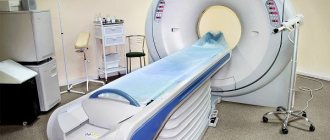
MRI of the cervical spine (magnetic resonance imaging) is a diagnostic examination that can help identify pathological processes and damage in the vertebrae, soft tissues and spinal cord.
The boundaries of the region under study are the base of the skull and the lower part of the neck. Thanks to the use of this method, it is possible to accurately recognize circulatory disorders, neoplasms, changes in intervertebral discs, and developmental anomalies of the cervical spine.
Table of contents
- In what cases is a CT scan prescribed, and in which MRI?
- Main indications for CT scanning
- When is the best time to do an MRI?
- Contraindications
- Advantages of each type of tomography
- Benefits of CT
- Benefits of MRI
- MRI of the brain or CT scan – which is better?
- What will be checked?
- When there are restrictions
- Technical specifications
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Computed tomography
is a type of analysis in which a layer-by-layer scan of the patient's organ is performed. A tomograph is used to carry it out. The principle of its action is the reflection of X-ray radiation from tissues and bones. The result of the study is presented in the form of a 3D image on the doctor’s monitor, and can also be recorded on disk.
The CT machine consists of a table and a circle with movable sensors, which, rotating during the examination, take pictures from different angles.
Since using this method the patient receives a certain (but not very large) dose of radiation, this test should not be performed frequently.
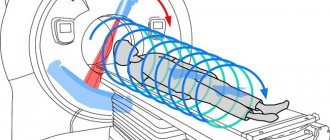
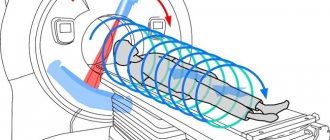
Magnetic resonance imaging
- This is an examination based on the effect of magnetic resonance and electromagnetic radiation, which is reflected differently from more or less dense tissues.
A tomograph is also used for it, but of a different, closed type. It is equipped with a retractable table on which the patient is placed, and a tube-shaped apparatus into which this table is pushed.
This is a fairly safe examination method, although there are a number of limitations in its use, mainly related to the presence of metal implants in the body.
Disadvantages of CT and MRI examinations
Of course, all types of research have both positive and negative sides.
The disadvantages of MRI include the following indicators:
- It is impossible to fully study hollow organs (urinary and gall bladder, lungs)
- It is impossible to carry out the procedure if there are metal objects in the patient’s body
- To obtain high-quality images, you need to remain still and calm for a long time.
The disadvantages of CT include the following indicators:
- Hazard to Human Health - Harmful Exposure to X-Rays
- There is no way to obtain information about the functional state of organs and tissues, only about their structure.
- Pregnant and nursing mothers and children should not undergo this tomography.
- You cannot undergo the procedure often
In any case, when visiting the attending doctor, the patient will be prescribed an examination that will provide the necessary and accurate result. If you are prescribed both methods of examination, then in this case the differences in the methods do not play a fundamental role.
When is the best time to do an MRI?
Such a study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of a tumor
- Regular headaches, dizziness, fainting
- The patient suffered a stroke
- Lost hearing or vision
- Injuries, hematomas and swelling
- Memory loss, problems concentrating
- Inability to perform CT
MRI is also prescribed to check:
- Correct course of treatment
- State of the brain after detection of a malignant tumor
- Pre- and postoperative control
Children may be prescribed magnetic resonance imaging if:
- He had pathologies during intrauterine development
- He lags behind his peers in various indicators
- Suffering from convulsions, dizziness, loss of consciousness
- Stutters or has other speech problems
Contraindications for tomography (CT and MRI)
Each of the procedures has contraindications that may interfere if you decide to undergo examination.
Computed tomography is not prescribed:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- For children at an early age
- In case of frequent procedure
- If there is plaster in the examination area
- In case of renal failure. Magnetic resonance imaging also has its contraindications:
- Claustrophobia, schizophrenia
- The presence of a pacemaker, metal implants, clips on blood vessels, or other metal objects in the patient’s body
- Pregnancy in the 1st trimester
- The patient is overweight (over 110 kg)
- Renal failure (when using contrast agents).
It is imperative to consult a doctor before undergoing the test.
Magnetic resonance imaging device
CT and MRI are used to diagnose and prescribe treatment for a huge number of diseases. You need to know that the purpose of a particular examination method depends on what part of the person’s body is being examined.
If in some cases both methods are prescribed for research and give the same result, then MRI is, of course, preferable in terms of health safety. However, its price is higher.
In any case, it is important to always remember that health is, first of all, in your hands, and the most important thing is to promptly identify diseases using any diagnostic methods and begin proper treatment.
Contraindications
Both studies are quite safe, but a number of restrictions on their use still exist. They must be kept in mind when deciding which analysis to perform: brain MRI or CT.
Computed tomography is not done in the following cases:
- When the patient is pregnant
- With a large weight (more than 130 kg) of the patient
Use it with caution for nursing mothers, and if the analysis has been carried out, then you should not breastfeed the baby for another day.
If the study is carried out with a contrast agent, then there are more contraindications:
- Allergy to iodine
- Diabetes
- Endocrine diseases
- Problems with the liver and kidneys
MRI should not be performed in patients who:
- There are metal prostheses made from materials that interact with a magnetic field
- Heart valves and pacemakers
- Metal clamps for vessels for aneurysm
- Hearing Aids
- Permanent dentures made of gold, steel and similar materials
The study is applicable with limitations when:
- Patient in the first trimester of pregnancy
- The patient suffers from a fear of enclosed spaces
- He has crowns and braces
Also, an obstacle to both studies may be the patient’s inability to lie still for the required time due to severe back pain.
If the patient knows about the presence of any limitation (pregnancy, previously diagnosed diabetes, metal implants, etc.), he must inform the doctor in advance.
Medical Center "SESANA"
This is a technically complex non-invasive diagnostic method, not
requiring the use of any radioactive substances (for example, barium) or exposure to x-rays. The operating principle of magnetic resonance imaging is based on the use of a high frequency electromagnetic field.
This is a highly informative method of research, which, due to its safety, can be carried out an unlimited number of times. However, MRI has certain contraindications, which will be described below.
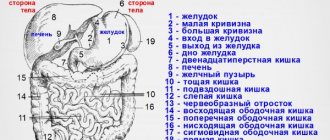
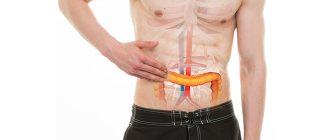
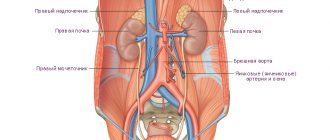
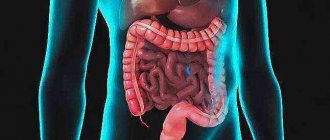
Using this research method, it is possible to visualize all organs, regardless of their structure and location in the abdominal cavity.
So, in what cases is a patient recommended to undergo an MRI:
- To determine the size and shape of the organ being studied.
- To detect or refute the presence of congenital malformations of the abdominal organs.
- Detection of benign tumors of the abdominal organs, for example: hemangiomas, adenomas, lipomas, focal nodular hyperplasias.
- Detection and characterization of malignant neoplasms, both at an early stage and metastasizing.
- Definitions of chronic diffuse changes in the liver - chronic hepatitis of various etiologies, fatty infiltration of the liver, amyloidosis.
- Detection of liver cirrhosis.
- Determining the pathology of the biliary duct system.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
- Determination of the degree of damage to internal organs after injuries and bruises.
- If acute processes and their complications are suspected, including acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, acute appendicitis, and so on.
- For focal lesions of the spleen: abscesses, hemorrhages, the presence of cysts, tumors, parasitic or specific lesions, calcifications, additional lobules.
- With splenomegaly of various origins
- If the patient is intolerant to radiopaque substances.
- If it is necessary to carry out repeated diagnostics more often than once a year, for example, when monitoring the dynamics of the development of a pathological process.
As noted above, despite the high efficiency of this process and its harmlessness, there are a number of contraindications for MRI, namely:
- Patient weight exceeding 110 kg.
- The patient's inability to remain still for a certain period of time (for example, if the patient being studied is a child or disabled).
- The patient has a pacemaker (the operation of the MRI machine may affect the operation of the pacemaker).
- There are implants in the middle and inner ear.
- Pregnancy up to three months.
- The patient is afraid of closed spaces.
To improve visualization of the abdominal organs and increase diagnostic efficiency, the patient is recommended to undergo certain preparation before MRI:
- The day before the MRI, avoid all foods that cause excess gas, as this may affect the diagnostic results.
- Take drugs - sorbents, such as activated carbon.
- Easily excitable patients should take sedatives.
- Patients with increased intestinal motility can take appropriate medications.
- In some cases, a cleansing enema is also necessary.
One of the advantages of magnetic resonance imaging is its high-quality image, which certainly increases the diagnostic value of this technique.
MRI of the abdominal organs is very significant for the detection of malignant neoplasms. When cancer is suspected, doctors use this method because it is harmless (that is, the patient does not receive a dose of radiation).
In addition, thanks to special protocols, it is possible to accurately determine the benignity or malignancy of adenomatous rectal polyps,
However, MRI is not used to detect and characterize kidney stones due to its ineffectiveness in this case. It makes sense to use spiral computed tomography to identify and characterize stones.
Benefits of CT
Computed tomography is one of the most accurate ways to study disorders associated with the state of the brain. It is especially effective when it comes to identifying abnormalities caused by traumatic brain injury, as well as other problems with the bones and dense tissues of the skull.
This happens because X-rays are reflected in a special way from dense bone tissue. At the same time, the radiation dose that the patient receives is much lower compared to other x-ray studies. In this way, various diseases can be diagnosed without the use of invasive methods, which makes the procedure painless.
Using CT, you can diagnose a stroke, arterial disorders due to atherosclerosis, changes in the structure of the cerebral cortex and lesions of the facial bones. It allows us to examine such disorders in great detail and identify the causes of diseases.
The procedure takes no more than fifteen minutes. With this type of analysis, there is no risk of distortion of the result if the patient accidentally moves.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia can easily tolerate a CT scan because an open machine is used, in which only the head is immersed, and not the whole body.
It is important that the CT result can be seen immediately, although in some cases the image may not have enough contrast.
Principle of operation
Optical neuroimaging is performed with a device that contains dozens of small LED lamps.
Thus, diffuse optical tomography does not expose the human body to intense radioactive and ultraviolet radiation, like traditional devices.
Consequently, this diagnostic method becomes absolutely safe for examining children and pregnant women. Neuroimaging is especially relevant for patients who need to examine the frontal lobes and parts of the cerebral cortex dominant for speech and self-reflection.
The technology works by in-depth illumination of local parts of the brain, and subsequent detection of color and dynamic changes in its tissues.
Using diffuse optical tomography, the following pathologies can be easily detected:
- Oncological diseases of the brain;
- Benign neoplasms that tend to grow;
- Hemorrhages;
- Hematomas;
- Blood clots in the vessels of the brain;
- Pre-stroke conditions;
- Neurodegenerative disorders;
- Autism;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Complications of severe traumatic brain injuries;
- Progressive inflammatory processes in brain tissue;
- Chronic and congenital disorders in the cerebral cortex.
There are situations in life when you simply cannot do without the help of medications. The attending physician will definitely select the drugs necessary in a given situation, and the article will help you understand the classification of beta blockers, their characteristics and methods of use.
Pick disease is quite often confused with Niemann Pick disease. What kind of disease is this and how is it different from the others? Who it is, and how to deal with it, you will find here.
Benefits of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is no less accurate than CT, but its scope is somewhat different. It allows you to examine and diagnose diseases of the soft tissues of the brain and shows results in three planes:
- Axial (horizontal projection)
- Frontal (direct projection)
- Sagittal (lateral projection)
MRI allows you to very clearly see problems with soft tissues: benign and malignant (cancer) neoplasms (their shape, location and volume), dysfunction of the pituitary gland, nerve and muscle fibers. In this way, you can see and measure the volume of edema, tumors of the nervous system, and more. The bones will be displayed indirectly.
This test is safe, so it can be used to diagnose pregnant patients, but only in the second and third trimester. It is also allowed to be used for diagnosing children from the age of three. But it is necessary to explain to the child how the research will take place so that he is not afraid and tries not to move during the process.
MRI can be done several times over a short period of time.
The procedure lasts about half an hour. During this period, the patient is required to lie still. Otherwise, the image may be distorted and the result may not be reliable or accurate.
For patients with a fear of closed spaces, anesthesia can be used.
CT or MRI: which is better?
There is no point in discussing which method is better or worse: these are completely different methods that are used in different situations. Each research method has its own indications and contraindications. Each method is informative for certain organs and tissues in specific cases. In some cases and when diagnosis is difficult, it is even necessary or recommended to use both tomography methods.
MRI allows you to see soft tissues more clearly, but does not “see” calcium in the bones at all. And CT allows us to study bone tissue in more detail.
The MRI procedure is indicated for examination:
- Tumors and metastases in soft tissues;
- Conditions of the spinal cord and brain;
- Strokes, multiple sclerosis, inflammation of brain tissue, brain tumors;
- Esophagus, trachea, aorta;
- Ligaments, muscle tissue;
- Joints and intervertebral discs;
- Pelvic organs. CT is prescribed for research and study:
- Lesions of the bones of the base of the skull, temporal bones, paranasal sinuses, facial skeleton, jaws, teeth;
- Vascular lesions;
- Chest organs;
- Parathyroid and thyroid glands;
- Diseases of bones and joints;
- Spine;
- Consequences of injuries. When choosing a method for diagnosing diseases, the doctor also takes into account the patient’s health condition and factors that may interfere with tomography.
Despite obtaining the same results in both tomographs (these are volumetric images), CT is harmful to human health. MRI diagnostics, on the contrary, is completely safe (even for pregnant and lactating women), but, unfortunately, more expensive.
The advantages of magnetic resonance imaging are:
- High accuracy of received information
- Safety for the patient, including pregnant women and children
- Possibility of repeated use of the procedure if necessary, due to its safety
- Acquiring 3D images
- The probability of receiving an error during scanning is almost zero
- No additional contrast required to study blood flow
- Great information value in the study of damage to the central nervous system, the study of vertebral hernias.
Advantages of computed tomography:
- Reliable information
- Possibility of obtaining three-dimensional images of the area under study
- Clearer pictures of the skeletal system
- Possibility of obtaining reliable information in case of internal bleeding, detection of tumors
- Short duration of the examination
- Possibility to undergo the procedure if there are metal or electronic devices in the body
- Low cost.
When there are restrictions
Magnetic resonance imaging can be done on pregnant women (excluding the first trimester) and children aged three years and older. Anesthesia can be used for a child, since he is not always able to remain motionless for a long period of time.
A CT scan for children and pregnant women is excluded, except in cases where the patient’s life depends on its implementation, and no other means can help, since during the procedure the patient receives a dose of X-ray radiation.
It can also be difficult for a patient with nervous disorders to remain motionless for the required period of time. In this situation, it is also possible to use anesthesia.
People who have metal objects in the body, as well as electronic pacemakers or heart valves, are contraindicated for MRI, since such things interact magnetically with the machine. Because of this, both distortion of the results and deterioration of the patient’s condition may occur. The exceptions are pins, crowns, removable braces and products made from non-inert materials (titanium and others). In this case, it is better for the patient to undergo a brain CT scan or similar analysis.
Patients who are claustrophobic can undergo a CT scan without discomfort because they do not have to lie down completely in the machine. If such a patient needs to have an MRI, he will have to use anesthesia, which seriously affects any organism.
The restrictions on the patient’s weight do not differ very much, but in some cases this factor can play a role: a C-tomograph allows a patient to be analyzed up to 130 kilograms, and an MRI machine – up to 150.
CT with contrast should not be performed on people who have been diagnosed with an allergy to iodine and other components of the injected substance, as well as those who have diabetes mellitus and other kidney diseases. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a different analysis.
MRI or CT – an alternative or an addition?
You can often hear that X-ray computed tomography has become obsolete due to the use of x-ray radiation for obtaining images, and that magnetic resonance imaging (MR), if not replaced, then will soon certainly replace computed tomography (CT) due to a wide range of possibilities for determining morphological and even functional processes in organs and focal formations.
Since both imaging technologies can use extracellular (and with MRI, even intracellular) contrast agents, this further increases the diagnostic capabilities of imaging methods. And if it is possible to obtain the same capabilities without “loading” the patient with X-ray radiation, the conclusion is that MRI inevitably wins over the “older” method of CT.
Why do you need contrast in MRI? Read here
But is this really so? Are both methods alternative or do they complement each other? And if they are supplemented, then when can you still get by using one of them? The answer is both simple and complex at the same time.
Life shows that, if possible, both diagnostic methods should be used. And if not? Let's look at several possible conditions of patients.
Group 1. Against the background of unchanged liver parenchyma, ultrasound suspected a small focal formation. MRI is preferred. We do not know the etiology of the formation, but we can assume that it is benign and are looking for a small hemangioma. Hypointense signal (T1), hyperintense signal (T2), signal characteristics almost like a cyst. If you still have doubts, use contrast enhancement. Bright contrast, focal points, on the periphery of the formation. In large hemangiomas, hyaline cartilage is so typical (especially in the presence of a gelatinous component) that contrast enhancement may even be avoided.
Should I be concerned if an MRI reveals a liver hemangioma? Read here
Contrast-enhanced CT shows the same signs of contrast-enhanced hemangioma. There is usually no differentiation of the cartilage structure on CT.
Focal nodular hyperplasia, hepatic adenoma, small hepatocellular cancer, hypervascular metastases - their morphology can only be assumed, and contrast enhancement is indispensable. If the speed of the examination and the throughput of the tomography machine are of paramount importance, then CT is preferable in this case.
Group 2. The liver parenchyma is heterogeneous; focal formations cannot be excluded. MRI is more sensitive to detect changes in the structure of parenchymal organs. In addition, additional capabilities (changing the direction and speed of fluid diffusion in intercellular spaces disturbed by inflammation or tumor - with DWI), as well as new techniques that have appeared (MRI elastography), and assessment of the chemical composition - MR spectroscopy make MRI the undisputed leader in this race .
In this group, CT has only a few advantages - scanning speed, and the absence of restrictions on other patient conditions - the presence of an automatic heart pacemaker, magnetized metal structures in the body. With age, patients become “more and more CT-friendly,” and such combinations should dominate in the population as a whole—children and young adults—ultrasound and MRI, middle-aged and elderly—ultrasound and CT. An aging population burdened with untreated chronic diseases makes it clear that X-ray imaging technologies will never last.
You can read more about contraindications for MRI here
Group 3. Patients with cystic formations of homogeneous or heterogeneous structure. There is no clear answer here. Calcium in the wall or soft tissue component is visible on CT, but not on MRI. Although at the last Congress in Chicago - RSNA2013 they showed technologies for differentiating calcium and contrast-enhanced vessels using MRI (which means this advantage of CT will soon disappear). The fluid is better visible on MRI. Additional information is provided by contrast enhancement technologies (CT has speed advantages).
Group 4. Pathological conditions of the biliary tract. There is no doubt - MRI with its MRCP technique is the optimal method (including non-contrast) research. But CT scans also provide a lot of diagnostic information.
What is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)? Read here
What is the conclusion?
Is MRI really winning? Alas, not yet everywhere and not always, even in advantageous positions. Why? Doctors do not know well the capabilities of MRI, they use them little, in the old fashioned way they focus more on CT, and where there is equipment, it is easier to sit and describe the pathology of the spine than to rack your brains over the problems of differential diagnosis of diseases of the internal organs. And such research takes longer.
MRI, CT or Ultrasound? Opinion of the executive director of MRT Expert Lipetsk Oksana Egorovna Volkova
However, not everything is measured by money. There is a good expression with deep philosophical overtones: “Treat people the way you would like them to treat you.” In relation to diagnostics, prescribe and perform for patients those tests that you would like to perform for your family and friends.
Author: Grigory Grigorievich Karmazanovsky Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor.
Head of the Department of Radiation Methods of Diagnostics and Treatment of the Federal State Budgetary Institution Institute of Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky" of the Ministry of Health, member of the European Society of Radiology (ECR), corresponding member of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), member of the presidium of the Russian Association of Radiologists (RAR). Laureate of the Russian Government Prize in the field of science and technology. Lecturer at the European School of Radiology.
You might be interested in:
Positron emission tomography is a breakthrough in the diagnosis of cancer
Whole body MRI: when is it necessary?
MRI of the liver: pros and cons
Technical specifications
MRI provides extremely clear images, excluding bones, in the form of projections from different angles; CT, on the other hand, has a less clear “picture,” but at the same time the structure of the bones is clearly visible in its results, and the image is presented on the monitor in the form of a 3D model.
Another important point is the amount of time you need to spend in the device. For CT it ranges from 5 to 15 minutes, for MRI – about half an hour. During this period, the patient should be as motionless as possible. But it is not so critical for the results of a CT scan if the patient moves a little. Such movement can introduce serious distortion into magnetic resonance imaging data.
A CT scan can help make an urgent diagnosis if a patient is seriously injured and has symptoms of a cerebral hemorrhage.
To choose the most effective examination method (brain MRI or CT), you need to pay attention to many factors. This can be done by a qualified doctor. The patient is obliged to provide all information that will help with this.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinics have the latest equipment, which allows you to get the most accurate results
- Radiologists, oncologists, surgeons and other professionals of the highest qualification categories take on the most complex and rare cases
- It’s easy to sign up for a consultation and find out more details - all you need is one phone call to 8 (495) 7-800-500
- MEDSI will help you choose the right examination (including brain MRI or CT), treatment and, if necessary, rehabilitation measures