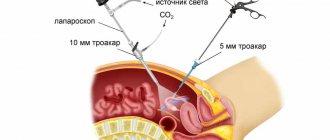
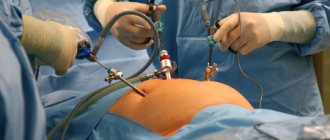
Today, the medical industry has fundamentally new technologies for surgical interventions. One of these achievements of modern science is laparoscopy - a safe, low-traumatic and short-term operation that does not require a long recovery period. Laparoscopic interventions are carried out using probes that are equipped with a camera and special lighting that allows you to examine all the details of the operated area. They are inserted through small (no more than two centimeters) incisions on the skin.
This surgical technique is widely used in gynecology - after such an operation there are no noticeable cosmetic defects left on the skin of the abdomen, moreover, rehabilitation proceeds quickly and without any serious complications. In some cases, after laparoscopy, women note the appearance of discharge - this can be either a natural phenomenon or a sign of a pathological process.
In our article we want to talk about the specifics of laparoscopic surgery, the rules of preparation for the procedure, the characteristics of the rehabilitation period of the female body and explain whether brown discharge after laparoscopy is a pathology.
When is laparoscopy used in gynecological practice?
Practicing gynecologists use this minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical technique much more often than other medical specialists. Indications for laparoscopic and hysteroscopy (a method of examining the cervix and uterine cavity) are:
- endometriosis – growth of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterine walls);
- fibroids are benign neoplasms that form in the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus);
- torsion of a benign ovarian tumor (cyst) or its rupture;
- ovarian apoplexy - a sudden violation of the integrity of its tissues;
- anomalies of the anatomical structure of the genital organs and malformations of their development;
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy - when the attachment of a fertilized egg can occur in the peritoneum, fallopian tube, cervix or ovary;
- initial stages of the malignant process.
Thanks to the capabilities of laparoscopy, the treatment of many pathologies of the female reproductive system has become much more successful.
In some cases, laparoscopic surgical intervention is performed for “acute abdomen” syndrome, which is caused by damage to organs located in the abdominal cavity and pelvis
Advantages of laparoscopy in operative gynecology
The laparoscopic method gives excellent results, expanding the possibilities for treating surgical patients. This especially applies to the presence of significant advantages compared to abdominal operations:
In gynecology, laparoscopic interventions are performed for various pathological conditions and diseases of the female reproductive system. Most often this is:
- diagnostic examination;
- removal of an ovarian cyst;
- elimination of tubal pregnancy;
- removal of adhesions from the fallopian tubes;
- hysterectomy;
- removal of fibroids - myomectomy;
- restoration of blood flow in case of torsion of the appendages or legs of ovarian cysts (up to removal);
- with polycystic disease;
And many other surgical procedures on the female genitals. Sometimes laparoscopic intervention is done immediately after hysteroscopy (Hysteroscopy how it is performed and why it is needed), if during the procedure good reasons for emergency surgery are discovered.
What is the normal environment in the vagina?
The vagina is acidic, with a pH ranging from 3.8 to 4.5. The mucous membrane is inhabited by normal microflora, consisting mainly of lactobacilli. But the composition of this flora may be influenced by physiological factors:
The following have a negative impact on the normal vaginal microflora:
- Menstrual bleeding with poor personal hygiene
- Promiscuous sexual contacts
- Antibacterial therapy, especially when self-medicating
- Abuse of hygiene procedures - frequent use of douches with bactericidal agents
- Neglect of personal hygiene in the intimate area (of the woman herself and her sexual partner)
- Poorly selected contraception
- Overwork
- Stressful situations
- Hypothermia
- Infections
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Abortion
- Diseases of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances
- Uncontrolled high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) due to diabetes
- Metabolic disorders and diseases, including obesity
Lactobacilli play an important role in maintaining a woman's health. This is due to a number of their features:
- They provide protection against pathogenic microflora, forming a biological barrier on the mucous membrane that prevents the attachment of microorganisms, their reproduction there and prevents the development of infectious diseases.
- It is the vital activity of lactobacilli that provides the pH level corresponding to an acidic environment. Pathogenic microorganisms cannot live in this environment, which has a bacteriostatic effect.
- Lactobacilli produce hydrogen peroxide, which destroys anaerobic pathogens.
- Their presence in the vagina stimulates local immunity.
In adult women, there are various glands in the vagina that produce vaginal secretions containing small amounts of fat. This is a “lubricant” that protects the mucous membrane from friction during sexual intercourse and helps remove foreign particles and cells, including dead cells of one’s own body.
Vaginal discharge is normal if it:
- insignificant in quantity,
- transparent,
- have no smell,
- The consistency is like a liquid gel.
The composition of these secretions includes:
- secretion of the vaginal glands,
- dead epithelial cells of the mucous membrane,
- lactobacilli.
When vaginal discharge changes color and consistency, its quantity increases, and an odor appears, this indicates problems with women’s health, regardless of whether surgical manipulation was performed.
Rules for preparing and avoiding complications
Before any planned operation, the patient is pre-examined. After a conversation with a medical specialist and a physical examination by a gynecologist, the woman undergoes:
- general clinical urine and blood tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram - assessment of coagulation system factors;
- determination of blood group and rhesus affiliation;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound;
- serological tests for the presence of antibodies to HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis viruses.
Preparatory measures include following a special dietary regimen and performing manipulations that cleanse the intestines. The operation is performed in the first half of the monthly cycle.
Long-term complications after intervention
If no consequences were found after the operation, this does not mean that they will not occur during the recovery period. The consequences of laparoscopy can be as follows:
- Thrombosis. It occurs only if there are certain predisposing factors: the patient’s age (in older women the risk of such a complication is much higher), atherosclerosis of blood vessels, pathologies of the cardiac system. To avoid such a “side effect,” the person is prescribed blood thinning medications, and during the intervention, the legs are wrapped with an elastic bandage.
- The presence of excessive bleeding that does not go away for a long time. Here you need to consult a doctor to establish and eliminate their cause.
- Nausea and vomiting, the cause of which cannot be determined.
- Fever that lasts more than 24 hours.
- Severe pain in the abdominal area.
- Swelling of the stitches and redness of the skin around them.
- Problems with consciousness.
- Metastases in the area of the trocar openings. This complication can develop during removal of a malignant tumor, when the affected cells enter the damaged skin or subcutaneous layer. To avoid this, doctors should use special plastic containers with an airtight lid.
- Failure of the menstrual cycle. To eliminate the consequences, the woman is prescribed a short course of hormone therapy. She also needs to use multivitamin complexes to restore weakened immunity.
Despite the fact that laparoscopy is considered the safest operation, even the most minimal negative factors can lead to the development of complications. If you have any of the symptoms listed above, you should definitely consult a doctor. The vigilance of the patient herself will help to quickly cope with the problem and allow her to lead a normal lifestyle.
8 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 13484
Laparoscopy is a surgical operation for resection of the affected organ or part thereof, performed through small incisions using trocars and a laparoscope. In addition, the laparoscopic method is used to diagnose diseases as it is extremely accurate.
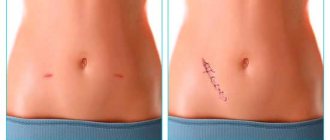
One of the prerogative aspects is the shortened postoperative period of laparoscopy. Rehabilitation is accelerated, since tissues and skin are not injured, as during abdominal surgery. For the same reason, the possibility of infection of incisions and the formation of adhesions is minimized.
Features of the postoperative period
The duration of recovery of the female body depends on the extent of the surgical intervention performed (for example, removal of an ovarian cyst requires rehabilitation of about 5 days). After laparoscopy, patients note a feeling of discomfort in the abdomen. This phenomenon is associated with the technique of manipulation - to increase the space for intervention, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity.
Postoperative sutures do not require special attention - there is no likelihood of them coming apart, healed scars are practically invisible
With low-traumatic laparoscopy, a woman’s body recovers much faster than after exploratory laparotomy, a surgical operation in which the abdominal wall is cut to access the internal organs. Limiting physical activity and following the advice of your doctor speeds up recovery.
Discharge after laparoscopy: normal or pathological?
In gynecological practice, laparoscopy is not the last place.
Thanks to this method of conducting operations, it became possible to minimize the trauma of interventions and speed up the recovery of women.
As a rule, recovery after surgery is quick and proceeds without complications. In some cases, discharge is observed after laparoscopy, which can be both a sign of normality and pathology.
Features of the technique
Laparoscopy in gynecology is more common than in other areas of medicine
Laparoscopy is used in the treatment of various diseases of the female genital organs:
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- In case of torsion of an ovarian cyst or its rupture.
- Apoplexy of the ovary.
- Torsion of fibromatous uterine node.
- Endometriosis.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Infertility.
- Developmental defects and structural anomalies of the genital organs.
- Oncological processes in the initial stages.
Laparoscopy is performed as a diagnostic or therapeutic operation. Thanks to its capabilities, the treatment of many diseases of the reproductive system has become more successful.
Sometimes surgery is performed for diagnosis, especially in the case of a so-called “acute abdomen.” In this situation, the pathology can be caused by lesions of the abdominal organs, injuries, or effusion in the pelvis.
Preparing for surgery
Any surgical intervention is carried out only after a preliminary examination. Of course, in the event of an emergency operation, no examination will be needed, because there will be no time for it, because you will have to wait a long time for the results.
Before planned laparoscopy, a complete examination with all tests is required.
What tests and studies need to be completed:
- Examination and conversation with a gynecologist.
- General blood and urine tests.
- Blood chemistry.
- Coagulogram: assessment of blood clotting.
- Finding out blood type and Rh factor.
- HIV, syphilis and hepatitis.
- Fluorography.
- ECG.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
It must be remembered that the operation should be carried out in the first half of the cycle after the end of menstruation. Preparation also includes a special diet and a cleansing enema. Before performing a laparoscopic intervention, the anesthesiologist and the attending physician must conduct an explanatory conversation with the patient.
Postoperative period
The duration of this stage of rehabilitation depends on the extent of surgical intervention. For example, after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the postoperative period lasts up to 5 days.
After surgery, you may feel discomfort. It is directly related to the technique of intervention.
The fact is that during the operation, air is pumped into the abdominal cavity in order to increase the space for manipulation.
Due to the low invasiveness of the surgical intervention, women recover faster and feel much better than after laparotomy.
Scars after surgery are almost invisible
The seams will not require special attention. They are invisible and do not require special care. Also, there is no chance of seams coming apart. If endometriosis is treated after surgery, additional hormone therapy will be required.
After surgery, recovery is fast. Following certain rules, such as limiting physical activity and carefully following the gynecologist's recommendations, will help speed up the recovery process.
Features of recovery after certain types of laparoscopy
After surgery for ectopic pregnancy, complications may develop:
- Spike.
- Inflammatory process.
- Bleeding.
- Discharge.
After treatment for an ectopic pregnancy, bleeding is sometimes observed that lasts for several days. They usually last no longer than 7 days.
Early restoration of the menstrual cycle may indicate either rapid recovery of the body or hormonal disorders. Discharges, the amount of which is small, usually do not cause concern.
If menstrual function is not restored within 2-3 months, it can be judged that the operation has greatly affected the female body. After such an outcome of an ectopic pregnancy, the patient will be prescribed hormonal medications.
After laparoscopic ovarian surgery, discharge is also observed, sometimes mixed with blood, which can last for 2-3 days, which is the norm. It is also possible that there will be no such symptoms, and the first menstruation will begin in 1-2 months. The woman will note that the cycle is proceeding as usual.
What kind of discharge may appear after laparoscopy?
Within three weeks after surgery, there is a slight, transparent discharge from the vagina, with a slight splash of blood. This phenomenon is normal and should not cause any concern to a woman - it is associated with the healing of damaged tissue.
Why does it hurt after laparoscopy?
During this time, the patient must carefully comply with all personal hygiene requirements and refrain from intimate contact. Intense bleeding (especially with blood clots) is considered pathological - this is a signal of internal bleeding.
Leucorrhoea that is brown or yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor indicates a bacterial infection. White discharge, accompanied by itching and burning, may indicate candidiasis (or thrush) - the presence of yeast-like fungi Candida Albicans in the genital tract.
In the postoperative period, a woman takes antibacterial drugs that weaken the immune system - this provokes the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Also very often, women notice changes in the menstrual cycle. In all of the above cases, the patient should contact the attending physician, who will take immediate action.
Discharge after laparoscopy
Today, the medical industry has fundamentally new technologies for surgical interventions.
One of these achievements of modern science is laparoscopy - a safe, low-traumatic and short-term operation that does not require a long recovery period.
Laparoscopic interventions are carried out using probes that are equipped with a camera and special lighting that allows you to examine all the details of the operated area. They are inserted through small (no more than two centimeters) incisions on the skin.
This surgical technique is widely used in gynecology - after such an operation there are no noticeable cosmetic defects left on the skin of the abdomen, moreover, rehabilitation proceeds quickly and without any serious complications. In some cases, after laparoscopy, women note the appearance of discharge - this can be either a natural phenomenon or a sign of a pathological process.
In our article we want to talk about the specifics of laparoscopic surgery, the rules of preparation for the procedure, the characteristics of the rehabilitation period of the female body and explain whether brown discharge after laparoscopy is a pathology.
When is laparoscopy used in gynecological practice?
Practicing gynecologists use this minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical technique much more often than other medical specialists. Indications for laparoscopic and hysteroscopy (a method of examining the cervix and uterine cavity) are:
- endometriosis – growth of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterine walls);
- fibroids are benign neoplasms that form in the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus);
- torsion of a benign ovarian tumor (cyst) or its rupture;
- ovarian apoplexy - a sudden violation of the integrity of its tissues;
- anomalies of the anatomical structure of the genital organs and malformations of their development;
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy - when the attachment of a fertilized egg can occur in the peritoneum, fallopian tube, cervix or ovary;
- initial stages of the malignant process.
Thanks to the capabilities of laparoscopy, the treatment of many pathologies of the female reproductive system has become much more successful.
In some cases, laparoscopic surgical intervention is performed for “acute abdomen” syndrome, which is caused by damage to organs located in the abdominal cavity and pelvis
Rules for preparing and avoiding complications
Before any planned operation, the patient is pre-examined. After a conversation with a medical specialist and a physical examination by a gynecologist, the woman undergoes:
- general clinical urine and blood tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram - assessment of coagulation system factors;
- determination of blood group and rhesus affiliation;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound;
- serological tests for the presence of antibodies to HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis viruses.
Preparatory measures include following a special dietary regimen and performing manipulations that cleanse the intestines. The operation is performed in the first half of the monthly cycle.
The duration of recovery of the female body depends on the extent of the surgical intervention performed (for example, removal of an ovarian cyst requires rehabilitation of about 5 days).
After laparoscopy, patients note a feeling of discomfort in the abdomen.
This phenomenon is associated with the technique of manipulation - to increase the space for intervention, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity.
Postoperative sutures do not require special attention - there is no likelihood of them coming apart, healed scars are practically invisible
With low-traumatic laparoscopy, a woman’s body recovers much faster than after exploratory laparotomy, a surgical operation in which the abdominal wall is cut to access the internal organs. Limiting physical activity and following the advice of your doctor speeds up recovery.
What kind of discharge may appear after laparoscopy?
Within three weeks after surgery, there is a slight, transparent discharge from the vagina, with a slight splash of blood. This phenomenon is normal and should not cause any concern to a woman - it is associated with the healing of damaged tissue.
Why does it hurt after laparoscopy?
During this time, the patient must carefully comply with all personal hygiene requirements and refrain from intimate contact. Intense bleeding (especially with blood clots) is considered pathological - this is a signal of internal bleeding.
Leucorrhoea that is brown or yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor indicates a bacterial infection. White discharge, accompanied by itching and burning, may indicate candidiasis (or thrush) - the presence of yeast-like fungi Candida Albicans in the genital tract.
In the postoperative period, a woman takes antibacterial drugs that weaken the immune system - this provokes the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Also very often, women notice changes in the menstrual cycle. In all of the above cases, the patient should contact the attending physician, who will take immediate action.
When will the discharge disappear and the cycle will be restored?
The following complications may develop after laparoscopy:
- adhesions;
- bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- pathological discharge.
After surgery for an ectopic pregnancy, women complain of bleeding that continues for a week.
Laparoscopy is considered a safe and low-traumatic method of surgical treatment, which is why complete recovery of the female body occurs in no more than two weeks.
For many, menstrual function does not change; surgery is always scheduled on the eighth day of the monthly cycle, and by the beginning of the next menstruation, the woman’s body has time to fully resume its physical activity.
Isolation of exfoliated endometrium with blood from the vagina indicates rapid rehabilitation or a hormonal imbalance. As a rule, a small amount of discharge should not cause any concern.
If the frequency of the menstrual cycle is not restored within three months, gynecologists assume a hormonal disorder and offer the patient the use of replacement therapy
As a rule, the first menstruation after surgery is very heavy and pronounced - this phenomenon is explained by the slow healing of internal organs.
There are other menstrual dysfunctions that are considered normal:
- "Shift" of the monthly cycle. The day of laparoscopy is considered the beginning of a new period; in this case, bleeding occurs after a certain period.
- The discharge of mucous-bloody leucorrhoea is noted immediately after surgical manipulation and lasts approximately 21 days. Their appearance should not be regarded as an alarming signal. If they have an unpleasant odor, you need to contact a laboratory center and have a smear from the genital tract analyzed.
- Long delay - it can be caused by psycho-emotional stress or the effect of anesthesia. The absence of discharge may be a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the female reproductive glands (ovaries). If, during a delay in menstruation, a woman experiences abdominal pain and notices the release of blood clots, she must seek medical help, do an ultrasound and undergo tests.
In addition, it should be remembered that monthly bleeding is controlled by complex biochemical processes occurring in a woman’s body, taking into account the physiological and nervous system - the functional activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Failure of the menstrual cycle can be associated not only with medical procedures, but also with any disorder in the female body. Only a qualified doctor can find and eliminate the cause of the absence of menstruation.
Resuming physical activity and sexual intercourse
The first month after laparoscopy, the patient needs to limit sports activities and any physical activity - returning to the usual rhythm should occur gradually. Intimate life can be resumed 2 weeks after surgery.
Surgical intervention using the laparoscopic method is prescribed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in case of pathological processes accompanying infertility - fallopian tube adhesions, endometriosis, cysts, fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc. The successful completion of the recovery period indicates that it is already possible to plan the birth child.
When treating infertility, not only surgical but also conservative treatment is used - the use of medications that affect the functional activity of the female reproductive system.
That is why it is necessary to plan the birth of a baby after consultation with a practicing obstetrician-gynecologist, who has studied the patient’s medical history in detail.
If laparoscopy is successful, pregnancy planning can begin within a few months.
The resulting pregnancy is the result of the effectiveness of laparoscopy and the course of medical therapy.
Possible complications
Side effects of this safe procedure are minimized. However, in addition to the appearance of pathological discharge, a woman may experience other symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- loss of consciousness;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- nausea, even vomiting;
- increased pain in the abdomen;
- swelling and hyperemia of suture areas;
- bleeding from wounds;
- pneumonia;
- stroke.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed; medications containing Simethicone can eliminate flatulence.
At the end of all the above information, I would like to add that in order to avoid all the unpleasant manifestations of the postoperative period, the patient must follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
In addition, approach the choice of a medical institution and specialist who will perform laparoscopy with all responsibility. And if all the rules of the rehabilitation period are followed, the woman will quickly return to her previous shape and active life without consequences for her health.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/prochee/vydeleniya-posle-provedeniya-laparoskopii
When will the discharge disappear and the cycle will be restored?
The following complications may develop after laparoscopy:
- adhesions;
- bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- pathological discharge.
After surgery for an ectopic pregnancy, women complain of bleeding that continues for a week.
Laparoscopy is considered a safe and low-traumatic method of surgical treatment, which is why complete recovery of the female body occurs in no more than two weeks. For many, menstrual function does not change; surgery is always scheduled on the eighth day of the monthly cycle, and by the beginning of the next menstruation, the woman’s body has time to fully resume its physical activity. Isolation of exfoliated endometrium with blood from the vagina indicates rapid rehabilitation or a hormonal imbalance. As a rule, a small amount of discharge should not cause any concern.
If the frequency of the menstrual cycle is not restored within three months, gynecologists assume a hormonal disorder and offer the patient the use of replacement therapy
As a rule, the first menstruation after surgery is very heavy and pronounced - this phenomenon is explained by the slow healing of internal organs.
There are other menstrual dysfunctions that are considered normal:
- "Shift" of the monthly cycle. The day of laparoscopy is considered the beginning of a new period; in this case, bleeding occurs after a certain period.
- The discharge of mucous-bloody leucorrhoea is noted immediately after surgical manipulation and lasts approximately 21 days. Their appearance should not be regarded as an alarming signal. If they have an unpleasant odor, you need to contact a laboratory center and have a smear from the genital tract analyzed.
- Long delay - it can be caused by psycho-emotional stress or the effect of anesthesia. The absence of discharge may be a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the female reproductive glands (ovaries). If, during a delay in menstruation, a woman experiences abdominal pain and notices the release of blood clots, she must seek medical help, do an ultrasound and undergo tests.
In addition, it should be remembered that monthly bleeding is controlled by complex biochemical processes occurring in a woman’s body, taking into account the physiological and nervous system - the functional activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Failure of the menstrual cycle can be associated not only with medical procedures, but also with any disorder in the female body. Only a qualified doctor can find and eliminate the cause of the absence of menstruation.
The effect of laparoscopy on menstruation
Doctors prescribe such an operation almost at the beginning of the cycle, that is, after the next menstrual flow. In this case, the operation without complications will not affect the cycle in any way, and menstruation will proceed as scheduled.
But after the procedure, the nature of menstruation may change, and therefore many women mistake heavy menstruation for bleeding. In addition, a delay in menstruation is also possible, but in such a situation it is better to consult a doctor, because the absence of menstruation may indicate an unsuccessful operation or a hormonal imbalance.
It must be remembered that the speed of the recovery period after laparoscopy will largely depend on the patient herself. Of course, this method involves minimal intervention in the woman’s body, but even here complications may arise, the presence of which may be indicated by one or another vaginal secretion.
Resuming physical activity and sexual intercourse
The first month after laparoscopy, the patient needs to limit sports activities and any physical activity - returning to the usual rhythm should occur gradually. Intimate life can be resumed 2 weeks after surgery.
Surgical intervention using the laparoscopic method is prescribed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in case of pathological processes accompanying infertility - fallopian tube adhesions, endometriosis, cysts, fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc. The successful completion of the recovery period indicates that it is already possible to plan the birth child.
When treating infertility, not only surgical but also conservative treatment is used - the use of medications that affect the functional activity of the female reproductive system. That is why it is necessary to plan the birth of a baby after consultation with a practicing obstetrician-gynecologist who has studied the patient’s medical history in detail. If laparoscopy is successful, pregnancy planning can begin within a few months.
The resulting pregnancy is the result of the effectiveness of laparoscopy and the course of medical therapy.
Recovery period
After laparoscopy on the organs of the reproductive system, some women experience bleeding that lasts for several days. This is caused by injury to the vessels and small capillaries, which completely penetrate the mucous membranes of the uterus, ovary and cervical canal.
If the operation was simple, for example, the intrauterine device (IUD) was removed or the uterine cavity was cleared of blood clots, then the discharge is not abundant and is observed for only 1–2 days. If more serious interventions were carried out (neoplasms were removed, complete or partial resection of adnexal organs was performed, etc.), then there is a high probability of bleeding after laparoscopy, which is also observed for several days, and then abruptly stops.
If the operation is successful, the majority of women begin to experience scanty brown or white discharge with small streaks of blood already on the second day. In this case, other symptoms are also observed, for example:
- Minor weakness.
- Nagging pain in the abdomen.
- Increase in temperature (no more than 37.5 degrees).
As a rule, such symptoms occur only on the first day after surgery. If they intensify and are observed for more than a day, then this is no longer considered normal and requires re-examination of the patient.
Possible complications
Side effects of this safe procedure are minimized. However, in addition to the appearance of pathological discharge, a woman may experience other symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- loss of consciousness;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- nausea, even vomiting;
- increased pain in the abdomen;
- swelling and hyperemia of suture areas;
- bleeding from wounds;
- pneumonia;
- stroke.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed; medications containing Simethicone can eliminate flatulence. At the end of all the above information, I would like to add that in order to avoid all the unpleasant manifestations of the postoperative period, the patient must follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. In addition, approach the choice of a medical institution and specialist who will perform laparoscopy with all responsibility. And if all the rules of the rehabilitation period are followed, the woman will quickly return to her previous shape and active life without consequences for her health.
Possible consequences
Consequences after such an intervention are rare and they appear in only 1% of all operations, but no one is 100% protected from them. During laparoscopy, the following complications may occur:
- Damage to adjacent internal organs by instruments inserted blindly into the abdominal cavity. However, if the technique of the operation is fully followed, then there should not be such consequences. In addition, the developers tried to make the instruments inserted inside as safe as possible. There are caps on the sharp tips. If the organ is damaged too much, then laparotomy (abdominal surgery) is used to eliminate the problem.
- Problems with breathing and heart function. They may occur if the patient has a predisposition to diseases of these systems. Complications are caused by gas injected into the abdominal cavity to improve visibility of organs. To avoid consequences, the specialist tries to reduce its pressure.
- Subcutaneous emphysema. It does not pose a threat to the patient’s health or life and goes away without additional treatment.
- Bleeding. The cause is a rupture of the vessel or its insufficient coagulation during the intervention. This complication can occur both during and after surgery.
- Tissue necrosis or burns. Occurs due to malfunction of instruments or medical error, due to which healthy areas are damaged. If the complication is not eliminated in time, there is a risk of developing peritonitis.
- Infection of a wound or operated organ with subsequent appearance of suppuration. Here the cause of the consequences is failure to maintain absolute sterility of instruments, the surgical field, or a decrease in the patient’s body’s defenses.
- Allergic reaction to medications used for anesthesia. Before the intervention, you need to interview the patient and do allergy tests.
When is laparoscopy performed for ovarian cysts?
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation and does not always require treatment, much less surgery.
But some types of it are very dangerous; they can develop into cancer. If, during an examination, this type of cyst is found on a woman’s ovaries, it is first treated with medication. And only if this treatment is ineffective we talk about surgery. When there are no contraindications, surgery is performed laparoscopically. Small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, into which instruments are inserted; with their help, the cyst on the ovaries is removed. If a woman is young and plans to have children in the future, then they only get rid of the cyst. In postmenopausal age, surgery may be performed to remove the fallopian tubes and other reproductive organs.
Advantages of the operation:
- formation of adhesions is unlikely;
- allows you to avoid the appearance of a postoperative hernia;
- absence of a large scar;
- there is no threat of injury to neighboring organs;
- shorter hospital stay after surgery;
- faster healing of sutures.
A few hours after such an operation, the woman can get out of bed, and after a couple of days she will be discharged from the hospital. There are not many complications due to laparoscopy of ovarian cysts. To avoid them, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist and strictly follow his instructions.
The nature of discharge after laparoscopy may vary. When after laparoscopy the brown discharge is not very abundant, this is normal and there is no need to worry. This color appears with residual bleeding. Discharge after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst of any other color is a reason to visit a doctor. Different colors of discharge indicate the following:
- Greenish or yellow discharge with an unpleasant odor is evidence that an infection is developing. Treatment with antibiotics is possible.
- If the discharge is white and has a cheesy consistency and is accompanied by itching or burning, then it is thrush. She does not need any special treatment, but a visit to the doctor cannot be avoided. This will relieve complications that weaken the body.
- Bloody and brown discharge after laparoscopy of a mucous type usually lasts a couple of weeks. If they do not change color or emit an odor, then this is normal. Otherwise, an examination is necessary to determine the cause of such discharge after ovarian laparoscopy.
- If the discharge is brown, profuse and with blood clots, you need to consult a doctor, it may be bleeding. This condition is dangerous.
To avoid all sorts of complications after surgery, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. The seams must be carefully processed. This will help avoid infection and not leave scars on the body in the future. It is better to avoid taking a bath in favor of a shower for several weeks after laparoscopy.
Since internal organs do not heal quickly after laparoscopy, the first menstruation is usually heavy and longer. Also, don't worry if:
- menstruation begins a few days earlier or later. Due to laparoscopy, such a shift is not considered a pathology.
- Brown spotting occurred immediately after surgery. They can last for several weeks. But if they change color to yellow or green and acquire an odor, then you should worry. The doctor will order a smear test to determine the cause.
- a long delay may occur. Since laparoscopic surgery is performed under anesthesia, it can affect the cycle. A possible cause is the woman's excitement.
If menstrual flow does not appear after laparoscopy, then you should think about reasons not related to the intervention. In this case, do not neglect a full examination. In addition to the smear, you will need to conduct a blood and urine test, and do an ultrasound of the organs located in the pelvis.
Pathological discharge after laparoscopy
Heavy bleeding that lasts more than 21 days is dangerous. Then medical attention is required, since life-threatening conditions are possible.
- Brown discharge after laparoscopy is normal and indicates residual metrorrhagia, but if it is not accompanied by increased pain, a sharp deterioration in well-being. Internal bleeding is possible, or the operation was performed poorly.
- Yellow discharge after laparoscopy, which has a foul odor, are symptoms of an infectious lesion.
- The white shade of secreted mucus with curdled “flakes” is a manifestation of thrush.
There is no need to call an ambulance in the last 2 cases, but treatment is necessary to prevent complications. Bloody discharge with mucus often lasts 2-3 weeks. They should not show purulent impurities, and the smell and consistency should not change.
Indications and contraindications for tubal removal surgery
Depending on the indications, tubectomy can be performed planned or urgently. The laparoscopic approach is considered preferable, but in some cases the operation is performed through a laparotomy incision in the abdominal wall. Indications for intervention must be clearly defined, because it has irreversible consequences and is considered radical.
Reasons for unilateral or bilateral tubectomy may be:
First or repeated ectopic tubal pregnancy, emergency - if a tube ruptures with bleeding;
- Impossibility of tubal plastic surgery during tubal pregnancy;
- Chronic inflammation of the organ - purulent salpingitis, hydrosalpinx, adnexitis;
- Tubal infertility when planning IVF;
- Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst or its rupture;
- Adhesive disease of the pelvis with tubal involvement;
- Removal of the uterus due to widespread endometriosis, tumors of the tubes or ovaries, the uterus itself, or the intestines;
- Severe intestinal diseases involving the appendages.
The most common reasons for surgery are tubal pregnancy and inflammatory processes , which are dangerous both in themselves and in terms of the development of ectopic pregnancy. If the embryo has begun its development in the tube, then surgery is inevitable, since its continued existence puts the woman’s life at risk due to the risk of rupture and bleeding.
In rare cases, during tubal pregnancy, surgeons offer organ-preserving operations with “washing out” the embryo and preserving the tube, however, as practice shows, such treatment makes the risk of repeated tubal pregnancy and tube obstruction even higher, and the woman will have to undergo radical surgery one way or another, this is a question only time.
Chronic salpingitis and hydrosalpinx also entail tubectomy and are increasingly becoming a reason for surgery due to their high prevalence due to the early onset of sexual activity, increased infection with pathogens of sexually transmitted infections, and the continuing number of instrumental abortions.
Salpingitis is an inflammation that can be chronic and contribute to the appearance of adhesions in and around the tube. Hydrosalpinx is an irreversible degenerative-inflammatory disease with expansion of the lumen of the organ and accumulation of fluid there. Both processes cause infertility.
A big risk is the presence of inflammation or hydrosalpinx when planning an in vitro fertilization procedure, since tubal pathology can interfere with the implantation of embryos introduced into the uterus and the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth.
The fluid accumulated in the tube during hydrosalpinx often contains dangerous pathogenic microorganisms, has a toxic effect on the endometrium and the fertilized egg, and can also cause mechanical leaching of implanted embryos from the uterus, especially during periods of exacerbation of inflammation. In this regard, irreversibly damaged tubes are recommended to be removed before IVF.
In addition to improving the survival rate of eggs during IVF, tubectomy for hydrosalpinx helps prevent possible tubal pregnancy. However, it is worth noting that the operation can impair the maturation of germ cells and ovulation, so it is usually prescribed for large tube sizes and in cases where hydrosalpinx was diagnosed more than six months ago.
In some cases, the tube is removed along with the rest of the internal organs of the female reproductive system due to oncological pathology. In particular, endometrial cancer, multiple fibroids or leiomyosarcoma, and ovarian malignancies require radical surgery, in which tubectomy is only one component of the intervention. For malignant neoplasms, a bilateral tubectomy is usually performed.
In more rare cases, intestinal pathology may be an indication for tubectomy. For example, destructive forms of appendicitis, Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis with intestinal perforation and peritonitis may be the reason for tubectomy on the right or left (pathology of the sigmoid colon).
Contraindications are similar to those for other operations. These are severe blood clotting disorders, decompensated pathology of internal organs, acute infectious diseases. During laparoscopy, strong adhesions and a high degree of obesity can become an obstacle.
Diet after tubal laparoscopy
Fallopian tube laparoscopy: diet. Fallopian tube laparoscopy, like any operation, is a certain stressful situation for the body. Therefore, in the postoperative period it is necessary to adhere to a certain diet and diet. The diet after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes should be gentle, the food is light, does not require a lot of energy for digestion, and does not provoke stool disorders and gas formation.
Following nutritional recommendations helps reduce the possibility of postoperative complications associated with the digestive system, and also promotes a speedy recovery. Before laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed, you need to find out what you can eat after the operation. This will help the attendants navigate what products can be brought to the patient and what should be limited.
General principles of nutrition in the postoperative period:
- On the first day you can drink still water, then by the end of the first day after surgery - low-fat broths
- Food should be boiled or stewed and have a rough structure so as not to damage the intestinal mucosa. In addition, after intubation, unpleasant sensations in the throat persist and rough food only further injures the already damaged mucous membrane
- Meals should be fractional: you need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions, so as not to overload the digestive tract and not contribute to the processes of decay in the intestines
- Nutrition after tubal laparoscopy should be high in nutrients, especially proteins and vitamins, which improves immunity and speeds up recovery processes.
What can you eat after tubal laparoscopy:
- Vegetables and fruits, especially baked apples and bananas
- Cream soups
- Chicken broth
- Lean types of meat (veal, chicken) and fish (hake, pollock, pike perch)
- Porridge – buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, rice – with caution
- Whole grain or bran bread
- Cottage cheese and low-fat cream, fermented milk products
- You can drink weak tea, diluted fruit and vegetable juices, still water
The following foods should be limited or excluded from the diet:
- Salty, spicy food
- Pickled products
- Fatty fish (trout, salmon) and meat (pork, lard)
- Smoked meats, fried foods with a high content of oil and fat
- Chocolates, pastries, cakes, fresh pastries
- Foods that contribute to increased gas formation in the intestines - black bread, beets, cabbage, legumes
- Some berries and fruits, such as quince, persimmon, dogwood
- Alcohol, coffee, carbonated drinks
You need to know what you can eat after tubal laparoscopy to prevent constipation. These are products such as fresh kefir, yoghurts without food flavoring and aromatic additives. The bacteria contained in fermented milk products that are beneficial for digestion prevent dysbacteriosis and the problems that accompany it. To improve peristalsis, you can eat dried fruits, including prunes.
It is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of fluid - about 2 liters per day. It can be plain water, fruit drinks, juices, compotes, jelly, weak tea. Excessive fluid intake can lead to the development of edema, which is also undesirable.
At first, the attending physician should regulate the diet and nature of the diet based on an assessment of the patient’s condition. Before discharge from the hospital, you should also receive recommendations from him about what to eat after tubal laparoscopy at home.
Alcohol after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is strictly contraindicated. This is due to many reasons:
- Alcohol toxins lead to intoxication of the body; their removal requires enhanced work of the detoxification system.
- Increased risk of infectious complications
- The combined use of alcohol with medications leads to liver damage and the development of acute toxic hepatitis.
- Regeneration processes slow down, chronic diseases worsen
- Alcohol contributes to blood clotting disorders
- Suppression of the nervous system due to alcohol consumption aggravates the course of the postoperative period
Taking alcohol together with antibiotics is especially dangerous for the liver (since it is where the processes of neutralization and breakdown of toxic substances occur) and kidneys (since they remove dangerous metabolites from the body in the urine). This does not mean that you need to give up alcohol forever, but during the rehabilitation period, complete abstinence from alcohol is necessary.
If a woman smoked before surgery, then in the postoperative period you should also limit yourself to smoking, since nicotine and tar contained in cigarettes can worsen the course of the postoperative period and slow down the regeneration processes.
Preparation and technique for removing the fallopian tube
Since tubal removal requires anesthesia, the patient will undergo careful preparation before the operation, including:
- Fluorography or chest x-ray;
- Cardiography according to indications;
- General clinical tests - blood, urine, group and Rh status;
- Examination for HIV, hepatitis, RW for syphilis;
- Coagulogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs;
- Examination by a gynecologist, colposcopy, taking smears for cytology and microflora.
After the research, the woman goes to a therapist, who gives his consent to the operation. Before the intervention, an anesthesiologist talks with her and determines the type of anesthesia and possible risks from it. The attending physician must be notified of all medications taken on a regular basis; anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and anti-inflammatory drugs are discontinued 2 weeks before tubectomy.
In the evening before the intervention, a cleansing meal, dinner and fluids are prescribed no later than 12 hours before the operation. The patient takes a shower the day before, removes hair from the perineum and pubis, and changes clothes. For severe anxiety, sedatives at night are recommended.
Surgery to remove the fallopian tube can be performed laparoscopically or by laparotomy. The differences are in the method of access to the pelvic organs, but laparoscopy has many advantages:
Preparing for a tubectomy
Preparatory processes for this operation may not be carried out at all, with the exception of the administration of painkillers if emergency surgery is required. This happens when an ectopic pregnancy or an infectious disease was detected at a late stage and the woman loses consciousness at this time, a tube ruptures, and so on.
If there is time for preliminary preparation, then a blood test is taken before the operation, painkillers are selected and the period of the cycle is selected when it is best to perform the operation with the fewest possible complications.