#!UZIna4alo!#
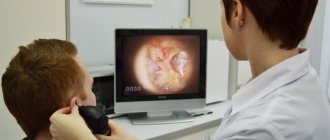
The importance of the carotid arteries, located in the neck and chest, in the human body is difficult to overestimate. The carotid arteries participate in the general blood flow and play a critical role in supplying the brain with oxygen. Any problems related to the carotid arteries can have a negative impact on your overall health. Therefore, today there are quite a lot of examination methods, including ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
What are vessels?
These are tubular structures that extend throughout our body and transport blood to organs and tissues. Among all the vessels of the body, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins are distinguished. Arteries are large vessels through which blood flows from the heart to other organs and parts of the body. They have a muscular membrane or elastic fibers in their structure, therefore they are very flexible and can shrink or expand depending on the volume of blood flowing through them.
Vessels of the neck and head
The arteries then divide into smaller diameter arterioles, which are also quite elastic. Capillaries are the thinnest vessels located inside organs and tissues, through which necessary substances are exchanged between blood and cells. The diameter of the capillaries is tenths of a millimeter. After leaving the intercellular space, the capillaries unite into larger vessels - venules.
Following the venules are even larger vessels - veins. They carry blood from organs and tissues back to the heart. The walls of the veins are thinner than those of the arteries and are not as elastic; they are easily compressed when pressed. But many veins have special valves that prevent blood from flowing back into them. With help you can examine arteries and veins with a diameter of 1-2 millimeters
.
Research Opportunities
Duplex scanning will allow a specialist to penetrate the spinal region and examine each vessel in order to quickly determine changes that have occurred in the brachiocephalic trunk, vertebral or carotid artery.
During the procedure, the doctor will be able to determine:
- the presence of blood clots or their absence;
- diameter of vertebral arteries;
- what condition are the walls of blood vessels in?
- how cholesterol plaques are located and in what state they are;
- presence of occlusion and degree of stenosis;
- if there are blood clots - vascular lumen;
- the patient has vascular diseases;
- blood flow speed;
- speed differences depending on the area;
- the nature of the blood flow (it can be turbulent or laminar);
- symmetry of the listed characteristics.
What vessels look on the neck and why?
During an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the neck, the doctor must carry out:
- brachiocephalic trunk;
- right and left subclavian arteries;
- right and left common carotid arteries;
- right and left internal carotid arteries;
- right and left external carotid arteries;
- vertebral arteries.
If necessary, the following can be additionally examined:
- jugular veins;
- veins of the vertebral plexus;
- supratrochlear arteries;
- ophthalmic arteries.
All of the above vessels are examined for the possible detection of the following pathologies:
- Atherosclerosis of extracranial arteries. It is possible to establish not only pronounced atherosclerotic changes, localization and size of plaques, degree of stenosis, complications, but also the initial manifestations of atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries in the form of thickening of the intima-media complex. In the presence of significant stenoses and vascular occlusions, the performance of cervical anastomoses, that is, bypass paths of blood flow, is assessed.
- Nonspecific aortoarteritis or Takayasu's disease. Using ultrasound, the doctor can distinguish aortoarteritis from atherosclerotic lesions and give a detailed description of blood flow disorders.
- Dissection. Ultrasound can reveal signs of arterial wall dissection during thrombosis of unknown cause or after injury.
- Arterial deformations. Ultrasound quite accurately shows the presence, shape and location of deformations of the examined arteries, as well as the effect of the identified deformations on blood flow.
- Steele syndrome or vertebral-subclavian steal syndrome. Ultrasound helps to establish the location of the lesion, the degree of narrowing of the artery, and the characteristics of hemodynamic disturbances in it.
- External compression of blood vessels by neighboring organs and tissues.
- Congenital anomalies of vascular development and their effect on the blood supply to the brain.
- Disturbances in the venous outflow of blood from the brain. Ultrasound helps to identify the signs and causes of this pathology.
But the main purpose of conducting an ultrasound examination of the extracranial arteries of the neck is to identify possible causes and further prevent the development of a dangerous disease - cerebral ischemic stroke.
Ultrasound technique
The patient lies on his back on the couch. The specialist places a 10-centimeter pillow under his shoulders. A conductor gel is smeared onto the patient’s neck, which removes the air layer between the dermis and the sensor and ensures close contact of the ultrasound with the body.
The sensitivity level on the device is adjusted until a clear picture appears on the monitor. The doctor begins to move the sensor along the neck. First, the lower section of one carotid artery is examined, its depth is examined, and the device is gradually raised to the jaw.
The procedure is then complemented by Doppler scanning, which shows areas with damaged vascular walls and impaired blood supply. If such deviations are detected, this area is examined more carefully. The scan is then performed in the same way for the other carotid artery.
Afterwards the transition is made to the neck. The sensor is installed so as to obtain a picture of the vascular network. During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to turn his head in different directions. The result is cross-sections in different directions. During an ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck, the diagnostician moves the device along the back of the patient’s head, eyelids and temples. The procedure lasts no more than 30 minutes. The results and conclusion are given to the patient immediately.
Who is indicated for ultrasound of the extracranial brachiocephalic vessels?
Ultrasound of the vessels supplying blood to the brain, located in the neck, is prescribed for the following complaints: headaches, dizziness, periodic disturbances of vision, memory, movement, speech, ringing in the ears, surges in blood pressure, loss of consciousness.
This study is also recommended to be periodically performed by all persons over 45 years of age to identify initial changes in the vascular wall, patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, who have had a stroke or transient ischemic attack, myocardial infarction, after operations on the vessels of the head and neck.
Vascular ultrasound to determine the causes of headaches
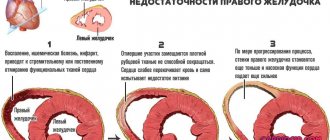
Headache can occur for a variety of reasons, so this symptom is not an indication for Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and main arteries of the neck. Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and main arteries of the neck. Sometimes, the cause of poor health may be the result of increased intracranial pressure. During the ultrasound, the condition of the internal jugular veins is assessed, since deterioration of blood flow through these vessels contributes to an increase in venous pressure in the head. This problem can occur with right ventricular heart failure or due to jugular vein thrombosis.
Sometimes the pressure may be unequal, so the speed of blood flow at the inlet (through the right internal jugular vein) can be reduced, and at the outlet it can be increased. Such anatomical features of the structure of the patient’s vessels should also be taken into account during diagnosis. Thus, during an ultrasound, it is necessary not only to obtain indicators, but also to take into account the presence of other symptoms before making a final diagnosis. Moreover, the results of such a study are not a sufficient reason to initiate treatment. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor can refer the patient to a CT scan of blood vessels, ultrasound of the heart and other diagnostic procedures and will tell whether all this is dangerous to health.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck, the price in Koasnoyarsk, Yekaterinburg, Moscow, Perm, Ryazan, Yaroslavl, St. Petersburg is practically the same. When searching on the Internet, you can find a video that will show the process of performing an ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head, and also show what the results look like. Ultrasound of neck vessels is normal - peak systolic velocity in the internal carotid artery does not exceed 125 cm/s, and plaques or thickening of the inner layer of the vessel are not visualized. A transcript of the data is provided by your attending physician.
What can an ultrasound scan of the cervical vessels show?
An ultrasound examination shows the doctor whether there are any obstructions in the vessels of the neck that are preventing normal blood flow. In this case, it is possible to accurately measure how narrowed the lumen of the affected part of the vessel is and to what extent. They also determine how firmly the plaque or thrombus is attached to the vessel wall, and whether there is a high risk of its rupture. You can clearly examine the condition of the walls of the blood vessels, whether there are any defects in them.
Ultrasound diagnostics quite reliably determines anomalies in the course of blood vessels and their deformations. In addition, when conducting a modern comprehensive ultrasound examination, the maximum and minimum blood flow speed, resistance indices and other parameters necessary to assess the sufficiency of blood supply to organs and tissues are assessed.
Pathologies
The sonologist must interpret the results obtained using his experience and knowledge. In conclusion, he indicates the exact location and size of the formation, the structure of the surrounding tissues, and also determines whether there are cavities and learns about the presence of contents in them. Besides. The features of blood flow in this area are clarified.
Normal non-epithelial tissues have a typical anatomical structure, without compaction or changes in echogenicity. Ultrasound diagnostics of soft tissues has other features.
Muscular
If a patient comes for a muscle ultrasound, then in conclusion he will see which muscle is affected and to what extent. In this case, it is not so important whether we are talking about the thigh, lower leg, back or, for example, buttock: the diagnosis will be equally informative.
Lipoma
Lipoma (benign growth filled with fat) - most often localized on the back or hips.
Reference! With this pathology, an ultrasound scanner allows you to see a hypoechoic focus with smooth contours.
If the structure of the formation is heterogeneous, then the sensor can detect fibrous inclusions. If you connect a Doppler, a blood flow study will show that there are no vessels inside the tumor.
Atheroma
Atheroma (cyst affecting the sebaceous gland) differs from lipoma only in the homogeneity of its structure.
Oncology
Oncological tissue lesions on ultrasound are visualized as foci with a good blood supply, the edges of which are clear or blurred, possibly grown into adjacent tissues.
Hematomas
Hematomas formed as a result of injuries or bruises look like lesions located in a “bag” containing blood. On the device screen, displacement of the affected area causes a shift in the level of fluid inside the hematoma. If the formation has festered, the scanner will show a change in its density.
Lymph node lesions
Lymph nodes normally measure 8-10 mm and are almost undetectable on an ultrasound monitor due to their structural similarity to surrounding tissues. However, with inflammation or cancer, their density and size increase, which is well recorded by the equipment.
Postoperative
After plastic surgery on the face, ultrasound control is necessary to determine the location of threads under the skin or fillers in the tissues. Ultrasound also helps to detect in time the onset of inflammation or the formation of adhesions under the skin - rough film seals made of connective tissue.
Articular and ligamentous apparatus
An ultrasound examination of joints and their ligaments provides a good opportunity to see ruptures, dislocations and damage to nerve endings. This is especially often used in the case of injuries to the tissues of the shoulder and other parts of the arm.
Important! If there is thickening of the tendons on the monitor, then we can talk about the beginning of the inflammatory process.
If the hypoechogenicity of the area is added to the thickening with the definition of fibrous foci and calcifications, then the inflammatory process becomes degenerative.
Articular tissue
If joint tissue is examined, the doctor may detect cavities with synovial fluid. For example, a Baker's cyst is a thickening of the synovial bursa in the fossa under the knee. On the screen it will be defined as a formation with a clear contour and high elasticity, filled with liquid content.
Fractures and bone growths
Ultrasound plays an important role in differentiating fractures of thin bones from other injuries, because such fractures are not easy to identify upon examination. Ultrasound is also indispensable in identifying pathologies of small joints and bone growths such as heel spurs on the foot. Spurs are a growth on the heel, structurally identical to bone tissue, but with increased thickness of the plantar fascia.
Hygroma
Hygroma is often determined by examining the tissues of the hand and wrist, as well as the wrist joint. This area is perfectly visualized thanks to a small amount of subcutaneous fat. Hygroma is a benign cystic formation in the cavity of which there is fluid.
On the monitor of an ultrasound machine, it looks like a lesion with clear edges, whose density depends on the characteristics of the fluid filling the hygroma. If it contains serous-fibrous contents, then the nature of the lesion will be less echogenic than when the cyst is filled with serous-mucosal contents.
Cervical
Ultrasound of the neck is in demand in pediatric practice for early diagnosis and timely treatment of torticollis in young children. The examination can also reveal pathology of local lymph nodes. Doppler scanning of this area is indicated if it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of the arteries in the complex diagnostics of the functioning of the cervical vertebrae, as well as the brain.
Hernia
A hernia requires determination of peritoneal defects and the degree of fullness of the hernial sac. If there is partial pinching, then peristalsis is maintained, and the movement of feces can be seen on the monitor screen. Abdominal examination is generally a fairly commonly used procedure.
Video 1. External hernias.
Echography of soft tissues allows you to see the pathological focus in a three-dimensional image, as well as evaluate its blood supply, find out the nature of tumors and pathologies of the articular apparatus. In addition, ultrasound of extraskeletal tissues makes it possible to determine how much inflammation has spread and whether there are degenerative processes in the area under study.
Ultrasound signs of the main detected pathologies
Atherosclerotic lesion of the vessels of the neck
The main causes of vascular obstruction are most often atherosclerosis or thrombosis. They lead to stenosis or occlusion of the lumen of the vessel. Stenosis is an incomplete narrowing of the lumen. Occlusion is a complete blockage of the lumen of a vessel in any area, as a result of which blood cannot flow further. In the neck, atherosclerotic plaques most often form in the area of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, the mouth of the vertebral artery, the siphon of the internal carotid artery, and the mouth of the subclavian artery. Doctors know these features, and therefore pay special attention to examining these particular places.
Carotid artery stenosis on ultrasound
The initial manifestations of atherosclerosis are characterized by an increase in the thickness of the intima-media complex from 1.0 to 1.5 mm. If the thickness of these layers is more than 1.5 mm, then they already talk about a plaque. During an ultrasound examination, the plaque may look completely different on the screen. They can be homogeneous and heterogeneous, hyperechoic, and isoechoic. The most unfavorable are considered to be atherosclerotic plaques that are heterogeneous in structure and have an uneven surface. They are at high risk of complications.
In case of stenotic lesion of the artery, the doctor measures the degree of narrowing of the vessel on a longitudinal or transverse section of the vessel, and measures the extent of the lesion. Plaques up to 1.5 cm in length are considered local, and longer ones are considered prolonged. This parameter is extremely necessary for assessing the significance of lesions and planning treatment tactics.
Arterial thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis differs from atherosclerosis, as a rule, by the following ultrasound signs:
- occlusion predominates more than stenosis,
- the lesion is longer in length,
- more often the echogenicity of intraluminal formations is relatively homogeneous, the echogenicity varies depending on the stage of thrombosis,
- in the area of the beginning of occlusion - the surface is flat,
- with prolonged existence of thrombosis, hypoplasia of the artery develops.
Arterial deformities
Deformities are the second most common changes after atherosclerosis. They can be congenital or acquired. In children under 18 years of age, deformities are considered normal. Children are born with a short neck, and the vessels have the same length as those of adults, and in order for them to “fit” in the neck, they have different bends and deformations. As the neck itself grows, the vessels align and acquire a straight course. In older people, under the influence of changes in blood pressure, the vessels stretch and can become tortuous again. The following types of deformations are distinguished by shape:
- tortuosity is a deformation with an angle greater than 90 degrees, they are C- and S-shaped;
- bends - deformations with an angle of 90 degrees or less, they have the worst effect on blood flow, as they lead to a narrowing of the lumen at the bend;
- loops are circular configurations of the artery, often congenital.
During an ultrasound examination, as a rule, the course of the vessel is clearly visible, and it is not difficult for the doctor to determine the type of deformation, its location, and the size of the angle.
Nonspecific aortoartery disease (Takayasu disease)
Unlike atherosclerosis, which affects more men, Takayasu's disease is more common in young women. The main ultrasound sign of damage to the carotid arteries is uneven, diffuse, hyperechoic thickening of the wall of the common carotid artery. Moreover, unlike atherosclerosis, the thickening is circular in nature, that is, it affects all the walls of the vessel. It becomes difficult to distinguish the individual layers in the wall.
Metabolic angiopathy
Metabolic angiopathy is a complex of structural changes in the vascular wall of arteries caused by various metabolic disorders. Most often occurs in patients with diabetes. In this case, small ones are visible in the wall of the vessel. Changes in the spectral characteristics of blood flow are characteristic: an increase in resistance indices is detected in the proximal part of the artery, a decrease in velocity in the distal part.
Arterial dissection
Dissection is called local separation of the wall as a result of its tear. Most often it occurs due to injury. At the site of dissection, detachment of the upper layer of the vascular wall occurs, blood begins to get under it and thrombose, forming a hematoma. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor sees a dissected wall with movable intima or the presence of a second lumen of a vessel with blood flow.
Cerebral venous circulation
There can be many reasons for the violation. During an ultrasound examination, the transcript may contain the following criteria indicating stagnation of venous blood in the brain:
- an increase in the diameter of the internal jugular vein (more than three times the diameter of the common carotid artery) as a result of compression in the proximal parts or valve insufficiency,
- reduced diameter of the internal jugular vein as a result of congenital hypoplasia or compression,
- bidirectional flow (reflux) in the vein as a result of valve insufficiency,
- an increase in blood flow velocity in the internal jugular vein is more than 70 cm/s, in the vertebral vein – 30 cm/s,
- lack of blood flow in the internal jugular vein (thrombosis),
- an increase in the diameter of the lumen of the vertebral vein by more than 2.5 mm in the spinal canal,
- compression of the vertebral vein: its uneven diameter, arched course or acceleration of blood flow at the site of compression.
Preparation for ultrasound of the aorta and renal vessels
Unlike standard vascular ultrasound, proper preparation is required before performing an aortic ultrasound. The patient will need to follow a diet that excludes most fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as freshly baked pastries. This is done to reduce gas formation in the intestines. If the patient suffers from flatulence, it is recommended that he take carminatives before the study. The procedure takes no more than half an hour. The last meal must have been more than 8 hours ago, which is why the examination is mainly performed in the morning.
Such preparation is required only in the case of ultrasound of the abdominal aorta; if it is necessary to examine the thoracic aorta, no preparation is necessary.
After the study is completed, the indicators are entered into the protocol, where the norm of the ultrasound of the aorta is indicated next to the data obtained. The results are assessed in the same way as with other ultrasound examinations of blood vessels.
Another important study is ultrasound of the renal vessels. In urology, one of the most commonly used vessels from which diagnosis begins is ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is used to diagnose injuries and bruises, neoplasms, atherosclerosis, after transplantation, etc.
The preparation rules are similar to those for ultrasound examination of the abdominal aorta: exclude gas-forming drugs and do not eat for more than 8 hours. But there is one more limitation - before the procedure you should not consume more than one hundred milliliters of water and diuretics, as this may distort the data obtained.
As you can see, preparing various vessels for ultrasound, be it renal vessels or the abdominal aorta, does not cause any difficulties, which allows the examination to be carried out in the shortest possible time.
The results of Doppler ultrasound of the renal vessels must be assessed by a urologist, after which appropriate conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed.
In modern medicine, vascular ultrasound has become an integral part of diagnosis and is used to identify both acute diseases that require immediate intervention, and to prevent or prevent others. All this is thanks to the main advantages of ultrasound: accessibility, speed and information content.
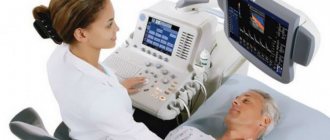
What is vascular duplex scanning and what does it show?
Duplex ultrasound scanning shows the doctor the condition of the arteries and veins, helps assess the speed and direction of blood flow through the vessels and identify places where it may be blocked. A duplex study is so called because it combines two types of ultrasound to produce an image:
- Traditional ultrasound, which creates images of blood vessels, tissues and organs,
- Dopplerography, which allows you to measure blood flow based on the Doppler effect: changes in wavelength when ultrasound is reflected from flowing blood.
The procedure allows the doctor to observe the blood flow through the vessels on a screen. If color three-dimensional image conversion is used, the study is called triplex scanning. Ultrasound ultrasound procedures can be done to study the vessels and blood flow of the lower and upper extremities, neck, head, kidneys, penis, blood flow through the mesentery to the liver, spleen, stomach and intestines.
Preparation
An ultrasound examination of the neck area does not require any preparatory measures on the part of the patient. It is better to take data on the current diagnosis for research. This may be: an extract from the medical history, the results of a doctor’s visit, data from other examinations (laboratory tests, X-rays, CT or MRI of the neck). All this information will help the sonologist focus on the desired scanning area and, if necessary, assess the dynamics of the development of the pathological process.
Decoding the results
A normal vascular ultrasound finding is blood flowing at a good rate through the vessels with no signs of narrowing or blockage.
Pathology of blood circulation in the vessels of the neck can be caused by a lot of reasons, but they are all very serious. In the absence of timely treatment, the consequences can be very unpleasant, even leading to a stroke.
Identification of possible diseases
The most optimal diagnostic method is ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head. It allows you to identify a specific violation. During an ultrasound examination, the condition of the carotid trunk is assessed. Ultrasound is good because it is completely safe for health, and its effectiveness is very high. The method is quite simple, but at the same time it makes it possible to timely diagnose almost the entire spectrum of vascular diseases. These diseases are fraught with many complications. Ultrasound of the neck vessels helps prevent them - after all, if treatment is started on time, many troubles can be avoided.
Medical indications
You should immediately undergo this diagnostic procedure if you suffer from frequent dizziness, weakness, tremors in the legs, or fainting. All this indicates that the vessels of the head and neck are “signaling” to you that there is a problem. Particular attention should be paid to your health if:
If at least one of the listed items is present, you are recommended to immediately conduct an ultrasound of the neck vessels. In addition, ultrasound examination can detect diseases such as stenosis. Timely diagnosis makes it possible to record indicators of venous outflow of blood from the cranial cavity.
Ultrasound of neck vessels
A doctor may prescribe such a procedure if he suspects the patient has the possibility of atherosclerosis and obstructed blood circulation in the brain. While listening to the cervical vessels, unpleasant noises may be detected - in this case, the patient is also advised to study. Factors such as:
- The presence of tumors in the neck and chest.
- High or low blood pressure.
- Cholesterol levels are too high.
- Weight is too high.
- Frequent stress.
- Bad heredity.
- Diabetes.
The “risk group” includes men who are overweight and over forty years old. cervical vessels reveals narrowing of the lumen in the arteries. Thus, the condition of the walls of blood vessels is diagnosed, possible thickening or thinning, blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques are detected. The vessels may be completely blocked, which is also detected on ultrasound. Timely detection of plaques and blockages allows for treatment and prevention of stroke.
Ultrasound of neck vessels
— diagnostic examination of the venous and arterial branches that provide blood supply to the brain and are located outside the cranial cavity.
There are three types of ultrasound diagnostics in this area: Dopplerography (USGD of neck vessels is an examination of vessels without studying blood flow), duplex scanning (determining blood supply and the condition of blood vessels) and triplex scanning (assessing the condition of blood vessels, blood flow speed, direction of blood movement). The decision to choose one or another diagnosis is made by the attending physician.
Based on the results of ultrasound, a specialist can assess the nature of the cervical blood supply, identify vascular pathology, aneurysms, vascular spasms, blood clots, congenital features of veins and arteries, and the nature of the blood supply.
Ultrasound has no absolute contraindications and can be prescribed to patients of any age, pregnant women and patients with chronic diseases. An ultrasound of the blood vessels in a child’s neck can be performed from the moment of birth.
Indications
Ultrasound is indicated for hearing and vision impairment, headaches of unknown origin, dizziness, memory impairment, decreased concentration, and tinnitus. If you have complaints of various neurological symptoms, it is advisable to do an ultrasound of the carotid arteries. For preventive purposes, scanning the arteries of the neck is recommended for people over 45 years of age, patients with hypertension, arrhythmia, cervical osteochondrosis, diabetes mellitus, as well as smokers.
Preparation
Diagnostics is carried out without preliminary preparation. It is advisable not to smoke on the day of the ultrasound to avoid additional vasoconstriction, and the list and composition of medications taken should be agreed upon with the doctor.
More details
Price
The cost of ultrasound of neck vessels in Moscow ranges from 1000 to 6200 rubles. The average price is 2490 rubles.
Where to do an ultrasound of the neck vessels?
Our portal contains all the clinics where you can get an ultrasound of the neck vessels in Moscow. Choose a clinic that suits your price and location and make an appointment on our website or by phone.
The neck occupies an important place in the human body. It is the connecting link between the body and the head; vital arteries pass through it. The neck contains the pharynx, larynx, trachea and the beginning of the esophagus.
Anatomically, the neck is divided into several areas:
- Front
- Rear
- Two side parts
- Two sternocleidomastoid
Neck diseases are almost always accompanied by headaches and the inability to turn the neck, because it is through the neck that the vessels that feed the brain pass.
Read about here.
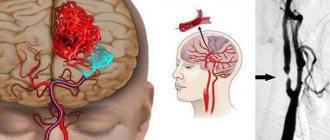
How to prevent a stroke
People with damaged arteries supplying the brain may not have any signs of the dangerous disease. Duplex scanning or MRI will help detect pathology; in addition, you should pay attention to symptoms such as dizziness or headache, numbness of any part of the body (often only on one side), and speech disorder. This symptom occurs for no apparent reason and can last for an hour or go away in a few minutes.
Experts call the described symptoms ischemic attacks; they should not be ignored under any circumstances. It has been proven that about 30% of people who have experienced an ischemic attack will suffer a cerebral stroke in the future. Timely tomography, ultrasound examination or ultrasonography will help to draw attention to the problem in time to take appropriate measures. Ultrasound of the carotid arteries, like MRI, does not take much time and will help the patient find out exactly whether he is at risk.
Vessels of the cervical spine and their diagnosis
The most important arteries that supply the brain and neck are the carotid arteries. They are separated by two common carotid arteries (internal and external).
The external carotid artery supplies the facial part of the head and neck. This artery also has its own branches (anterior, posterior and medial). It is located in the area of the parotid gland.
The internal carotid artery is responsible for feeding the brain and eye area. The internal artery is divided into cavernous, cerebral, cervical and petrosal.
In addition, the posterior and middle arteries of the brain are also distinguished, which are responsible for blood circulation in the cerebral hemispheres, temporal and occipital lobes.
The appearance of pain in the neck may indicate problems with the vessels of the cervical spine. Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the cervical spine will help diagnose this disease.
With the help of ultrasound, a specialist has the opportunity to assess the general condition of your blood vessels and determine whether there is a possibility of disturbances in blood circulation.
Ultrasound is also used to determine:
- Is there a violation of the outer lining of blood vessels, arteries and veins (tissue condition)
- Compliance of the vessel lumen with standards (lumen diameter)
- Vessel patency
- Vessel geometry
- Condition of the vascular network
- Aneurysms
The scope of application of ultrasound includes research:
- Facial vein
- Subclavian artery
- Internal and external carotid arteries
- Jugular veins
- Basilar artery
- Arteries of the spinal column
Read about here.
This procedure also has another, more precise name, Doppler ultrasound (USDG). Doppler ultrasonography involves a combination of classical ultrasound with Dopplerography (visual identification of blood vessels)
What does cervical vascular narrowing look like?
The size of the cervical vessels may deviate from the norm, which is the result of disruptions in metabolism or the appearance of disturbances in the structure of the body. Over a long period of time, such changes are imperceptible; the boiling point is the cerebral blood supply. As soon as the nutrition of the head cells ceases to be complete, a person experiences characteristic pain.
The development of degenerative-dystrophic diseases in the neck occurs with damage to the vertebral artery, which passes through the vertebral lumens at the transverse vertebral processes.
The formation of osteophytes leads to compression of the vessel, against which numerous autonomic disorders develop.
The diameter of the vertebral arteries with atherosclerosis decreases , as the vascular lumens are filled with plaques. They are formed as a result of disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
Plaques form lipoproteins that are slowly deposited on the vascular walls, creating congestion. In this case, the vascular wall begins to be damaged, and an accumulation forms in this place:
- platelets;
- leukocytes;
- red blood cells
The listed blood cells form a blood clot, which is capable of fibrotization over time.
Deviation from the norm in the diameter of the vertebral arteries may be accompanied by the following pain manifestations:
- feeling of stiffness;
- manifestations of crunching;
- feeling of discomfort.
The described signs signal vertebral osteochondrosis . Sudden movements of a person are always accompanied by pain, radiating to the arms and shoulder girdle. Against this background, muscle spasms may occur, limiting the mobility of the vertebrae in the neck. With osteochondrosis, the linear speed of blood flow through the vessels will be increased.
A headache may occur
What does the pain in the head indicate? Headaches caused by narrowing of the cervical arteries have different manifestations and can be:
- tightening (muscle tension);
- dull (arteriospastic disease);
- bursting (liquorodynamic pathology);
- pulsating (arteriodilatatory disease);
- aching (vein disease).
Advice! If you have frequent headaches, you should visit a doctor, as many of them develop due to narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck.
Preparation procedure and indications for ultrasound examination
During the study, the specialist installs special sensors at the suspected location of the veins in the neck and reads the information received through the sensors to the computer. In this case, the patient is in a lying position with his head thrown back.
The screen displays images of colored waves that indicate the movement of blood. From this image, the specialist determines where the flow is obstructed, at what speed the blood moves and where the blood flow is blocked.
The procedure for ultrasound scanning of the cervical spine lasts on average 15-20 minutes.
- In the evening and morning before the test, you should refrain from coffee, tea, alcohol, energy drinks and smoking, as this may affect the results.
- Eliminate high-fiber foods (bread, meat, cereals) from your diet.
- Avoid physical activity (sports) on this day.
- If you are taking medications that normalize blood pressure and heart medications, then you must inform the ultrasound doctor about this.
If you experience sudden attacks of headaches that subside after taking antispasmodics, then this is a reason to undergo examination of the vessels of the neck and brain.
Also among the indications:
- Neck pain
- The presence of a crunch when moving the neck
- People who smoke for a long time
- Osteochondrosis
- Diabetes
- Increased blood pressure
- Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides
- Heart attacks and strokes in the past
- The appearance of pulsation in the cervical region
- Headaches, migraines
- Fainting
- Increased anxiety
- Feeling of heaviness in the head
- Absent-mindedness and memory impairment
- The appearance of tinnitus
- Decreased vision
- Insomnia
All symptoms may be a manifestation of a disorder in the circulatory system in the neck. If you do not respond to these manifestations in time, there is a risk of complications, the worst of which is a stroke.
Read about here.
Stories from our readers!
“I cured my bad back on my own. It's been 2 months since I forgot about my back pain. Oh, how I used to suffer, my back and knees hurt, lately I couldn’t really walk normally... How many times I went to clinics, but they only prescribed expensive pills and ointments, which were of no use at all.
And now it’s been 7 weeks, and my back joints don’t bother me at all, every other day I go to the dacha to work, and it’s a 3 km walk from the bus, so I can walk easily! All thanks to this article. A must read for anyone who has back pain!”
Decoding
The data obtained during the study is deciphered by the doctor who performs the ultrasound of the cervical spine. The anatomy and patency of blood vessels, diastolic and systolic blood flow, its nature and direction are determined. The final result of the study looks like a three-wave chart (beginning, middle and end). It must be symmetrical; standard values can be shifted up to two millimeters.
The norm is:
- absence of diseases, external compression of blood vessels and turbulence of blood flow in places with missing capillaries;
- arterial walls of the brain and neck are 0.9-1.1 millimeters thick;
- complete vascular patency;
- blood flow speed – not higher than 0.3 m/s;
- vertebral arteries of equal diameter, 2 mm each, no less.
The normal amount of blood transported to the brain should be at least 15 percent of the total volume moving from the heart. The carotid artery is located on the left side of the aortic arch, and on the right its length is always slightly shorter (7-12 and 10-15 cm). When conducting a study, normally the intracranial branches should be in the outer part. In this case, the speed of blood flow should not differ.
If the thickness of the arterial walls is more than 1.2 mm, this indicates the appearance of atherosclerotic changes. In this case, immediate treatment is required to prevent plaque from forming on the carotid artery. The blood flow should pulsate continuously.
Interpretation of ultrasound examination - signs of major diseases
Tortuosity and kinks of blood vessels indicate atherosclerotic lesions. Its second sign is the thickness of the arteries. In case of disease, the general indicator is more than 0.87 mm, and the carotid indicator is more than 0.9 mm. These values are considered key in determining pathology.
Thrombosis is characterized by clogging of the lumens and changes in their diameters. Deformation of the arteries is accompanied by their kinks and tortuosity. Takayasu's disease is defined by inflammation of the internal vascular walls, which leads to their thickening and blockage.
Metabolic angiopathy is a syndrome. In this case, increased sensitivity of blood vessels is observed. Angiopathy can be of two types, with:
- micro-small capillaries are affected;
- macro- large vessels suffer.
To determine the disease, the speed of blood flow peaking in diastole is checked. When pathology is detected, neoplasms appear in the lumens, the wall thickness changes and stenosis appears.
Arterial dissection is an intimal deformation. Blood leaks through it and spreads, causing separation of the walls. As a result, stenosis is formed. Dissection of the artery is accompanied by thickening of the vascular walls.
Venous cerebral discirculation is common during diagnosis. In the latent stage there are no signs. With the active development of the pathology, venous encephalopathy appears with clear symptoms. This is a violation of arterial blood flow, increased pressure in the skull and dilation of the veins. The most common disease is damage to the brachycephalic arteries.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the study include:
- neurological symptoms that may indicate a malnutrition of the brain (dizziness, lack of coordination, tinnitus, insomnia, etc.);
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- the presence of factors that increase the risk of development (high blood cholesterol, heavy smoking, excess weight, etc.), or the first signs of cerebral atherosclerosis;
- chronic hypertension;
- transient ischemic attack;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- history of stroke or heart attack;
- diabetes;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- planned heart surgery;
- pulsating formations in the neck area;
- thrombosis of veins and arteries;
- vascular disorders (stenosis, atherosclerosis, aneurysms);
- increased fatigue;
- scoliosis and mental development disorders in children.
There are no contraindications to Doppler ultrasound, since the procedure is non-invasive and absolutely safe for the patient.
This video provides more details about the indications and procedure: