An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in the blood is not a specific marker indicating a specific disease.
The list of probable pathological conditions in which ESR is higher than normal includes diseases of infectious, tumor, autoimmune or hematological origin.
Despite the non-specificity, analysis of the ratio of erythrocytes and plasma continues to be an important link in the chain of general or biochemical blood testing. Why is it carried out, and what do the results mean?
What is erythrocyte sedimentation rate?
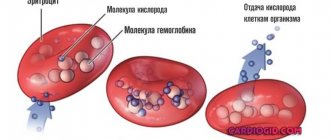
Erythrocytes, or red blood elements, have a higher specific gravity than the organic mass called blood plasma. In the bloodstream, all these components constantly move, so the blood looks like a homogeneous substance. At rest (in a test tube), red cells begin to gradually fall to the bottom of the container.
In the blood of a healthy person, the sedimentation of erythrocytes is a smooth process, but with pathologies and intoxications, the rate of precipitation of red elements noticeably increases.
ESR is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h), as it is determined by the height of the plasma column exfoliated from the red blood cells in a test tube for 1 hour.
Low ESR - reasons
Reasons for low ESR standards:
- sickle cell anemia - develops as a result of a violation of the formation of normal hemoglobin chains in red blood cells
- deficiency of fibrinogen - a blood plasma protein that is a blood clotting factor
- polycythemia, caused by an increase in the number of red blood cells
A doctor will refer you to test the level of red blood cells if you suspect the development of inflammatory diseases (as in the case of checking the leukocyte level in women by age and men). If inflammation has already been detected, it monitors its progress. For preventative purposes, request a referral for erythrocyte sedimentation testing once a year.
What does increased ESR in the blood mean?
Since the study of this interesting pattern, reference - standard - indicators of ESR in the blood have been identified and approved. They were determined as a result of many years of observation of healthy and unhealthy people.
In healthy people, the ESR level is approximately the same and does not exceed 15-20 mm/h.
If the test result shows higher numbers, this means that the ESR value in the blood is increased.
The mechanism for accelerating the shedding of red cells is due to the appearance in the plasma of a large amount of proteins formed during infectious and inflammatory processes. They adhere to red blood cells, which leads to their adhesion and the formation of conglomerates (“columns”) of them. Adhesion is observed in a large number of diseases, but its main feature is that it accelerates the fall of red blood cells under the influence of the Earth’s gravitational field. Simply put, red blood cells stuck together are more quickly attracted by gravity to the bottom of the test tube.
Erythrocyte sedimentation after an hour
Why are high triglycerides dangerous?
As we mentioned above, elevated triglycerides (triglycerides / TRIG) in the blood serum indicate not only the risks of developing atherosclerosis, but also such serious diseases as diabetes, pancreatitis and liver dysfunction (from “obesity” to cirrhosis).
Triglycerides and sugar (diabetes)
High levels of triglycerides may indicate resistance (from the Latin resistentia - “resistance”) to insulin. That is, a very important hormone, the main task of which is to reduce the “excessive” concentration of glucose in the blood plasma. Thus, if a person's body becomes insulin/resistant, then blood sugar levels increase significantly, which quickly leads to the development of a disease such as diabetes mellitus (type II).
According to WHO: insulin/resistant syndrome, as one of the 5 important “points” of the metabolic syndrome (usually in conjunction with another “point” of the five - hypertriglyceridemia / i.e. increased levels of triacylglycerides), affects about 60 million people. However, most of all, doctors are not even concerned about these large numbers, but about the number of people who DO NOT KNOW that they already have serious problems with insulin!
Moreover, recently, the risks of developing this disorder (according to the American Diabetes Association) have increased even among adolescents and young adults. Mainly, “thanks to” a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet (for example, snacking on store-bought sweets and drinking Coca-Cola). That is why, even if you think that your health is simply excellent, still undergo a medical examination at least once every 4-5 years. Including a lipid profile (another name is LIPID PROFILE ) - a biochemical blood test to determine the amount of fats (triglycerides), as well as lipids of all fractions.
Triglycerides and the pancreas
Scientists have found that an increased concentration of triglycerides in the blood (over 5.2 mmol/l / or 500 mg/dl.) significantly increases the risk of developing (AP) acute pancreatitis (i.e. inflammation of the pancreas.). And very high levels (more than 11.2 mmol/l / or 990 mg/dl.) already precede serious complications of AP, fraught with death (from 7 to 15% of cases). Since it is believed that too high levels of concentration of free fatty acids (not “bound” in the blood serum by albumin) have a TOXIC effect on pancreatic tissue. Thus, this situation requires an urgent reduction in high triglyceride levels (with the help of medications)!
Triglycerides and fatty liver
Elevated triglyceride levels are one of the main causes of “fatty” liver. What usually happens: in 70% of cases due to excessive “love” for alcoholic beverages and in 30% “thanks to” addictions to “wrong” food. Naturally, the highest concentration of fats/triglycerides will “accumulate” - not even in the “folds” of the abdomen, but precisely in the liver, a kind of “lipid factory”. As a rule, “fatty liver” does not have pronounced symptoms (provided that “obesity” is reversible), and therefore is fraught with great dangers, one of which is cirrhosis. Hitting unexpectedly and very painfully (even though it was visible from afar)!
Having seen high TG numbers in a blood test, the attending physician will certainly ask the patient about the severity under the right hypochondrium, and will palpate the liver (for enlargement). And finally, he will prescribe (if necessary) liver function tests (LFT). Those. a whole range of biochemical blood tests that detect the amount of bilirubin (total and bound), ALT (alanine/transaminase) and AST (aspartate/transaminase). Where, for example, an increase in ALT values, in relation to AST values, directly indicates to the treating specialist that there is liver damage.
Reasons for high rates in adults
Several dozen diseases can be hidden behind an ESR value raised above normal. The result of the analysis serves as an impetus for additional and deeper diagnostic procedures to find the cause of an increase in values above normal. The provoking factors are almost the same for representatives of different sexes, for adults and children.
Increase in men
In both men and women, ESR is higher than normal when:
- diseases of the urinary system;
- various anemias;
- disorders of fat metabolism;
- connective tissue diseases;
- autoimmune and tumor pathologies;
- long-term use of certain medications.
It should be remembered that after undergoing surgery or infections, the ESR value may be higher than normal for some time (up to 30 days), even in the absence of symptoms.
Among women
To the reasons listed above for an increase in ESR, several specific factors unique to women can be added. Their erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases when:
- pregnancy;
- in the first months after childbirth;
- during menstruation.
The reason for the acceleration of ESR above normal is often medications taken by a woman for a long time - hypocholesterol, antihypertensive drugs or contraceptives.
During pregnancy
Pregnancy is considered a physiological cause of ESR deviation above normal. The value of the indicator can increase to 25 mm/h in the second trimester and up to 35 mm/h in the third. Gynecologists look quite calmly even at indicators of 45 mm/h.
If the doctor has the slightest suspicion of the pathological nature of the increased ESR, the woman will be asked to retake tests or undergo additional tests. But most often this is not required, since elevated values during pregnancy are usually associated with iron deficiency anemia, and this condition can also be detected with a general blood test.
Increased ESR in a child
In pediatrics, an ESR higher than normal can mean infectious, inflammatory and other pathological conditions:
- scarlet fever;
- whooping cough;
- rubella;
- mumps;
- measles;
- tuberculosis.
Fractures and other bone injuries, allergic reactions, anemia, bleeding, and sore throat are also causes of a high ESR value in a child.
True, elevated test results do not always indicate illness. For example, in infants receiving breast milk, a high ESR can be caused by the mother's dietary habits. The predominance of fatty foods in the diet may increase the rate. Values also increase in response to paracetamol.
False increase in ESR
Exceeding the ESR norm is possible even without the presence of ailments in the body. There are a number of natural reasons:
- taking medications containing hormones;
- allergic reactions;
- excessive consumption of vitamin complexes, especially vitamin A;
- errors in diet;
- individual characteristics of the body. Statistics show that almost 5% of the planet's population has an accelerated red blood cell sedimentation reaction;
- bearing a child. In pregnant women, ESR can increase three times or more, which is not considered a pathology;
- insufficient absorption of iron by the body, its deficiency;
- age from 4 to 12 years. During this period, especially in boys, an increase in ESR is possible, associated with the development and formation of the body. There are no infections or inflammations.
An increase in ESR above normal in some cases accompanies certain chronic conditions. These include:
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- recent hepatitis vaccination;
High levels of obesity also cause red blood cells to sediment faster than they should.
Methods for determining and deciphering ESR in blood
In modern diagnostics, 2 methods of determining ESR are used: according to Westergren and according to Panchenkov. If a pathological condition is suspected, it is completely unimportant according to which of the methods the indicator is increased - according to Westergren or according to Panchenkov, if the results are interpreted according to the scale of a particular method.
According to Westergren
Westergren analysis is used in Western countries as a method that is more sensitive and accurate. Blood is taken from a vein or finger, placed in a test tube named after the researcher Westergren, and left for 1 hour. After 60 minutes, the column of exfoliated plasma is measured and the result is recorded in mm/h.
Determination of ESR according to Westergren
Panchenkov method
The method developed by scientist Panchenkov is less accurate at rates exceeding 20 mm/h. The higher the settling rate, the less accurate this method is compared to the Westergren capillary.
Capillary blood (from a finger) is taken for analysis. To prevent the blood from clotting during the study, it is mixed with an anticoagulant (sodium citrate or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) in both cases.
Determination of ESR using the Panchenkov method
Preparing for analysis
To obtain true test results, the patient must specially prepare for the test. Blood is usually donated early in the morning on an empty stomach, when ALT levels in the blood are most stable and true. A week before the test, you need to give up alcohol and consult a doctor about the medications you are taking. You cannot eat eight hours before donating blood. Blood for research is taken from a vein into vacuum tubes. Serum is tested to determine ALT levels.
How to reduce high rates?
As follows from what was written above, ESR above normal is not an independent disease, but only an indirect sign indicating the likelihood of an inflammatory process or infection. Therefore, the only way to lower high values is by curing the underlying disease. Depending on the etiology, this may require drug therapy with antibiotics, antivirals, or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Even after the symptoms of the disease disappear, the ESR is in no hurry to return to normal levels, continuing to be high for several more weeks.
You can help the body cope with the disease faster with the help of immunostimulating agents, if approved by the attending physician. Healthy habits, proper nutrition, and sufficient physical activity will help strengthen your immune system.
Folk remedies that tell you how to reduce ESR should not be taken seriously. But you can heed the advice to drink fruit and vegetable juices, herbal teas and fortified decoctions, as these actions will help get rid of anemia, a common cause of increased ESR.
Norms depending on gender and age
To have an idea of the normal ranges of the indicator, consider the ESR norms for different groups of subjects. The standards for women, men and children have certain differences.
Among women
For representatives of the female population, a wider range of values has been established since youth than for persons of the opposite sex. In girls under 15 years of age, the ESR rate ranges from 2 to 15 mm/h; from 15 to 50 years of age, it is allowed to increase to 20 mm/h, and after 50 – up to 30 mm/h. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate can increase to 45 mm in women expecting a child.
In men
For the strong half of humanity, the following ESR boundaries have been established:
- up to 20 years – 1-10;
- up to 60 years – 2-15;
- over 60 – up to 20 mm.
This difference in norms is explained by the greater number of red blood cells in the blood of men than in women.
In children
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate in children should not exceed 10 mm for boys and 15 mm for girls 10-15 years old. Deviations are considered not only values above normal, but also values of ESR that are too low (less than 1 mm), so pediatricians are looking for reasons why the value increases and why the value decreases.