on the physical phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. When performing a study, the patient is placed in a powerful magnetic field, and an impulse is applied to the organ being studied, which changes its internal magnetization. After this influence ceases, the magnetization returns to the initial level. Its changes are repeatedly read by the computer. As a result, a three-dimensional image of the object under study is formed.
What is the difference between a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and a computer scanner?
How does CT differ from MRI? For examination in a computed tomograph, specialists use X-rays, which are characterized by significantly lower intensity than in an X-ray machine. Due to the narrowly focused beams, the device scans the body only at a certain point.
During MRI, a reaction occurs at the atomic level. This is the peculiarity of the method. Electromagnetic radiation has no effect on the human body. After this examination, no changes in body parameters were detected. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner is designed in such a way that only hydrogen atoms react to its electromagnetic field. Since the amount of water differs in different organs, the reaction occurs with varying intensity. This is precisely what the secondary radiation detector records.
Information after tomography is displayed via a computer and takes the form of images, 3D models of the organ. Photos, if necessary, can be transferred to digital media.
Indications
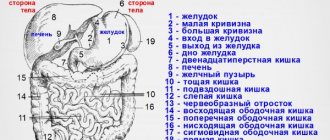
In gastroenterology, the main diagnostic methods are radiological and endoscopic. Of the radiation methods, ultrasound is the most widely used. CT and MRI are prescribed by doctors as additional diagnostic procedures to identify focal formations (tumors), diseases of the liver, spleen and pancreas.
Table 1. Indications for use.
| MRI | CT | |
| Abdominal injury | Violation of integrity, bruises of soft tissue structures | Foreign bodies, damage to parenchymal and hollow organs, hematoma formation |
| Study of the structure of the abdominal organs | Benign and malignant neoplasms, metastatic lesions, cysts, inflammatory diseases | The same, plus liver cirrhosis is clearly visualized |
| Assessment of the functioning and condition of the biliary tract | Tumors, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, clarification of the severity of pathological changes in inflammation of the gallbladder and common bile duct | Same |
| Stomach examination | Detection of oncological pathology, assessment of the prevalence of the tumor process (damage to lymph nodes, germination of nearby structures) | Same |
| Bowel examination | The need to distinguish benign from malignant formations; Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis (virtual colonoscopy) | |
| Lymph node examination | Distinction between tumor and inflammatory infiltration, metastatic lesions | Same |
| Visualization of abdominal vessels | Vascular anomalies, aneurysms, vascular obstruction, narrowing, blood clots | Same |
Help The doctor prescribes CT and MRI to study the structure of internal organs that are technically difficult or for some reason impossible to examine using X-rays and ultrasound, as well as in complex diagnostic cases to clarify the data of these studies.
Comparative characteristics
Which is better: CT scan or MRI of the abdomen? The abdominal cavity contains most of the body's vital organs - the digestive, urinary and endocrine systems. Any organ included in the listed systems can be examined.
If the question concerns the information content of the organs being examined, then both tomographs will be able to distinguish between malignant neoplasms and the peculiarities of the functioning of all systems. MRI and CT will scan the stomach well and determine pathologies of the intestines and kidneys/liver. However, MRI will not show stones in organs, so to diagnose sand and stones in the kidneys/gallbladder, you need to choose CT.
What else can’t a magnetic tomograph handle? He will not be able to clearly visualize the skeletal system due to the peculiarities of the magnetic field - in dense structures there are not sufficient quantities of hydrogen molecules. A resonance tomograph works not with the organ itself, but with the hydrogen molecules in it. Therefore, scanning of the skeletal system can only be done using X-rays, as well as the abdominal lymphatic system.
Advantages of MRI:
- children can be examined from birth;
- the procedure is harmless to the body;
- no need to take tests before the examination;
- Pregnant/nursing mothers can be examined;
- universality of diagnostics - a complete examination of the body in one procedure.
However, the cost of diagnostics is high - from 3,000 rubles. and higher. This is a big minus. Therefore, patients choose computed tomography or ultrasound.
Advantages of CT:
- low cost compared to MRI;
- you can be examined with implants in the body;
- there is no need to be immobilized for a long time;
- detects stones/sand well in cavities;
- clear visualization of bone structures;
- ability to identify tumors, cysts and internal bleeding.
Computed tomography can completely replace resonance if there are no contraindications to X-ray irradiation.
Contraindications
Limitations in the use of CT are associated with the effect of ionizing radiation on the patient’s body. This study is contraindicated in pregnant women. It is not advisable to prescribe it to women who are breastfeeding. Due to the technical capabilities of the device, it is not performed on patients weighing more than 150 kg.
Enhanced CT has additional contraindications:
- impaired liver and kidney function;
- allergy to contrast;
- serious condition of the patient (coma, shock of various nature);
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Although MRI is considered a safer study, it also has its contraindications:
- metal objects in the human body (foreign bodies, fragments);
- ferromagnetic implants (dentures on metal pins, pacemakers, artificial joints, heart valves, automatic medication dispensers, metal osteosynthesis devices, clamps and clips on blood vessels after surgery, hearing aids).
Under the influence of a magnetic field, they can change their temperature, move when heated and damage surrounding tissue.
Carrying out MRI in patients with fear of closed spaces causes certain difficulties. In this category of people, the study can be performed provided that open-type tomographs are used.
It is difficult for young children, restless patients, and those with neurological pathologies to remain motionless for some time, which is necessary to obtain a clear image. In such cases, they resort to short-term anesthesia (medical sleep).
Features, advantages of CT and MRI
Many patients prefer CT only because this study is cheaper. The effectiveness of the research at an affordable price is quite high. MRI is somewhat more expensive, but it is worth pointing out its important advantage, which is the safety of the study. This diagnostic method can be performed without restrictions, unlike CT.
CT diagnostics are based on the principle of scanning with X-rays, and MRI is based on the principle of the influence of a magnetic field on hydrogen atoms that fill all cells of the body.
CT is used for the most accurate examination of any area of the body. This method is considered to be the most accurate in the study of cancer. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to obtain tissue sections literally down to 0.5 mm. To improve visualization, specialists administer contrast agents.
CT has the following advantages:
- Short duration of the procedure.
- The opportunity to study all processes in the body.
- To make an accurate diagnosis, you can perform the required number of sections.
MRI provides data about all internal organs, their features, location, size, shape. Thanks to it, it is possible to trace the relationship of pathological processes with other organs.
The advantages of MRI are:
- No repeated ionizing radiation.
- Visualization of inaccessible changes in brain tissue density.
- Obtaining an image in any projection.
- Visualization of sections of the skull, spinal cord, brain, spinal column.
- The fastest possible detection of certain anomalies (Arnold-Chiari, corpus callosum, areas of cerebral ischemia, brain abscesses, contusion areas, areas of brain tissue edema).
- Discovering the causes of dementia.
- Providing valuable information on sagittal slices. Shows the condition of the intervertebral discs, vertebrae, and ligaments.
Which study should you choose?
It is impossible to say with certainty that one procedure is better than another. Each of them has its own differences, pros and cons.
Advantages
Thanks to the development of computed tomography, doctors have the opportunity to study in detail the structure of organs in the body of a living person, without violating the integrity of the skin or penetrating into its cavities. In this case, it is possible to consider even small structures smaller than a centimeter in size and to distinguish nearby objects from each other with minimal differences in density.
Moreover, on the monitor screen, if necessary, you can change their sizes. CT opens up opportunities for a detailed study of pathological changes (their location, size, structure).
Please note: The disadvantages of the method include radiation exposure and complications associated with the use of contrast.
MRI is an extremely valuable research method. Let's take a closer look at its advantages:
- does not harm the patient’s health;
- not associated with radiation;
- makes it possible to scan in different projections and at different angles;
- visualizes soft tissue well (muscle, fat and cartilage);
- allows you to examine the vascular bed without introducing contrast;
- can be used in children and pregnant women.
CT scan
Let's look at the features of a computed tomograph. The examination is carried out using x-rays, as with conventional fluorography. This is a significant disadvantage of this type of diagnosis. Compared to MRI, CT scans do not take much time - there is no need to remain in a fixed position for a long time.
In addition to this advantage, there are other positive features of CT:
- the procedure can be performed with any implants in the body - metal and electronic;
- the examination is not contraindicated for those suffering from claustrophobia and epilepsy;
- the device does not create much noise during operation and does not cause discomfort;
- the cost of the examination is much cheaper than using a magnetic tomograph.
Note! Modern computed tomography offers an improved research method using spiral diagnostics: its second name is multispiral.
What does it mean? This is a layer-by-layer scanning of the organ being studied, as with MRI. The device creates about 300 images in different planes in one revolution. Thanks to spiral scanning, it became possible to obtain objective information about the cavitary organs and soft tissues, which was previously impossible.
The cost of MSC tomography is higher than that of conventional computer tomography, but good informative results are obtained. How is a patient examined using a spiral tomograph? The same as with conventional computer diagnostics.
Comparison
What's better? Let's summarize.
| CT | MRI | |
| What is the method based on? | Exposure to ionizing radiation | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| Evaluation of results | Informative (better visualizes hollow organs and various injuries) | Informative (reliably identifies the tumor process, allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels and soft tissues) |
| Tolerability of the procedure | Possible complications | Well tolerated, but some patients find it difficult to remain motionless for long periods of time |
| Its duration | Up to 10 minutes | 30-40 minutes |
| Safety | Radiation exposure; side effects associated with contrast administration | Safe |
| Price | High | 1.5-2 times higher |
Cardiac MRI with contrast
To improve the degree of visualization, an MRI of the heart is performed with contrast - a special substance that colors the walls of blood vessels and makes them visible to the magnetic field. The need to use contrast is determined by the attending physician. In some cases, the need to administer a contrast agent arises during the procedure if this will lead to a more accurate diagnosis.
Today, many clinics perform cardiac MRI with gadolinium. Preparations based on this rare earth element are absolutely safe for health, practically do not cause allergic reactions and allow you to get a clearer picture of the condition of the blood vessels.
What does a CT scan show?
Most often, computed tomography is used to study organs of a hollow structure, including the stomach, intestines, and bladder. The method is used in a number of the following cases:
- suspicion of the presence of formations of various natures in the genitourinary system;
- the appearance of internal bleeding;
- the need to assess growing inflammation of internal organs;
- suspicion of the presence of voluminous neoplasms in the form of cysts, polyps, stones;
- the presence of pathological abnormalities of the abdominal cavity;
- the formation of acute and chronic liver lesions in the form of liver cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- the need to study the venous and arterial systems of the cavity using a contrast agent.
What are the main differences between the methods?
Before talking about the differences between MRI and MSCT, it is necessary to identify the similarities between these methods:
- minimum preparation time for conducting the study;
- identification of pathologies in the initial stages of diseases;
- especially thin cut;
- non-invasive;
- injection of contrast fluids to obtain an improved image.
Both of these methods are completely safe for the patient
MRI differs significantly from MSCT in the following parameters:
- Opportunity: MSCT most fully visualizes hard tissues, MRI – soft tissues.
- MRI is not prescribed for patients with implanted metal objects.
- MSCT is contraindicated for nursing mothers, pregnant women and children.
- MRI differs from MSCT in the number of procedures performed. MRI has no limitations.
- Time spent on the procedure. An MRI takes on average about one hour. MSCT lasts from 5 to 30 minutes.
- Various contrast fluids are used for examinations: MRI - gadolinium-based fluid, MSCT - iodine-based.
- Method for diagnosing the disease: MRI uses a magnetic field, MSCT uses x-rays.
- Cost of the procedure.
This video compares MSCT and MRI, if you want to know which is better, then watch the video:
What does MRI diagnose?
The most informative MRI procedure of the abdominal cavity becomes when it is necessary to diagnose the following pathologies:
- diseases of the spleen, pancreas;
- pathologies of the liver and ducts of the organ;
- establishing the degree of liver cell necrosis in hepatitis or cirrhosis;
- purulent foci in the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space;
- hematomas;
- abscesses;
- cystic formations;
- malignant lesions;
- abdominal aortic aneurysm.
With the help of MRI, the doctor is able to correctly determine the type of formation and diagnose a benign tumor from cancer metastases. When contrast is used, an accurate picture appears in cases of circulatory disorders in the abdominal cavity and hidden bleeding.
Preparation for examinations
Unlike other examination methods, abdominal scanning requires special preparation. When performing an MRI or CT scan, the diagnostician recommends:
- In 2-3 days, change your diet to a lighter and more balanced one. It should not contain products that stimulate intestinal motility, provoke gas formation or cramps. The “forbidden” list includes dishes made from cabbage, radishes, and bread with a high fiber content.
- It is necessary to exclude milk and carbonated drinks for several days.
- To improve bowel cleansing, you should do an enema in the evening and take a laxative.
- It is recommended that you visit the radiologist's office on an empty stomach. This helps control nausea when the contrast agent is administered. In addition, eating 8-10 hours before the procedure allows you to cleanse the digestive tract and eliminates diagnostic errors.
When examining the abdominal cavity, you should first take Smecta or No-Shpu. The drugs soothe the mucous membrane, eliminate gas formation and interference on the sections.