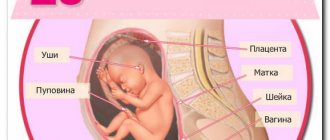
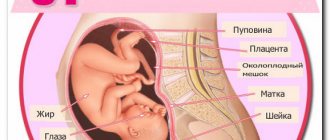
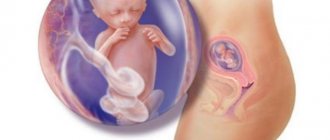
For every girl, the time of waiting for the birth of her beloved child is the happiest and most exciting time. I would like to know what it is like, how it develops, what happens to it even in the very early stages of pregnancy. Every pregnant woman worries about her baby being healthy and developing properly. It is ultrasound that allows you to monitor the process of fetal development throughout the entire 9 months.
What is ultrasound
Ultrasound has been known for its special capabilities for a long time and longer than x-rays. Their properties and capabilities are different, but in the field of obstetrics, ultrasound has become simply a panacea for solving many problems and has provided answers to the most common questions. In addition, ultrasound allows you to diagnose a variety of congenital diseases or pathologies in the early stages with an accuracy of 95-100%. It began to be used in the middle of the twentieth century and since then every pregnant woman has the opportunity to see her unborn child. What is the essence of this device?
The device consists of a sensor and a receiver. The sensor sends invisible ultrasonic waves, which, when entering the body, are transformed, and the receiver deciphers them and creates a picture.
Modern equipment allows ultrasound examinations to be carried out at the highest level of quality and opens up many opportunities for doctors and future parents to monitor the process of fetal development.
Today, obstetricians and gynecologists are required to conduct several ultrasound sessions during pregnancy. To be precise, three. Why do these studies need to be done? When should this be done?
Why does this method have a number of limitations, and which ones exactly?
It's all about the nature and properties of ultrasound. As I already wrote in the main article of this site, dense tissues reflect ultrasonic waves very well. And very dense fabrics reflect them almost completely. Therefore, something that is surrounded by very dense tissue cannot be examined with ultrasound.
Ultrasound cannot penetrate these tissues. It reaches them and is completely reflected from them. And what is located further, behind these dense tissues, remains inaccessible to our beam.
Comprehensive ultrasound in Moscow
Comprehensive ultrasound in the Moscow region
Detailed information about the clinic and each doctor, photos, ratings, reviews, quick and convenient appointments.
Ultrasound in the first trimester
The first ultrasound examination is carried out at 9-14 weeks of fetal development. Already at this time, you can see whether the baby is growing and developing correctly and in a timely manner. It is at this time that the first deviations and pathologies can be identified (all organs have already been formed in these weeks), and timely actions can be taken to solve such problems. Ultrasound in the first trimester allows you to get answers to the following questions:
- The most accurate gestational age is established;
- Single or multiple pregnancy;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Risk of miscarriage;
- Condition of the uterus and placenta;
- The size of the fetus is measured;
- It is possible to determine the sex of the child;
- The most accurate due date is calculated.
In addition, an ultrasound in the first trimester is also performed to determine the size of the collar zone - the correctness of chromosomal development is also very important. If this zone exceeds 2.7 mm, then doctors can talk about the presence of pathologies such as Down syndrome. If ultrasound finds this kind of abnormality, then additional studies and blood tests can confirm the diagnosis. The main thing is to identify the threat in time at an early stage of development. Unfortunately, Down syndrome cannot be treated by modern medicine. But its timely determination allows the mother to prepare for this kind of responsibility.
An ultrasound scan during the first trimester is extremely important and should not be skipped by a pregnant woman. Thanks to it, your doctor will be able to establish correct and most accurate monitoring of your child’s development process. Also, after the examination, you can get the first photo of your baby - the ultrasound specialist can do a screening for you.
It is worth noting that conducting research at earlier stages is not recommended. Although ultrasound offers many benefits, it can still have some side effects. If you are not bothered by pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, then postpone the first examination until the deadline of the first trimester. Early research can only be carried out on the recommendation of a doctor and for compelling reasons.
Why and to whom is diagnostics recommended?
Three-dimensional examination of the fetus gives an accurate picture of its development. A three-dimensional image allows you to examine the child in great detail, tracking the slightest deviations from the norm. Conventional 2D ultrasound as a screening event is performed three times during pregnancy.
A 3D examination is prescribed to a woman for the following medical reasons:
- dynamics of fetal changes;
- unfavorable genetic history;
- pregnancy as a result of IVF, ICSI;
- surrogacy;
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- determining the condition of the fetus during a complicated pregnancy;
- suspicions of chromosomal abnormalities, fetal diseases;
- multiple pregnancy;
- clarification of the age of the fetus;
- determining the position of the child.
In some genetic diseases, the sex of the child plays a role. A three-dimensional image allows the doctor to timely adjust pregnancy management. A woman’s desire to monitor the baby’s condition serves as a justifiable reason for carrying out the procedure as a screening measure.
Second ultrasound
The second ultrasound examination is carried out at 20-24 weeks. At this time, you can learn a lot more about the baby. The doctor measures the size of the fetus: the circumference of the abdomen, head, and length of the femur. These parameters will help determine developmental deviations. In addition, you can determine how well the blood flow is developed inside the placenta, as well as the uterus, their level of maturity, as well as where and how they are located. The condition of the placenta can tell a lot. If there are seals in it, then this is a harbinger of various infections, and its detachment can lead to miscarriage or premature birth. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent such situations.
In addition, it is at the second ultrasound that the sex of the child is determined with 100% accuracy. The genitals become larger and more clearly defined. It is during these weeks that you can talk about who you will have - a boy or a girl.
During the second ultrasound, amniotic fluid and the cervix are examined. This allows you to prevent a number of pathologies. Timely therapy or timely hospitalization will help normalize the process of fetal development and will lead to the threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
Unlike the test that is done in the first trimester, the screening that will be done this time will allow you to have a more accurate picture of your baby.
How to do it and do you need to prepare?
The event is no different from a regular ultrasound scan. The decisive difference is the duration of the session.
The usual procedure takes a woman about 20–25 minutes of time. Examination of the baby in three planes will take a little less than an hour.
A special gel is applied to the surface of the abdominal skin to ensure smooth sliding of the sensor.
A number of studies related to the pathology of pregnancy are performed transvaginally. Both transabdominal and transvaginal procedures do not require special preparation, diet, or fluid intake on the eve of the examination.
Third ultrasound
This ultrasound procedure is performed at 32-34 weeks. By this time, the intrauterine development of the fetus is coming to an end, and the fetus itself turns head down. An ultrasound can confirm or refute this fact. And then the obstetrician-gynecologist can plan in advance a strategy for how the birth will take place. If the baby has not turned over by this time, the doctor can take a number of actions to correct his position. Head presentation is very important for the correct and normal course of the birth process. At this stage, thanks to an ultrasound, you can find out how much the child weighs and how tall he is. The latest research will also help determine when you can give birth. This is especially important if you are having a caesarean section.
During these weeks, the position and condition of the placenta is also examined. It is this fact that can indicate whether a woman can give birth on her own - if the placenta is attached to the very top of the uterus. If it is displaced towards the cervix, then such placenta previa is an indication for cesarean section. The maturity of the placenta indicates a woman’s readiness for the birth process. If the placenta matures ahead of schedule, this indicates that the birth should be carried out ahead of schedule in order to avoid transfer of the fetus.
At the final ultrasound, you have the opportunity to see your baby as he will be born.
First ultrasound during pregnancy: decoding the size of the fetus
Upon completion of the ultrasound procedure at the 1st screening period, the size of the fertilized egg is deciphered. At the moment, the doctor is assessing particularly important indicators:
- Diameter of the fertilized egg (DPR);
- The length of the distance between the crown and the coccygeal region (KTR) - at 11-13 weeks, the normal value varies from 45 to 80 mm;
- The length of the distance between the temples of the head (BDP) - according to the norm, should have a value no higher than 2.8 cm;
- The length of the distance between the frontal and occipital bones (LZR) - according to the norm, the maximum value is 3.1 cm;
- Using the formula BPR/LZR*100%, the cephalic index is calculated, with the help of which the shape of the head of the unborn child is assessed;
- The size of the uterus, which helps to most accurately determine the number of weeks of pregnancy.
If decoding the size of the fetus at 10-14 weeks shows data that lags behind the normal value, then there is a possibility that the fetus is growing and developing with some delay. When indicators of all sizes are equally less than normal, a doctor can diagnose a symmetrical form of IUGR.
If the size of the head, arms and legs shows a normal value, and the body is reduced in size, then they speak of an asymmetrical form of IGR.
Regardless of what form of IDP is diagnosed by a doctor, the pregnant woman is recommended to undergo additional studies, after which she chooses a correction method. Significant deviations in the size of the fetus from the norm become a reason for prescribing hospital treatment to a pregnant woman.
When deciphering an ultrasound protocol, many doctors resort to the help of special tables.
In addition to the main indicators, it is often necessary to decipher such a parameter as the cephalic index. Each person's head shape is characterized by individual characteristics. Before judging dolichocephaly, mesocephaly or brachycephaly, the doctor determines the index during an ultrasound examination.
With its help, you can determine as accurately as possible what shape the child’s head will have.
To calculate CI, the BPR value must be divided by the LZR value, after which the resulting indicator must be expressed as a percentage (*100).
The majority of people have a mesocephalic head shape, which will be indicated by a CI that is within the established norm of 71-85%. If the cephalic index is slightly outside the average range, then this does not indicate an anomaly, but only indicates dolichocephaly or brachycephaly. With dolichocephaly, the cephalic index is below normal (85%). However, it is impossible to determine with maximum accuracy what shape the baby’s head will have. With dolichocephaly and brachycephaly BPR, the value that makes up the cephalic index may have individual normative boundaries. In addition to the BPR, indicators such as LZR and the value of the circumference of the fetal head will also be required. In the case when the interpretation of the ultrasound protocol indicates a deviation in the smaller or larger side of the BPR value, the doctor can assume that the shape of the child’s head is elongated or rounded.
Since the cephalic index is not very significant, the diagnostician may not evaluate it during the first screening examination. According to experts, the shape of its head depends on how the baby is located in the uterus. So, in a fetus with its legs down, the likelihood of dolichocephaly increases significantly. It is extremely rare that a CI deviating from the normal value signals the presence of chromosomal abnormalities.
Is it harmful to do an ultrasound?
Many women are very worried about whether the ultrasound examination will harm the baby. Medicine does not give clear answers to this question, but no obvious threats to the baby were identified. It is precisely because of this ambiguity that the number of sessions is reduced to a minimum - 3 for clearly defined periods. In our country, the maximum number of ultrasounds can reach 10. But they are carried out only for good reasons and the strong recommendation of a doctor. This will help protect your baby’s development and make it as healthy as possible in the presence of various types of threats.
What are these “thick fabrics”?
Bones
This is why it is impossible to study the adult brain using ultrasound. The brain of a small child is possible. Because in the skull of a small child there is a small window: the fontanel. The ultrasonic beam penetrates through this window. As soon as the fontanel becomes overgrown, studying the brain using ultrasound becomes impossible.
Air
Impenetrable to ultrasonic waves and air.
It is for this reason that ultrasound of parenchymal organs, that is, organs consisting of tissue, can be done. Such as liver, spleen, kidneys. But you cannot examine those organs that contain gases: stomach, intestines, lungs.
It is for this reason that the patient’s body is lubricated with a special gel before the ultrasound examination begins.
The gel is needed to ensure close contact between the sensor and the human body. So that there is no air gap between the sensor and the human body, which would significantly deteriorate the quality of the study. This gel is called contact gel.
So, we agreed that those organs that do not contain gas and are not covered on all sides by bone tissue are available for ultrasound.
3D ultrasound
Today it is also possible to conduct 3D research. It makes it possible to get a three-dimensional picture and view the child from all sides. 3D ultrasound is a real joy for the expectant mother. Thanks to him, you can quite accurately see the baby’s face, especially in the weeks of the last trimester, and see how he moves and breathes.
Thanks to modern equipment, we can see our baby in the womb. Ultrasound during pregnancy at various stages gives you the opportunity to take care of your baby even when you cannot touch him.
Where to do it and how much does it cost?
A scanner operating in three-dimensional mode is available in specialized clinics, obstetrics and gynecology centers. A regular antenatal clinic will offer a standard two-dimensional examination, which will provide a free two-dimensional pregnancy diagnosis.
It is no secret that specialized institutions are equipped with better quality equipment. Obstetrics centers and clinics are ready to provide the service inexpensively, costing from 1.5 to 2.5 thousand rubles.
The price includes a medical report on the condition of the fetus, a photograph and a video recording of the examination. The quality of the equipment and the doctor’s rating significantly affect the price.
Some private clinics offer three-dimensional examination at a price of 3.5 - 4 thousand rubles. Clinics implementing a pregnancy management program conduct 3 d research free of charge, including recording data on a digital medium.
Examination of some organs requires special conditions
Urinary bladder
The bladder can only be examined when it is well filled. When it is empty and in a collapsed state, it simply cannot be distinguished from the surrounding tissues.
Uterus, ovaries and prostate gland
A full bladder requires examination of organs such as the uterus, ovaries and prostate gland. In this case, a full bladder serves as an amplifier for ultrasonic waves and helps obtain a clearer image.
In addition, a full bladder displaces intestinal loops from the pelvis. Air-filled intestinal loops significantly interfere with research. Therefore, their removal also contributes to better visibility and image clarity.
Treatment and correction
Cleft lip and cleft palate are treated only through surgery. During plastic surgery, the nature of the anomaly is taken into account - the location and severity of the pathology. Based on the data, the surgeon determines the favorable time for the procedure before the child reaches the age of 6 months. Once a child born with a cleft begins to grow teeth, the operation becomes more complicated.
Indications and contraindications
Plastic surgery is strictly prohibited in the following cases:
- if the newborn is malnourished and weighs less for his age;
- in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- in case of disruption of the respiratory system;
- if anemia is present, newborn jaundice;
- in case of injury during labor;
- with incorrect functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems;
- with obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract.
In other cases, the pediatrician writes a referral for planned surgery.
Types of correction methods
There are 3 types of surgery depending on the severity of the pathological process:
- Cheiloplasty. It is prescribed for incomplete formation of a cleft, when only the tissue structures of the lips are subject to deformation. During surgery, the surgeon lengthens the lips, suturing the edges to hide the anomaly as much as possible.
- Rhinocheiloplasty is applicable in the presence of a complete type of pathology that requires correction of the soft tissues and cartilaginous processes of the nasal cavity. The operation is a two-stage operation. It begins with establishing the correct position and subsequent fixation of the cartilages, which are freed from the superficial tissue layers. As soon as the nasal cavity returns to its natural appearance, the specialist proceeds to stitching the lips.
- Rhinocheilognatoplasty. The operation is performed with the simultaneous presence of a cleft palate and cheiloschisis. During the procedure, the plastic surgeon restores the condition of the lips and nasal cavity, and also corrects the shape of the hard palate. Rhinocheilognatoplasty is one of the complex operations with a high risk of injury.
In case of complex destruction of the nasal cavity, some surgeons recommend performing operations after reaching 5-6 years of age to avoid disproportion of the nose.
Rehabilitation period and care
After surgery, the newborn must undergo rehabilitation, which is divided into 3 main periods.
| Stage | Rehabilitation measures |
| In stationary conditions | After the operation, the child remains in hospital for 5-10 days. During this period, tube feeding is prescribed and painkillers are administered. The water balance in the body is restored. A fixing bandage is applied to the operated area to prevent the sutures from coming apart. The maxillofacial system retains its physiological shape. |
| At your place of residence in the clinic | After discharge, the child is registered at a local clinic, where he is observed by a pediatrician. The specialist writes out a referral for physiotherapeutic procedures to accelerate tissue regeneration. The child should take medications for pain relief if necessary. If there is a speech disorder, the help of a speech therapist is required. To restore your bite, you need to undergo treatment at the dentist. |
| At home | It is required to constantly work with the child to restore speech function, to follow the recommendations of the attending physicians. |
Is it possible to prevent the development of the disease?
You can reduce the risk of developing malformations of the maxillofacial part of the skull by following 3 rules:
- When planning a pregnancy, a woman should maintain a healthy lifestyle before conception. It is required to be examined for the presence of diseases and undergo treatment if the results are positive. It is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and smoking for 4-5 months.
- During pregnancy, you should not be exposed to chemicals. If possible, stop taking medications. A woman will have to monitor her daily diet and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
- During the embryonic development of a child, a woman is advised to limit contact with sick people. It is necessary to reduce the risk of disease from infectious and viral agents.
If a specialist sees a cleft lip on an ultrasound, then it will not be possible to prevent the development of an already begun pathological process. Treatment is carried out only by surgical intervention after the birth of the child.
The formation of a cleft lip is not only a cosmetic defect, but also threatens health problems. Respiratory activity and speech function are impaired, and the ability to eat normally is limited.
Types of sensors
Different organs of the human body are located at different depths.
Organs such as the thyroid gland, mammary gland, superficial lymph nodes and soft tissues of the human body are superficial organs.
And such as the liver, gall bladder, kidneys, pancreas - organs located quite deep.
To see both well enough, different sensors are used. They differ in that they generate ultrasonic waves of different frequencies.
The deeper the organ is located, the lower the frequency of the ultrasound wave must be to examine it. And, conversely, the more superficial the organ is located, the higher the frequency of oscillation of the ultrasonic wave should be. It is the frequency that determines the depth to which the ultrasonic beam penetrates.
In addition, ultrasound examination methods are now increasingly used, in which a sensor is inserted inside the human body. This is a transrectal examination of the prostate gland where a probe is inserted into the rectum. Transvaginal examination of the uterus and ovaries, when a probe is inserted into the vagina. Transesophageal echocardiography is a study of the heart where a probe is inserted into the esophagus.
And very complex and expensive ultrasounds are those studies in which a microscopic sensor is inserted into the deep cavities of the human body. For example, into the renal pelvis or into the common bile duct.
Each method has its positive and negative sides. But a correctly selected set of studies in each specific case makes it possible to obtain maximum valuable information in the shortest possible time.