The importance of cardiac ultrasound during pregnancy
Before the invention and implementation of echocardiography, heart disease was diagnosed using indirect signs, auscultation of noises, percussion to determine the boundaries and position in the chest. Ultrasound of the heart allowed doctors to look inside, see contractions of the heart muscle, valve apparatus, measure the size of individual parts, wall thickness and many other parameters characterizing the functioning of the organ. It is indispensable for identifying congenital and acquired defects, diseases of the myocardium, pericardium, and monitoring treatment.
During pregnancy, the volume of circulating blood increases. The heart muscle must contract harder to maintain blood flow, which causes moderate hypertrophy. After delivery, the load returns to normal and heart parameters are restored.
If a pregnant woman is predisposed to heart disease, or, for example, she suffered from rheumatism, the heart muscle cannot cope with blood flow, blood stagnation occurs, the chambers enlarge, and heart failure develops. This condition is dangerous for the expectant mother and child. Therefore, for timely detection of disorders and treatment, pregnant women are prescribed cardiac ultrasound.
This study may be needed not only during pregnancy, but also in preparation for it. It is also used to identify pathologies in the fetus. Ultrasound is mandatory for women with heart disease, even if they do not have specific complaints.
Evaluation parameters - norms and deviations
Position
The heart may be completely or partially located outside the chest (ectopia cordis). The position of the heart in the chest can be changed, as occurs with congenital diaphragmatic hernia or pulmonary hypoplasia.
Heart axis
The cardiac axis is the angle between the interventricular septum and the anteroposterior diameter of the thorax. Normally, the cardiac axis is 45 ± 15°. The heart is usually deviated to the left. It is located almost entirely on the left side of the chest. An altered cardiac axis indicates an abnormality. Altered axis is often associated with outflow abnormalities
Transposition of organs (situs inversus)
To judge the position of the fetal organs, it is important to find out which is the left side of the fetus by looking at its presentation and position. After this, you need to make sure that the fetal stomach is on the left. After confirming the normal position of the abdominal cavity, the transducer is tilted towards the head to see if the apex of the heart points to the same side as the stomach.
Normal situs or situs solitus has all left landmarks such as the stomach, spleen, abdominal aorta and apex of the heart on the left. While the liver and inferior vena cava (IVC) are on the right. The mirror image of this arrangement is called situs inversus. The incidence of cardiac abnormalities in the presence of situs inversus is 2%.
Any positional abnormality between these two ends of the spectrum can be referred to as heterotaxy syndrome. These syndromes have a very high incidence of cardiac abnormalities, up to 75–90%.
Structural outlines of the fetal heart
The parameters of compliance of the size and shape of the heart chambers with the norm are assessed. The condition of the valves and great vessels is assessed.
Heart rhythm disturbances
Rhythm disturbances are usually detected by a doctor. The radiologist first needs to rule out a structural abnormality. Then, using M-mode and pulsed Doppler, the heart rhythm can be assessed.
The fetal heart rate varies from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm). A rate below 120 beats per minute is called bradycardia, and a rate above 200 beats per minute is called tachycardia. When the fetal heartbeat is first visualized around 5 weeks gestation, the rate can sometimes be around 90 beats per minute, but the rate soon increases. The most common rhythm disturbance observed in practice is premature atrial contraction, followed by a compensatory pause. Heart blocks of varying degrees may be observed. Supraventricular tachycardia is one area in which fetal therapy has made an impact.
Functional assessment of the fetal heart
Two general points are assessed:
- Heart size: normal cardiothoracic ratio 1:2.
- Heart compression: This is most often a visual impression.
Enlargement of the fetal heart and poor contractility are often observed with fetal hypoxia, i.e., with placental insufficiency. Impaired cardiac function often results in pericardial effusion.
Indications for cardiac ultrasound during pregnancy
When registering at the antenatal clinic, a pregnant woman undergoes a number of tests, including an ECG. If there is a suspicion that she has a pathology from the cardiovascular system, she is prescribed an ultrasound of the heart. Management of such a pregnancy is carried out jointly with a cardiologist. Basically, if any violations are detected, maintenance drug therapy is carried out. In case of serious life-threatening disorders, termination of pregnancy is possible.
In pregnant women who do not have heart disease, ultrasound is performed for the following complaints:
- fast fatiguability;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- unpleasant sensations in the heart area, reminiscent of trembling;
- cyanosis of the lips, nail plates, tip of the nose, ears;
- cold extremities.
Also, an ultrasound of the heart is indicated if during examination they find:
- noise on auscultation;
- enlarged liver, which may indicate blood stagnation;
- arrhythmias;
- decreased weight gain or weight loss.
These symptoms are considered in conjunction with increased blood pressure, a history of chest trauma, heart surgery, myocardial infarction, and thrombosis.
Principles of performing cardiac ultrasound in pregnant women
First of all, you need to pay attention that before going to a specialist for a heart examination during pregnancy, you need to do blood tests, urine tests, and also undergo an echocardiographic examination procedure.
It is worth noting that no preparation is required before the examination. It is enough to be in a good mood, because stress can have a negative impact on the results of the examination during pregnancy.
An ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy does not cause any pain in women, and is not particularly different from any other type of ultrasound examination. When conducting a study, a special conductive layer of gel must be applied to the patient’s chest. It is along this path that the specialist will conduct the sensor. The results of the study are transmitted in real time to the monitor of the ultrasound machine, and the doctor immediately reports them.
If a specialist, when performing an ultrasound scan during pregnancy, is able to identify any deviations from the norm in the development of the heart, the woman must additionally consult with a cardiologist to make a final diagnosis. It is worth remembering that only a disease detected in time can be cured quickly and without consequences.
Interpretation of results: norm and pathology
On a cardiac ultrasound you can see in real time:
- chambers (right and left ventricle, right and left atrium);
- interventricular and interatrial septum;
- heart walls;
- valves (mitral, tricuspid, aortic and pulmonary arteries);
- pericardium and pericardial cavity;
- large vessels, including coronary vessels;
- speed and rhythm of contractions;
- blood flow in the heart and blood vessels (using the Doppler effect), etc.
The thickness of the walls and interventricular septum (IVS), the diameter of large vessels, the dimensions of each chamber at systole (SSR) and diastole (DDC) are measured, and their volume is calculated. Using Doppler sonography, blood flow velocity, blood volume during systole and diastole, and ejection fraction (EF) are determined.
In conclusion, the doctor describes all the data obtained and indicates the presence of changes:
- defect of the septum, valve apparatus;
- vascular blockage, myocardial ischemia, scar tissue;
- inflammatory tissue lesions (myocarditis, pericarditis);
- the presence of fluid in the pericardial cavity;
- valve dysfunction;
- congestion (decompensation of the heart muscle);
- arrhythmia;
- myocardial hypertrophy in hypertension;
- narrowing of the aorta, etc.
The diagnosis is made by a cardiologist based on the results obtained and the clinical picture of the disease.
Indications and purpose
Many expectant mothers are interested in why ultrasound of the fetal heart is prescribed during pregnancy. The main purpose of the procedure is to identify myocardial and vascular diseases at an early stage of intrauterine development. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to provide timely assistance to the child at birth, prepare the necessary medications and equipment.
Is it possible to carry a healthy baby with a heart defect in the mother?
Congenital and acquired heart defects can be a contraindication to pregnancy. But now drug support methods are so effective that after a thorough examination, some women are allowed to give birth. This also applies to those who have had heart surgery. The rehabilitation period is usually 12 months, after which, if your health allows, you can plan conception.
During pregnancy, pregnant women are observed by a cardiologist. They undergo cardiac ultrasound in each trimester of pregnancy, sometimes more often according to indications. Delivery occurs by caesarean section.
Pregnancy can trigger the development of defects, for example, rheumatism. Worsening of the condition is usually observed in the last months of pregnancy. Management of such pregnant women requires careful monitoring of cardiac function using ultrasound.
Absolute contraindications are complex defects: tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation of the aorta, stenosis of the pulmonary artery, etc.
Benefits and harms
Ultrasound diagnostics accompanies the expectant mother throughout the entire period of pregnancy. It is carried out to study the condition of internal organs and to study the development of the fetus. It is quite obvious that women are concerned about the safety of the procedure and the likelihood of negative effects not only on the adult body, but also on the embryo.
Ultrasound is one of the few diagnostic methods that are allowed during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the vibrations produced by the sensor are painless and do not pose a threat to the health of the woman and the fetus. During the procedure, there is no tissue damage or provocation of the development of embryonic defects.
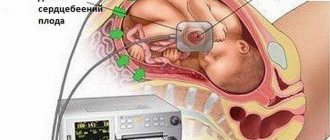
Ultrasound of the fetal heart during pregnancy: what can be detected
An ultrasound of the fetal heart is prescribed to identify developmental defects. Already at 12 weeks, the heart of the embryo is clearly visualized, but not all structures are distinguishable. Therefore, a repeat examination is carried out at 18–27 weeks.
Indications for the procedure are:
- bad heredity;
- previous miscarriage;
- endocrine pathologies in the mother (lupus, diabetes mellitus);
- infections during pregnancy (toxoplasmosis, rubella);
- use of antibiotics, antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants during pregnancy;
- the age of the pregnant woman is over 35 years;
- suspicion of developmental anomalies in previous examinations (heart rhythm disturbances, chromosomal diseases, changes in the nuchal region).
During the first examination, it is possible to identify incompatible with life:
- defects in the structure of chambers (atrium, ventricle);
- hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery trunk;
- aresia of the tricuspid valve.
During the second screening, septal defects, valve lesions, tetralogy of Fallot, patent ductus arteriosus, transposition of the great vessels and other defects are visible.
EchoCG: the essence of the procedure
Echocardiography is an ultrasound test aimed at studying the functioning of the fetal heart. The method is absolutely safe for both the expectant mother and the child. The research is based on the use of ultrasonic waves: the human ear is not capable of perceiving them, but special sensors are able to record their length, amplitude and other indicators.