According to the pregnancy management program, a comprehensive examination of the woman is carried out three times. In the second trimester, analysis of hormonal blood biochemistry and ultrasound examination are mandatory. Based on ultrasound data at 20 weeks of pregnancy, possible deviations in the development of the embryo of a genetic nature are diagnosed, the woman’s reproductive organs are assessed, and the baby’s gender is determined.
The results of laboratory microscopy determine:
- the degree of provision of nutrients to the child (AFP protein);
- quality of fetal preservation (hCG hormone);
- level of uterine development and uteroplacental blood flow (E3).
The objectivity of the study is assessed by the total result of screening indicators. Routine screening is carried out from 20 to 24 weeks, provided that the pregnancy proceeds without complications. Otherwise, the timing and frequency of ultrasound may vary at the discretion of the doctor observing the pregnancy.
Why is ultrasound diagnostics needed at 20 weeks of pregnancy?
At 20 weeks, an ultrasound is performed to see how the baby’s body is forming and whether there are any developmental abnormalities. From eighteen weeks of pregnancy, the fetal organs are sufficiently developed to be assessed.
Doctors analyze the size of these organs and their compliance with standards:
- heart;
- lungs;
- brain;
- main bones.
During this period, the condition of the amniotic fluid is assessed especially carefully. With each week, the amount of amniotic fluid should increase so that the growing embryo does not become dehydrated.
Possible complications
The twentieth obstetric week of pregnancy is a relatively calm time. During this period, the likelihood of miscarriage is low, however, the development of this complication cannot be excluded. Therefore, if a woman already feels fetal movements, she needs to monitor their appearance. And if the baby does not make itself known for more than a day, it is better to consult a gynecologist.
Hypertonicity
A common complication is high uterine tone. In the later stages (after 36 weeks), the tone of the uterus is a natural process of preparation for the upcoming birth. But at week 20 this condition is dangerous, as it can cause a miscarriage. Reasons that may cause uterine tone at 20 weeks:
- excessive physical activity or emotional stress;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- the development of an inflammatory disease affecting the internal genital organs;
- Rhesus conflict;
- low attachment of the placenta.
The tone of the uterus is manifested by the fact that the woman feels tension in the organ. As a rule, this sensation is described as a mild pain of a pulling nature. In addition, a woman may feel that her pregnant belly has become very heavy.
Therefore, if you have a tummy tug at 20 weeks of pregnancy, you should not ignore this symptom. Especially if the pain is accompanied by spotting at 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Edema
Many pregnant women experience edema. However, physiological edema, which does not pose any particular danger, appears after 30 weeks. If swelling appears at week 20, this may be a sign of gestosis - a serious complication.
How to understand that swelling has appeared? As a rule, the limbs begin to swell first. Therefore, if your shoes suddenly become too small or you cannot put a ring on your finger, you should consult a doctor.
Advice! Edema can also be hidden. They can be detected by regular weighing. If you suddenly begin to weigh a lot more, it means that fluid is retained in the body.
Pain
At this stage, pregnant women most often complain of pain in the back and lower back. This is due to changes in posture. To eliminate the cause of pain, it is recommended to use special bandages.
An alarming symptom is abdominal pain. If you often have stomach pain during the 20th week of pregnancy, you should definitely consult a doctor. Abdominal pain is not necessarily related to pregnancy. They can be triggered by malfunctions of the digestive system or kidney diseases.
Painful sensations cause cramps in the legs, which can bother a pregnant woman. The reason for their occurrence is the increased load on the legs. To reduce the likelihood of cramps, try to rest your legs more often.
Colds
Even if all preventive measures are taken, it is not always possible to avoid infection with ARVI. Of course, a common cold at 20 weeks of pregnancy no longer poses a serious threat to the baby. But if you suffer from a cold on your feet and do not treat it, the disease can cause serious complications that will negatively affect the course of pregnancy.
Therefore, if signs of a cold appear, you need to take a sick leave, and if you have a fever, stay in bed. You need to treat a cold by following the instructions given by your doctor.
So, the 20th week of pregnancy is approximately the middle of the gestation period. This period is relatively calm, since the baby is no longer as vulnerable as in the first weeks. And the expectant mother herself feels much better, although some discomfort associated with the growth of the abdomen may still be present.
Preparation for the procedure
An ultrasound scan for the twentieth week of the pregnancy cycle will require a little preparation from the woman:
- Before the examination, you should definitely carry out hygiene procedures. It is better to wear clothes for an ultrasound in such a cut that it is easy to expose the stomach.
- Since the uterus has already enlarged due to its growth, there is no need to drink water before the procedure. It will be possible to distinguish the child’s organs on the screen.
- The day before diagnosis, you should exclude: citrus fruits, seafood, carbonated drinks. To reduce the amount of gas in the intestines, you can drink activated charcoal two to three hours before your visit to the doctor.
For examination by a diagnostician, the expectant mother should bring:
- pregnant woman's card;
- all previous tests;
- medical insurance;
- passport.
Screening can be carried out both in a private clinic and in a district clinic. If the expectant mother prefers to go to the clinic, it is worth taking a diaper with her, which will be needed for the ultrasound.
Main stages
In the second trimester of pregnancy, an ultrasound examination is usually performed using the abdominal method; the procedure consists of several stages:
- The doctor applies a special gel to the woman’s stomach and runs a special ultra-wave sensor along the outside of the uterus.
- After this, an image of the fetus is displayed on the screen.
- The built-in program measures the child’s indicators.
- The doctor collects this data and makes an analysis based on it.
- After the procedure, the doctor gives the mother a protocol with a transcript of the study results.
If a woman has excess weight concentrated in the abdominal area, doctors prefer to use a vaginal probe to get a full view of the inside of the uterus.
Step-by-step ultrasound transvaginal method:
- A condom is placed on the intravaginal sensor. After this, the sensor is lubricated with gel.
- The doctor inserts a probe into the woman's vagina, examining the reproductive organs and the development of the fetus in the womb.
- The data is displayed on the monitor screen. The ultrasound doctor begins to decipher the obtained parameters and, upon completion of the analysis, announces them to the expectant mother.
How can a baby's formation be seen on an ultrasound?
Determining the sex of the fetus is an optional point in the management of a pregnant woman, and if future parents do not want to know the sex of the baby in advance, they can refuse such a diagnosis. However, in cases where the patient has hormonal imbalances, this indicator is very important for the prenatal examination protocol.
Disorders of the functional activity of endocrine organs always negatively affect the development of the baby’s body and can provoke the occurrence of serious congenital anomalies - pathologies of adrenal function and other pathological processes in the endocrine system.
Carrying out a diagnostic procedure is mandatory at every screening of pregnant women (to monitor the situation over time) in cases where a child is born in a family with:
- hermaphroditism - the presence of a defect in the reproductive system, in which there are external and internal signs of both sexes;
- hypospadias – an anomaly in the development of the urethra;
- adrenogenital syndrome - congenital virilizing adrenal hyperplasia.
According to medical statistics, male infants most often have minor anomalies in the development of the genital area; in girls these problems are much more complex. Despite the fact that the formation of the genitals occurs already in the sixth week, they can be examined in detail on an ultrasound monitor only in the twentieth. For this purpose, practitioners use one of the most informative diagnostic methods - transvaginal ultrasound. It is with this method that you can create a 3D image and improve the visualization of the baby.
If happy parents are expecting a girl, the picture will show the following indicators: 4 parallel lines in the perineal area - an analogue of the labia minora and majora
If, during an examination, a result that is unclear for interpretation by a specialist is received (when the genitals look abnormal), the pregnant woman is sent for molecular genetic testing, in which the number of chromosomes present in her blood is calculated.
This case requires constant monitoring, additional examination, and, under certain circumstances, appropriate measures to terminate the pregnancy.
What does an ultrasound show?
During an ultrasound, a diagnostician and geneticist look at the developmental parameters and structural features of the fundamental organs of the fetus.
Using ultrasound you can determine:
- functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- brain activity and growth;
- possible developmental delay;
- bone growth;
- lung function;
- functioning of the digestive system;
- the presence of genetic or chromosomal diseases in the fetus.
The video shows the 4D ultrasound technique in the second trimester. At the time of photography, the fetus is 19 weeks old. Author: Marina Kiseleva.
Clarification of gestational age
At week 20, using an ultrasound examination, the exact gestational age is calculated. This is done according to the baby’s development indicators based on the table of fetal fetometry norms.
Number of embryos
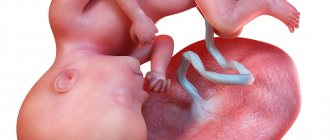
An ultrasound allows you to find out the exact number of fetuses and even hear the baby’s heartbeat. If a woman is pregnant with twins or triplets, an ultrasound in the second trimester will show exactly how many developing embryos are in the uterus.
In cases where a woman is expecting two or more babies, doctors make sure that the children’s development is uniform. It is important that the fruits do not have significant differences in growth and that each receives its own portion of oxygen and nutrients.
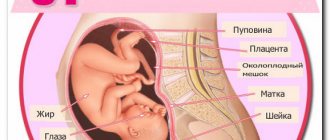
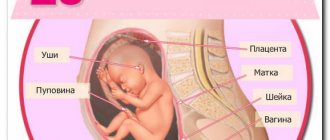
Location of the placenta
The location of the placenta is another indicator of fetal ripening and pregnancy during this ultrasound.
Doctors look at the following sensor readings about the placenta:
- the thickness of the placenta varies up to 25 mm;
- the length from the pelvic outlet to the lower edge of the placenta is no more than 70 mm;
- degree of maturity of the placenta – 0;
- the amniotic sac must be intact.
Fetal presentation
The doctor must look at the display to see the full image of the baby’s position (fetal presentation) inside the mother’s womb. This gives him the opportunity to assess which largest part of the unborn baby’s body is located near the exit from the uterus.
There are two types of presentation of the baby in the uterus:
- Head presentation is considered normal. Positioning the head closer to the exit allows the birth process to be carried out without complications.
- The pelvic location is a less successful option, however, there is no reason to worry. Medicine has learned to work with this position of the child in the womb. In addition, at week 20, the baby may roll over several times during the day, and the position with the pelvis facing the exit is not diagnostic.
Fetal development
At the age of 18 to 20 weeks, the child’s basic vital organs are already quite clearly developed.
An ultrasound at 20 weeks of pregnancy shows the development of the following baby organs:
- The brain has an almost complete structure. The nervous system is already developed, and nerve cells are already contained in this structure.
- The spine is completely formed at this point. The vertebrae, muscles and tendons between them are visible.
- Hair appears: eyelashes and eyebrows grow on the child’s face.
- The nose and ears have almost reached their final form.
- The heart beats from 120 to 160 beats per minute.
Survey time range
The specific timing of the second examination is based on the criteria for fetal growth and development. At 19-20 weeks, the baby’s production of somatotropin growth hormone increases. The baby increases significantly in size, which allows the doctor to examine its body parts and internal organs in detail. By this period, the baby’s skeletal system is clearly visualized. The doctor can evaluate the probable malformations of its development (curvature of the main skeletal rod, the length of the bones in relation to the norm, the size of the head frame, facial bones).
Internal organs and systems are also formed by 20-21 weeks of intrauterine development. The state of health of the heart, nervous, genitourinary, and digestive systems can be fully analyzed. It is during this period that possible pathologies of a hereditary nature, or deviations that arose during the growth of the baby, are identified:
- severe defect of the nervous system (anencephaly);
- a serious form of genomic pathology (Down syndrome);
- chromosomal pathology – Edwards syndrome, otherwise trisomy 18 syndrome;
- rare genetic diseases (Turner syndrome and Patau syndrome).
Abnormalities in laboratory tests, on the basis of which the doctor can make a disappointing diagnosis
If the doctor doubts the reliability of the diagnosis, the woman is asked to undergo amniocentesis in a hospital setting to confirm or refute the alleged abnormalities. This is a rather risky and complex manipulation of collecting amniotic fluid for detailed analysis, but the reliability of the results reaches 96%. Some pathologies detected in time, for example, heart defects, can be eliminated through intrauterine surgery. Then, by the time of birth, the baby will be healthy.
Based on ultrasound data in the second trimester, the doctor can diagnose diseases in the baby that make viability impossible. As well as severe deviations, when the child’s life activity will be impossible without the support of medical equipment. In this case, the question of termination of pregnancy arises. The possibility of abortion lasts only up to twenty-two weeks.
Later, the operation will have the nature of an artificial birth. For a woman, this is not only physical pain, but also serious psychological trauma.
Additionally
At the twentieth week, the child begins to differentiate night and day, actively work with his legs (pushing) and arms (clinging to the umbilical cord, sucking fingers). In addition, the baby may change facial expressions (smile or frown). Hair and nail plates are formed. An ultrasound examination at 20–24 weeks allows you to identify, and, if possible, correct deviations in the intrauterine development of the baby. It is absolutely impossible to ignore screening at this time.
Ultrasound norms at 20 weeks of pregnancy
There are certain standard indicators of normal development at 20 weeks of pregnancy. They are not universal, because every child is unique and his development also occurs individually. But their transcript is available for mothers to review before consulting a doctor.
The table shows basic data on fetal development:
| Parameter name | Standard in mm |
| Biparental fetal size | 45–53 |
| Fronto-occipital size | 56–68 |
| Head circumference | 154–186 |
| Abdominal girth | 137–166 |
| Calf length | 27–33 |
| Shoulder length | 26–36 |
| Forearm length | 23–29 |
| Nasal bone | 5,8-8,2 |
| Collar thickness | 2,8-3 |
An ultrasound examination will enable the doctor to make a conclusion about whether the indicators and diagnostic results are normal.
Fetometry standards
Normal fetal fetometry at 20 weeks of pregnancy:
| Week of pregnancy | Fruit weight, g | Coccygeal-parietal size (CTR), cm | Bust girth (BG), mm | Thigh length (DB), mm | Biparietal size (BPR), mm |
| 20 | 345 | 24,1 | 48 | 34 | 47 |
Doppler
At the 20th week of pregnancy, Doppler testing is prescribed to double-check the results of the functioning of the cardiac organ. Normal heart rate is 120–160 beats/min in the twentieth week.
This examination must be carried out for the following indications:
- pregnant woman over 35 years old;
- unsuccessful previous pregnancies;
- diagnosis of low water;
- retardation in fetal development;
- multiple births.
Norms for Doppler measurements at 20 weeks of pregnancy:
| Artery name | FROM TO | IR |
| Uterine arteries | up to 2.2 | up to 0.56 |
| Spiral arteries | up to 1.73 | up to 0.39 |
| Umbilical artery | up to 3.9 | up to 0.79 |
| Middle cerebral artery of the fetus | up to 3.9 | up to 0.79 |
Explanation:
- Resistance index (RI): the ratio of the difference between systolic and minimum (diastolic) blood flow velocities and its maximum value.
- Systole-diastolic ratio (SDR) is the ratio of maximum systolic to end-diastolic blood flow velocity.
Recommendations
The expectant mother’s weight gain is in full swing, 500–800 g per week. The total gain by week 20 should be no more than 4–5 kg.
Weight gain occurs individually for each woman, but if it occurs at a rapid pace, this indicates the presence of excess fluid in the body. In some cases, this occurs due to a complication – preeclampsia.
If weight gain occurs due to increased appetite, then you should listen to the advice of doctors:
- Starting from the first weeks of pregnancy, you should carefully monitor your diet. Eliminate harmful foods: salty, spicy, spicy, smoked.
Avoid foods that are fatty, rich in sugar, or canned. You should avoid fast food containing trans fats. Limit consumption of flour, sweet, fried foods. Avoid sweet carbonated water and alcohol.
- Increase the amount of foods containing nutrients and minerals. The future baby and mother need calcium. The daily requirement for it is from 1000 to 1300 mg per day.
Proper nutrition during pregnancy is very important
- Choose the right foods that will not cause bloating. These include fruits, leafy greens, and whole grain pasta. All of them contain dietary fiber, which has a positive effect on digestion. In this case, you should limit your consumption of cabbage and onions. To control heartburn and bloating, you should drink more water and eat small meals often.
Don't forget about physical exercise. They are important for a woman’s health, will help prevent complications, and make future childbirth easier. Doctors recommend doing gymnastics daily for half an hour.
Aerobics and swimming are useful. Kegel exercises help to stretch the pelvic muscles. Sports such as cycling, martial arts, and ball games are contraindicated for pregnant women.
Tips for women 4 months pregnant:
- To relieve swelling in the legs, you should take a lying position, raising your legs above the level of your heart.
- Cramps in the calf muscles can be relieved by drinking plenty of fluids.
- To find a comfortable position during night or daytime sleep, you can use a blanket bolster or a special pillow that is placed between your legs.
- In order to have a full and sound sleep, you should ventilate the room in the evenings, and always go to bed at the same time, no later than 11 p.m. To restore strength, sleep at night should be at least 8 hours.
- For a sound sleep, you can take a relaxing warm bath with ylang-ylang essential oil before bed, and drink a glass of warm milk.
- After waking up, you should get out of bed slowly, without sudden movements.
- You can avoid heartburn if you limit your food intake in the evening and do not lie down in a horizontal position immediately after eating.
- Spend more time walking in the fresh air. This will relieve headaches and restore emotional balance.
- To prevent constipation, it is useful to drink plum juice and prune infusion. In the morning, drink 1 tbsp. warm water.
Diet for constipation in women during pregnancy.
Sample menu You should give up many medications. They can cause miscarriage, abnormalities in the child, and developmental delays after birth. Any remedy must be agreed with your doctor.
The second trimester is characterized by a phase of rapid growth of the unborn child. For this reason, you should especially monitor the mother's health during the 20th week of pregnancy. You should pay attention to any deviations from the norm and consult your doctor in time.
Determination of gender
20 weeks is the right period of pregnancy to find out the sex of the baby. Since in the first trimester the baby is still underdeveloped, it is very difficult to examine his genitals. By the 20th week of pregnancy, if the child does not cover his genitals with his arm and leg, it is not difficult to establish his gender.
At this stage of development, in 95% of cases, an ultrasound can accurately show who the expectant mother is expecting: a daughter or a son.
Photo gallery
The photo gallery shows photographs showing what a boy looks like at 20 weeks of pregnancy and a photo showing a girl in the second trimester.
Girl
Boy
Common features of fetuses of both sexes
At an early stage of differentiation, the reproductive organs of fetuses of both sexes are very similar and can only be distinguished from each other using high-resolution equipment, such as 4D.
As for the remaining parts of the body of babies developing in the womb, they are structured the same regardless of the child’s gender. Observations have shown that girls grow more slowly, and boys are more sensitive to nutritional deficiencies and other unfavorable factors.
Accuracy of the study
An error during an ultrasound examination occurs in 5% of 100 cases.
There are several reasons why the study is wrong in its data:
- outdated equipment;
- unqualified doctor;
- short gestational age;
- features of maternal anatomy.
Diagnoses that can be mistaken by ultrasound:
- frozen pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- false absence of pregnancy;
- genetic diseases of the fetus;
- gender of the child.
Video
The video shows the ultrasound process in the second trimester of pregnancy, during which the sex of the child is determined. The ultrasound specialist also shows the location of the baby’s main organs in the picture. The author of the video is Tanya.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 2 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Probability of errors in ultrasound diagnostics
The risk of obtaining unreliable results in determining the sex of the unborn child is possible only in the first trimester of pregnancy. The longer the period, the higher the visualization of the genital organs and the less error in the final ultrasound data. In some cases, diagnosis can be difficult not only due to the early stage of pregnancy, but also due to the location of the internal organs of the expectant mother (intestines and bladder) and the unfortunate position of the fetus - it can close or turn away.
The doctor may make a mistake due to bends in the umbilical cord, swelling of the girl’s fingers or labia. The receipt of inaccurate data is not always due to the fault of a medical specialist - not all factors depend on his qualifications and attentiveness. And if in the early stages of the baby’s gestation period inaccuracy is associated with a short period of time, then in the second trimester errors occur due to the quality of diagnostic equipment and from the fetus itself, which can turn “the wrong way.”
In the third trimester, there is also a possibility of receiving inaccurate final ultrasound data - the baby becomes large and cannot move freely in the womb. This phenomenon affects the resulting image; the doctor always warns about the remaining probability of error regarding determining the sex of the child.
Experienced ultrasound diagnostic specialists and obstetrician-gynecologists who have been working with expectant mothers for a long time can determine with great certainty at an early stage who will be born to a married couple.
In conclusion of all the above information, I would like to emphasize once again - today, examination of a pregnant woman and unborn child using ultrasound waves is the safest, high-quality, informative and reliable method. Despite the fact that every parent wants to know who will be born - a boy or a girl, it is much more important that the child is born healthy.