Cells of the human immune system are not only the first to help the body in the fight against pathogens and toxic substances, but also play an irreplaceable role in the diagnosis of various diseases.
Therefore, the presence of plasma cells in a blood test is considered an indisputable sign of a recent infection or a currently developing inflammatory process. Such information is quite easy to obtain and does not require any complex diagnostic techniques.
The presence or absence of plasma cells can be determined during a general blood test, thanks to which an experienced specialist can easily find out the reason that provoked the appearance of these formed blood components, which are atypical for a healthy person.
What are plasma cells
Plasmocytes (or plasma cells) are a type of white blood cell that produces specific antibodies in the human body.
Each plasma cell is an activated B lymphocyte that synthesizes antibodies for one specific antigen. This is part of human immunity. When the human brain receives a signal that an antigen has entered the body, it sends a command to B lymphocytes, which settle in the lymph nodes and are converted into plasma cells. These cells produce immunoglobulins - antibodies that protect the human body from foreign substances, bacteria and viruses.
At the same time, memory T cells begin to form, storing information about the antigen. They allow the immune response to be carried out much faster in the future than with a standard reaction, because no time is wasted on identification. This is how immunity to the virus is formed. The lifespan of plasma cells is 4-5 days, while T cells have been present in the body for decades.
Prevention of the condition
There are no specific interventions in medicine
, which could prevent the appearance of plasma cells in the blood. However, as mentioned above, high rates are directly related to the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, so the following recommendations can be used to prevent it:
- Complete medical examination and immunization in a timely manner.
- Improve your diet by giving up unhealthy foods and fast food in favor of healthy foods.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day, which will help improve metabolic processes.
- Spend more time outdoors.
- Support the body during cold periods with vitamin complexes.
Thus, if plasma cells are detected in a general blood test, then it is necessary to find out the cause
.
For no reason, these immune cells cannot appear in the blood. Their presence indicates the presence of some antigen against which they are fighting. Also, the cause may be cancer and autoimmune diseases, the existence of which even the person himself does not know for a long time. Therefore, if these cells are present in the blood, you should not refuse additional research.
The presence of plasma cells in a child’s general blood test may cause concern for parents
It is important to remember that the opinion about the foreign origin of these cells is erroneous. Let's consider what they are, what they are intended for, how many of them are considered normal, and what measures need to be taken if their number according to the test results is exceeded.
Increased plasma cells in children
In young patients, the reasons for the increase in the content of the described blood elements are not much different from adults. Although in children the main factor is still childhood infectious diseases, such as measles, rubella, chickenpox and others, since they most often develop at this age.
Separately, it is worth mentioning plasmacytoma, which, although most typical for adults after 40 years of age, can sometimes affect children's bodies. The essence of the pathology is the malignant degeneration of plasma cells into mutated elements (myeloma). With this disease, plasma cells in the child’s blood increase to high levels, which can immediately lead the doctor to think about the presence of a severe pathological process.
This disease is accompanied by intense pain in the bones, bleeding, fractures and often increased thrombus formation. Therefore, if a child experiences similar symptoms, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible to establish a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Plasmocytes in the blood plasma cells
- Functions of plasma cells
- Normal plasma cells
- If plasma cells are enlarged
Plasmocytes (plasma cells) are a class of leukocytes that are formed from B-lymphocytes, the main function of which is the production of specific antibodies (immunoglobulins). Plasmocytes in the blood (plasma cells) are activated B lymphocytes that are capable of synthesizing antibodies specific to one specific antigen.
Functions of plasma cells
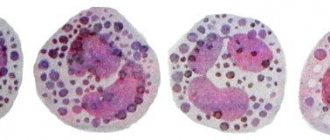
Plasmocytes are one of the types of reticular (connective) tissue cells that are characterized by basophilia of the cytoplasm. In mature plasma cells, the distribution of chromatin in the nucleus is peculiar, which gives the nucleus the appearance of a wheel.
In addition, along the periphery of the nucleus there is a light “halo” that looks like a ring or sickle. Plasmocytes range in size from 6 to 16 microns, their shape is mostly round, sometimes oval; the location of the core is usually eccentric.
Basophilia of the cytoplasm is determined by a high concentration of RNA, which is manifested when stained with pyronin and studied under a fluorescent microscope.
These cells are connected by a number of transitional forms (plasmoblasts, immature plasmacytes) by reticular cells, which are their ancestors.
The cytoplasm of reticular cells acquires, as RNA accumulates, the basophilia characteristic of plasma cells.
Plasmocytes are part of the immune system. The main function of plasma cells is the production of specific antibodies.
After the B-lymphocyte receives a signal about a specific antigen, it, settling in the lymph nodes, begins to transform into a plasma cell (plasma cell).
At the same time, the formation of memory cells begins, capable of responding to the appearance of the antigen months and years after the first invasion.
If the same antigen invades the body again, the memory cells immediately go into action and immediately begin the synthesis of antibodies in huge quantities, without wasting precious time on recognizing the antigen.
Normal plasma cells
Plasmocytes are predominantly localized in the lymph nodes, red bone marrow and spleen. Normally, there are no plasma cells in the peripheral blood in adults, but in children the content of single plasma cells is acceptable.
Plasmocytes are a cellular element that is normally found in the tonsils, in the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, nose, and gastrointestinal tract, where their presence appears to be a response of the immune system to the effects of bacterial antigens that normally inhabit these organs. Plasmocytes are also found in the omentum, in addition to excretory functioning glands (salivary, mammary), adventitia of large vessels; their single presence is found in the spleen and lymph nodes.
If plasma cells are enlarged
If the number of plasma cells is increased in the peripheral blood, which can be reflected in the leukocyte formula and detected in a clinical blood test, this may indicate some pathological processes in the body:
- pathological processes and diseases in which antigen is present in the blood for a long time: tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases, serum sickness, septic conditions and others;
- viral diseases: measles, infectious mononucleosis, chickenpox (chickenpox), rubella;
- plasmacytoma;
- oncological diseases;
- exposure to ionizing radiation.
Normal blood sugar after eating Normal blood sugar after eating. Methodology and preparation for analysis. Diagnostic value of blood glucose analysis after meals.
Segmented neutrophilsWhat are segmented neutrophils? How to properly prepare for the analysis. Normal, increased and decreased. Indications for analysis for segmented neutrophils.
What does the ESR indicator in a general blood test indicate? The ESR indicator in a general blood test. Normal ESR in the blood, low and high levels. Indications for analysis and preparation.
Literature
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what a “plasma cell” is in other dictionaries:
plasma cell
— Antibody-forming Topics of biotechnology EN plasma cell ... Technical Translator's Directory
Plasma cell plasma cell. A highly specialized cell that secretes immunoglobulins; characterized by pronounced basophilia of the cytoplasm, formed at the final stage of differentiation of B lymphocytes... ... Molecular biology and genetics. Dictionary.
— (cellula, cytus), the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms, an elementary living system. Can exist as a department. organism (bacteria, protozoa, certain algae and fungi) or in the tissues of multicellular animals, ... ... Biological encyclopedic dictionary
CELL, in biology, the main component of which all plant and animal tissues are composed. A cell is the smallest living particle that can exist independently and has its own self-regulating chemical system.... ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
— The cell is an elementary unit of structure and vital activity of all living organisms (except for viruses, which are often spoken of as non-cellular forms of life), possessing its own metabolism, capable of independent existence,... ... Wikipedia
cell (of an organism)
— ▲ cell organism cell is the elementary unit of all living organisms; has all the properties of a living system; can exist as a separate organism (bacteria, protozoa, algae) or as part of the tissues of multicellular organisms (fungi ... Ideographic Dictionary of the Russian Language
This term has other meanings, see Membrane A picture of a cell membrane. The small blue and white balls correspond to the hydrophilic “heads” of the lipids, and the lines attached to them correspond to the hydrophobic “tails”. The figure shows... ... Wikipedia
The presence of plasma cells in the blood indicates that an inflammation process is occurring in the human body as a result of infection or the disease was suffered recently. A highly qualified doctor is able to quickly and accurately diagnose the cause of the production of plasma cells, and accordingly prescribe the correct treatment.
Plasma cells are produced from B lymphocytes. Plasmocytes are located in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes. Their appearance occurs as a result of the body's reaction to external stimuli.
Antibody production occurs in the following stages:
when an inflammation process occurs in the body, the brain sends a signal to B lymphocytes to fight the infection;
then B-lymphocytes enter the lymph nodes, moving into the plasma cell required to get rid of the problem;
then the production of the antigen necessary to fight the infection begins.
The lifespan of plasma cells is approximately 4-5 days, but there are cells that can remain in the waiting stage and live for a longer period. In exceptional cases, the residence time of plasma cells in the bone marrow can reach half a century. Thanks to this, immunity to infections is developed. In the absence of pathologies in adults, plasma cells will not be detected in a general analysis. They may rarely be present in a child.
If plasma cells are found in the blood, this means that an inflammatory process is currently occurring in the body of an adult or child, caused by an infection, or the disease was recently suffered. Such diseases include: cancer, colds, mononucleosis, dysbacteriosis, autoimmune disorders and other pathologies in which the body produces plasma cells. If the analysis reveals 1 or 2 plasma cells, then there is no reason to worry. If the number is larger, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination of the body and select the appropriate treatment.
Biology and medicine
Plasma cells are microscopic factories, each of which produces huge quantities of antibodies ready to fight a strictly defined antigen.
Plasmocytes, derived from B lymphocytes, are protein-synthesizing cells rich in ER elements, located near small blood vessels in the organs of the immune system, in the mucous membrane of the digestive and respiratory systems.
They produce antibodies (immunoglobulins), which determines their most important role in protecting the body.
Upon encountering and recognizing an antigen, B cells undergo characteristic ultrastructural changes, becoming lymphoblasts.
It goes like this. After stimulation by antigen, differentiating lymphoblasts appear in the germinal centers. The plasma cells formed from them are located in the medullary cords of lymphoid cells passing between the medullary sinuses.
The maturation of antibody-forming cells in areas remote from where antigenic stimulation occurred is also observed in the spleen (here plasma cells are detected mainly in the marginal zone).
Subsequently, many B lymphoblasts mature into antibody-producing cells (AFCs), which proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells in vivo. These form and release large quantities of receptor molecules in soluble form - antibodies.
Normally, plasma cells are found only in secondary lymphoid organs and tissues, and, in addition, they are quite numerous in the red bone marrow.
Antibodies produced by one plasma cell have the same antigen specificity and belong to the same immunoglobulin isotype.
Plasma cells: pathology
EPIGENETIC REGULATION OF PLASMA CELL DIFFERENTIATION
Carrying out analysis and deciphering it
In a person without health problems, the number of plasma cells does not exceed two cells per thousand others. Therefore, when up to 200 cells are taken for analysis, they are often not diagnosed at all. For an infant, the normal level of plasma cells in the blood is 2%. Only an increase in the number of plasma cells is diagnosed, since a decrease in their number in the blood is not detected and does not cause health problems.
The most common type of diagnosis of plasma cells is a general blood test, during which various blood pathologies, causes of dizziness, increased body temperature, lethargy and increased fatigue are identified. Material for analysis is collected from a finger or vein. Preference is usually given to the first method, it is the simplest, especially when collecting blood from a child, and less expensive financially. No special preparation is required to take the test. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach.
You need to make sure that the patient has no symptoms of measles, meningitis, rubella, encephalitis, or leukemia. Timely therapy will allow you to get rid of many concomitant diseases. Often the number of plasma cells increases with infectious mononucleosis, which without proper treatment can lead to serious complications.
A blood test for plasma cells will help determine the progression of many infectious diseases, including cancer, which will allow timely treatment to begin and shorten the recovery period. With the right approach to examination, a qualified doctor will be able to easily determine the cause of the inflammatory process. A general blood test is an accessible and simple way to diagnose the level of plasma cells in the blood.
So, more details. Plasma cells are a class of white blood cells that produce antibodies. They are formed from B lymphocytes.
Some people mistakenly believe that these cells are harmful formations that signal the presence of pathology. Plasmocytes are the body’s reaction to the action of external factors. They are constantly present in it: in the lymph nodes, in the spleen, and also in the red bone marrow.
A good specialist, having detected plasma cells in a general analysis, will conclude that the patient has recently suffered from one of the infectious diseases. And also that this virus is still in the body.
Plasmocytes arise due to infection and inflammation. B lymphocytes enter the lymph nodes, where they are transformed into plasma cells, which produce antigen to fight infection.
Research to identify the indicator
The attending physician may order a general blood test when the patient has had fever, pain and aches in the joints, and swollen lymph nodes for a long time. Biological fluid is collected from a finger, or less commonly from a vein. No specific preparation is required. It is enough not to eat food 6-8 hours before the test. Typically, lab results will be available the next day.
Attention! Timely diagnosis will help to quickly identify the disease and begin treatment. As a result, recovery will occur faster.
Based on the results obtained, the attending physician develops treatment tactics, taking into account the patient’s age and the characteristics of his body. To search for a specific pathogenic microorganism, the following methods are prescribed with a high degree of reliability:
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) – a method for diagnosing infectious and endocrine pathologies based on the antigen-antibody reaction;
- polymer chain reaction (PCR) is a modern, accurate, informative method that allows you to detect the causative agent of infection in the body.
But most often, a simple finger test is enough for diagnosis.
What does the detection of plasma cells in the blood indicate?
If plasma cells are detected in a general blood test, additional examination may be necessary. To identify the specific causative agent of a particular pathology, there are diagnostic methods with the maximum degree of reliability, such as PCR, ELISA and others.
To perform such an examination, venous blood is taken to calculate, in addition to plasma cells, additional formed elements of the blood flow, which make it possible to establish a specific antigen.
The presence of plasma cells in a blood test indicates the following diseases:
- Influenza, acute respiratory diseases (ARI), acute viral respiratory infections (ARVI).
- Bacterial infections with staphylococcus, streptococcus and other pathogens.
- Septic lesions.
- Various types of infections.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Oncological diseases.
- Consequences of radiation.
- Plasmacytoma, mononucleosis, chicken pox, measles and others.
A clinical blood test for plasma cells is taken at the first symptoms of illness. Such signs include increased body temperature, dizziness or headache, aching joints and other eloquent indicators of the penetration of a bacterial or viral infection into the body. If at least one of the listed symptoms appears, it is necessary to establish the cause of the painful condition as soon as possible, especially when it comes to a child. Moreover, a blood test for plasma cells is a simple and accessible method of laboratory diagnosis.
If a blood test shows plasma cells, it means that you recently encountered a virus, bacteria, or there is an inflammatory process in the body. This information can be tracked even in a general blood test, and a competent therapist can easily determine the reason that could provoke the appearance of plasma cells in the body.
Why do plasma cells appear in the blood?
Do not think that plasma cells are foreign bacteria that have infected the body. Plasma cells are our body’s reaction to an external pathogen, but they are produced from B lymphocytes, which means they are constantly in the lymph nodes, red bone marrow and spleen. The main function of these organs is the production of antibodies, that is, immunoglobulins. The process looks something like this:
- When a pathological process develops in the body, the brain sends signals to places where B lymphocytes accumulate.
- After receiving a signal indicating a specific antigen, the B lymphocyte settles in the lymph nodes and begins to transform into a plasma cell, which is necessary to eliminate this type of problem.
- At the end of the transformation process, the plasma cell begins to synthesize antibodies to the specified antigen.
- Most plasma cells live for about 3-4 days before they die, but some enter a waiting phase. These plasma cells are concentrated in the human bone marrow. These memory cells are activated as soon as antigens of the same type enter the body again. The lifespan of such plasma cells can be 40-50 years. They provide resistance to some infectious diseases.
What do plasma cells indicate in a blood test?
Normally, a general blood test should not contain plasma cells; in children, single indicators of these cells are acceptable. If plasma cells are detected in adults, it means that one of the following diseases has been suffered or is currently relevant:
- rubella;
- measles;
- chickenpox;
- mononucleosis;
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections, influenza;
- serum sickness;
- septic conditions;
- infectious diseases of various origins;
- infection with bacteria of streptococcus, staphylococcus, candida and others;
- autoimmune diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases;
- plasmacytoma;
- exposure to ionizing radiation.
If plasma cells are elevated, additional tests should be taken and symptoms studied to establish a diagnosis. However, you shouldn’t worry too much - after suffering from a cold, for example, plasma cell counts persist for several days.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of use
- Copyright holders
- Adenoma
- Uncategorized
- Gynecology
- Thrush
- About blood
- Psoriasis
- Cellulite
- Ovaries
How is the analysis for plasma cells carried out and their norm?
A plasma blood test does not require careful preparation; it is enough to follow generally accepted rules. That is, you need to come to the laboratory in the morning and not eat before taking material for research. The blood substance is collected from a finger, by piercing it with a scarifier and taking a few drops using a flask. Then a microscopic examination of the blood substance is performed. And after 1 day you can get the result of an analysis of plasma cells in the bloodstream.
If plasma cells are detected in the bloodstream, this is clearly a sign of a pathological process. The disease is either in an active stage at the moment in the body. Or plasma cells in a blood test indicate residual effects after an illness. Because plasma cells are not detected in a healthy person.
Plasma cells of the bloodstream in a blood test are normally found in the amount of one or two per thousand other shaped particles of the blood mass. The difference is observed only in newborns - in infants, the normal number of plasmacytes in the blood varies within 1-2% of the total number of other blood cells.
Disease prevention
There is no effective prevention for plasmacytosis, but early detection will help you receive treatment on time and increases the chances of recovery.
Plasmacytoma and myeloma are related cancers. In these diseases, plasma cells in the bone marrow—plasmocytes—grow. Plasmacytoma most often appears as an isolated bone tumor, but sometimes it can be multiple. Such lesions are characterized by bone destruction, but the bone marrow remains intact. Over time, plasmacytoma spreads to many places in the bone marrow and then develops into multiple myeloma. This disease is more common than plasmacytoma. It affects the bone marrow cells of the vertebrae of the spine, ribs, sternum and skull bones. Pale pink or gray nodules of tumor tissue appear, dissolving the surrounding bone tissue.
Symptoms of the disease are detected only when pain appears. In rare cases, the tumor spreads to the spleen or lymph nodes. When a tumor appears, the number of plasma cells increases, which are an important part of the body’s immune system, because they produce immunoglobulins that recognize and destroy “strangers” that have entered the body - bacteria, viruses, etc. “Unhealthy” plasma cells also produce immunoglobulins, but at the same time they also produce paraproteins - proteins similar to immunoglobulins, but formed only from their “fragments”.
How is the disease diagnosed and classified?
Multiple myeloma has characteristic symptoms that allow a preliminary diagnosis to be made and additional tests to be prescribed.
The course of this disease is characterized by:
- kidney dysfunction,
- high calcium levels in the blood,
- anemia,
- increased fatigue, drowsiness,
- Frequent infections that become chronic,
- emaciation,
- weakness and numbness of the limbs,
- characteristic destruction of bone tissue,
- cold allergy,
- high blood viscosity syndrome,
- neurological symptoms.
There are three types of progression of this disease.
1) Symptomatic. The amount of monoclonal protein in the blood serum increases, the number of plasmatic (clonal) cells in the bone marrow increases to 10% or higher, hypercalcemia and anemia develop, the kidneys suffer, and lytic bone lesions appear.
2) Smoldering or asymptomatic. In the presence of characteristic changes in the blood (high paraprotein in the serum and an increase in the number of plasma cells in the blood), there are no lesions of other tissues and organs.
3) Unspecified monoclonal gammopathy. It is characterized by a normal level of paraprotein and an increase in the number of plasma cells without damage to other tissues and organs.
According to another classification, the disease comes in five main forms - A, G, D, E and Bence-Jones; M myeloma and non-secreting multiple myeloma are also very rare.
According to the clinical and anatomical classification, there are 4 forms of the disease:
- Diffuse-focal form,
- diffuse,
- multifocal,
- Other rare forms.
After collecting an anamnesis, the patient is prescribed blood and urine tests, x-ray diagnostics of bones, and bone marrow analysis for the presence of tumor cells.
An ultrasound scan reveals an enlarged spleen and characteristic changes in the liver parenchyma (the so-called nutmeg liver).
Immunological studies are required using antisera to immunoglobulins and their parts, urine testing according to Zimnitsky, electrophoresis of urine and blood for proteins.