Author: Oleg Maltsev
Not many people are interested in whether it is possible to have surgery for a cold, thinking that a slight illness will soon pass and it is not worth undergoing surgery because of this. However, the disease is a serious contraindication to most medical procedures.
General idea of enemas
Enema translated from Greek means “washing.” The procedure involves the introduction of liquid through the anus for the purpose of cleansing. But enemas can be used to diagnose or treat certain diseases. Siphon enemas are sometimes used. To carry out these procedures you need an Esmarch mug.
The device is a container resembling a heating pad, 1 - 3 liters in volume with a rubber tube. The container can be made of rubber, silicone, plastic or metal. Regular pharmacies sell Esmarch rubber mugs. Plastic and metal appliances are durable, but more expensive. If you do not plan to use the device often, it is enough to buy a rubber one.
The mug comes with a long hose. This important part is needed in order to attach the container to a high stand while the patient is in a horizontal position. A nozzle is attached to the hose. There may be several different lengths and shapes in the package. Some are intended for vaginal use, others for anal use.
Another part of the device is a small faucet. It is needed to control the flow of fluid. Thanks to this, you can increase the pressure of water or medicine. It is necessary to regulate the flow of liquid after the tip has already been inserted into the anus.
What tests are required before laparoscopy?
There are diagnostic tests that require a series of tests. These include laparoscopy, which is not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic procedure. What tests will your doctor require before laparoscopy?
Why is laparoscopy needed?
Laparoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used in many branches of medicine. This method is used by gynecologists and surgeons.
Laparoscopy allows you to establish acute pathology in the abdominal cavity and diagnose acute and chronic gynecological diseases. This manipulation is an invasive technique, since the abdominal wall is punctured.
Diagnostic laparoscopy can identify the following pathologies:
- complications of peptic ulcer – perforation and perforation;
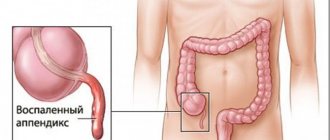
- inflammation of the appendix;
- intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis;
- abdominal hernia;
- ovarian cysts;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian apoplexy.
Therapeutic laparoscopy eliminates the above diseases.
For better visualization, the abdominal cavity is filled with air, after which the doctor examines it using a laparoscope. After surgery, the patient is discharged on the third day, which is much earlier than with surgery with extended access.
Laparoscopy is performed in an operating room with the participation of a surgeon, anesthesiologist and nurse
What you need to prepare
Since the technique is invasive, it will require a series of tests. This is necessary in order to assess the risk of the procedure, identify the presence of contraindications and prevent complications.
This applies to planned laparoscopy, for which the patient can be fully prepared. If an emergency procedure is necessary, no preparation is provided.
Contraindications to laparoscopy
This procedure is less traumatic than surgery with laparotomy access. However, there are also several contraindications for it:
- a large number of adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- severe coagulopathy;
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system.
What tests need to be taken for laparoscopy?
- General clinical tests - blood and urine. They allow you to detect the presence of inflammation, anemia and some other conditions that can complicate the procedure.
- Blood chemistry.
More accurately identifies the inflammatory process and indicates a possible pathology of blood clotting. You can also detect a deficiency of protein, iron, and electrolytes. - Blood for viral hepatitis. Standard examination before any operation.
- Wasserman reaction to exclude syphilis.
- In gynecological practice, it is necessary to take a smear to determine the degree of cleanliness of the vagina.
- Blood test for HIV.
- Fluorographic examination of the lungs. To exclude active pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Electrocardiographic study - to assess the state of the cardiovascular system.
- Ultrasound examination - it must be done to identify adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
- Coagulogram – to identify pathologies of blood clotting. This is necessary to assess the risk of bleeding during manipulation.
Electrocardiography is necessary to exclude cardiac pathology
In addition to laboratory and instrumental examination methods, a physician and surgeon's opinion may be required.
This is necessary in cases where a person has a chronic pathology in the abdominal cavity.
All required tests must be taken in advance, since some of them take quite a long time. It is best to start taking them 7-10 days before the intended operation. You will have to wait the longest for test results for HIV and viral hepatitis.
The expiration dates for all results are different. The longest validity period is for fluorographic examination. It is six months.
Blood for hepatitis, HIV, Wasserman reaction is valid for a month. General clinical tests, blood biochemistry, coagulogram can be taken no later than three days before surgery.
Conclusions from instrumental examination methods are valid for two weeks.
You can take all the required tests at the medical institution where the operation will be performed. This is convenient for both the patient and the doctor.
A sufficiently large set of studies before laparoscopy is necessary to increase the safety of the procedure. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to correctly assess the risk of laparoscopy and compare it with the likely benefit.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/endoskopiya/kakie-analizy-trebuetsya-sdat-pered-provedeniem-laparoskopii
What types of enemas are there?
As noted above, enemas may differ in their purpose. Most often they are produced for:
- bowel cleansing;
- diagnostics;
- treatment of intestinal diseases.
A siphon enema is done when a regular one does not give the expected result. Artificial emptying is done not only before surgery. Women before childbirth or cesarean section also need to cleanse the intestines. During the postoperative period, patients should not push excessively. In addition to pain, this can affect the condition of the stitches. Therefore, patients need to take the enema seriously, without shame or inappropriate jokes about it.
A diagnostic enema is used when it is necessary to examine the intestines. A special medicine is injected into the rectum using a Bobrov device. A contrast agent is administered during an X-ray examination of the intestines. Using this procedure, doctors are able to detect various diseases or examine the condition of the intestines as a whole.
Therapeutic enema is used, for example, in the treatment of staphylococci or other infections. The medicinal liquid is injected into the rectal cavity. Half an hour before, they do a cleansing. A siphon enema can be done before intestinal surgery. It allows you to remove decay products and putrefaction from the body. But the main indication for it is getting rid of toxins and poisons.
Siphon cleansing is a specific procedure. It is carried out only in a hospital by doctors or nursing staff. If the procedure is performed by a nurse, the doctor must be present. Rinsing is done until clean water appears. Carrying out a siphon enema before surgery is an event that is unpleasant for the patient not only physically, but also psychologically. Therefore, the doctor needs to be tactful and discuss all aspects with patients in advance.
Thyroid surgery for colds
The thyroid gland is located near the respiratory organs. If the patient is ill before the intervention, then you need to inform the doctor about this and undergo tests to identify the cause of the infection.
For example, a cough is typical when the thyroid gland is damaged and does not perform its function. The presence of neoplasms can cause a sore throat. Therefore, if certain symptoms are caused by a problem with the gland, then surgery can be done.
In cases where the cold did not arise against the background of these problems, the doctor considers each case individually. But most doctors strongly recommend to wait and recover.
Postponement of surgery is possible only when the intervention is not urgent. If the procedure cannot be delayed and the patient’s life depends on it, then the doctor makes a choice in favor of a medical measure.
How to properly cleanse with an enema
The purchased Esmarch mug must be washed before use. Sterilize the parts. The disposable device is sold sterile and must be thrown away after use. Fill the mug with water. Typically, boiled water at room temperature is used for an enema. It is forbidden to use hot or very cold water, as this can damage the intestinal mucosa.
The next step is to hang the mug on a tripod so that the water flows freely down the hose. Attach a previously suitable tip and lubricate it with Vaseline or vegetable oil. You need to run water through a hose to get rid of the air. As soon as the air comes out, turn off the tap. The patient should be placed on a couch and covered with plastic oilcloth. Its free end should be lowered into the basin so that the liquid can drain freely.
Before the procedure, you need to wash your hands thoroughly. The patient lies down on the couch closer to the edge on his left side. Legs must be bent at the knees and pulled towards the stomach. Gently spread the buttocks and insert the tip into the anus. To avoid injury, the tip should be inserted slowly with a rotating motion. After this, the tap can be opened. At first, it is better to keep the water pressure small.
If you feel the urge to defecate, the water supply must be stopped by turning off the tap. To reduce discomfort, you can do circular massage movements of the abdomen. If the tip is clogged with feces and water does not pass through, it is removed. It is necessary to empty Esmarch's mug completely, but a small amount of water should remain at the bottom so that air does not enter the intestines. After this, the tip is removed, and the patient must lie down for 5-10 minutes.
Nasal congestion: respiratory rhythm disturbance
A runny nose is one of the main symptoms of colds. The airways are clogged with mucus, so during anesthesia, problems with the patient's breathing rhythm may begin. There is no point in clearing the sinuses, because the secretion forms again and again.
Another problem associated with the respiratory tract is inflammation. Intubation, which may be necessary in emergency situations, will be difficult. But even if it can be carried out, it is fraught with the development of purulent complications due to an increased bacterial background.
Contraindications to the procedure
Although the cleansing procedure using an enema is considered safe, there are still contraindications to its implementation. Some women get into cleansing to lose weight. But you need to take into account that during cleansing, not only waste and toxins are removed from the body, but also useful substances. It has been observed that women who practice enemas develop arrhythmia due to loss of minerals such as potassium.
Therefore, before you begin cleansing with enemas, you should consult your doctor. Contraindications to an enema are:
- purulent diseases;
- the presence of ulcers in the anus and colon;
- peritonitis;
- appendicitis;
- stomach or intestinal bleeding;
- anal fissures;
- bleeding of hemorrhoids;
- rectal prolapse.
It should be remembered that bowel cleansing is possible during planned operations, but in emergency cases, when doctors are forced to operate without delay, bowel cleansing becomes impossible.
Therefore, in the postoperative period, additional recommendations will be given to avoid congestion and constipation.
An enema before surgery is done in the evening and again in the morning. Cleansing the intestines makes the surgeon's job easier during surgery. Therefore, do not refuse the procedure just because of psychological discomfort.
Cleaning the intestines before surgery without an enema is not always possible or effective. Doctors are trying to move away from barbaric procedures, which are often not carried out under strict sanitary conditions. Medicinal laxatives come to the rescue.
Medical procedures for elevated body temperature
Often a cold is accompanied by an elevated body temperature. To decide whether to perform surgery or not, the doctor must find out the reason. If this occurred against the background of a disease, to eliminate which surgical procedures should be performed, then this is not a contraindication.
A sharp rise in temperature for no apparent reason or due to a cold is a reason for additional diagnostics. It is impossible to perform an operation in such a situation; it can cause a lot of complications, including death.
Why cleanse your stomach before surgery?
Surgery is a complex specialty that requires emergency intervention. To prevent complications, operations on the abdominal organs require cleansing the stomach and intestines of food masses and formed feces.
A proper diet on the eve of the upcoming operation, normalization of the drinking regime, and effectively selected laxatives will help to cause the passage of feces naturally, without stress to the body, and will replace unpleasant enemas.
In medicine, there are mandatory indications for the use of bowel cleansing before surgery:
- Resection of part of the small and large intestine.
- Gastrostomy placement (an operation connecting the stomach to the intestine).
- Reconstructive, repeated surgical interventions.
Tests before the upcoming laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a modern method classified as minimally invasive surgery, which can be used for both diagnostics and therapeutic procedures. The name of the intervention comes from the Greek word “laparon”, which means “belly”, and, therefore, the operation is performed on the abdominal and pelvic organs.
Next, we will talk about what laparoscopy is, its capabilities and contraindications, features of the method, as well as what tests must be taken before laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy is one of the most high-tech areas of surgery
More and more types of operations are becoming available laparoscopically, and therefore they take less time, are less traumatic and less painful than open procedures, and leave minimal incisions on the skin. They help to minimize the time a patient spends in the hospital, and the modern instruments used to perform them ensure high precision of the manipulations performed.
Laparoscopy capabilities
The following types of operations are performed using laparoscopy:
- Many gynecological interventions: for infertility, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, etc.
- Suturing of perforated ulcers of hollow organs (stomach, duodenum).
- Resections of the stomach, duodenum, and intestines.
- Removal of abdominal tumors.
- Splenectomy.
- Dissection of adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
The above are just some types of surgical interventions. Over time and with the advent of new instruments and techniques, the range of pathologies for which laparoscopy can be used is expanding.
Depending on the purpose, laparoscopy can be:
- Diagnostic, during which it is possible to identify any other pathology.
- Medicinal. During this type of operation, anomalies in the structure of organs, neoplasms are eliminated, and other necessary manipulations are performed.
- Test. During which the progress of the operation is monitored, its results are observed.
Laparoscopy ─ diagnostic or therapeutic manipulation of the abdominal organs
During the procedure, the purpose of laparoscopy may change, for example, diagnostic or control laparoscopy may become therapeutic.
Emergency intervention
In some cases, laparoscopy may be required immediately. Indications for emergency laparoscopy are suspicions of:
- The presence of bleeding in the abdominal cavity (for example, with an ectopic pregnancy, uterine perforation).
- Torsion of a neoplasm (for example, ovarian cysts).
- Acute purulent process in the pelvis in women.
- Acute appendicitis.
- Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels.
- Closed abdominal injuries with polytraumas.
Contraindications
The operation is not performed during menstruation. Most often, laparoscopic interventions are performed in the first phase of the cycle or immediately after ovulation (especially if these are operations for infertility).
Also, such operations are not performed during periods of acute inflammatory diseases, with extensive adhesions in the abdominal cavity, severe cardiac or respiratory failure and other decompensated concomitant pathologies.
Indications and contraindications are ultimately determined by the attending physician, based on the possible benefits and expected risks for the patient.
Research
For laparoscopy it is necessary to undergo tests. What tests and studies to prescribe before the intervention is determined by the doctor referring for laparoscopy. The standard list looks like this:
- Wasserman reaction, blood for HIV, hepatitis B and C.
- Blood for blood type and Rh factor.
- Fluorography (valid for 1 year).
- Electrocardiography.
- Feces for helminth eggs.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Women need to take a vaginal smear for flora and consult a gynecologist.
- 2 weeks before surgery, a clinical blood test, a general urine test, and a coagulogram must be taken.
The doctor must be notified of the presence of allergic reactions to certain types of medications.
Methodology
5 days before the day of surgery, it is advisable to adhere to a diet with limited foods that contribute to increased gas formation in the intestines, namely, eat less cabbage, legumes, and black bread.
On the eve of the operation, a cleansing enema is performed, and if necessary, also in the morning.
12 hours before the intended intervention, you should not take food or water.
During laparoscopy, an endovideo camera and special instruments are used
Next about the intervention itself:
- To perform the laparoscopy itself, general anesthesia is required.
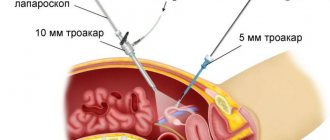
- After the patient has been put under anesthesia, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide, thus achieving the best view of the abdominal organs and providing a large space for manipulation.
- A telescope with a camera and a special illuminator and manipulative instruments are inserted through small holes on the anterior abdominal wall.
- After the surgeon has carried out all the necessary manipulations, the instruments are removed from the abdominal cavity, and the holes for their insertion are sutured.
Recovery period
After the intervention, early activation of patients is important. You can sometimes get up within a few hours after surgery. It’s better to start with short walks, gradually increasing the duration and load, gradually returning to your usual lifestyle.
If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe painkillers that will relieve pain.
Usually, discomfort in the area of instrument insertion goes away within a couple of days after laparoscopy, and after 2-3 days the patient can be sent home if the intervention was performed in a hospital.
The entire recovery period should take place under close medical supervision to avoid the development of complications.
Source: https://diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/analizy-pered-laparoskopiej.html
Review of approved laxatives
How not to get confused and choose an effective, safe laxative before surgery is a question that worries doctors and patients. The pharmaceutical market is teeming with various laxatives, one after another released every day in new packaging.
Candles
- Glycerin suppositories affect intestinal motility. Irritate the nerve endings of the mucous membrane, stimulate peristalsis. Does not soften feces and often leads to trauma to the anus. Doctors prescribe suppositories before surgery once a day. Today, a small microenema called Microlax, containing 5 mg of active substance, is popular; it easily and painlessly copes with the problem. Approved for use before surgery.
- Bisacodyl suppositories belong to the group of fast-acting laxatives. The effect of the drug is observed within an hour. Bisacodyl improves peristalsis, activates the secretion of intestinal mucus, and ensures smooth passage of feces through the intestines without traumatizing the mucous membrane. The drug is prescribed before and after surgical interventions. Taken the night before. The doctor may prescribe an additional 1 suppository in the morning a few hours before surgery. Bisacodyl is suitable for daily use.
Pills
Most medications are available in the form of powders and rectal suppositories to combat constipation. The form helps to locally influence the problem that has arisen. There is not much choice among tablet laxatives, so the price suits you and there are indications for use. Before surgery you can use medications:
- Senna herb produces results within half an hour. It is allowed to use before surgery without fear of consequences. Use 2 or more tablets. The medicine is suitable for one-time use and for the treatment of chronic constipation. An imported drug with the active ingredient of senna - Senade.
- Bisacodyl is available in powder and tablet form. The drug enhances peristalsis and cleanses the intestines of feces. Take 1 - 2 tablets in the evening. Wait for the result in the morning.
Powders
- Realaxan is available in powder form in different fruit flavors. Active ingredient: Macrogol. The patient drinks the prepared drug, due to its properties of retaining water, the stool softens, the intestinal contents increase, and the receptors of the colon are irritated. The natural mechanism for excretion of feces is activated. 1 sachet of medicine diluted in a glass of water works wonders. The medicine is drunk in the morning and evening before the operation. Limit fatty foods a day, go on a mini-diet for a day using light soups, lean meats, salads, and dairy products. Macrogol and analogues are widely used in surgical practice: before studies to identify problems with the gastrointestinal tract, before surgical interventions. The remedy can be used for a long time for chronic constipation, but you need to check with your doctor.
- Transipeg is a powder analogue of Macrogol. Replaces Realaxan if the latter is intolerable. The period of action of the drug is 1-2 days. Transipeg is excreted unchanged from the gastrointestinal tract and is safe for use. Drink the medicine in the morning. Take a sachet and dilute it with water. The drug cleans efficiently, is suitable for long-term use and for one-time use (before laparoscopy).
- Cleaning your colon before surgery can be a budget-friendly option. The famous magnesia has been used in medicine for a long time and is suitable for economical treatment. Antispasmodic, vasodilator, diuretic, choleretic and many characteristics associated with one medicine. Magnesia will replace enema procedures. It effectively cleanses the gastrointestinal tract from stagnant food masses. The drug affects the intestinal processes of osmosis, reduces the absorption of water from the intestines. As a result of the use of the medicine, the stool softens, the content of the colon increases, irritating the enteroreceptors. A person performs a painless act of defecation. Apply 10-30 g of powder, diluted in half a glass of warm water in the morning or at night.
- Duphalac has a similar effect as previous drugs. Normalizes stool, cleanses the intestines, improves the quantitative composition of intestinal microflora. The medication contains lactulose, which is necessary to maintain physiological intestinal microflora. It is considered an effective and safe hyperosmotic laxative. Used in children from birth. The drug is prescribed for surgical interventions on the anal area. Available in powder form for oral use. Adults are prescribed from 15 to 45 ml of medication 1 time per day.
Tests before laparoscopy: list, explanation
1489 to the entry What tests need to be taken before laparoscopy are disabled.
No complex preparation is required for laparoscopy. Before the operation, the doctor must check the patient's condition to ensure that there is no possible risk of complications. The patient needs to undergo tests, for which the doctor gives directions. Without them, the patient will not receive permission for laparoscopy.
List of tests for laparoscopy
Basic tests before laparoscopy, the results of which are needed for admission to surgery:
- Complete blood count (CBC).
- Biochemical analysis.
- General urinalysis (UCA).
- General smear on the flora.
- Coagulogram.
- Test for HIV, hepatitis B and C.
- Wasserman reaction (test for syphilis).
- Oncocytology.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound.
- Blood type, Rh factor (to eliminate errors and be safe during laparoscopy).
Depending on the presence of other diseases or the purpose of laparoscopic surgery, the doctor decides what additional tests and studies need to be performed.
Preoperative preparation may include visits to other specialists to evaluate contraindications. For diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine and gastrointestinal systems, the patient is first sent to see other doctors to confirm or refute contraindications.
Additional research:
- Fluorography.
- Examination of stool for the presence of helminths.
Each general test (blood, urine, smear) is valid for 2 weeks . After the expiration of the period, the patient must be tested again. A smear for oncocytology and stool for helminths are valid for a year. The Wasserman reaction, blood test for HIV and hepatitis are valid for 3 months. The validity period of an ECG is 1 month, fluorography is 11 months.
Particular attention is paid to the number of platelets and the content of prothrombin, fibrinogen, bilirubin, urea, glucose, and total protein in the blood.
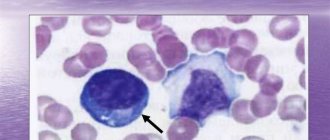
General blood analysis
Clinical analysis (CBC) is a diagnostic method in which blood is taken from the ring finger. The goal is to identify anemia or inflammatory disease.
The main indicators that pay close attention before laparoscopy (including diagnostic):
- leukocytes. A decrease in indicators indicates leukopenia, an increase indicates any inflammatory disease in the body.
- hemoglobin. A decrease in indicators indicates insufficient oxygen supply to the body, an increase indicates heart defects, smoking and dehydration.
- red blood cells. A decrease indicates pregnancy, anemia, blood loss, destruction of red blood cells, and an increase is observed with neoplasms, polycystic disease, and hormonal disorders.
- platelets. A decrease in indicators indicates a diseased liver, bacterial infections, anemia, hemolytic disease, immune and hormonal diseases. An increase is observed after operations, with cancer, benign tumors, and inflammation.
- ESR. A decrease in indicators indicates an increase in albumin (a group of proteins), bile acids, and circulatory failure. An increase is observed with a decrease in albumin, red blood cells, an increase in fibrinogen, as well as in infectious and inflammatory diseases, liver and kidney damage, fractures, postoperative periods, and endocrine disorders. If a woman is found to have an increase in ESR, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination and check the gastrointestinal tract system.
- hematocrit Low levels indicate a deterioration in blood viscosity and anemia. An increase is observed with dehydration, lack of oxygen, and congenital heart defects.
The doctor evaluates all indicators and discrepancies from the norm.
For example, if leukocytes, red blood cells, ESR and platelets are elevated, and other indicators are within normal limits, then we will talk about the presence of an inflammatory process and neoplasms, due to which laparoscopic treatment methods are planned. If red blood cells, platelets, and hematocrit are low, and other indicators are within normal limits, then the patient most likely has anemia.
Interpretation of biochemical blood test. Click to enlarge
Blood chemistry
This diagnostic method before laparoscopy allows us to judge the functioning of all organs. The main goal is to check the condition of the heart, endocrine system, liver and kidneys. It reveals:
- Total protein. A decrease indicates starvation, liver disease and serious bleeding of an acute and chronic nature. Increase – about dehydration, oncology, acute infections.
- Bilirubin. A decrease indicates the use of certain groups of drugs, alcohol and coffee, and coronary heart disease. Increase – about hepatitis, acute infections and viruses, tumors and cirrhosis of the liver, anemia, inflammatory diseases.
- Urea. A decrease indicates fasting or strict vegetarianism, pregnancy, poisoning with toxic substances, and impaired liver function. Increased – kidney disease, cardiovascular failure, severe blood loss, excess protein intake.
- Fibrinogen. A decrease indicates the formation of microthrombi, toxicosis, hypovitaminosis, poisoning, and liver cirrhosis. Increase – about pregnancy, heart attack, diabetes, pneumonia, tuberculosis, oncology and infectious diseases.
- Glucose. A decrease indicates poor nutrition, starvation, excessive stress, bad habits, malignant tumors, excessive consumption of baked goods, fast food and sweets. An increase occurs with diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, cancerous tumors, diseases of the endocrine system, and metal poisoning.
Analysis of biochemistry results provides an almost accurate picture of the patient’s body condition.
General urine analysis
Normal urinalysis results. Click to enlarge
OAM is the simplest and most painless diagnostic method before laparoscopy, with the help of which acute and chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system and other inflammatory diseases are determined. Together with blood tests, the overall picture will allow you to better understand the functionality of the body.
The main values of TAM, which are given attention before performing a laparoscopy operation:
- Amount of urine. A decrease is observed in the initial stages of acute renal failure, polycystic disease, and chronic kidney disease. Increased in diabetes mellitus, acute renal failure, heavy drinking.
- Color. A specific color change, depending on the shades, is caused by urolithiasis, tumor decay, red blood cells in the urine, liver disease and consumption of coloring foods.
- Transparency. Cloudy urine is characteristic of cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Smell. Harshness or a specific odor is observed with hereditary diseases, increased acidity or diabetes.
- Reaction. High acidity indicates previous infectious diseases.
- Protein. An increase in the amount is observed with inflammation and kidney disease.
- Glucose. Presence in urine indicates diabetes mellitus.
- Leukocytes. Indicate an inflammatory process in the body.
A general urine test is necessary to assess the functioning of the genitourinary system and kidneys.
General smear
A flora smear is a method for diagnosing diseases and assessing the state of the microflora of the vagina, urethra and cervical canal. The goal is to identify infections and inflammations. Analysis shows:
- Leukocytes. Enlargement is a sign of inflammation or pregnancy.
- Lactobacilli. A decrease in their number is a symptom of bacterial vaginosis.
- Yeast. A high rate indicates thrush.
- Key cells. Enlargement is a sign of gardnerellosis.
- Leptothrix. Occurs when mixing infections: bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
- Mobiluncus. The appearance in the results is a sign of candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis.
- Trichomonas. The appearance is a symptom of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Gonococci. The appearance is a sign of gonorrhea.
- Escherichia coli. An increase in the number indicates the onset of bacterial vaginosis, neglect of intimate hygiene, and stool getting into the smear.
- Staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci. Enlargement is a sign of infection.
A flora smear assesses the general condition of the reproductive organs.
Decoding the coagulogram. Click to enlarge
Coagulogram
This test before laparoscopy examines the blood clotting system, regulated by the endocrine and nervous systems. The goal is to determine how the operation will go, whether the surgeon will be able to stop the bleeding and save the patient in an unforeseen situation. Particular attention before the operation is paid to the following indicators:
- PT and INR. A decrease in readings may be a sign of thrombosis. Increased – liver diseases, intestinal dysbiosis, amyloidosis, nephrotic syndrome, etc.
- APTT. Shortening the value is a sign of increased coagulability. Lengthening – insufficient coagulation, severe liver disease, etc.
- PTI. A decrease is observed with increased coagulability during pregnancy, thrombosis, cirrhosis, and hepatitis. Increased – deficiency of blood factors, vitamin K, etc.
- Fibrinogen. A reduced amount is a symptom of congenital deficiency, liver disease, bone marrow damage, prostate cancer, etc. An increased amount is observed during infections, injuries, stress, menstruation, heart attacks, pregnancy, lung cancer, and also in the postoperative period.
- RFMK. An increase occurs with sepsis, thrombosis, shock, complicated pregnancy, etc.
Not all doctors are able to decipher this analysis.
Cytological smear analysis
Oncocytology is a method for diagnosing oncology in the reproductive organs. The goal is to detect the presence of cancer cells or other viral diseases.
Abnormalities in the analysis do not always imply the presence of cancer. A positive result may be a consequence of pathologies:
- HPV;
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea;
- fungal diseases.
If infections are found, therapy is prescribed, after which the test is repeated to monitor the dynamics.
Electrocardiogram and ultrasound
An ECG is prescribed to study the heart's function in order to assess the patient's readiness for laparoscopy. Contraindications to laparoscopic surgery are diseases of the heart, respiratory system, liver and kidneys.
No matter how many studies the doctor prescribes, they are carried out as soon as possible. CBC, coagulogram, Wasserman reaction, analysis for Rh factor, blood group, HIV and hepatitis - the material is taken from a vein once, checked for all the necessary indicators, and this already means that half of the tests have been passed.
Source: https://oyaichnikah.ru/diagnostika/analizy-dlya-laparoskopii.html
Rules for cleansing the stomach without an enema
Effectively cleansing the large and small intestines before surgery without an enema has become possible thanks to numerous high-quality laxatives. Relying on one drug is not enough. It is necessary to additionally follow the rules for the cleaning to go well:
- see the instructions, take the drug according to the recommendations;
- Do not increase the dosage yourself! Medicines have side effects caused by overdose. The same applies to the frequency of administration. If the instructions say about a one-time dose of the drug, then it is taken only 1 time per day;
- Before using the medicine, consult your doctor. If the prescribed medicine is not suitable, change it or consult your doctor;
- Pay attention to contraindications to drug treatment. For hemorrhoids, anal fissure, paraproctitis, and gastrointestinal bleeding, most laxatives are not used. Be carefull!
Tests for laparoscopy (list): ovarian cysts, fallopian tubes, gallbladder, etc.
Laparoscopy, although it is a low-traumatic procedure, belongs to the category of full-fledged surgical interventions performed using general anesthesia and entailing a violation of the integrity of tissues and organs.
Therefore, before starting the procedure, the doctor needs to make sure that the patient’s body can tolerate it without serious consequences. For this purpose, tests are prescribed for laparoscopy, which must be taken in advance.
Usually, a list of them can be obtained at a preliminary appointment with the specialist who issued the referral for the operation.
How to properly prepare for laparoscopy
The main goal of research before laparoscopy of ovarian cysts, interventions in the gallbladder and other organs is to identify hidden pathologies that can lead to complications in the postoperative period. In addition, it is important to bring the body into a state in which the doctor can perform surgical procedures with minimal difficulty.
In order for the studies to show a reliable result, and the body to be ready for intervention, preparation for laparoscopic surgery begins with correcting the patient’s diet:
- Foods that cause fermentation in the intestines and flatulence are removed from the menu - all types of cabbage, black bread and fresh milk, vegetables and fruits that contain a lot of fiber, as well as legumes. Such restrictions are especially important if laparoscopy is performed on the abdominal organs.
- At least a week before laparoscopy, avoid alcohol, strong coffee, and energy drinks. These products thin the blood and may cause bleeding during and after the procedure.
- The day before surgery, you are allowed to consume only clear broth, fermented milk drinks and water. Eating should be stopped at least 16 hours before surgery. Stop drinking 6-8 hours before laparoscopy.
- The evening before the operation, the doctor may advise you to do a cleansing enema and, if necessary, repeat the procedure in the morning 2-3 hours before the intervention.
As for taking tests for laparoscopy, they should be taken no earlier than 2 weeks before the scheduled procedure. Many studies also require preparation: following a diet 2-3 days before collecting biological material, taking tests on an empty stomach, etc.
What tests should the patient do?
Shortly before the scheduled date of surgery, the patient is required to undergo a series of tests and undergo a comprehensive examination. You can find out what tests are taken before the intervention at a preliminary appointment with the specialist who refers you for the operation. As a rule, the list of tests before laparoscopy includes the following types of laboratory tests:
- biochemical and general (clinical) blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood clotting test;
- blood for Rh factor and blood group (necessary for emergencies when a donor blood transfusion is required);
- blood for infections (HIV, syphilis, hepatitis);
- genital smear for flora and gonorrhea.
In addition, the list of necessary tests for women includes a cytological smear from the cervix.
It is necessary to take tests before laparoscopy in a timely manner so that before the operation the doctor can analyze the results and decide whether the operation can be performed.
In most cases, their duration is limited to two weeks. This is the time period that most studies actually do.
In addition to laboratory tests, within one week before surgery you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- ECG;
- fluorography.
In addition, the patient must inform the doctor in advance, at least 2 weeks before the intervention, about the medications he is taking. They may need to be discontinued, replaced with analogues, or dosage adjustments.
Test results or what may be grounds for canceling the operation
Since there are numerous contraindications for the operation, the doctor during preparation pays attention to the following signs of changes in the body:
- An increase in leukocytes in the blood and urine, the presence of cylindrical bodies and protein in the urine, which occur in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. In this case, the operation is postponed to a later date, and the necessary treatment is carried out.
- A decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells indicates anemia, which can cause complications after surgery. If such violations are present, the operation is postponed and therapy is carried out.
- The presence of infections in smears and a positive Wasserman reaction are direct contraindications to laparoscopy. Surgery is possible after a full course of treatment and rehabilitation.
- A decrease or increase in blood clotting is a relative contraindication. If the pathology cannot be treated, the possibility of intervention with the introduction of anticoagulants or drugs that prevent bleeding is considered.
- If pathological cells are detected in the test results before laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes (smear for cyto-oncology), it is necessary to undergo a more detailed examination on CT or MRI, as well as other tests (biopsy, repeat cyto-oncology, tumor markers).
If the deviations are minor, as, for example, happens during pregnancy, hormonal imbalance or diseases that are not direct contraindications to laparoscopy, the operation will not be canceled. However, the doctor will take into account existing concomitant diseases and take measures to prevent possible negative consequences.
Source: https://DiagnozPro.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/analizy-dlya-laparoskopii
Options for cleansing enemas at home
A cleansing enema at home before surgery may consist of solutions:
- Plain water to completely cleanse the colon. The norm for an adult is from 1 liter to 1.5. For the procedure, you will need an Esmark mug, located at a height of 50 cm from the patient on a tripod. Before the manipulation, the anus and tip are lubricated with Vaseline to ensure comfortable and painless administration of the liquid. Water at room temperature is filled into the mug and the tip is inserted into the back hole. The air from the enema is released before this. The liquid is poured in slowly. If the patient notices abdominal discomfort, the procedure is stopped until the symptoms disappear. Then the manipulation continues. After injecting the liquid, it is necessary to place the patient on his back and massage his stomach. Turn over on your right side and wait for the result. The procedure is carried out the day before the operation.
- Soda solution is an effective method for cleansing the intestines. An enema requires compliance with proportions. First, put the water on the fire, heat it to 40 degrees. Add a couple of spoons of soda. Carry out the enema manipulation according to the principles described above. Another enema is required to cleanse. For it, the water must be heated to 20 degrees with the addition of a few tablespoons of soda. Use an Esmark mug to perform the manipulation.
Preoperative cleansing of the intestines from feces is carried out using enemas. The procedure is not always sterile. It is recommended to use medications.
Tests before laparoscopy: which ones need to be taken before this study
Laparoscopy is an examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs using the endoscopic method. The high efficiency and low invasiveness of the procedure allows the use of laparoscopy not only for diagnostic, but also for therapeutic purposes.
Laparoscopy refers to minor surgical interventions during which penetration into the internal environment of the body occurs, therefore tests before laparoscopy are necessarily included in the patient’s preoperative preparation plan.
It is important to know
In the abdominal cavity, in addition to diagnostic procedures, the laparoscopic technique is used for therapeutic purposes: drainage of the abdominal cavity, cholecysto-, gastro-, colonostomy, appendectomy and others.
In gynecology, laparoscopy as a surgical approach is widely used in the treatment of many diseases: infertility, uterine fibroids, adnexal adhesions, polycystic ovaries.
With invasive interventions, which include laparoscopy, there is always a risk of developing certain consequences (purulent infection, bleeding). To minimize the likelihood of complications, an examination is carried out with tests to make sure that the patient does not have acute infectious diseases, heart disease, lung disease, or a tendency to bleed.
Necessary tests before laparoscopy
The main tests that are taken for laparoscopy are:
- Clinical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Coagulogram.
- Blood type, Rh factor.
- For syphilis, hepatitis, HIV infection.
- Fluorography or chest x-ray.
- ECG.
A clinical blood test reflects the response of the hematopoietic system to physiological and pathological processes occurring in the body.
Hemoglobin is a pigment found in red blood cells. A decrease in hemoglobin levels is evidence of the development of anemia.
Red blood cells, whose main function is to transport oxygen to tissues. A drop in serum concentration or a sign of anemia, or blood thinning during pregnancy. The number of red blood cells increases during fasting, hyperhidrosis, and when staying in high mountain areas.
Leukocytes.
Since they play a mainly protective role in the body, their increase indicates acute inflammatory infections, leukemia of various etiologies, malignant tumors, massive bleeding, poisoning, states of shock, and burn disease. Leukopenia is caused by inhibition of cell maturation in hematopoietic organs, with hemoblastosis, with viral infections, with collagenosis.
Platelets are involved in the process of thrombostasis. Thrombocytosis accompanies injuries with muscle damage, burns, blood loss, and removal of the spleen. Thrombocytopenia is observed in thrombocytopenic purpura, infectious-toxic conditions, parasitic infections, diseases of the hematopoietic system, leukemia.
The ESR indicator plays an important role in the diagnosis of pathological conditions. It increases in infectious and inflammatory processes, rheumatism, kidney and liver diseases, and cancer. Decreases with blood thickening, neuroses, epilepsy.
A general urine test shows the condition of the kidneys, urinary tract and metabolic processes in the body.
Based on biochemical blood parameters, one can judge the functional activity of many organs and systems: liver, gall bladder, pancreas, kidneys, endocrine organs.
A coagulogram shows blood clotting data. An increase or decrease in indicators requires preoperative preparation to prevent bleeding during surgery.
An analysis to determine the blood type and Rh factor during laparoscopy is necessary because during the operation unforeseen situations may arise that require blood transfusion.
Blood testing for hematogenously transmitted infections (syphilis, HIV infection and others). If they are detected in a patient, special conditions for surgical procedures are required to prevent infection of personnel.
An ECG characterizes the work of the heart.
Fluorography or x-rays of the lungs are done to exclude tuberculosis and other diseases of the respiratory system.
In women, hysteroscopy is used for diagnostic purposes and minor surgical interventions on the uterus.
If emergency surgery is necessary (for example, when an ovarian cyst ruptures), the list of tests for laparoscopy is reduced. They do an ECG, blood and urine tests, determine the blood type, Rh factor and blood clotting indicators.
What is important to know about preparing for the procedure, the specialist explains in this video.
Test results, contraindications for surgery
If the tests show significant deviations from the norm, then laparoscopy is postponed until the condition stabilizes and the parameters normalize.
In the blood test: leukocytosis or leukopenia, accelerated ESR, thrombocytopenia, reduced hemoglobin and a decrease in the number of red blood cells.
In blood biochemistry: decreased total protein, increased levels of aminotransferases, creatinine, glucose, uric acid.
In the urine there are signs of kidney pathology: protein, leukocyturia, hematuria.
The coagulogram shows changes in bleeding and blood coagulation time, prothrombin index and other indicators indicating a violation of the blood coagulation system.
These pathological changes in the analyzes are relative contraindications for laparoscopy. After the patient has been prescribed pathogenetic therapy and the indicators have returned to normal, the procedure is allowed.
Absolute contraindications include:
- acute massive blood loss;
- critical condition of the body with the development of multiple organ failure: cardiac, respiratory, hepatic, renal;
- significant disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity stage 3-4;
- aneurysms of abdominal vessels;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- ascites;
- obesity 3-4 degrees.
Source: https://endoskop.guru/zhivot/laparoskp/pdgtvk/analizy-pered-laparoskopiej.html