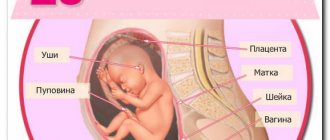
From the 31st week of pregnancy, the baby takes its final position in the uterus. In addition to the fact that it is already difficult for the child to make turns, the expectant mother also feels stiffness in her movements and clumsiness. By this time, some pregnant women find it difficult to walk. The expectant mother's breasts are also preparing for the upcoming feeding function.
In the third trimester, you should undergo a complete medical examination. An ultrasound scan at 31 weeks of pregnancy is mandatory. At this stage, this study is able to identify possible threats to the course of pregnancy and at the same time check the condition of the child.
The degree of maturity of the baby’s lungs at 31 weeks of pregnancy is equal to one. For a successful birth, you must listen to all the recommendations of your obstetrician-gynecologist. Also, during the entire period of pregnancy, you should not skip an ultrasound; this diagnosis must be completed on time. After all, an ultrasound examination is necessary not only to take a photo of the baby and find out its gender, but also to monitor the child’s condition, in order to ensure that developmental indicators correspond to the deadline. If the images are taken using 3D ultrasound, then the iris of the eye can be seen in the photograph.
Survey objectives
At week 31, a third prenatal screening is scheduled, the task of which is to summarize the results of the first two and find out how the baby is feeling at this stage. The research is now very informative from the point of view of planning tactics for the upcoming birth. Many babies already at this stage assume their final body position, in which they will be born. This makes it possible to minimize the number and risks of birth injuries, because with a breech or transverse presentation, a woman may be required to have a caesarean section.
An ultrasound at 31 weeks of pregnancy allows you to clearly and carefully examine the structure of the baby’s internal organs, since all of them are already quite large and are perfectly visualized. An ultrasound examination is considered routine; it is carried out free of charge in a consultation at the place of residence of the expectant mother.
In addition to screening tasks, an ultrasound scan of the third trimester also has additional tasks - the scan should clarify the condition of the child , the characteristics of the uterine placental blood flow, show the baby’s growth dynamics, and clarify the expected date of birth, which is just around the corner.
Outside of the plan, pregnant women with twins or triplets, pregnant women through IVF, as well as women with a severe obstetric history, including after a previous cesarean section, can count on an ultrasound scan at this time, since at such a long time it is important to monitor the condition of the postoperative scar on the uterus.
Calculate the gestational ageIndicate the first day of the last menstruation12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031JanuaryFebruaryMarchAprilMayJuneJulyAugustSeptemberOctoberNovemberDecember20192018Calculate
Pregnancy with twins
The female body is designed to bear one child, so pregnancy with twins or triplets, which often occurs after artificial insemination (IVF), is considered dangerous for both the woman and the babies. The most common occurrence is twins. In medical practice, there are several types of such pregnancies. They depend on the number of placentas and membranes.
The most common type of twins is diamniotic, which is divided into dichorionic and monochorionic. The dichorionic type of diamniotic twins is considered the most favorable for the health of infants. At the same time, each baby has his own personal space, because the amniotic sac is divided in half by the amniotic septum. In addition, each baby has its own placenta.
With such a pregnancy, there is a risk of developmental delays in one of the babies, but this does not always happen. A woman with this condition is advised to be under close medical supervision, undergo regular tests and follow all doctor's recommendations.
Carrying out the procedure
An ultrasound at 30-31 weeks is done externally, transabdominally, in which the device’s sensor is located on the woman’s anterior abdominal wall. The uterus is so large that the pregnant woman’s build no longer plays any role; excess weight and fat folds on the abdomen cannot hinder visualization.
The doctor uses a vaginal sensor only if the woman is at risk of premature birth, or rather, the obstetrician-gynecologist is inclined to believe that there is abnormal cervical dilatation for this period.
No preparation is required for an ultrasound . If a woman wants to have a 3D or 4D ultrasound scan, she should be aware that such an examination takes longer than a traditional ultrasound - from 40 to 55 minutes. It makes sense to take with you to any type of ultrasound an exchange card and passport, replacement shoes and a clean diaper so that you can cover the couch on which you will lie during the scan.
What will the study show?
The size of the fetus at 31 weeks is quite large, so it is not possible to examine the baby as a whole; no sensor provides such a wide view. They will examine the child in parts - head and face, neck and chest, spine and stomach, limbs. The baby's height exceeded 40 centimeters, and his weight was more than one and a half kilograms. Some babies may weigh close to 2 kg.
The baby stores subcutaneous fat, which allows him to quickly gain weight, and after birth it will protect the baby from freezing, because thermoregulation functions will not yet be adjusted. Due to fat, the baby’s body takes on a more attractive appearance – cute folds appear on the arms and under the knees, dimples appear on the cheeks, and wrinkles are smoothed out. The baby at 31 weeks looks almost the same as it will look immediately after birth.
The child has fully formed all senses. He hears and even partially sees, distinguishes the voices of people close to him from unfamiliar and frightening sounds, distinguishes darkness from light. If you point a switched-on flashlight at your stomach, your baby will reflexively close his eyes. He's already opening his eyes when he's awake, and if he's lucky, he might be able to demonstrate this during the ultrasound.
The lungs are preparing for independent breathing. While the baby does not know how to do this, his lungs begin to produce a special substance - a surfactant, which will not allow the alveoli to stick together during exhalation after the baby is born.
At 31 weeks, the formation of grooves or convolutions in the baby’s brain continues, he becomes “smarter”, and the connection between the brain and muscles becomes more streamlined. The baby's movements are now, although less active than before, but they are filled with meaning - he can purposefully pull his fists into his mouth, grab the umbilical cord, touch his face.
Motor activity is not as intense as in the second trimester, because the baby is already feeling noticeably tighter in the mother’s womb.
The baby assumes a compact position, which makes it difficult to see the genitals, so determining gender in the third trimester can be more difficult than in earlier periods.
The stomach and intestines, bladder and kidneys are actively working. The baby swallows amniotic fluid, hiccups, pees, and original feces, called meconium, are deposited in the intestines. The baby sleeps and is awake. During periods of wakefulness, he can play with his fingers or the umbilical cord, which can also be seen on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner.
Decoding and norms
Understanding what is written in the ultrasound report is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. The doctor necessarily measures the basic parameters, which are called fetometric. These are the dimensions of the head - fronto-occipital and biparient, as well as the length of the paired leg bones - femur and tibia, and arms - humerus and forearm bones. The diameter of the chest and two circumferences of the abdomen and head are also subject to measurements. Then the results obtained are compared with a special table.
Fetometry table for 30-31 weeks of pregnancy (average values only):
| BPR, mm | LZR, mm | DBK (thigh), mm | DKG (shin), mm | DPK (shoulder), mm | DCP (forearm), mm | Chest diameter, mm | Head circumference, mm | Abdominal circumference, mm |
| 78-80 | 97-101 | 57-59 | 53-56 | 53-55 | 46-48 | 79-81 | 285-294 | 264-274 |
The conclusion of the ultrasound necessarily describes the anatomical features of the child’s development. At this time, the doctor has every opportunity to examine the baby’s internal organs, making a conclusion about the presence or absence of congenital defects.
The placenta at 31 weeks has the first degree of maturity, in some cases it qualifies as transitional - from the first to the second, although aging of the placenta to the second degree after 35 weeks is normally considered normal. The amount of water gradually becomes less, because the baby grows and needs more and more space in the uterine cavity. This week, the amniotic fluid index is considered normal, equal to 82-88 mm (on average).
Decoding the results
At the 31st week examination, the doctor examines the condition of the mother and fetus. He reports the presence or absence of pathologies already during the procedure.
The specialist transmits the ultrasound results to the doctor in the form of a description. Using this decoding, a woman herself can understand how well her child’s indicators correspond to the norm:
Minor fluctuations in indicators are not critical. This also applies to how much the baby weighs. This parameter depends on its individual characteristics.
The doctor also checks the condition of the internal organs. The digestive and sensory organs are fully formed by this time. The brain already has convolutions. The testicles have not yet descended, the lungs continue to form.
Possible problems
Deviations of a particular child’s indicators from the average values indicated in the table can be both physiological and pathological. If an ultrasound at 31 weeks reveals a developmental delay, then the lag is quite significant - about 2 weeks from the established obstetric due date (at 31 weeks the baby’s size corresponds to 29 weeks). Exceeding the values by the same difference can also indicate pathology - edema, genetic abnormalities, developmental defects, intrauterine infection.
Small deviations should not disturb the expectant mother and her loved ones. The physiological difference may be due to the hereditary characteristics of the child’s appearance and physique - some are born larger, others thinner, some have long legs “like mom”, while others have short legs “like dad”. Noses can be snub-nosed or with a hump, and everyone’s head is also different. At week 31, the baby is already developing according to an individual program laid down by nature, he is who he is.
Cloudiness of the waters, as well as a suspension detected in them based on ultrasound results, may indicate that the child is unwell - hypoxia, or a previous intrauterine infection. If the woman has a complicated medical history, she will definitely undergo an ultrasound with Doppler to understand how well the placenta is supplied with blood and whether the baby has enough oxygen and nutrients.
The threat of premature birth may be indicated by shortening and softening of the cervix, as well as the tone of the uterine muscles and incomplete closure of the cervical canal. A baby born at 31 weeks may survive and has everything he needs, but will require more careful care. The doctors’ task is to maintain the pregnancy for at least another month and a half.
Interpretation of fetal ultrasound
Already from the 11th week of pregnancy, detection of fetal pathologies is allowed. In Russia, two main standard protocols are defined for which data is decrypted.
These studies are conducted at 11–13 weeks of pregnancy and at 19–22 weeks. In order to more accurately decipher the data, you need to know the norms of fetal development at different stages of gestation.
First fetal screening. At this time, a detailed examination of the fetal collar zone is carried out - the area between the tissues and skin in the neck area. The thickness of the collar zone is designated by the abbreviation TVP. Normally, TVP should not exceed 2.7 mm.
* Percentile is a descriptive statistics term. The average value is indicated in the “50th percentile” column; in the “5th percentile” and “95th percentile” columns are the minimum and maximum allowable values, respectively.
The nasal bone is another parameter that is examined at this time. Normally, the bone should be visualized.
| Gestational age in weeks | Standard value for the length of the nasal bone, mm |
| 10-11 week | determined |
| 12-13 week | 2,0-4,2 |
| 14-15 week | 2,9-4,7 |
Another indicator that is measured at this stage is CTE (coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus).
For a baby at 11–13 weeks, the norm is considered to be a CTE in the range of 45–80 mm.
In addition to the CTE, the doctor evaluates the biparietal and fronto-occipital dimensions of the fetus. The first is the distance from one temple of the head to the other and is normally up to 28 mm. The second - the distance from the frontal to the occipital bone - normally does not exceed 31 mm.
* Percentile is a descriptive statistics term. The average value is indicated in the “50th percentile” column; in the “5th percentile” and “95th percentile” columns are the minimum and maximum allowable values, respectively.
Separately, the doctor evaluates the diameter of the ovum...
... and calculates the heart rate (HR).
If the indicators do not correspond to the norm, the pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a genetic consultation and additional examination.
Second fetal screening
The norms of fetal development in the second trimester are shown in the table:
* Percentile is a descriptive statistics term. The average value is indicated in the “50th percentile” column; in the “5th percentile” and “95th percentile” columns are the minimum and maximum allowable values, respectively.
If there are any changes in these indicators, we can assume deviations in the development of the child in the womb. By the way, during the second screening the fetus is visible much better than during the first, so the doctor can judge not only about genetic abnormalities, but also about other defects (they are recorded separately in the examination report).
Third fetal screening
As part of the third screening, such baby parameters as height, weight, biparietal head size, hip and chest length are assessed. The standards for the listed parameters are described in the table above. Below are the normal indicators of BPR and LZR.
* Percentile is a descriptive statistics term. The average value is indicated in the “50th percentile” column; in the “5th percentile” and “95th percentile” columns are the minimum and maximum allowable values, respectively.
During the 3rd screening, the doctor assesses the condition of the placenta, its degree of maturity and thickness . The placenta is the connecting link between a mother and her baby. It remains for the entire duration of pregnancy. It exists in order to nourish the child with the necessary nutrients.
Normal placenta maturity:
Standards for placental thickness:
Norms of AFI (amniotic fluid index)
* Percentile is a descriptive statistics term. The average value is indicated in the “50th percentile” column; the remaining columns indicate the minimum and maximum acceptable values, respectively.
Fetal size by week of pregnancy
Each trimester carries out its own research and takes its own measurements. Interpretation of ultrasound indicators helps to determine the size of the child at the time of its development.
Below is a table of fetal sizes and weights by week. It is worth saying that the readings are average and may differ from reality. This is especially true in the last months of pregnancy.
A newborn may be born weighing 2300 grams, or may be born weighing 4500 grams. In both cases, he can be absolutely healthy.
| Duration in weeks | Height in cm | Weight in g |
| 11 | 6-9 | 11-16 |
| 12 | 9-11 | 16-21 |
| 13 | 10-12 | 20-30 |
| 14 | 12-14 | 30-50 |
| 15 | 14-16 | 50-75 |
| 16 | 16-18 | 75-115 |
| 17 | 18-20 | 115-160 |
| 18 | 20-22 | 160-215 |
| 19 | 22-24 | 215-270 |
| 20 | 24-26 | 270-350 |
| 21 | 26-28 | 350-410 |
| 22 | 28-30 | 410-500 |
| 23 | 30-32 | 500-600 |
| 24 | 32-34 | 600-750 |
| 25 | 34-36 | 750-850 |
| 26 | 36-37,5 | 850-1000 |
| 27 | 37-39,5 | 1000-1200 |
| 28 | 38-40 | 1200-1350 |
| 29 | 39-40 | 1350-1500 |
| 30 | 40-41 | 1500-1650 |
| 31 | 41-42,5 | 1650-1800 |
| 32 | 43-44,5 | 1800-1950 |
| 33 | 44,5-45 | 1950-2100 |
| 34 | 44,5-46 | 2100-2250 |
| 35 | 46-46,5 | 2250-2500 |
| 36 | 46,5-48 | 2500-2600 |
| 37 | 48-49 | 2600-2800 |
| 38 | 49-50 | 2800-3000 |
| 39 | 50-51 | 3000-3200 |
| 40 | 51-54 | 3200-3500 |
What is an ultrasound at 30-34
In the third trimester of pregnancy, ultrasound is performed transabdominally. The woman lies on her back. A sensor using a special gel moves across the abdomen. Ultrasound passes through the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall to the fetus and reproductive organs of the mother and is partially reflected from them. As a result, on the monitor screen the doctor sees the black and white image necessary for the assessment. In case of severe inferior vena cava syndrome, when, due to compression of large vessels by the uterus, while on her back, the pregnant woman becomes ill and loses consciousness, the examination is allowed in the lateral position.
To make the ultrasound diagnostic procedure easier, a woman can empty her bladder. No special preparation is required for the study. However, if it is necessary to measure the thickness of the postoperative scar on the uterus, the bladder must be filled. To do this, you need to drink 0.5-1 liter of liquid in 30-60 minutes.
What is looked at by ultrasound at the 31st week of pregnancy: description and table of normal indicators
› Ultrasound during pregnancy
02.07.2019
At the 31st week of pregnancy, an ultrasound allows you to check the presentation of the fetus, which has taken its final position. The examination also checks the readiness of the child’s organs for birth. Such diagnostics allows you to determine the birth technique and, if necessary, adjust the course of pregnancy.
Indications and contraindications
The last ultrasound is usually done at 31 weeks. The doctor looks at the position of the fetus, the umbilical cord and studies the degree of development of its organs. The procedure has no contraindications.
The walls of the placenta protect the fetus from any unpleasant sensations during an ultrasound.
The last ultrasound can be scheduled at 32 and 33 weeks. In this case, at the 31st week, an examination is carried out for a number of alarming signs:
- Floaters before the eyes. Sometimes such a symptom does not indicate pressure fluctuations, but the development of internal edema.
- Increased fatigue and regular cramps. These are signs of late toxicosis.
- Pain in the head, dizziness. Often indicate a gestational condition.
- Suspicion of oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
- Cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
- Any unusual vaginal discharge.
- Excessively frequent fetal movements. Sometimes they indicate oxygen starvation.
- Past acute colds and viral diseases.
The described symptoms may be a reason to refer a pregnant woman for an ultrasound scan.
To watch a video review from the doctor:
Preparation and performance of ultrasound
The last ultrasound does not require special preparation. All that is required of a woman is to sign up for an examination and come at the appointed time. Before the procedure you need to take a shower.
You need to take with you: a referral from a doctor, shoe covers, a diaper for the couch, disposable wipes for wiping off the gel. In paid clinics they give out all this.
At the 31st week, fetal fetometry is performed transabdominally. The examination goes like this:
- The couch is covered with a towel. The woman exposes her abdominal area and lies down on the couch.
- The doctor applies a sound-conducting gel to her stomach. It is cold and sometimes causes discomfort.
- The specialist moves a sensor over the woman’s stomach. He examines the image that appears on the screen and tells the woman about the presence or absence of pathologies.
- The woman stands up and wipes the remaining gel from her stomach.
The duration of a conventional two-dimensional ultrasound is only 15–20 minutes. Three-dimensional and four-dimensional studies last much longer - up to an hour.
What will an ultrasound show at 31 weeks?
31 weeks, at which the pregnant woman will have her last third ultrasound examination. Only in exceptional cases will a specialist prescribe a third ultrasound at 32-33 weeks. During an ultrasound examination, the sonologist considers the following indicators:
- Number of breathing movements;
- Motor activity;
- Heartbeat;
- The degree of maturity of the placenta;
- Location of the umbilical cord (excluding entanglement of the fetus).
The specialist examines the condition of the child’s organs, records all indicators, compares them with the norm, and determines the condition of the uterus, cervix, and placenta.
The amount of amniotic fluid, fetoplacental, and uteroplacental blood circulation are subject to assessment. Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels is considered a necessary procedure at 31 weeks.
During this period of pregnancy, you can observe the emotional activity of the fetus during an ultrasound, as well as examine the baby’s first movements and his ability to suck a finger. After the ultrasound diagnosis, the mother will receive a cute photo of her baby.
Treatment of colds in the third trimester
The 31st week of pregnancy is a period when all the internal organs and systems of the baby are already fully formed. At this stage, a cold is no longer so terrible for the fetus, but this does not mean that viral and bacterial infections can not be treated.
Of course, it is strictly not recommended to select any medications on your own during this period, because many drugs can harm the little person. Only a specialist should be involved in the selection of medications. At home, you can use safe folk methods:
- As your temperature rises, you need to drink more. Herbal tea, compote, plain water with lemon are suitable for this. If the thermometer reaches 38 degrees, you can take Paracetamol.
- Rinsing your nose will help get rid of nasal congestion. To do this, you can use saline solution or herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula).
- Peppermint candies will help with a sore throat. You can also drink warm tea or eat some honey.
- Bed rest is recommended for mom. Homework is best left for later now. To restore strength, you need to sleep more.
You might be interested in: What to do if you become pregnant at 10 years old
If you have a severe cough or fever, you should not do home treatment. In such a situation, it is better to entrust your health to a doctor.
Interpretation of ultrasound normal indicators: 31 weeks of pregnancy and pathology
For many expectant mothers, it is difficult to understand what is written in the ultrasound report, but it is not at all difficult. The doctor determines the main ultrasound parameters of the fetus at 31 weeks of pregnancy (they are called fetometric):
- head size;
- length of paired leg bones;
- arm length;
- chest diameter;
- abdominal circumference.
The table shows approximate values typical for 31 weeks of pregnancy, and any deviation from the norm is not a cause for concern:
| Parameter | Value, in mm |
| Head size | 70-85 |
| Head circumference | 272-315 |
| Fronto-occipital size | 90-110 |
| Tibia length | 43-56 |
| Femur length | 50-66 |
| Humerus length | 46-59 |
| Abdominal circumference | 248-302 |
Possible problems and complications during this period
31 weeks is the period of pregnancy when the main growth of the fetus begins. At this time, a woman should pay special attention to her health and monitor her weight. If your body weight increases at a rapid pace, you should urgently consult a doctor, because... this may indicate the presence of edema in the body.
Knowing the symptoms will allow a woman to take the necessary measures in a timely manner, as well as avoid the development of critical complications.
The reason for immediately contacting a doctor should be the manifestation of the following clinical picture:
- severe headaches or dizziness (indicate unstable blood pressure);
- the appearance of ripples before the eyes (signals a sharp increase in pressure or internal swelling);
- regular feeling of fatigue and seizures (may indicate late toxicosis);
- constant swelling of the lower or upper extremities (signal of kidney dysfunction);
- intestinal disorder (hormonal changes, but the symptom may also appear due to the development of an intestinal infection).
During this period, women notice when the baby becomes active, moves and calms down, i.e. falls asleep. If the expectant mother does not feel the movements and tremors of the child during the day, then this may indicate that the pregnancy is fading. In this case, a woman should urgently seek help from a gynecologist.
Measures to correct fetal position
Currently, in some cases of breech presentation, external rotation of the child is performed under ultrasound guidance. To do this, you should choose a maternity hospital where there is a truly experienced specialist with similar skills. The revolution does not take place immediately before birth, but at approximately 34 weeks.
You can also correct the position of the fetus yourself using special gymnastics for pregnant women, but the result of this action can be unpredictable.
In case of breech and other abnormal presentations, you should obtain detailed advice from your attending physician on all available measures. At this stage, the approximate date of planned birth is determined. When measuring the main skeletal bones and other parameters in children, some individual variability appears, but the average indicators are as follows:
- abdominal girth – 24.7 cm (OJ);
- head circumference – 29.2 cm (LZD);
- fronto-occipital distance – 97 mm (OG);
- biparietal diameter – 80 mm (BPR);
- femur length – 58 mm;
- forearm length – 50 mm;
- shin length – 57 mm;
- shoulder length – 52 mm.
The degree of lung maturity at 31 weeks is assessed as first. The given data may fluctuate both up and down depending on the size of the fetus. The baby's weight should be approximately 1200 - 1600 g and height approximately 42 cm. The weight of the fetus may be exceeded, but it is not advisable for it to be less than the minimum value.
Baby development at 31 weeks
The development of the baby at the 31st week of the gestational period is still ongoing. Despite the fact that all the systems of his body are almost completely formed and started their work, some of his vital signs still need improvement.
For example, at this stage of development, the child quickly and productively gains a thin layer of subcutaneous fat, which will become an indispensable source of energy for him in the first days.
The fetus's respiratory system is almost fully developed, but it will only be able to take its first full breath once it gets out of its mother's belly.
The skin of the fetus becomes denser, acquires a uniform color and smoothes out. The vellus hairs that grew after the twentieth week of pregnancy fell out completely.
Video:
The child's brain is developing. New neural connections are strengthened and formed, the number of convolutions in its structure increases.
The fetus learns to respond to various stimuli - light, sound, light pressure on the stomach.
By this period, he already knows how to smile when hearing his mother’s voice or other pleasant sounds from the outside world. You may be lucky and be able to see his smile during the ultrasound.
The iron received by the child from the mother’s body gradually accumulates in his liver in order to subsequently launch the processes of hemoglobin activation.
The child actively moves his arms and legs. Listen to the shocks you feel. The norm is four to eight pushes per hour.
If the fetal movements are chaotic, are not subject to any systematization and cause you severe, sharp pain, contact the gynecologist supervising your pregnancy.
READ When is the best time to do a 3D ultrasound during pregnancy?
Uncoordinated, restless movements of the fetus may be a sign of hypoxia - a lack of oxygen that needs to be eliminated as quickly as possible.
Biometric indicators of the fetus at 31 weeks of gestation (normal):
- biparietal size - eighty-two millimeters;
- fronto-occipital size - one hundred millimeters;
- head circumference - three hundred millimeters;
- abdominal girth – two hundred and fifty millimeters;
- thigh length – sixty millimeters;
- first degree of lung maturity;
- height - four hundred twenty millimeters;
- weight – 1600 g.
These ultrasound indicators are averaged. If your baby is a few millimeters larger or smaller than the declared biometric data, then it’s okay.
Standards for a child
If any pathologies were detected during the ultrasound, for example, serious developmental delays, a re-diagnosis is carried out at 35 - 38 weeks. What are the main biometric parameters that are measured during an ultrasound?
- height;
- weight;
- head circumference;
- abdominal girth;
- the length of the tubular bones of the skeleton - femur, forearm, tibia;
- fronto-occipital size;
- size of nasal bones;
- biparietal size.
The baby's circulatory system is also examined, the heartbeat is measured, the blood supply to the placenta and the overall quality of blood flow in the uterus and umbilical cord are assessed. At this stage of pregnancy, you should carefully monitor hypoxia and oxygen starvation, since this deviation is extremely common.
Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios serve as prerequisites for a thorough examination of the child’s kidneys and genitourinary system for intrauterine developmental anomalies. Some disorders, such as hydronephrosis, may require emergency surgery immediately after birth. Interpretation of ultrasound data should be carried out by a competent and experienced physician.
If you have doubts about the qualifications and friendly attitude of the doctor, you can contact another specialist. Indicators for a healthy placenta during the second ultrasound are as follows:
- distance to exit - at least 70 mm;
- no hematomas, hemorrhages or detachment;
- first degree of maturity.
The main task of this ultrasound is to determine the readiness of the woman’s body for natural childbirth. If cord entanglement, breech presentation, preeclampsia, or premature aging of the placenta is detected, a cesarean section will be chosen.
Vital activity of the unborn child at 31 weeks
Some babies already have a daily routine; a woman can notice moments during the day when the child becomes active, moves and calms down, and falls asleep. The child moves more, causing serious discomfort to the expectant mother, even causing pain. The baby actively moves his arms and legs, hitting the walls of the uterus. Excessively active movements at 31 weeks may indicate oxygen starvation of the fetus, or signal that the mother’s position is causing discomfort to the baby.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to pay special attention to fetal movements. If a woman does not notice the baby’s movements for a long time, she urgently needs to contact a gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy, and possibly undergo an emergency ultrasound. Normally, the fetus should remind itself of itself at least 10 times in 12 hours with active movements.
In what situations should you urgently go to the doctor?
At 31 weeks, mommy already has time to get used to the fact that her health is not always satisfactory. She often faces pain, chronic fatigue, difficulty breathing and many other delights of pregnancy.
Despite this, it is important to be able to distinguish between truly alarming symptoms, and if they occur, it is important to immediately go to the hospital. These include:
- Cramping pain, intensity and regularity is constantly increasing. This sign indicates the onset of labor, since during false contractions there is no regularity.
- The girl feels sick, dizzy and weak.
- The water broke, the stomach became very tense, and contractions began.
- Bloody or brown discharge appears.
- The pressure has decreased significantly or, conversely, increased.
- There was vomiting and abdominal pain.
Any warning signs should definitely not be ignored. At 31 weeks, mother and baby face many dangers. It often happens that every minute counts. You shouldn't leave everything to chance. It’s better to play it safe once again and consult a doctor.
Read more about false and true contractions in our article.
What position should the fetus be in?
At gestational age 30-31 weeks, the fetus in most cases is in a longitudinal position. With polyhydramnios, in women who have given birth many times, and in other cases, the baby may be positioned transversely or obliquely. The correct position is longitudinal, the presenting part should be the head. Sometimes the buttocks or legs of the fetus are located above the entrance to the small pelvis, then they talk about breech presentation. Until the 34th week of pregnancy, it is believed that the baby has enough space in the uterus, and he can still roll over and take the correct position. To promote this, you can do special gymnastics.
What complications can be identified?
Using ultrasound of the placenta, the location of the placenta, its thickness and features are determined. Low placentation and placenta previa are fraught with an increased risk of placental abruption with the development of life-threatening bleeding. Thickening of the placenta occurs with Rh conflict, intrauterine infection and other reasons. Hyperechoic inclusions are often detected on ultrasound. They represent areas of calcification in the placenta and are signs of natural degenerative processes. However, their detection before 34 weeks should be the reason for Doppler testing to assess uteroplacental blood flow.
Describe the course of the umbilical cord and its structure. Normally, it contains three vessels: two arteries and one vein. If a single umbilical cord artery or entanglement of the umbilical cord is detected, additional Doppler examination is necessary.
The amount of amniotic fluid is determined. Oligohydramnios occurs when renal function is impaired, placental insufficiency, or premature rupture of amniotic fluid. Polyhydramnios occurs with infection, gestosis, and diabetes.
Why do you need an ultrasound during pregnancy?
Carrying out ultrasound analysis is caused by the need to examine the child in the womb for pathologies or the absence thereof.
Ultrasound in the early stages is performed to determine the presence of pregnancy and its duration, the number of fertilized eggs. This type of research is useful in that it can detect ectopic pregnancy - a dangerous condition that requires immediate medical intervention, including surgical methods. If, using ultrasound, this pathology is detected in the early stages, the pregnant woman has the opportunity to avoid surgical intervention.
At the stage of the first screening (11-13 weeks), the walls of the uterus, the uterus itself and its appendages are studied, and the following indicators of embryo growth are considered:
- chorion - it contributes to the development of the placenta;
- The yolk sac is an important component for the development of the embryo.
In subsequent stages, ultrasound helps to identify existing pathologies, such as placental abruption, threatened miscarriage, and increased uterine tone. It is timely diagnosis of deviations that helps to eliminate them and avoid subsequent complications.
During the second screening, a number of indicators are examined, which will then need to be deciphered:
- the uterus, fallopian tubes and the condition of the ovaries are examined;
- fetometry is performed, with the help of which the sizes of individual parts of the fetus are determined and their compliance with the gestational age is assessed;
- the condition of the organs connecting the child with the mother (placenta, umbilical cord) is studied, the structure of the amniotic fluid is assessed;
- The state of the child’s internal organs is analyzed.
This ultrasound may reveal some pathologies, such as oligohydramnios or too low attachment of the placenta. Thanks to ultrasound, it is possible to identify both curable and incurable fetal defects.
The third screening is carried out for the following purposes:
- identification of serious fetal malformations that cannot be detected in the early stages;
- determination of fetal presentation (breech or cephalic);
- determination of the child’s body weight;
- assessing the risk of abnormal brain formation;
- examination for umbilical cord entanglement;
- assessment of the fetal heartbeat - rapid or rare;
- assessment of fetal growth;
- assessment of the risk of developing heart defects in the fetus.
An ultrasound in the third trimester can already show the baby’s lungs and their readiness to work in a normal environment in the event of premature birth. During the last screening, much attention is paid to the skull, deviations such as cleft palate, cleft lip, etc. are monitored.
On the eve of the birth itself, an ultrasound allows you to find out some nuances that may be important for the birth process itself. In particular, only thanks to ultrasound it is possible to see the entwined umbilical cord with 100% accuracy, and this is a very important aspect in the birth process, because it can become a threat to both the baby’s health and his life.
Some pregnant women are prescribed ultrasounds more often than prescribed. Such pregnant women include those who have: diabetes mellitus, blood and lymph diseases, and negative Rh factor.
Results of Doppler study
Doppler data at 31 weeks are normal:
- The resistance index inside the uterine artery is 0.34 – 0.61;
- IR inside the umbilical cord arteries is approximately 0.53 – 0.76;
- Systole-diastolic ratio of the uterine artery 1.4 – 3.5;
- The SDO of blood flow inside the umbilical cord artery remained the same as at week 30 – 2.88 – 2.96;
- SDO inside the baby's middle cerebral artery is about 4.4;
- IR inside the middle cerebral artery – approximately 0.8;
- IR VSA reaches 0.80 – 0.85.
Additional Research
If during a routine ultrasound the obstetrician suspects a pathology of the circulatory system, additional Doppler sonography is prescribed. The main goal of this event is a thorough examination of the condition of the blood vessels of temporary organs and the child. Even with the most powerful and accurate equipment for ultrasound diagnostics, more than 50% of disorders in the structure and function of the heart remain insufficiently studied. Children with oxygen starvation, which develops due to malfunctions of the umbilical cord or placenta, are most susceptible to developmental defects.
According to pediatric neurologists, more than 80% of disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system appear precisely because of intrauterine oxygen starvation. Such disorders include, for example, encephalopathy and cerebral palsy. Hypoxia is usually detected at an earlier stage, but since it is closely related to the aging of the placenta, the development of oxygen starvation is possible at any stage of pregnancy, even in the last trimester. When diagnosing intrauterine heart defects and other major blood vessels, a decision is made on resuscitation measures immediately after birth. Among the identified pathologies are cardiomyopathy, myocardial hypoxia, and heart block.
The area of study included the umbilical artery, fetal aorta, middle cerebral artery, as well as the arcuate arteries of the mother's uterus and the maternal inferior vena cava.
The benefit of Doppler ultrasound is that you can prepare in advance everything you need for an emergency operation on a newborn baby. This allows you to save the child’s life in time and minimize the risk of death. In severe cases, hospitalization of the expectant mother in a hospital and childbirth with drug support are prescribed.
Source: 1pouzi.ru
Ultrasound at the 30th week of pregnancy is an examination whose purpose is to monitor the dynamics of the growth rate of the fetus, the condition of its internal organs, as well as the placenta, uterus and its cervix.
This diagnosis is carried out unscheduled: in case of suspicion of any pathology or to monitor the effect of the treatment.
Sometimes it is based on the data of this diagnosis that a decision is made on how to further treat the woman, as well as on the possibility of her discharge or, conversely, hospitalization of the future mother in the department of pathology of pregnant women.
- Ultrasound at 30 weeks of pregnancy
- What changes occur at 30 weeks
- Norms and interpretation of ultrasound at this gestational age
- What happens at 31 weeks
- Doppler study at this time
- When and why is the third planned ultrasound examination done?
- Ultrasound 3rd trimester with Doppler
Ultrasound at 30 weeks of pregnancy
It is carried out without preliminary preparation. This is how all ultrasound examinations are done in the third trimester. A woman comes to the diagnostic room at the appointed time, lies on her back, opening her entire abdomen from the pubic bones to the sternum for examination.
Alternatively, an ultrasound at 30-31 weeks of pregnancy can be performed at home or in the ward using a portable ultrasound scanner. This is indicated in cases where there is bleeding from the genital tract in any quantity.
What changes occur at 30 weeks
- active recruitment of subcutaneous fat continues
- The lungs continue to develop, but they are not yet ready for independent breathing
- baby blinks
- the child is very active: if he is not sleeping, he moves his limbs a lot (if this causes pain to the mother, you need to see a doctor - this may be a sign of hypoxia), if he is sleeping, he frowns, clenches his fists, shrugs his shoulders
- vellus hair gradually disappears
- the number and depth of brain convolutions increase
- the liver stores iron for hemoglobin.
Norms and interpretation of ultrasound at this gestational age
On video: 30-31 weeks of pregnancy on ultrasound, boy.
- biparietal diameter (BPD, BPD): 71-85 (average value - 80) mm
- fronto-occipital distance (FOD): 89-105 (median - 97) mm
- head circumference (OG): 26.5-30.5 (average – 29.2) cm
- abdominal girth (AB): 23.8-29 (average figure – 24.7) cm
- weight: 1420-1520 g
- height: 40-41 cm
- thigh length: 52-62 (58) mm
- shoulder: 49-57 (52) mm
- forearm: 42-50 mm
- shin bone length: 49-57 mm
- lungs: first degree of maturity
Ultrasound at 30-31 weeks of pregnancy also evaluates the condition of the uterus, amniotic fluid, cervical canal, and placenta:
- the presentation of the fetus should already be established; it's best if it's the head
- Placental maturity: should be scored as "1"
- the distance from its lower edge to the exit from the uterus is at least 70 mm
- there should be no calcifications or infarctions in the placenta
- hematoma behind the placenta or area of its detachment - indications for hospitalization
- amniotic fluid may contain a small amount of suspension: these are skin epithelial cells, lanugo
- the internal and external pharynx must be closed
- cervical length – 30 cm or more.
Doppler ultrasound at 30 weeks of pregnancy
- Resistance index (RI) of placental vessels: 0.54-0.77
- SDO (systole-diastolic ratio) in the same place: 2.88-2.94
- IR of the arcuate arteries of the uterus: 0.34-0.62
- SDO of the uterine arteries: 1.4-3.5
- IR of the internal carotid artery (ICA) of the child according to ultrasound at 30-31 weeks of pregnancy: 0.85-0.86
- SDO VSA: 4.0-6.8.
What happens at 31 weeks
- the main forces are devoted to storing subcutaneous tissue, as a result of which the skin is no longer so wrinkled, and the arms and legs are “rounded”
- liver develops
- improvement of neural connections of the brain continues
- lungs prepare to breathe
- The volume of pancreatic cells increases, but they do not yet produce enzymes.
Ultrasound norms (in parentheses the average value inherent in 50% of fetuses at this period is indicated)
- BPD: 73-87 (82) mm
- LZR: 93-109 (100) mm
- OG: 27.3-31.5 (30) cm
- Coolant: 24.7-30 (25.7) cm
- hip: 54-64 (60) mm
- shoulder: 50-60 (54) mm
- forearm: 44-52 mm
- shin: 51-59 mm
- lungs: 1st degree of maturity.
31 weeks of pregnancy: weight and height norms according to ultrasound:
- weight: 1550-1690
- body length: about 42 cm.
Norms for the condition of the birth canal and amniotic fluid after 30 weeks
The same as at 30-31 weeks.
Doppler study at this time
Ultrasound at 31-32 weeks - Doppler standards are as follows:
- IR of the arcuate uterine arteries: 0.34-0.61
- SDO of the uterine arteries:
- IR of the umbilical artery: 0.53-0.76
- the ratio of systolic to diastolic velocity (SVR) of blood flow in the umbilical artery: at week 31 the norm is still the same as the week before (2.88-2.96), and from week 32 – 2.48-2.52
- IR BCA: 0.80-0.85
- SDO in the middle artery of the child’s brain: 4.4 or more, IR in the same place – about 0.8.
When and why is the third planned ultrasound examination done?
An ultrasound of the third trimester of pregnancy is done at 32-34 weeks. The objectives of this study are:
- Assess the development of the baby's systems and organs.
- Conduct an analysis of the degree of readiness of the mother's body for childbirth.
- Examine possible obstacles to natural birth: entanglement in the umbilical cord, low attachment of the baby's place (before this period, if low placentation is diagnosed, there is a chance that the placenta will rise).
- Specify the approximate date of birth.
- Identify certain fetal organ defects that may require emergency surgery after birth, or even early delivery (eg, hydronephrosis).
Ultrasound 3rd trimester with Doppler
It can be performed on all pregnant women without exception, but in the following cases it is mandatory:
- multiple pregnancy
- high or low water
- severe pregnancy
- gestosis
- fetoplacental insufficiency
- umbilical cord entanglement
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the term
- Fetal size lags behind gestational age
- maternal diabetes.
Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester is represented by the following normal indicators:
- Systole-diastolic ratio in the arteries of the uterus: 1.82 at the beginning of the 3rd trimester, 1.73 in the middle, by the end of pregnancy it decreases to 1.6 or less. Pathology during this period will be an SDO indicator of more than 2.6.
- The average speed of blood movement through the uterine arteries: 60-72 cm/s.
- Pulse index (PI) in the arteries of the uterus: 0.4-0.65.
- In the fetal aorta: SDO on average – 7.3, a range of 4.1-9.5 is allowed; IR there – 0.66-1.0.
- In the internal carotid artery SDO: 4.1-6.8. An indicator of less than 2.3 will be pathological.
So, ultrasound at 30 and 31 weeks of pregnancy is needed in order to identify the pathology of pregnancy and assess the nature and extent of the disease. According to the ultrasound examination and Doppler picture at this stage, the doctor determines the tactics for further management of pregnancy and childbirth.
ATTENTION! The information on the site is for reference or popular information only. Correct treatment and prescription of medications can only be carried out by a qualified specialist, taking into account the diagnosis and medical history.
Successful diagnosis and treatment, health and well-being! Your uzilab.ru.
04/29/2015 UziLab
Source: uzilab.ru
Evaluation indicators
When performing an ultrasound examination, the motor activity and heart rate of the baby are assessed. Normally, the fetal heart beats 120-160 times per minute. A significant increase or decrease in heart rate is a poor prognostic sign and requires urgent hospitalization and a decision on delivery.
The dimensions of the fetus obtained by ultrasound at 30 weeks of gestation must correspond to the following values:
- biparietal head size –71-85 mm;
- fronto-occipital head size – 89-105 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 239-290 mm;
- head circumference – 265-305 mm;
- thigh length – 52-62 mm.
The weight of the fetus according to ultrasound at 30 weeks is about 1300 grams.
Ultrasound norms 31 weeks of pregnancy:
- biparietal head size – 73-87 mm;
- fronto-occipital size of the head – 93-109 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 247-301 mm;
- head circumference –273-315 mm;
- thigh length –54-64 mm.
When performing an ultrasound at 31 weeks of pregnancy, the approximate weight of the fetus is calculated as 1500 grams.
The obtained fetal size values are compared with standard values. They must correspond to the duration of pregnancy. However, these values are very variable. The assessment must be made taking into account the constitutional characteristics of the baby’s parents.
When the size of the fetus decreases by 2 weeks or more, they speak of intrauterine growth restriction. At 30-31 weeks it is most often asymmetrical, i.e. there is a lag only in the size of the abdominal circumference. This is often due to the existence of fetoplacental insufficiency. At an earlier age, a symmetrical form of fetal growth restriction begins to develop, the causes of which are most often chromosomal abnormalities and intrauterine infections.
Decoding indicators
The ultrasound examination protocol indicates many different indicators:
- BPR - biparietal head size. The value is determined by measuring the distance from the upper surface of the parietal bone to its inner surface.
- AB - abdominal circumference. To measure this indicator, the specialist installs a sensor according to the longitudinal projection of the thoracolumbar spine. Then he turns it 90 degrees, visualizes the contour of the abdomen, and takes the appropriate measurements.
- Lengths of tubular bones. These indicators combine the sizes of the legs and arms of the fetus and show whether there are any pathologies of the limbs. The protocol indicates specific values for the humerus, ulna, femur, and tibia.
The protocol also describes the anatomy. Here the internal organs are indicated and it is noted whether they are normal or whether there are any pathological changes. The document also provides characteristics of the placenta. They reflect its ability to supply the fetus with all the necessary substances.
Ultrasonography
Typically, at the 31st week of pregnancy, a third planned ultrasound examination is performed, the purpose of which is to monitor the development of the child and assess whether the indicators are normal. This ultrasound allows you to assess the degree of development of the brain and other internal organs. If an ultrasound at 31 weeks is performed in 3D or 4D format, you can clearly see all the outlines of the child’s face. Poor visualization of a clear image on ultrasound may be due to several reasons:
- increase in the subcutaneous fat layer of a woman;
- small volume of amniotic fluid;
- the fetus is in an awkward position for studying.
It is very difficult to obtain high-quality photographs and video recordings of ultrasound in late pregnancy. The sex of the baby is determined at the second scheduled ultrasound, but the formation of the genital organs continues today. At this stage, testicular descent has not yet occurred in male children, and future girls still have open labia.
Baby development
You can find out what mood your child is in now by his movements. If the little one wants to eat, he will move more actively, thereby expressing his dissatisfaction. When their mother sings, children often calm down and calm down. The baby will also enjoy the smooth dancing of a woman. Sometimes it happens that some children stay awake at night, preventing the pregnant woman from sleeping. Singing or walking slowly can help calm your baby. This will help the baby fall asleep.
External changes:
- The baby's weight at 31 weeks of gestation is about 1500-1600 grams, and its height reaches approximately 40-42 centimeters.
- Heart rate on CTG is 140-160 beats per minute.
- The baby can already reach your ribs with his legs. At the same time, its tremors can be quite painful. No need to worry. Soon the tummy will drop and the tremors will become less painful.
- Now there is an intensive deposition of the fat layer in the baby. His skin becomes lighter, and the capillaries are no longer visible.
- There are already hairs on the head, and eyebrows and eyelashes are visible on the face. On the toes and fingers, the nails reach almost the edge of the finger.
By 31 weeks, the baby opens and closes his eyes, squints from bright light and flinches from sharp sounds. His mother’s voice calms him, but other people’s voices alarm him.
Now the baby has developed a new corneal reflex. If he accidentally touches his eye with his pen, he will involuntarily close it.
Preparing for the study
There is no need to prepare in any special way for an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman. To obtain accurate results, you do not need to perform an enema or test on an empty stomach.
A woman must have with her:
- results of past examinations;
- medical card;
- towel;
- diaper.
Before the procedure, there is no need to remove all jewelry, watches, or leave your phone outside the room, as is done during an MRI.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for ultrasound at 31 weeks are:
- assessment of the general condition and development of the fetus;
- analysis of a woman’s readiness for childbirth;
- determining the type of birth (natural or cesarean);
- identifying possible circumstances that may complicate the operation;
- clarification of the date of birth;
- anomaly detection.
A woman is prescribed not an ultrasound, but Doppler ultrasound in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- gestosis;
- oligohydramnios;
- diabetes;
- thrombophilia;
- heart diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- Rhesus conflict;
- multiple pregnancy;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- post-term pregnancy.
What does an ultrasound show?
First of all, the position of the fetus matters, because the fundamental strategy for childbirth depends on it. There are cases when a child unpredictably changes its position right before birth from oblique or transverse to normal, but such cases are rare, and one cannot count on a happy accident. The placenta plays a very important role in supplying the embryo with oxygen and nutrients, and during the study the degree of its maturity is assessed.
Premature aging of the placenta leads to its detachment, which in turn provokes bleeding. This condition can cause premature birth and pose a threat to the life of the newborn. Childbirth at 31 weeks is pathologically early even for twins, so in order to avoid emergency situations during an ultrasound examination, the obstetrician assesses the likelihood of labor starting in the near future. Pregnant women who have been diagnosed with true placenta previa are at risk for preterm birth.
How is the procedure performed?
There are several stages of a painless ultrasound procedure:
- The patient is asked to lie down on the couch and expose her stomach.
- The specialist applies a special gel to the skin. Some women experience discomfort in this case, because... the product is cold.
- The scan begins when the doctor places the probe in the desired position and moves it across the abdomen.
The procedure lasts about 15 minutes. The duration is influenced by the professionalism of the doctor and the location of the fetus. After completing the study, the woman removes the remaining gel from the abdomen with a napkin or towel. The doctor announces the results of the examination.