In this article we will consider what it is - ultrasound with color circulation. We will also describe the transcript of this study.
The purpose of ultrasound examination is to diagnose internal organs along with obtaining an accurate image of them. The method is often used during pregnancy to assess the health of the unborn baby. A timely procedure allows you to identify different types of pathologies in the early stages of development. But the result of the ultrasound technique cannot always provide complete information in order to give an accurate diagnosis. The use of ultrasound with color flow allows doctors to obtain the most accurate results. Next, we will talk in detail about conducting this type of diagnostic study.
What it is?
Using ultrasound, doctors can conduct research to obtain accurate information about blood flow, characterized by speed, pressure, direction of movement, nature, and, in addition, degree of patency.
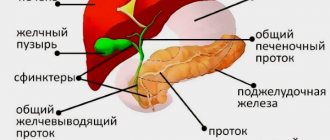
What is the addition of CDC to ultrasound? This study represents the addition of Doppler blood flow assessment to conventional ultrasound examination. The Doppler effect makes it possible to organize the sending and return of ultrasound using a specific sensor. The blood flow in the color flow mode, depending on its direction and speed of movement, has a shade of one of the colors. If blood moves towards the sensor, then only red tones can be encoded, otherwise blue tones can be encoded.
Thanks to the color mapping option, doctors have the opportunity to visually assess the nature of blood flow on ultrasound with color flow, and, in addition, visualize the vascular lumens. The results of such measurements are represented by the difference between the reflected frequency indicators and the original values. In addition, this procedure allows you to diagnose blood flow speed indicators with its direction, as well as obtain information about the vascular structure and patency. This research technique allows you to diagnose:
- How thick are the vascular walls?
- Are there mural thrombi or atherosclerotic plaques?
- Determination of the degree of pathological tortuosity of blood vessels.
- Is there a vascular aneurysm?
This study helps to detect vascular pathology; the results make it possible to clarify the malignancy of the processes, the type of tumors and the risk of their development and growth. Considering that this technique has no contraindications or painful symptoms, it can be applied to any patient repeatedly, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations.
Indications and contraindications for CDK
CDC in ultrasound is prescribed if there is pain in the arms, neck, shoulders, abdominal cavity and sternum. Such symptoms are inherent in many diseases - liver, diabetes, vascular diseases, etc.
If scanning is prescribed for pregnant women, then starting from the second trimester, otherwise it will be uninformative. It is mandatory to conduct this type of ultrasound at 30-34 weeks. This is necessary to examine the placenta. With vascularization, blood flow changes and fetal development is disrupted. Also, CDK is done when:
- Swelling of the legs, the appearance of cramps in the limbs. Especially if nodes appear on the veins, and after pressing on the skin, hematomas and bruises remain. It is also a dangerous symptom when your feet are cold and “goosebumps” run all over them.
- Rh conflict in the fetus and mother.
- Rejection of necrotic tissue that cannot be treated.
- Incorrect positioning of the fetus, entwining it with the umbilical cord.
- Multiple pregnancy or if a woman suffers from diabetes, VSD, or hypertension during pregnancy.
- Gestose.
- Pregnancy (how it proceeds, the general condition of the woman).
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland or its pathologies.
- Non-healing trophic ulcers.
- Problems with amniotic fluid.
- Fetal development assessment. This allows you to obtain not only valuable data about the baby’s health, but also about the level of oxygen that enters the body, identify hypoxia and find its causes.
- Pathologies of the structure of the vascular system, aneurysms.
- Study of brachiocephalic vessels (right arteries: carotid, subclavian, vertebral).
- The appearance of atherosclerotic formations.
- Pain in the lower extremities when running or walking.
- Changes in the normal thickness of vascular walls.
- Poor wound healing.
- The presence of foreign bodies or neoplasms in the body. With the help of CDK, stones are easily distinguished from polyps and tumors (due to the blood supply to the studied areas).
Also, ultrasound with colorectal dosage can be prescribed as a preventive study or to clarify the diagnosis. For example, checking the condition of a pregnant woman or if there is a threat of miscarriage. CDC is prescribed to establish the exact location of the disease and its degree. Such examination before surgical operations simplifies the work of doctors and helps reduce the time the patient spends under anesthesia.
Ultrasound is considered a safe examination and is prescribed even for infants. The diagnosis has virtually no contraindications, but in some cases it is not done. During an ultrasound examination, the sensor slides over the skin, but this is prohibited if there are open wounds, eczema, or burns in this area. Also, an ultrasound is not done immediately after a colonoscopy or FGDS, since after them there are many air bubbles left in the intestines, which interfere with getting an accurate picture.
Ultrasound with Color Doppler: abdominal region
Ultrasound examination of this cavity makes it possible to examine a specific organ. And the use of color Doppler mapping allows specialists to see on the monitor in real time not just the organ being examined, but also absolutely all the fluids in it and nearby. This type of diagnosis gives a very broad picture of the health and general condition of the internal organs, which is why thanks to ultrasound with colorectal dosage, a tumor, some pathology and many different diseases can be detected in the early stages.
Decoding: norms and pathologies
The result obtained during the study is an image in several projections in real time and scale. At the same time, the picture displayed on the monitor screen can display not only vascular anomalies, but also blood clots, plaques, thickenings, neoplasms and even foreign bodies.
Thyroid gland
Ultrasound of a pathologically altered thyroid gland in color-dynamics mode can detect several types of blood supply (vascularization), which may indicate pathology:
- lack of blood flow (with cysts or dense nodes);
- marginal vascularization of the node (for benign formations);
- intranodal blood flow (in case of malignant formations);
- mixed blood supply to the node (with hormone-producing tumors);
- increased blood flow throughout the gland (with toxic goiter, accompanied by hyperfunction of the thyroid gland).
Normally, the gland should be no more than 18/25 cm3 (in women/men, respectively), without formations (nodules), and with uniform blood flow.
Fetus
The cause of the pathology of the blood supply to the fetus - its hypoxia - can be either the mother’s body (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, gestosis, pathology of the vessels of the uterus or placenta), or the fetus itself (chromosomal abnormalities - “cleft lip”, “cleft palate”, Down’s disease and others ). Ultrasound diagnostics with Doppler examination allows you to exclude/confirm any of these abnormalities. In this case, a specialist can assess the threat of miscarriage, premature birth or loss of a child, as well as diagnose placental insufficiency in a timely manner.
Ultrasound color flow data are also used to create a fetal biophysical profile (FBP), which fully reflects the intrauterine state of the child.
Technique
The technique for performing Doppler color mapping differs little from conventional ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. The patient is placed on the couch, and the doctor applies a special gel to his stomach. A sensor moves over this substance. Nothing is injected directly into the patient's body.
The main difference in performing this procedure from a conventional ultrasound examination is the image on the monitor. On it, the doctor sees not just a picture, but an image distinguished by colored splashes that indicate the vascular system of a particular organ. It is also worth noting that this examination, as a rule, is not accompanied by any unpleasant or painful sensations.
It is worth noting that ultrasound with color circulation is performed not only in the abdominal sector. The examination can also be carried out in relation to the thyroid gland, mammary glands, fetus in the womb, upper and lower extremities, and so on.
Carrying out the procedure
Carrying out color circulation is a standard ultrasound scanning procedure. You need to take a diaper and wipes with you to remove the gel. For pregnant women, scanning can be carried out (if the peritoneal organs are checked) using a transrectal or vaginal probe. The same method is used in the diagnosis of gynecological diseases, uterus, ovaries, and disorders of the organs located in the pelvis.
If the head or neck is being checked, the examination can be performed while sitting. When the abdominal cavity is examined - lying down. If a vaginal sensor is inserted, the woman lies down on the couch and spreads her legs slightly bent to the side. A condom is placed over the sensor and then inserted into the vagina. When scanning through the abdominal wall, a gel is applied to the abdomen. The sensor slides over it. The doctor presses it firmly against the skin for better visualization.
How to prepare for research
The set of preparatory actions immediately before diagnosis directly depends on which area of the human body will be examined. If the procedure involves an ultrasound examination of the extremities, there will be no special instructions. Patients are simply advised to give up tobacco and alcohol products and not eat foods that accelerate the movement of blood vessels.
If an ultrasound of the uterus with colorectal dosage is planned in the presence of pregnancy for the purpose of examining the fetus or for any other reason, then as part of the preparation it is necessary to drink enough fluids and follow a diet. You should for some time exclude from your diet all foods that lead to flatulence and fermentation processes in the intestines. It is necessary to come directly to the examination procedure exclusively on an empty stomach in order to maximize the reliability of the planned examination.
Below we will describe how an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland is performed.
How do you prepare for CDC and other Doppler studies of the kidneys?
Another advantage of Doppler ultrasound examinations is the minimal preparation of patients for diagnostic procedures.
Another advantage of Doppler ultrasound examinations is the minimal preparation of patients for diagnostic procedures. When conducting examinations of the vessels of the head, legs, uterus, and external genitalia, no preparation is needed at all. Patients are prepared only for examination of objects located in the abdominal cavity, including the kidneys. This need is associated with the presence of gas bubbles in the intestines that interfere with ultrasonic waves, dissipating them. This leads to a fuzzy, blurry picture, which distorts the idea of the real state of things, so preparatory measures consist of minimizing the number of air inclusions in the intestines.
What is MSCT with contrast?
To minimize gas contamination of the intestines before Doppler of the renal vascular bed, it is necessary to adhere to certain dietary restrictions for several days before the study. Vegetable protein (especially legumes) and baked goods made from wholemeal rye and wheat flour should be excluded from food. The consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits, fruit juices, and dairy products is also reduced to a minimum. Patients suffering from a tendency to increased gas formation in the intestinal lumen (flatulence) are recommended to use carminative drugs (Espumizan, Disflotil) containing the substance simethicone. Also in such a situation, enterosorbents such as Enterosgel can be useful.
Renal vessels are examined using Doppler on an empty stomach, mainly in the morning. Abstinence from eating should be at least 8-12 hours for adults, about 6 hours for children. For patients with hunger pain, diabetes, and young children, the period of food refusal is reduced to 3-4 hours.
Read more about preparing for a kidney ultrasound examination.
When are patients prescribed a thyroid test?
This is done in a number of cases:
- When patients experience increased nervousness.
- In the event that a person has difficulty swallowing.
- When severe pain occurs in the head and neck area.
- If you have complaints about poor sleep.
- Against the background of weight loss without any justified reasons.
- In situations where a person has a fever for a long time, which may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
In all these cases, an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland with color circulation is indicated. Studies of other organs are described below.
Indications for Doppler examination of renal vessels
Symptoms that may be a reason for conducting ultrasound examinations include pain in the lumbar and lower abdominal region.
One type of Doppler diagnostics of vascular disorders in the excretory organs is prescribed for symptoms of renal pathologies and general manifestations indicating the likelihood of damage to the kidney vessels. Symptoms that may prompt ultrasound examinations include:
- pain in the lumbar and lower abdominal region;
- changes in the volume, mode and frequency of urination, pain during this physiological process;
- the presence of persistent swelling of facial tissues, extensive swelling of other localizations;
- stable hypertension at a young age, or resistant to the effects of antihypertensive drugs;
- laboratory tests of urine or blood indicating the presence of nephrotic or uremic syndrome.
In addition, Doppler ultrasound can be used in the following pathological conditions:
- signs of insufficiency of the function of excretory organs (azotemia, uremia);
- suspicion of abnormally developed renal vascular structures;
- assumptions about the presence of tumor-like growths in the tissues of the kidneys or adrenal glands;
- suspicion of deterioration of renal hemodynamics due to the formation of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques, stenoses and aneurysms in the renal vessels.
The advantage of the Doppler technique for studying the vascular network of excretory organs is the ability to assess the hemodynamics and architecture of blood vessels in the present time. In addition, Doppler sonography is completely harmless, and therefore has no contraindications for use at any age and for any general condition of the patient.
Important! Doppler of the vessels of the excretory organs is more informative and diagnostically valuable than tomographic angiography, although the study is much simpler and does not require complex and time-consuming preparation.
Ultrasound of the scrotum
Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs proceeds similarly to most diagnostic techniques in the presence of diseases of the abdominal cavity. It is worth emphasizing that quite often such an examination is prescribed in conjunction with an examination of the kidneys and urinary tract. Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs using CDC should be regularly performed not only by young patients, but it is especially important for men over forty years of age. This prevention allows you to avoid many complications and pathologies of the male reproductive system.
How is a fetal examination performed?
Studying the condition of the fetus using an ultrasound sensor is carried out only through the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. The intravaginal method is not suitable in this case. A pregnant woman should come for diagnostics in loose and comfortable clothes. This is necessary in order to easily expose the abdomen during examination. The study of the fetus is carried out only as planned. Typically, the study is carried out three times during the entire period of gestation. An unscheduled procedure is recommended for:
- suspected premature delivery;
- the likelihood of the presence of intrauterine abnormalities;
- suspected miscarriage;
- bad habits of the mother.
Diagnostics does not have a negative effect on the body of the mother and child.
Who is this study for?
Regardless of the symptoms, first of all, a man needs to see a doctor, and only after undergoing an initial examination, the urologist, if necessary, will prescribe an ultrasound of the scrotum with colorectal dosage. Typically, such a study is prescribed if the following diseases or symptoms are recognized:
- Presence of infertility and trauma.
- The appearance of a foreign body.
- In order to clarify or refute the established diagnosis.
- Against the background of pain or discomfort of unknown origin.
- When the shape and size of an organ changes.
Why is an endometrioid cyst an avascular but not anechoic formation?
Endometrioid (“chocolate” cyst, endometrioma) is one of the types of external genital endometriosis and has a diameter of 3 to 20 cm. In 1/3 of cases, such neoplasms form on both appendages. Most often, endometrioid cysts are located behind the reproductive organ. They are motionless and, as a rule, single-chambered, however, sometimes they are so close to each other that they look like two or three-chambered.
Endometriomas appear differently on ultrasound. Most often, their internal contents have a low or medium degree of echogenicity, which creates a “frosted glass” effect. The walls are usually quite thick; with CDK, the internal contents always appear avascular, and isolated areas of vascularization are detected along the periphery. Thus, an endometrioid abnormal inclusion is considered an avascular lesion but is not anechoic.
Features of the event
The examination in question is one of the most efficient and comfortable for the patient. The general scheme for performing this procedure follows the following algorithm:
- The doctor applies a special gel to the area to be examined.
- The area is then scanned using a special sensor.
- Next, the resulting visual picture of the organ being studied is analyzed in order to exclude various types of neoplasms along with thickenings or blood clots.
Anechoic avascular formation: features
On the monitor during ultrasound examination, the anechoic formation looks like darkened roundness. These structures also do not allow ultrasound to pass through, so a specialist will quickly notice them during the examination. The formations are often benign in nature, but over time they can develop into malignant ones.
Focal pathology usually consists of soft, loose tissue. With the deposition of calcium salts, the echogenicity of the structures increases. The pathology is usually diagnosed as a cyst or galactocele.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands with Color Doppler
Women can not perform ultrasound examination using color circulation on all days of the cycle. For example, during ovulation, hormonal levels change, which affects breast tissue.
Due to such modifications, ultrasound examination during ovulation and the presence of bleeding is not necessary, as the result may be false. Based on the above information, ultrasound examination should be performed six days after menstruation. It is during this period that the results will be most reliable.
How the research is carried out
To perform an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, the woman is naked to the waist, after which she lies flat on the couch, on the left side of the device. The procedure begins with an examination of the left breast, onto which a special transparent gel is applied (removes the air gap between the transducer and the skin).
Initially, the sensor is placed on the peri- and subareolar zones (around and above the nipple), where the doctor scans the breast in several positions. After examining the nipple area, the sensor begins to move from the periphery to the center clockwise. In this way, almost the entire area of the organ is assessed.
After completing the examination of the left gland, the doctor moves on to the right one. Sometimes, for better access, the patient is asked to turn on her left side, after which the condition of the glandular tissue of the mammary gland, its capsule, ducts, vascularization (blood supply) and surrounding structures is assessed using the previous algorithm. It is possible to perform an ultrasound in a sitting position.
It is mandatory to examine regional lymph nodes for pathological damage (inflammation, metastases). When any formation is detected, the doctor enters its characteristics into the ultrasound protocol (size, shape, structure, echogenicity, type of blood flow, location, quantity).
How often can you do it
Despite the fact that ultrasonography is recognized as a safe method of functional diagnostics, the study should be done according to medical indications. Often the procedure is prescribed as a control for the treatment of the inflammatory process, before, during and after a puncture biopsy of the cyst.
Breast examination results
In order to decipher the results, you need to have deep knowledge in the field of research, so it is simply impossible for a person without a medical education to do this. The treating doctor must examine the circulatory system and all areas for the presence of neoplasms.
This point can be seen in the blue and red areas, indicating the direction along with the nature and speed of the flow of liquids. With the help of ultrasound examination with color flow in the mammary glands, it is possible to distinguish benign neoplasms from malignant pathologies. Images on the screen are displayed in “B-mode”.
The Doppler effect is the basis of modern vascular research
The Doppler effect is used to study the vascular bed and the characteristics of hemodynamics - the movement of blood through the vessels.
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the partial reflection of ultra-high frequency sound by various tissues and their structural components. Stationary objects reflect a sound echo of the same frequency (wavelength) as the sent signal. If the object of study is in forward motion, the frequency of the reflected ultrasound changes in proportion to the speed of the object's movement. This is the Doppler effect, on which the study of the vascular bed and hemodynamic characteristics - the movement of blood through the vessels - is based.
Normally, blood is in constant motion, so the ultrasound reflected from red blood cells will have a changed frequency, which is detected by special sensors. The computer-converted data is displayed on the screen in the form of graphics, allowing one to draw conclusions about the following characteristics of blood vessels and hemodynamics:
- shape of the vascular bed;
- vascular wall thickness;
- the presence of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques in the lumen;
- blood flow speed;
- direction of blood flow.
These data are of great diagnostic value, making it possible to identify vascular pathologies even at the stage when the disease is latent and does not manifest itself in any way. Early diagnosis of vascular pathologies makes it possible to adopt adequate therapeutic or surgical treatment methods, preventing the development of more severe consequences.
Breast cancer on ultrasound
It often happens that the doctor doubts the diagnosis of a malignant tumor based only on the results of an ultrasound examination. At an early stage of oncology, the tumor may not be visible at all, but with the help of the CDC technique, neoplasms are quite easily identified.
Thanks to this improved research, women can begin treatment for breast cancer at the very first stage, which may lead to a complete cure.
Combined use of color Doppler and three-dimensional ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology
Ultrasound machine HS40
Top seller in high class.
21.5″ high-definition monitor, advanced cardio package (Strain+, Stress Echo), expert capabilities for 3D ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology practice (STIC, Crystal Vue, 5D Follicle), high-density sensors.
Introduction
Ultrasound has evolved from being an exciting new technology to becoming the best diagnostic tool in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. In addition to ultrasound examination in B-mode, functional examination using the Doppler method made it possible to conduct a detailed functional examination in case of infertility, in the early stages of embryo development, as well as to study the development of blood vessels in tumors of the pelvic cavity [1-3]. The development of the method of transvaginal ultrasonography and, in particular, the study of blood flow using the Doppler method, has allowed a new look at the physiology and pathophysiology of the reproductive cycle, implantation and early pregnancy [4,5]. These new methods have already found their place in clinical practice.
3D ultrasound is still considered a relatively new method, but over the past 5 years it has proven its value and importance for clinical work, especially in obstetrics and gynecology. This study allows you to obtain and save a three-dimensional image. The saved three-dimensional data can be transformed, which allows you to obtain an image in all mutually perpendicular planes when rotating or translating the section plane. The same technique makes it possible to display a three-dimensional image of a three-dimensional object on the screen [6].
To obtain a three-dimensional image, it is necessary to use special three-dimensional sensors. A specially designed 3D transducer is connected to a 2D ultrasound scanner via an integrated control and data storage system. A scanner-specific 3D transducer moves within a specified volume, covering many individual section planes at precisely defined intervals. This is done automatically using an electric drive located inside the sensor housing. For endovaginal sensors, data is read by rotating the transducer [6-13]. For abdominal sensors, the transducer moves along a predetermined arc [6,7].
Once all 3D image data has been saved, all three orthogonal scanning planes are simultaneously displayed on the monitor screen. The corresponding ultrasound slice planes are marked with lines along the edges of the image. By controlling three manipulators, the researcher can rotate all planes to obtain an optimal image of a three-dimensional object. The three-dimensional image is stored and can be printed after the examination.
The purpose of this review is to summarize the advantages and disadvantages of the new techniques transvaginal color Doppler and three-dimensional ultrasound in the field of gynecology and obstetrics.
Application of Color Doppler and Three-Dimensional Ultrasound in Gynecology
As a non-invasive method, ultrasound is the most convenient method for detecting uterine abnormalities. Two-dimensional ultrasound allows you to obtain transverse and longitudinal sections of the uterus. Endovaginal three-dimensional ultrasonography allows the researcher to obtain an image of the uterus in three planes: transverse, longitudinal and frontal (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1.
Transverse, longitudinal and frontal sections of a normal uterus.
A three-dimensional examination is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis when congenital anomalies of the uterus are suspected, which are accompanied by an increased risk of miscarriage, fetal loss or premature birth [5]. This diagnostic method allows you to see and evaluate the uterine cavity (Fig. 2) and myometrium, i.e. all the necessary information to detect uterine abnormalities.
Rice. 2.
Image of the uterus with the septum in the frontal plane.
It is recommended to examine the uterus during the luteal phase of the cycle due to increased thickness and echogenicity of the endometrium [13]. Color Doppler provides additional information about the structure of the uterine septa. Since colored spots are visible among the echo signals of the endometrium, which is in a state of secretory transformation, it can be assumed that there are vascularized myometrial fibers in the septum (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3.
Duplication of the uterus during transvaginal examination. Note the two unconnected endometrium in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. Color Doppler examination reveals small vessels of the myometrium.
By simultaneously assessing all three planes, the physician can accurately determine the location of the endometrial polyp (Figure 4) and submucosal fibrosis. Transvaginal examination appears to be particularly useful in the differential diagnosis of pathological thickening of the endometrium.
Rice. 4.
The uterus in the frontal plane. The arrow points to the endometrial polyp.
In Fig. Figure 5 shows an example of a focus of increased echogenicity inside the endometrium. Ultrasound examination in B-mode does not provide information about the nature of this formation. However, color mapping reflects the presence of evenly spaced vessels in the periphery, which is characteristic of a benign lesion.
Rice. 5.
Vascularized endometrial polyp on transvaginal color Doppler examination.
Pulsed Doppler examination reveals moderate resistance to blood flow (IR = 0.65), typical of an endometrial polyp (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6.
The same patient. The benign quality of the uterine mass formation is manifested by color and pulsed Doppler examination by the average value of the resistance index (IR = 0.65).
With polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as with ovarian tumors, it is possible to obtain an image in three mutually perpendicular planes. However, in these cases, the use of three-dimensional ultrasound is not as valuable as for uterine anomalies.
Application of Color Doppler and Three-Dimensional Ultrasound in Obstetrics
Three-dimensional imaging of the surface of the fetal body opens up completely new possibilities in assessing the anatomy of the fetus and identifying anomalies in its development. It is possible to selectively image the fetal body or the affected body part by performing simultaneous imaging in three orthogonal planes. The technique allows you to obtain real-time images in the third plane, which conventional ultrasound does not allow. This diagnostic method allows for detailed examination of the fetal area of interest by moving cursors, which appear as lines along the edges of the image, one at a time or simultaneously. The surface of the area being studied can then be imaged on the screen. The ability to obtain a truly three-dimensional image, as well as rotate it, allows the physician to examine fetal anomalies from multiple angles, providing a clear “plastic” view of the anomaly.
This diagnostic method is especially effective for facial deformities, cleft lip or palate, malformations or dystopia of the arms and legs, as well as spina bifida. Significant progress in ultrasound research techniques, in particular, the introduction of transvaginal ultrasonography, has made it possible to conduct detailed studies of early embryonic development. Moreover, the Doppler method provides a lot of information about the physiology and pathology of the blood circulation of both the embryo and the mother. This non-invasive method allows you to study the characteristics of fetal hemodynamics during its adaptation to hypoxemia and (or) a significant decrease in the supply of oxygen to the blood and organs of the fetus. Using this method as a second-level test in cases of pregnancy that occurs with complications, with the help of Doppler data, it is possible to adjust the observation and treatment.
Unlike 3D ultrasound, this method is easy to perform, does not take much time and can be repeated. We hypothesize that the combined and simultaneous use of color Doppler and three-dimensional ultrasound in dynamic monitoring of the embryo will provide valuable information.
Discussion
Two-dimensional ultrasound is highly sensitive for uterine abnormalities. However, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish between individual types of anomalies. For an accurate differential diagnosis of a saddle uterus, completely or partially divided by a septum, a coronal plane examination, which is provided by three-dimensional ultrasonography, may be necessary.
Transvaginal color Doppler provides a direct image of the uterine vasculature, which is displayed simultaneously with the conventional B-mode image. This provides the clinician with reliable differentiation of different types of uterine duplication.
The same technique can be used to study blood flow in the uterus and ovaries in patients suffering from diseases of these organs. The tumor vasculature is formed by vessels that arise from the existing vasculature of the host body in response to stimulation from the malignant tumor. Moreover, in comparison with the normal vascular architecture, the blood vessels of a progressive tumor are characterized by underdevelopment of the muscular layer. The relative thinness or absence of the muscular lining of the vessels of a newly formed tumor causes a decrease in peripheral resistance.
Assessment of blood flow properties is the main feature of color and pulsed Doppler studies, which makes it possible to distinguish between malignant and benign formations. The combination of 3D and Doppler is believed to provide a more accurate characterization of overall blood flow.
The ability to save a volumetric image, load it again, transform it, and analyze the picture again and again are important advantages of this method and at the same time a test of strength for a doctor who uses three-dimensional ultrasonography.
The use of both diagnostic ultrasound methods (color Doppler and three-dimensional) in routine examination makes it possible to test and compare their advantages and disadvantages.
Literature
- Kurjak A. Atlas of transvaginal color Doppler. London, Parthenon Publishing, 1994.
- Kurjak A and Kupesic S (eds). Slide Atlas of transvaginal color Doppler. London, Parthenon Publishing, 1995.
- Kurjak A, Kupesic-Urek S, Schulman H and Zalud I. Transvaginal color Doppler in the assessment of ovarian and uterine blood flow in infertile women. Fertil Steril 1991.5: p. 870.
- Kupesic S. The first three weeks assessed by transvaginal color Doppler. J Perinat Med 1996; 24: pp. 301-17.
- Kurjak A and Kupesic S. Transvaginal color Doppler and pelvic tumor vascularity lessons learned and future challenges. J Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995; 6: pp. 145-59.
- Merz E. Three-dimensional ultrasound in the evaluation of fetal anatomy and fetal malformations. In: Chervenak FA, Kurjak A (eds) The Fetus as a Patient. The Parthenon Publishing Group. New York-London. 1996: pp. 75-87.
- Merz E, Bahlmann B and Weber G. Volume scanning in the evaluation of fetal malformations: a new dimension in prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995; 5: pp. 222-227.
- Steiner H, Staudach A, Spitzer D, Graf AH and Wienerroither H. Bietet die 3D Sonographie neue Perspektiven in der Gynaekologie und Geburtshilfe? Geburtsch U Frauenheilk 1993; 53: pp. 779-782.
- Steiner H, Staudach A, Spitzer D and Schafer H. Three-dimensional ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology: technique, possibilities and limitations. Human Reproduction 1994; 9: pp. 1773-1778.
- Feichtinger W. Transvaginal three-dimensional imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1993; 3: pp. 375-378.
- Merz E, Weber G, Bahimann F and Macchiella D. Transvaginale 3-D-Sonographie in der Gynaekologie. Gynaekologie 1995; 28: pp. 270-275.
- Merz E, Bahimann F, Weber G and Macchiella D. Three-dimensional ultrasonography in prenatal diagnosis. J Perinatal Med 1995; 23: pp. 213-222.
- Jurkovic D, Geipel A, Gruboeck K, Jauniaux E, Natucci M and Campbell S. Three dimensional ultrasound for the assessment of uterine anatomy and detection of congenital anomalies: a comparison with hysterosalpingography and two dimensional sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995; 5: pp. 233-237.
Ultrasound machine HS40
Top seller in high class.
21.5″ high-definition monitor, advanced cardio package (Strain+, Stress Echo), expert capabilities for 3D ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology practice (STIC, Crystal Vue, 5D Follicle), high-density sensors.
Advantages of ultrasound using color circulation
Currently, many experts prefer this research method due to the following advantages:
- The safety of the procedure, since its implementation does not lead to irradiation of patients.
- Speed and convenience of research.
- Possibility of early diagnosis of malignant tumors.
Due to the absolute safety of ultrasound examination using colorectal dosage, it can be performed on pregnant and lactating women, since this diagnostic technique does not pose any threat to the life of the pregnant child.
Thus, today, a research technique with color circulation comes to help in diagnosing diseases, which makes it possible to examine the structure of the circulatory system of organs and assess the state of the existing blood flow. Color Doppler mapping in general, in combination with ultrasound, gives excellent results.
The popularity of ultrasound examination in combination with color Doppler mapping is ensured by a number of factors. The method combines such important qualities as safety and content, as well as convenience and the ability to obtain a large amount of important information in a short time.
CDC is in some cases an indispensable means of diagnosing existing or future health problems. We told you that this is color circulation in ultrasound. The decoding has also been described.
What is color circulation with ultrasound?
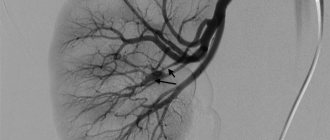
What is CDK BCS? Diagnostics are prescribed for the study of brachiocephalic vessels, which include:
- right subclavian artery;
- right carotid artery;
- right vertebral artery.
All these vessels supply blood to the brain and surrounding tissues. This method, used to study the brachiocephalic vessel, is based on the Doppler effect, which is based on the ability of moving objects to reflect ultrasonic waves. In this case, the moving objects are red blood cells.
When performing color circulation of the vessels of the neck or other vessels on the echogram, the doctor sees a color indication of the direction of blood flow and its strength. Vascularization is being studied, that is, the provision of blood vessels to organs and parts of the body, on which their blood supply will directly depend.
If a simple ultrasound is performed, the image will be in the form of a two-dimensional black and white picture, in this case the doctor can conclude that the anatomy of organs and blood vessels has changed. In the case of using CDK, it is possible to detect not only anatomical changes in blood vessels, but also to determine the speed of blood flow and functional indices of blood flow.
This method is often used when diagnosing pregnant women, as it allows one to assess how the placenta works, ensuring the vital functions of the fetus. With its help, you can determine in which organ located in the pelvis, blood flow disturbances have occurred.
The color flow of the veins of the lower extremities or any other vessels is no different from conducting a conventional ultrasound, so there is no need to be afraid of this diagnostic method. During such diagnostics, ultrasound is sent into the vessels being examined, and based on the responses received, the doctor makes appropriate conclusions about the movement of blood, the speed and pressure of the blood flow.
In addition to the fact that using this method, the vascularization of the organ under study is studied, with CDK it is possible to determine the structure of blood vessels and their patency. For each type of vessel, the corresponding frequency of ultrasonic radiation is set.
A color mapping study is the safest method that allows you to examine the blood flow in the desired organ, and it is completely painless. If necessary, vascularization of blood vessels and other indicators characterizing blood flow can be carried out several times in a row.