06/01/2018 Category: Analyzes and examinationsAuthor: Natalya Grebennikova
Future parents, having seen the coveted two stripes, look forward to meeting their baby. Thoughts about what he will be like, who he will be like, occupy every pregnant woman, without exception! With the development of technology, we have the opportunity to lift the veil of secrecy and get to know the tiny little man before meeting him in person. Ultrasound diagnostics of the fetus is aimed, first of all, at assessing the development of the baby, but a big bonus is the opportunity to see him (or her?) long before birth. What is the essence of routine and unscheduled ultrasound procedures, how safe are they for mother and child, the most important indicators and their interpretation - this is what our article is about.
- Features of the procedure and timing
Video: 3-D ultrasound at different stages of pregnancy - Video: 4-D ultrasound
- Video: Ultrasound in the early stages
- Decoding data obtained from ultrasound
Fetal size table by week
- Head size chart by week
- Table of the circumference of the baby's head and abdomen by week
- Table of sizes of tubular bones of the limbs
- Important findings from the first study
Table of normal TVP values at 10–14 weeks
- KTP size chart according to gestational age
- Video: anatomical data of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy
- Video: how many times during pregnancy can you do an ultrasound
- Video: Tutta Larsen about the influence of ultrasound on the unborn baby
Why is the study done and to whom is it recommended?
If a woman is in a state of anxious anticipation of pregnancy and listens carefully to herself in search of its signs, then an ultrasound procedure at the first suspicion of pregnancy will save her a lot of nerve cells.
Women (especially those who have experienced several unsuccessful pregnancies or are experiencing difficulties conceiving) react very sharply to changes in their own bodies and look forward to a happy pregnancy. In this case, doctors recommend undergoing an ultrasound examination in 1-2 weeks to dispel doubts and not worry in vain.
If pregnancy has occurred, week 2 is marked by the attachment of the egg to the uterine wall, which changes hormonal levels.
Reference! At this time, it is already possible to establish an “interesting situation” with the help of hCG.
In a blood or urine test of the expectant mother, a laboratory technician can detect hCG, a hormone responsible for “tuning” the body to pregnancy. The determination of this component is also the basis of pharmacy pregnancy tests. In rare cases, as early as 2 weeks, a woman may experience early toxicosis, which is characterized by nausea and aversion to certain odors.
At the beginning of pregnancy, most women experience:
- state of drowsiness and fatigue;
- decreased or increased appetite;
- change in food preferences (aversion to one product and craving for another);
- breast enlargement and some soreness;
- slight increase in body temperature.
The main and most serious sign of pregnancy remains a delay in menstruation.
Child development in the 3rd trimester
This period is very difficult and important for both the woman and her baby. The fetus is rapidly gaining weight, its organs and reflexes are actively developing. He can already swallow, grasp, suck perfectly well, and his ability to hear, touch and see is gradually improving. Time is already divided into periods of sleep and wakefulness, and the mother notices this very well from the baby’s movements.
Week 26
The baby has already grown to 31–21 cm, and has gained weight to 700–800 g. He makes regular breathing movements. The cells responsible for thinking in the brain mature and a sleep cycle gradually becomes established.
Week 27
At this stage, the length of the fetus is 32–33 cm, and its weight is 800–900 g. Its muscles and skeleton continue to strengthen, neural connections become more active, hormones are synthesized in the pituitary gland, vellus hair darkens, and meconium is formed in the intestines - the first feces .
Week 28
Now the child has grown to 33–34 cm and weighs 900–1000 g. He is able to distinguish the taste and smell of all substances and products that enter the mother’s body. Often, from this age, a baby gets used to his mother’s favorite dishes. The baby's eyes and eyelids have developed so much that he can blink.
Week 29
The baby has already acquired considerable size, namely height - 35-36 cm, and weight - 1100-1200 g. He has eyelashes on his eyelids, fairly good hearing and reacts to noises by shuddering or blinking. You can listen to your heartbeat without a stethoscope.
Normal parameters that guide diagnosticians when creating a description of ultrasound images during pregnancy
Week 30
By the end of the 7th normal month, the child’s height becomes 36–37 cm, and his body weight becomes 1200–1300 g. Now the development of his nervous system and psyche is in full swing, and clearly monitored periods of sleep and wakefulness appear. The skin does not become wrinkled as before, but a fat layer forms under it.
31 weeks
At 31 weeks, the baby became 38 cm long and now weighs 1400–1500 g. He is actively preparing for extrauterine life - gaining weight, muscle mass, all organs are gradually completing the process of formation. Due to the fat layer and muscles, the fetus becomes more rounded and adapted to future existence.
Week 32
Now the baby has grown to 39–40 cm, and weighs 1600–1700 g. He is already cramped, and in the near future he needs to take the correct position for childbirth. Therefore, the head begins to grow rapidly, as well as the brain. Larger sizes cause it to hang downwards, and the child turns to the required position.
Week 33
The body length is 41–42 cm, and the weight is 1700–1800 g. At this stage, the fetus should already turn upside down, which is called correct presentation. Subcutaneous fat continues to form, the brain improves, and the lungs begin to secrete surfactant - a mixture that envelops the lung vesicles from the inside.
Reference! At 33–34 weeks, a routine Doppler ultrasound is performed. Its results allow the doctor to assess the condition of the fetus and choose the most appropriate delivery tactics.
34 week
Now the child is 42–43 cm tall and weighs 1900–2000 g. His skin is moist, covered with fine hairs, and he himself is wrinkled and red. Heartbeats are perfectly audible, and their frequency is 120–140 beats per minute. During this period, your own metabolism is formed.
Week 35
At this stage, the baby has grown to 43–44 cm, and weighs 2100–2300 g. The muscles become even stronger, the subcutaneous layer accumulates. He can already actively react to bright light and even hiccup. In boys, the testicles should descend into the scrotum at this time.
Week 36
The child’s height has already reached 44–45 cm, and his body weight is 2400–2500 g. He learns to breathe through his nose, because previously he had to do it through his mouth, he can distinguish flavors and remembers what he hears.
Week 37
The fruit becomes approximately 46–47 cm in size and weighs 2700–2800 g. Its skin becomes lighter and the fluff disappears from the body. The immune, endocrine and central nervous systems are improved. The heart is well formed, and the baby is actively preparing for the first breath.
Week 38
Now the baby is already very big and weighs 3 kg, and his height reaches 47 cm. His lungs are ready for independent breathing. Gradually, the baby moves lower and lower into the mother’s pelvic area.
Week 39
The baby has grown further, and now it is 48–49 cm long and weighs approximately 3200 g. The head has dropped lower and rested against the entrance of the pelvis. The fundus of the uterus drops, and it becomes easier for mommy to breathe. The child's body produces cortisol, which ensures the final formation of the lungs. The baby's skin turns pink.
40 week
By this time, the child has already fully formed - he has reached a weight of 3-3.5 kg, and has grown to 50-55 cm. With his movements in the mother’s belly, you can easily guess where the back is, and where the leg or buttocks are. With correct presentation, the head is felt just above the pubis, and sometimes the mother feels the blows of her limbs on the bladder. The baby’s needs for oxygen and nutrients increase, and the placenta is no longer able to provide them in full. Therefore, the long-awaited birth will most likely happen in the next few days.
Intrauterine growth and fetal development by week of pregnancy
41 weeks
The baby’s comfortable life ends sooner or later, and it’s time to leave their home. Due to rough estimates of the expected day of delivery, the latter may occur at 37–42 weeks. And this will be considered absolutely normal.
42 week
The 42nd week, which is determined by the obstetric calendar, is the last date when a woman can give birth on her own. Later, the baby’s skull will begin to ossify, and natural childbirth may result in trauma for both mother and fetus. Therefore, you should not delay in such situations, but pack your things and ultrasound images and go to the maternity hospital.
Of course, every expectant mother is very interested in knowing how her baby is developing, but even such a harmless examination as an ultrasound is better not to undergo many times. In a normal pregnancy, three screening tests are enough to make sure that everything is fine with the baby.
Mother's condition and how pregnancy develops?
What happens at this stage of pregnancy? A group of cells that will soon become an embryo begins to grow rapidly. The fertilized egg already has a full set of chromosomes: 23 from each parent.
The sex of the unborn baby has already been formed, although the expectant mother will not be able to find out with the help of an ultrasound for a long time. The sex of the child is determined at conception; the chromosome of the father's sperm is responsible for it (X - there will be a girl, Y chromosome - there will be a boy).
Signs of pregnancy may not appear in a woman for 1-2 weeks.
Important! If the pregnancy is long-awaited, then you should prepare for it in advance - for example, start taking special multivitamin preparations or just folic acid. This substance will protect the unborn baby from a wide range of birth defects.
A diet rich in folic acid includes apricots, carrots, asparagus, pumpkin, egg yolks and spinach.
Decoding data obtained from ultrasound
Fetometry is a method of determining the size of the fetus using ultrasound. There are data that are measured at every mandatory ultrasound, and there are those that are indicative and informative only for certain periods. The data below is approximate and applies to even weeks of pregnancy.
At each ultrasound diagnostic session, the baby’s height and weight, abdominal and head circumference, as well as the length of the tubular bones of the limbs are measured.
Fetal size table by week
| Duration in weeks | Weight (g) | Length(cm) |
| 8 | 1 | 1,6 |
| 10 | 4 | 3,1 |
| 12 | 14 | 5,4 |
| 14 | 43 | 8,7 |
| 16 | 100 | 11,6 |
| 18 | 190 | 14,2 |
| 20 | 300 | 16,4 |
| 22 | 430 | 27,8 |
| 24 | 600 | 30 |
| 26 | 760 | 35,6 |
| 28 | 1005 | 37,6 |
| 30 | 1319 | 39,9 |
| 32 | 1702 | 42,4 |
| 34 | 2146 | 45 |
| 36 | 2622 | 47,4 |
| 38 | 3083 | 49,8 |
| 40 | 3462 | 51,2 |
| 42 | 3685 | 51,5 |
Head size chart by week
| Duration in weeks | Average fronto-occipital size (FOR) in mm | Average biparietal size in mm |
| 12 | — | 21 |
| 14 | — | 27 |
| 16 | 45 | 34 |
| 18 | 54 | 42 |
| 20 | 62 | 48 |
| 22 | 70 | 54 |
| 24 | 78 | 61 |
| 26 | 85 | 67 |
| 28 | 91 | 73 |
| 30 | 97 | 78 |
| 32 | 104 | 82 |
| 34 | 110 | 86 |
| 36 | 114 | 90 |
| 38 | 118 | 94 |
| 40 | 120 | 96 |
Table of the circumference of the baby's head and abdomen by week
| Duration in weeks | Head circumference in mm | Abdominal circumference in mm |
| 10 | 50 | 50 |
| 12 | 71 | 61 |
| 14 | 97 | 78 |
| 16 | 124 | 102 |
| 18 | 146 | 124 |
| 20 | 170 | 144 |
| 22 | 195 | 169 |
| 24 | 219 | 193 |
| 26 | 243 | 217 |
| 28 | 265 | 241 |
| 30 | 285 | 264 |
| 32 | 304 | 286 |
| 34 | 317 | 306 |
| 36 | 326 | 323 |
| 38 | 333 | 336 |
| 40 | 337 | 347 |
Please note that during the initial stages of intrauterine development, the child’s head significantly exceeds the abdominal circumference in size. During growth, these indicators are compared, and by the end of pregnancy, the abdominal circumference should not be much larger than the size of the head.
Table of sizes of tubular bones of the limbs
| Duration in weeks | Length of the tibia bone in mm | Femur length in mm | Length of forearm bones in mm | Humerus length in mm |
| 12 | — | 7,3 | — | — |
| 14 | — | 12,4 | — | — |
| 16 | 18 | 20 | 15 | 18 |
| 18 | 24 | 27 | 20 | 24 |
| 20 | 30 | 33 | 26 | 30 |
| 22 | 35 | 39 | 30 | 35 |
| 24 | 40 | 44 | 35 | 40 |
| 26 | 45 | 49 | 39 | 45 |
| 28 | 49 | 53 | 43 | 49 |
| 30 | 53 | 57 | 46 | 53 |
| 32 | 56 | 61 | 49 | 55 |
| 34 | 60 | 65 | 52 | 59 |
| 36 | 62 | 69 | 54 | 62 |
| 38 | 65 | 73 | 56 | 64 |
| 40 | 67 | 75 | 58 | 66 |
Important findings from the first study
As mentioned above, at the first screening, the thickness of the nuchal space (TN) is necessarily measured. This is an area that is filled with fluid and is located between the soft tissues around the spine and the inner layer of skin. An increase in this space may be a sign of chromosomal mutations, so the ultrasound doctor will refer the pregnant woman for consultation with a geneticist if this is detected.
Table of normal TVP values at 10–14 weeks
| Gestational age | TVP in mm |
| 10 weeks – 10 weeks 6 days | 1,5 |
| 11 weeks - 11 weeks 6 days | 1,6 |
| 12 weeks - 12 weeks 6 days | 1,6 |
| 13 weeks - 13 weeks 6 days | 1,7 |
Another important indicator of the first trimester is the coccygeal-parietal size (CPR). The data obtained as a result of the measurement gives an idea of the gestational age. Often it is the first ultrasound that sets the most accurate date.
KTP size chart according to gestational age
| Gestational age | Average CTE value in mm |
| 10 weeks | 31 |
| 10 weeks 6 days | 41 |
| 11 weeks | 42 |
| 11 weeks 6 days | 49 |
| 12 weeks | 51 |
| 12 weeks 6 days | 62 |
| 13 weeks | 63 |
| 13 weeks 6 days | 74 |
| 14 weeks | 76 |
The fetal heartbeat is the most important indicator that the baby is viable and developing normally. The heartbeat can be heard as early as 4 weeks of pregnancy on a transvaginal ultrasound. Abdominal examination can distinguish it later - starting from the 6th week. You can listen to your baby’s heartbeat at home using special devices called a fetal doppler.
You can listen to your baby’s heartbeat at home using a fetal doppler, which consists of a sensor and an analyzing part - just like an ultrasound machine
The purity and rhythm of the heartbeat, as well as its frequency, are indicative. Fetal arrhythmia may indicate the presence of a heart defect or oxygen starvation; additional noises also indicate hypoxia. The heart rate (HR) is different during each week of pregnancy, gradually decreasing.
| Gestational age | Heart rate (beats per minute) |
| 10 | 161–179 |
| 11 | 153–177 |
| 12 | 150–174 |
| 13 | 147–171 |
| 14 | 146–168 |
Rapid and slow heartbeat (tachy- and bradycardia) of the fetus occurs as a response to a decrease in oxygen in the mother’s blood, for example, due to smoking. In such cases, hospital treatment of the pregnant woman is carried out.
At the first ultrasound, the doctor pays attention to the structure and presence of the facial skeleton and internal organs, and, if necessary, refers the pregnant woman to a geneticist to double-check the results.
Video: anatomical data of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy
What indicators are important in the second trimester
Important indicators of the second trimester, in addition to the mandatory biometric data (height, weight, CTE and BDP, head and abdominal circumference, bone length), are:
- The presence/absence of malformations, which are best visible at 20–24 weeks.
- Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the placenta - the organ that supplies the baby with vital substances. For example, the normal thickness of the placenta at 20 weeks is 21.96 mm, and permissible fluctuations range from 16.7 to 28 mm. The longer the period, the thicker the placenta becomes, reaching approximately 33.5 mm by 40 weeks. Ultrasound also evaluates the location (attachment along the posterior wall, along the anterior wall, to the fundus of the uterus) and degree of maturity:
- zero - corresponds to a normal period of up to 30 weeks;
- first - 30–34 weeks;
- second - 35–39 weeks;
- the third - after 39 weeks.
- Quantity and quality of amniotic fluid. The doctor compares the amniotic fluid index with the gestational age. Strong fluctuations in numbers in both directions indicate high or low water levels. These two conditions are treated with medication, and in the second case, therapy is aimed more at supporting the baby. According to its qualitative characteristics, amniotic fluid should be transparent, without admixtures of mucus and pus, which indicate infectious inflammation.
- Umbilical cord. The presence of entanglements is checked, which at this stage do not pose any particular danger; the baby can be turned with the help of exercises or persuasion. Yes, yes, you can talk to the baby and he will turn over. Checked personally!
- The condition of the cervix is at least 3 cm long and the internal os is closed. If the indicators are different, the woman is given an obstetric pessary (a mechanical device in the form of vaginal rings) to prevent premature dilatation of the uterus.
What does the ultrasound specialist pay attention to during the third study?
At the third ultrasound, fetal presentation is assessed. Normally, there is a cephalic presentation, when the baby’s head is turned down. Breech presentation is often an indication for caesarean section. The position of the fetus can be longitudinal, oblique and transverse. Natural birth is possible in the first case; in other cases, surgical delivery is necessary.
Traditionally, the size of the baby is assessed, as well as the condition of the placenta, its size, degree of maturity and location. The amniotic fluid parameters are assessed similarly to the second study.
Video: general information about the types of ultrasound and its effect on the baby
What does the examination show?
Many women on the 10th day of delay want to know whether an ultrasound will show pregnancy? The period is too short, so it is unlikely that the doctor will prescribe a study in these weeks specifically regarding its onset.
Most likely, the procedure will be prescribed for:
- Preparations for pregnancy-stimulating activities.
- Checking the results of stimulation already performed.
- Study of the endometrium.
- Examination of the uterine cavity for the presence of fibroids, cysts and blood clots.
Attachment of the fetus to the wall of the uterus occurs at 3-4 weeks, in fact, this time is considered the onset of pregnancy.
At 1-2 weeks, doctors do not yet talk about expecting a baby, we are only talking about the 2nd week of the menstrual cycle. The body is still preparing for possible changes, but the woman will not yet be able to find out for sure whether they happened or not.
The second week brings many changes to the female body. The main one is the readiness of the egg to transfer the mother’s genetic information to the child (the color of her eyes and hair, height and character traits), that is, maturation.
The egg is still located in the follicle (the so-called formation with cloudy liquid). But after strong stretching, its walls burst, “releasing” the mature egg into the abdominal cavity. From here it needs to get to the uterus, and the first step at this stage of the journey is moving into the fallopian tube. This is where fertilization of the female cell occurs, which becomes the beginning of pregnancy.
After this, the fertilized egg ends up in the uterus. Where the burst follicle was located, the corpus luteum of the ovary is formed. It is a temporary endocrine gland necessary for the production of progesterone.
In the second week of expecting a baby, the following happens:
- for the full development of the embryo, the formation of extra-embryonic organs begins, they will provide its nutrition and protection;
- the amniotic sac begins to develop, which will subsequently perform protective and excretory functions;
- the embryo develops a heart tube;
- Two folds form on the back of the unborn baby, at the edges of which the formation of the spinal cord and brain begins.
What is an ultrasound examination during pregnancy?
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound), sonography, is a method of non-invasive diagnosis of internal organs and tissues, which is based on the analysis of various reflections of ultrasonic waves from various tissues of the body. Ultrasound of pregnant women can be abdominal, when the abdominal area is examined, and transvaginal, when the sensor is inserted into the vagina.
Features of the procedure and timing
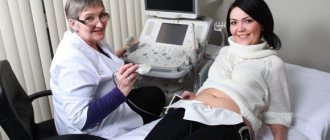
The abdominal examination procedure is quite simple and probably familiar to everyone. During the procedure, a sensor called a transducer is placed on the woman's abdomen, which produces high-frequency sound waves. Due to the high intensity, such a sound cannot be perceived by the human ear, so the diagnosis, although sound, is silent for us. High-frequency sound, called ultrasound in physics, penetrates into the pregnant woman’s abdomen, encountering various obstacles along the way in the form of organs and tissues, from which it is reflected. All structures of the body of the mother and baby have their own density, and therefore the sound “bounces off” from them with varying strength. The received signal is returned back to the sensor, processed and sent to a powerful computer, which converts all these differences in the speed of sounds into an image. The resulting image is seen by the doctor and the patient on the monitor.
An ultrasound specialist moves a special sensor over the pregnant woman’s abdomen and reads the displayed data from the monitor
The diagnosis does not cause the slightest discomfort, except, perhaps, stickiness on the stomach after a special conductive gel.
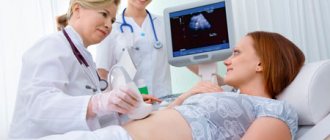
Transvaginal examination is a less comfortable procedure, but more informative, since it allows you to examine the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy, when it is still very small.
During a transvaginal ultrasound, a sensor is inserted directly into a woman's vagina.
Typically, the doctor begins the examination with an abdominal sensor, resorting to a vaginal one if the fetus is poorly visible in the early stages.
This is a painless procedure that is considered completely safe for mother and baby and very informative for gynecologists managing pregnancy. That is why the ultrasound method is so popular in modern obstetrics and gynecology.
Ultrasound as a research method is a relatively young field that emerged in the second half of the last century. In 1958, the British doctor D. Donald first examined the head of a baby in the womb using ultrasound. Ultrasound techniques became widespread in the mid-60s in developed countries. This was facilitated by the opening up of opportunities to study the anatomy of the fetus, as well as the emergence of scientific experiments confirming the safety of the procedure.
The end of the last century was marked by a breakthrough in the technological side of the issue: ultrasound scanners have become much more powerful, allowing you to see not only the outline of the head, but also how the baby sucks his finger or blinks.
Ultrasound of a pregnant woman is aimed at solving the following important problems:
- Confirmation of the fact of pregnancy in the early stages.
- Assessment of the most important parameters of the development of the unborn baby and correlation of the obtained data with the expected gestational age.
- Assessing the vital activity of the embryo.
- Identification of potential developmental defects.
- Study of the placenta - its size, maturity, place of attachment.
- Study of amniotic fluid - its quantity and quality.
- And finally, the exciting and pleasant task of determining the sex of the baby. Although some parents deliberately ask not to tell the doctor for various reasons.
For example, in the USA and Great Britain, the Gender Reveal Party is popular - a party at which happy parents find out the gender of their baby. During the ultrasound procedure, the doctor does not name the gender of the child, but writes it down and silently seals it in an envelope. The envelope goes to the pastry chef, who bakes a cake with the color of the sponge cake corresponding to the gender of the child - pink or blue. The design of the cake itself continues to remain a secret, and only by cutting it will future parents find out who they are expecting!
The cake is covered with white icing with intriguing inscriptions, for example, “Boy or girl?”, “Will you have...”
In addition to abdominal and transvaginal ultrasound, diagnostic methods are classified according to the number of measurements studied:
- 2D;
- 3D;
- 4D.
The image obtained as a result of a two-dimensional study resembles a black and white picture, and three- and four-dimensional images make it possible to see the baby, his facial features, what he is doing at the moment.
In budgetary medical institutions, 2D diagnostics are traditionally carried out, when the study is carried out in 2 dimensions (width, height). The resulting image consists of sticks and dots, often randomly placed - in the eyes of non-specialists. But the doctor clearly sees in such a picture the most important parameters of the baby’s development. This type of ultrasound is performed at all stages of pregnancy.
The black and white image, consisting of sticks and dots, is a two-dimensional projection of a tiny person
A more modern method that allows you to see the baby in a three-dimensional image is 3D fetal ultrasound. The holographic image allows you to see the baby’s facial expressions and gestures at a power and frequency of ultrasound similar to 2D ultrasound. The quality of the image and the duration of the diagnosis differ: unlike a 20-minute two-dimensional ultrasound, a 3D examination takes at least 45 minutes. It is optimally carried out between 20 and 33 weeks, since at this time the baby is quite mobile and has mature features. 3D ultrasound is not a mandatory procedure (unless there are medical indications) and is performed at the request of future parents along with mandatory two-dimensional diagnostic procedures.
Three-dimensional images allow you to lift the veil of secrecy and get to know the baby in person and examine facial features
Video: 3-D ultrasound at different stages of pregnancy
More and more private clinics are offering 4D ultrasound during pregnancy. It differs from 3D in that the fourth dimension is connected: you can “spy” what the baby is doing in real time. The result of this research is the first documentary film about the life of a baby even before birth. The effect on the baby is similar in strength and power to the standard ultrasound procedure, and it can be performed in the second trimester. The duration of the procedure is from 45 to 60 minutes.
Video: 4-D ultrasound
Today, ultrasound examinations of the fetus have become part of screening and are mandatory during pregnancy. An order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation “On improving prenatal diagnostics in the prevention of hereditary and congenital diseases in children” was issued, according to which the mandatory conduct of ultrasound diagnostics is approved:
- the first at a period of 10–14 weeks, according to other sources the deadline is 13.6 weeks;
- the second - in the period 20–24 weeks;
- third - 32–34 weeks.
Sometimes they send for an ultrasound earlier than 10 weeks. This happens in cases where it is necessary to make sure that the pregnancy is uterine, whether there are any threats of failure due to the tone of the uterus, and whether the fertilized egg is in order. In addition, in the period from 5 to 8 weeks, the heartbeat of the embryo can be used to determine whether the pregnancy is proceeding normally. If the heart rate tends to slow down, there is a risk of missed pregnancy or complications. Also, ultrasound in the early stages shows the location of the chorion - the future placenta.
On an ultrasound up to 10 weeks, the expectant mother will see only a dark circle - this is the fertilized egg with the yolk sac located next to it
The first mandatory ultrasound is an integral part of screening, when a woman undergoes an ultrasound examination and on the same day (or in the coming days) donates blood from a vein for various markers of chromosomal mutations. Such a serious developmental defect as Down syndrome can be determined already at this stage, so the size of the fetal nasal bone and the thickness of the nuchal fold are of utmost importance. If the first ultrasound reveals a pathology, then a second ultrasound is prescribed to confirm or refute the data obtained. There are cases when the results of one study showed all the signs of Down syndrome, and the second refuted them. The parents took the risk and... a healthy baby was born!
The first ultrasound is a very exciting event for expectant parents and especially for women. After all, if she is one of the lucky ones who did not know the delights of toxicosis and other not-so-pleasant manifestations of pregnancy in the early stages, then the thought probably crept in more than once: “Is there really a little man growing inside me?!”
When I was expecting my first child, I fell into this lucky number - I was not tormented by toxicosis, my taste preferences did not change, the smells did not irritate me, I just wanted to sleep terribly. Therefore, I did not fully realize that I was in a position. There was no euphoria or feeling of connection with the baby. But then the day of the first ultrasound came. I saw this lump on the screen, I heard my heart beating - and a wave of happiness flooded me. I left the office and burst into tears of joy: I’m definitely going to be a mother, everything is fine with the baby!
I also knew about the nasal bone as an important indicator of normal development, so I asked the doctor about it with trepidation. Having heard that the sizes corresponded to the norm, I exhaled with enormous relief. I think all women will support me, because the most important thing is to know that the child is developing normally.
The first ultrasound already clearly shows the profile of the man, his spine, brain, limbs and heart
Video: Ultrasound in the early stages
The second mandatory study is carried out at 20–22 weeks (no later than the 24th). The main goal is to study the functioning of the baby’s cardiovascular system and identify possible malformations of its development. Also in the second trimester, there is a possibility of detecting isthmic-cervical insufficiency - shortening of the cervix, which is a direct threat of miscarriage. Since the baby has already grown significantly compared to the first screening, it becomes possible to diagnose various anatomical defects of the fetus - from severe anencephaly (absence of the brain), clefts of the hard and/or soft palate to fusion of the fingers.
And of course, during this ultrasound, the doctor will tell you the gender of the baby! Or it won’t tell you if the baby turns its butt or spins around, preventing you from seeing your private parts.
I went through all the stages of ultrasound examinations twice during my pregnancies, and the second screening was the most anticipated. During the first pregnancy, the doctor did not immediately tell the gender of the baby, but during the second, the research procedure began from that moment! Although deep down in my heart, even without an ultrasound, I knew that I was expecting boys.
At the second ultrasound, the baby has grown noticeably and therefore no longer fits completely “into the frame”
At the third ultrasound, much attention is paid to assessing the degree of maturity of the placenta, its thickness and location. Fetometry indicators - data obtained from ultrasound examination - are compared with standard ones, paying attention to the circumference of the head and abdomen, the length of the bones of the limbs, fronto-occipital and biparietal dimensions.
Biparietal size (BDS) is a kind of “width” of the fetal head, which is measured from temple to temple.
In addition, an additional study of the blood flow of the fetus and placenta using Doppler ultrasound is carried out.
In the third trimester, the fetus has almost finished developing, so the appearance of a 32-week baby is not much different from a newborn
Before birth, an ultrasound is performed to assess the weight of the fetus and the presence of umbilical cord entanglement. If the baby is very large - over 4 kg, and the mother is thin, with a narrow pelvis, this may be an indication for a caesarean section.
Before my second birth, I also had an ultrasound. They gave me an approximate weight - 3700 g. My son was born on 3740! But they didn’t say anything about the entanglement of the umbilical cord: either they didn’t want to worry, or they didn’t notice... As a result, the son was born with a double entanglement, however, the umbilical cord was unwound even before they raised him higher to show me.
Preparing for an ultrasound
No special preparation is required for the research procedure. Depending on the location of the ultrasound, you will need one or another set of things with you.
When visiting an ultrasound room during an antenatal consultation, you may need:
- exchange card, medical policy, passport;
- a diaper or sheet on which you will lie;
- shoe covers - upon request;
- napkins for removing gel from the abdomen, however, practice shows that government institutions also provide a napkin after the procedure;
- For an ultrasound in the first trimester, you will need a condom, which will be placed on the vaginal sensor.
If you visit a private clinic or ultrasound room, then you will need with you documents, a referral from a doctor - if you are going to a clinic where you are not registered, and the future father - if possible and willing. They even specifically invite you to come to the second ultrasound with your husband or loved one.
Since my husband is in the military and is always away, my mother went with me during my first pregnancy. And the second time, the eldest son was the first to know about the appearance of a future partner in games and fights.
It is recommended to go for an abdominal examination with a full bladder, but for a transvaginal examination, on the contrary, it is advisable to empty it.
How do they do it?
At the very beginning of expecting a baby, an ultrasound is performed using a transvaginal sensor. However, the diagnostician can only guess for now whether pregnancy has occurred or not, because the period is too short for precise formulations.
At 1-2 weeks, one of two types of studies is usually used:
- Through a transvaginal sensor, which is inserted into the vagina.
- Through the anterior abdominal wall - in this case, a conductive gel is applied to the abdomen, which allows you to obtain an image of acceptable quality.
Contraindications and recommendations for women in the second week of pregnancy
During this period, the complete formation of the egg and the fusion of germ cells occurs, so it is important for representatives of both sexes not to harm this process through careless behavior or the use of toxic substances.
Nutritional Features
The diet should be balanced and rational. It is recommended to maintain a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, fats and avoid eating unhealthy foods. You should also be mindful of the liquid. Many women, having reduced the amount of tea, coffee and soda consumed, forget about drinks. It is advisable to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day. This can be simple purified water, sugar-free fruit drinks, compote, etc.
Should you take vitamins?
If a woman follows a nutritious and balanced diet, taking additional multivitamins is not required. At the planning stage, women and men are recommended to take folic acid. Expectant mothers are advised to take this drug during the first trimester.
Sex at 2 weeks pregnant
Is it possible to have sex at 2 weeks pregnant? - it is possible without restrictions. The knee-elbow position (man behind) and the classic position (man on top) are considered the most favorable for conception. For better sperm movement after intimacy, a woman can raise her pelvis and stay in this position for 10-15 minutes. It is also useful to simply lie in bed for half an hour after sexual contact. Thanks to this, sperm will not flow out of the genital tract, but will move more intensively towards the egg.
Physical activity
At 2 weeks of gestation, it is recommended to perform physical exercises that improve blood flow in the pelvic organs. Walking in the air will be useful. Excessive exercise and training, which increase intra-abdominal pressure, should be avoided.
Medical procedures and medications
In the second week, it is better to refrain from performing any medical procedures and taking medications. The likelihood that they will affect the course of pregnancy is minimal, but it is better not to risk it. In any case, it is better to consult a doctor.
How to prepare?
Preparation for an ultrasound examination depends on the method used, as well as on the specific requirements of the clinic.
If the procedure is performed in a budget clinic, take with you:
- a towel or sheet to put on the couch;
- wipes to wipe off the gel (which is usually applied in abundance).
If the test is performed using a vaginal probe, the bladder will have to be filled. The doctor will recommend drinking enough liquid (preferably pure water) about half an hour before the examination. It is better to come to the ultrasound in advance and drink water right here, and not at home or on the road, so that the urge to urinate does not interfere with the examination.
Reference! To avoid increased gas formation, a few days before the procedure, eliminate foods that can cause fermentation (yeast products, legumes, raw cabbage, nuts, grapes and seeds, dairy products, soda).
What examinations need to be completed in the second week of gestation
At this stage, most women do not need to undergo examinations or tests. If previous tests have revealed progesterone deficiency, a test may be ordered to determine progesterone levels. Progesterone is responsible for the beginning of the formation of the placenta and preparation of the uterine cavity for implantation.
Normally, progesterone levels begin to increase from 10-12 days of gestation. If there are disturbances in its production, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Who is the study recommended for?
Doctors advise doing an ultrasound 1-2 weeks after conception in the following cases:
- if there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy;
- if a woman suspects that pregnancy has occurred and is very worried about this;
- if there is a risk of certain pathologies that can be prevented;
- if there is no menstruation, then you need to know whether pregnancy has occurred or not. If it is not identified, then you need to consult a doctor in order to start treatment on time;
- when you feel a nagging pain in the lower abdomen or existing inflammatory processes.
Is ultrasound harmful for a baby?
Feedback from ordinary people about the effect of ultrasound on a child is diametrically opposed: some say in horror that the wave radiation erases the genetic code, while others remember this procedure with warmth. In many foreign countries, an ultrasound is performed during every pregnant woman's visit to the doctor. There is also information that in Canada, in some clinics, ultrasound is performed only once during pregnancy, since it is considered harmful to the baby.
There are no physical research methods that would not disturb the baby in any way. The ultrasound causes him discomfort, so some children begin to increase their activity during the procedure, suck their thumbs, and cover themselves with their hands.
The first ultrasound machines had high power, so studies in the 70s of the last century discovered the negative impact of the procedure on animal embryos. However, the experimental studies used higher doses of sound radiation, which are not used during standard ultrasound of pregnant women. Epidemiologists claim that a regular ultrasound examination does not harm the baby, so the WHO officially allows 4 ultrasound procedures during pregnancy, provided that they are not performed before 10 weeks unless absolutely necessary.
Therefore, you need to take into account the seriousness of ultrasound as a physical factor and you should not try to discern the baby’s gender 10 times if he refuses to turn around. But there is no need to refuse officially approved screening.
What can be seen in the photo of the fetus?
When doing an ultrasound in the first and second weeks, women most often do not know whether pregnancy will be visible during the examination.
The first time after conception, a number of biochemical processes and various changes occur in a woman’s body.
Some of them can be seen on the ultrasound image:
- the precursor of the embryo - the dominant follicle, looks like a small tubercle, clearly visible during ultrasound examination;
- the uterine mucosa thickens, this is a characteristic sign of an increase in the amount of estrogen that occurs during pregnancy;
- The corpus luteum formed at the site of attachment of the egg is clearly visible.
Early pregnancy symptoms at 2 weeks
New physical sensations that give reason to worry - this is what the expectant mother may encounter in the current period of time. Symptoms often have a psychological basis, when you want to feel pregnant. At the same time, unconsciously, from the first weeks after fertilization, a woman is looking for changes in herself. How true these expectations and signs are will become clear in a couple of weeks.
| Breast soreness | Pain and changes in the mammary glands are often one of the first signs of the birth of a new life. The breasts are prepared for milk production and feeding 7-8 days after conception and the start of production of the hormone progesterone. The nipples become larger and more sensitive. Characterized by pain when touching the chest. |
| Change in mucous secretions | The amount of natural vaginal discharge increases. If at the time of ovulation they resembled egg white in structure, then during pregnancy the discharge becomes thinner and has practically no color. The smell should be neutral or absent. |
| Emotionality | The rapidly growing concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood causes changes in the psychological state of the pregnant woman. Behavior and course of action can become unpredictable for the pregnant woman herself - now she feels good and comfortable, and a minute later tears are already rolling down. |
| Drowsiness | At the initial stage, the female body requires a lot of strength to control the development of the small life inside. Fatigue and drowsiness become the expectant mother’s companions for the entire first trimester. So nature itself makes sure that the woman rests more at such an important moment in the intrauterine development of the life of the unborn baby. |
| Heaviness in the lower abdomen | Heaviness and discomfort can be disturbing due to their incomprehensible occurrence. These sensations in the lower segment of the uterus are associated with the period of implantation of the fertilized egg. They are short-term in nature, but, nevertheless, can be a positive sign of fertilization. |
What happens to the embryo during all 9 months?
Even when external signs of pregnancy are completely absent, the baby is already actively developing. The desire to know everything down to the smallest detail is quite logical. Unusual, but true, because only during intrauterine development does a person grow at maximum speed. It is about 50 cm in 9 months.
All 9 months are divided into 3 trimesters and 40 weeks. It is very difficult to determine the reliable date of conception; this is due to the individual characteristics of the female body. Therefore, doctors count from the first day of the last menstruation. This value is called the obstetric gestational age.
In order to be able to observe and control the entire process, in medical practice pregnancy is usually divided into trimesters:
- Lasts from the beginning of conception to 12 weeks.
- Starts at 13 weeks and ends at 28 weeks.
- 29 weeks and up to 40.
Sometimes it happens that a woman carries a child for more than 40 weeks. The reason for this may be errors in calculations or the provision of incorrect information about the last menstruation.
To study the development in more detail and monitor the process of the baby’s formation, it is best to consider his growth week by week. Let's consider what changes happen to a woman and her baby. Detailed weekly ultrasound photos will help you visually assess the process of fetal development.