How to prepare for hysteroscopy
In order to prepare for surgery, a number of laboratory and clinical examinations are required, as well as consultations with other specialists in case of problems with the health of other organs and systems.
And also, some changes in lifestyle a few days before the operation. Often, women are interested in information about whether it is possible to have sex before hysteroscopy. Here you need to take into account the time period for which sexual intercourse is planned before the operation. If a week in advance, then you can have sex before hysteroscopy. But three days before the upcoming operation you should abstain from sexual intercourse. Since this can provoke the development of infectious complications.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Also, it is necessary to take into account the diet on the eve of surgery. You should exclude “heavy” foods and include easily digestible foods in your dinner, which should be consumed no later than six o’clock in the evening if hysteroscopy is planned in the morning. Also, in the morning, on the day of surgery, food consumption should be completely eliminated. And significantly limit fluid intake.
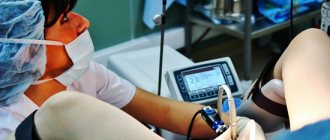
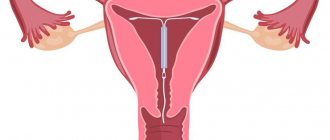
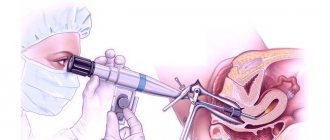
Hysteroscopy is performed on the fifth to ninth day of the menstrual cycle in order to prevent bleeding, due to the presence of a thin uterine mucosa and the lack of increased blood supply. Next, the woman is placed on a regular gynecological chair, anesthetized, and the operation itself begins. Using special instruments, after treating the vagina and cervix with a disinfectant solution, the cervical canal is expanded and a hysteroscope is inserted through it into the uterine cavity.
After that, for better visualization and expansion of the uterine cavity, a gas or liquid medium is used and diagnostics is started, and then, when pathological foci are identified, their removal is started. During the entire operation, the pressure of the injected gas, or the amount of liquid, as well as the patient’s vital parameters, are carefully monitored.
During the examination, the clinical picture of what is happening is displayed in the form of an image on the screen, which the operating doctor is guided by. At the end of the operation, separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity and the cervical canal is performed, with further histological examination of the resulting material.
Recommendations for recovery
Normally, the recovery period lasts about a month. After curettage and hysteroscopy, you must strictly adhere to the following recommendations during this time:
- don't have sex. In addition to the fact that this will cause pain, there is also a risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the organ cavity;
- do not swim in open bodies of water, pools, or even take a bath. Only showers are allowed;
- refuse to visit saunas and baths;
- do not neglect the rules of intimate hygiene and wash yourself at least twice a day;
- take antibiotics, strictly adhering to the regimen chosen by the doctor;
- measure body temperature twice during the day;
- avoid excessive physical activity and heavy lifting;
- do not use tampons. Preference should be given to pads and changed every 3-4 hours. Blood is a favorable environment for the development and reproduction of bacteria;
- organize your diet correctly. It is extremely important that the menu contains a sufficient amount of vegetables, dairy products and fruits;
- systematically undergo examination by a gynecologist;
- ensure timely emptying of the bladder.
Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is considered a minimally invasive operation, the risk of complications still exists. A woman must properly prepare for this procedure and strictly follow all medical recommendations after it. Due to this, the occurrence of undesirable consequences is observed much less frequently.
Postoperative period
Any woman undergoes hysteroscopy. However, not everyone undergoes resectoscopy. What is the difference between these concepts?
- In definition. Hysteroscopy is an examination of the uterine cavity to identify tumors. And resectoscopy is a surgical intervention performed in connection with the detection of these same formations.
- In the method of implementation. The first option uses only a gyroscope, and the second uses additional tools: a scalpel, forceps and much more.
Thus, these two procedures have their similarities and differences. However, the reasons for carrying them out are approximately the same:
- Sterility.
- Presence of polyps.
- Pain during the menstrual cycle.
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene standards.
One way or another, after diagnostic hysteroscopy it is often necessary to perform resectoscopy. After hysteroscopy of the uterus, it is necessary to perform a surgical intervention.
After the operation, which lasts 6 hours, the patient is discharged home in normal condition. In case of violations, they are left under medical supervision.
Upon discharge, each woman is warned about what she can and cannot do. So, after hysteroscopy you cannot:
- Have sex. This may cause excessive bleeding or complications during healing. Sex is not allowed for 7-21 days.
- Use douching or tampons. They can cause erosions or other problems in the uterus.
- Lift weights. This may cause the seams to come apart.
Sometimes, immediately after surgery, a woman may experience the following complications:
- Bleeding after hysteroscopy. In this case, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors to identify and treat the causes.
- Infection. This should only be treated in a hospital setting.
- Detection of side effects after anesthesia. This may include dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. In this case, the patient is recommended to remain in the hospital until these effects are completely eliminated.
- Causing injury to the cervical canal. The patient stays until he returns to normal.
In any of these cases, a woman needs to take care in advance of taking days off from work in order to avoid unnecessary problems.
The postoperative period is divided into two periods: the early postoperative period and the late postoperative period. Such a division is necessary to determine the woman’s health status in relation to the ongoing processes in accordance with the recovery period.
This stage takes a period of time from the end of the operation until the woman is discharged from the hospital. Since discharge from the hospital is a purely individual issue and depends on the patient’s condition after surgery, as well as on the presence or absence of complications, this period is different for each patient.
The early postoperative period is characterized by bloody discharge from the genital tract and may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region of a pulling nature.
The patient is prescribed a protective treatment regimen and recommendations are given. Since sexual intercourse is excluded during this period in order to prevent complications, after hysteroscopy of the uterus you can become pregnant only no earlier than a month later. But this is risky, as it can jeopardize the physiological gestation of the pregnancy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
This period begins from the moment of discharge and lasts approximately six months. During this time, restoration processes occur in the uterine cavity, cervix, and vagina. With drug therapy, ovarian function is restored. All these processes bring the female reproductive system into “shape”, with the goal of the full functioning of the genital organs and the fulfillment of the reproductive task.
Pregnancy after RDV with hysteroscopy is a very real event. In most cases, when a woman has problems conceiving, and there have also been episodes of gynecological diseases, in order to successfully conceive, the woman is recommended to undergo diagnostic hysteroscopy. At the end of the study, separate diagnostic curettage is performed if there is a suspicion of changes in the endometrium.
As a result, after ten days the patient receives a histological conclusion about the state of the uterine mucosa at the cellular level and its ability to bear physiologically. Since after curettage the endometrium is completely renewed, this increases the chances of pregnancy and its bearing.
Moreover, after hysteroscopy, pregnancy occurs, as a rule, after two to three months. But it is better, of course, to adhere to generally accepted recommendations and plan a pregnancy no earlier than six months later.
Often women are concerned about the advisability of performing hysteroscopy before cryotransfer. Of course, the procedure is very successful in cases of infertility and the subsequent use of in vitro fertilization, although it is not a panacea in the fight against infertility. Hysteroscopy is not one of the basic examination points before IVF, but reproductive doctors often recommend it.
This is prescribed for the purpose of diagnosing gynecological pathology and its timely treatment through either hysteroresectoscopy or drug therapy, in order to exclude the occurrence of complications after cryotransfer and further pregnancy. In this case, the end justifies the means. Since the IVF procedure requires lengthy preparation and considerable financial expenses, hysteroscopy increases its effectiveness.
It is not uncommon that during diagnostic hysteroscopy, pathology is detected, for example, adhesions of the uterine cavity, or endometrial polyps, which are the cause of infertility. This operation allows not only to diagnose the pathological condition, but also to immediately get rid of the cause of the impossibility of conception, by removing polyps and cutting adhesions, and so on.
The most interesting question for women deciding to undergo hysteroscopy is: how long before you can get pregnant? After all, this is the most desirable result. Considering all of the above, it can be noted that there are those women who became pregnant after hysteroscopy literally within a month or two. But problems may arise that can delay pregnancy even during the period allowed for planning after surgery.
So, the time it took for clinic patients, in particular Altravita, to become pregnant after hysteroscopy ranges from three to six months to a year (as a result of the use of assistive technologies and natural conception). At the same time, both therapeutic and diagnostic hysteroscopy of the uterus was performed. Those women who became pregnant had no complications in the postoperative period, and their gynecological problem that prevented pregnancy was eliminated.
Hysteroscopy for a frozen pregnancy or for the purpose of terminating a short-term pregnancy is not performed. For this purpose, there is an interruption by curettage of the uterine cavity or by medication, depending on the stage of pregnancy. Hysteroscopy can be prescribed by a doctor only if, after a medical termination of pregnancy, there is a suspicion of retention of parts of the ovum, as well as to diagnose the reasons for the cessation of pregnancy development and its fading.
In any case, hysteroscopy is a diagnostically important operation, and can only be prescribed by a doctor and only for medical reasons.
Pregnancy and hysteroscopy
There are certain recommendations for pregnancy after hysteroscopy, adhering to which the recovery process will proceed much faster. During the first month, a woman needs sexual rest. This is primarily due to the fact that the organ at this moment is not protected from negative influences from the outside. A sexually transmitted infection can penetrate the uterine cavity, and the condition will significantly worsen.
In addition, during the first week and a half, spotting from the vagina is observed. It also makes intimacy impossible. The woman’s well-being during this period is deteriorating.
Preparing for tumor removal is simple. Necessary:
- shave the labia majora and pubis;
- cleanse the intestines;
- Before starting the procedure, empty your bladder.
After the procedure, the woman may be prescribed additional treatment. This may include:
- taking antibiotics, painkillers and hormonal drugs;
- herbal medicine.
A mandatory step is to follow all recommendations received from the doctor.
If the cause of infertility was a uterine polyp, then after its removal, conception and development of pregnancy occurs in a short time. The gestation itself proceeds calmly, without serious complications.
You can plan to conceive no earlier than three calendar months after the planned operation.
Planning a pregnancy, especially if there are any problems with its implementation, begins with a thorough examination of the woman. Naturally, in addition to the health of all organs and systems, special attention is paid to the reproductive health of women. And here there may be obstacles in achieving the goal of becoming parents. For a full approach to this issue, among other things, the hysteroscopy method is used.
Hysteroscopy is carried out for the purpose of diagnosing a particular condition that prevents pregnancy. If, under the conditions of this diagnosis, a cause is identified (polyp, myomatous node, synechiae), it is immediately eliminated. And, of course, in the absence of mechanical and other obstacles, the chances of pregnancy increase. Hysteroscopy is not a panacea in the treatment of infertility, but it makes it possible to achieve pregnancy, increasing the percentage significantly.
As a rule, when no complications are observed and the postoperative period proceeds smoothly, the planned conception, following the recommendations, can be started no earlier than six months later. Since it is during this period that the endometrium is restored quite completely and the hormonal levels are functionally ready after hysteroscopy to ensure conception and the physiological course of pregnancy.
There may be cases when the patient became pregnant after hysteroscopy two to three months later, earlier than the recommended period. In such a situation, pregnancy is under constant dynamic monitoring, since the incompletely restored functions of the reproductive system may not be able to cope with the resulting load in the form of pregnancy.
In any case, the approach to each patient is individual. And if the recovery period proceeds normally, the cycle has normalized in terms of regularity and duration, the symptoms that may have previously bothered the woman have gone away, and ovulation has been established after hysteroscopy - you can get pregnant in the third month. But it is better to consult directly with your doctor.
The period of time when hysteroscopy has already been performed, after how long you can become pregnant, directly depends on the gynecological pathology, and not on the operation itself. Since various types of diseases that prevent pregnancy require, in addition to surgery, drug treatment.
In situations where pregnancy is prevented by an endometrial polyp, or a myomatous node, adhesions, and so on, they resort to hysteroresectoscopy, which allows not only to see the expected diagnosis and confirm it, but also to carry out surgical treatment, eliminating the cause of infertility. During the operation, using a microsurgical power tool under image control on a monitor, the pathological area of tissue is removed by excision and grinding (in the case of a large myomatous node), and then the removed tissue is removed from the uterine cavity.
In these cases, the desired pregnancy after hysteroscopy of the polyp can be planned no earlier than six months later, and maybe a little more. Since this condition, although eliminated surgically, there is a need to treat the underlying cause. And to prevent relapses, hormonal therapy with oral hormonal contraceptives is prescribed for a course of three or more months, and only then is it recommended to plan conception, after stopping the drugs.
If a woman has been diagnosed with a myomatous node, which was removed through hysteroscopy of the uterus, pregnancy cannot be planned immediately. This is explained by the fact that at the site of the removed node there are sutures that require a period of healing, and also, in order to treat the hormonal disorder that caused the appearance of the node, a long course of hormonal drugs is prescribed. And all this is aimed at restoring the reproductive health of the uterus to carry a full, healthy pregnancy.
This operation is not mandatory in the list of examinations for the upcoming in vitro fertilization, but its diagnostic value is very high. And this affects the early detection of pathologies that are not noticeable through ultrasound examination, treatment and improvement of the reproductive organ. According to the observation of reproductive doctors, after hysteroscopy, pregnancy occurs more often with the use of assisted reproductive technologies. And those who have undergone hysteroscopy and become pregnant are proof of this.
A very common question from patients is: “If hysteroscopy is performed, after how long is it allowed to become pregnant?” This is especially of interest to patients directly targeting IVF. Also, as in the case of physiologically occurring conception, IVF is recommended to be carried out after hysteroscopy no earlier than six months later.
And after a successful attempt to implant an embryo into the uterus, the woman is kept under close supervision, and this observation is largely associated not with the operation performed, but with possible gynecological pathology in the past, and, of course, with the use of assisted reproductive technologies.
In any case, planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy or hysteroresectoscopy must be done under the strict guidance of the attending physician, who takes into account all aspects of the postoperative period. We will look at what exactly the postoperative period includes in the next article.
Pain syndrome after hysteroscopy
After hysteroscopy surgery, some so-called side effects may occur. Among other things, the first symptom that disrupts a woman’s general condition and affects her psychological well-being is pain.
Let's look at what the hysteroscopy procedure is, based on this, the origin of the pain syndrome will be clear.
Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic operation to confirm or refute a particular diagnosis, as well as to clarify the causes of long-term infertility problems and their elimination.
Most often, this research method is carried out practically on an outpatient basis, that is, without the occurrence of long-term disability, and the duration of the study can be from one to three days. At the same time, there is standard preparation for this type of surgical intervention. The woman is notified of a routine examination and blood tests.
Next, they explain the procedure for performing hysteroscopy, in which the woman is positioned on a gynecological chair, slightly different from the one usual for examination, and anesthesia is performed through intravenous anesthesia.
Next, a two-handed examination is carried out to determine the location of the uterus and its size, the external genitalia and cervix are treated with iodine solution or alcohol, after which the cervix is fixed using special forceps by the front lip.
Then, using a probe, the length of the uterine cavity is determined, and after preliminary expansion of the cervical canal, the uterine cavity is filled with gas or a special liquid solution, which allows the uterine cavity to expand and make it accessible to inspection with a hysteroscope. After which the hysteroscope itself is used, and based on the image on the screen, a complete diagnosis of the uterine cavity is carried out, the mouths of the fallopian tubes are examined, possibly their patency, and the cervical canal of the uterus is examined.
Taking into account all aspects of the hysteroscopy operation and pain relief, it can be noted that the pain that occurs after the procedure is associated with some aspects of its implementation. When patients complain that after hysteroscopy the lower abdomen and lower back hurt, this is a rather physiological reaction of the body to surgery.
Also, when the lower abdomen pulls after hysteroscopy, this moment is provoked by the expansion of the cervical canal before the procedure. The same pain is typical after fractional curettage, which completes hysteroscopy.
The pain is nagging in nature, most often localized in the lower abdomen, possibly in the lumbar region, and causes discomfort. If a woman’s pain threshold is reduced and her sensations disturb her general condition, the doctor may additionally prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers, such as Ketorol, Dexalgin, and so on. At the same time, after using the drugs, the intensity of pain in the lower abdomen after hysteroscopy should decrease, and the woman’s general condition should improve.
If the pain becomes unbearable, acute, cramping or constant with a tendency to increase pain, such pain is not acceptable after such a type of intervention as hysteroscopy or hysteroresectoscopy, and requires emergency medical care. Since they can be caused by possible complications of the intervention, which include surgical (perforation of the uterus, bleeding), anesthetic, as a result of the use of gas (gas embolism) to expand the uterine cavity.
A frequently asked question is: how long does the stomach hurt after hysteroscopy? The answer will be individual for everyone, it all depends on the woman’s pain threshold. But there are also generally accepted limits for the duration of unpleasant sensations. The most intense pain occurs on the first day after surgery, but after the effect of the narcotic analgesics that were used during the operation has expired.
Then, every day it will weaken. Normally, after a hysteroscopy operation, the lower abdomen hurts for about two to three days, or even less. This is due to tissue trauma and rapid recovery. While the uterus contracts, the stomach pulls after hysteroscopy. During the period when the uterus shrank and returned to its previous size, the pain subsided.
However, there is an opinion that pain after hysteroresectoscopy is more intense, due to the fact that this is not only a diagnosis - examination, but also removal of the pathological focus, than after diagnostic hysteroscopy. There will be no exact answer here, everything is purely individual. Due to the invasiveness of the method, when during hysteroscopy a pathological focus is discovered and it is removed, violating the integrity of the tissue, the pain can reasonably be stronger.
In any case, regardless of the reasons, the attending physician should know about all painful sensations. And in this case, he will differentiate the origin of the pain and, accordingly, prescribe analgesic therapy or provide other medical assistance in order to improve the general condition of the patient.
But the symptom of pain is not the only manifestation after hysteroscopy. Let's take a closer look at the duration and nature of the discharge in the next article.
Stages of implementation
- Anesthesia is usually intravenous.
- Treating the genitals with antiseptic solutions.
- Dilation of the cervical canal.
- Insertion of the hysteroscope.
- Injection of fluids or gas to expand the cavity and improve visualization.
- Examination of the endometrium, the mouths of the fallopian tubes, determining the exact localization of the pathological area.
- Removal of the altered area of the endometrium.
- Quality control of pathological tissue removal.
- Removing instruments from the uterine cavity.
When can you be sexually active after hysteroscopy?
Taking into account the above-described aspects of the operation, after the examination the woman is given appropriate recommendations for restoring the body. After hysteroscopy, antibacterial therapy is prescribed to exclude infectious complications and the development of endometritis. For the same purpose, sexual abstinence after hysteroscopy is recommended.
Thus, a sexual partner can be a carrier of even the most banal pathogens that normally “live” in a woman’s vagina. But, since the local immunity of the vagina is provoked by the operation, sex after hysteroresectoscopy can lead to the development of undesirable consequences - from the banal “thrush” to pelvioperitonitis (an infectious process of an ascending type).
So, how many days after hysteroscopy can you have sex? Following generally accepted recommendations, the calculation is not carried out in days. Only after three to four weeks, in the absence of complications and additional complaints from the patient, is sexual activity allowed after hysteroscopy. When you can start having sex, you should remember about contraceptive methods, since the body is not yet ready for pregnancy, this takes time. And now, when you can engage in intimate life after hysteroscopy, you should also especially not forget about the banal rules of personal hygiene.
General recommendations for sexual activity after polyp removal
As you can see, abstinence is 1-2 months. Gynecologists advise waiting until after your period for any surgery because there is still a risk of infection and bleeding. For those who have already had their ban on sex lifted, there are a number of recommendations:
- It is mandatory for both partners to wash and shower before sex.
- Use a condom at first.
- Avoid rough and sudden movements, deep penetration.
- A woman’s anatomy is individual, so she herself will discover the position that will be the least traumatic.
- Stop if sex brings pain or spotting.
- If you have any unpleasant symptoms, contact your gynecologist.
During sexual rest, many couples practice oral sex. The danger is bacteria from a man's mouth, which enter the vagina and can cause inflammation. If the actions are carried out by a woman for a partner, then there are no prohibitions.
Bleeding after hysteroscopy
The method of instrumental examination of the cavity of internal organs using an endoscope in the gynecological field of modern medicine is called hysteroscopy. This manipulation was first successfully performed in 1870 by the Italian physician Pantaleoni to determine the condition of the uterine cavity using a tube with an external lighting device similar to a cystoscope.
Modern hysteroscopy is considered the most informative among all other instrumental techniques for diagnosing and treating all intrauterine pathologies. There are two types of research:
- Diagnostic - allows you to identify the pathological process inside the uterus.
- Operating – performed for topical diagnosis, targeted biopsy or surgical intervention in the uterine cavity.
As with any invasive procedure (associated with penetration through the skin or mucous membranes), performing hysteroscopy requires high surgical qualifications of a specialist and compliance with all the rules of the technique. Violation of these requirements can lead to serious consequences that pose not only a danger to a woman’s health, but sometimes to her life.
A diagnostic procedure is prescribed for:
- disorders of the menstrual cycle in various periods of a woman’s life (juvenile, reproductive, perimenopausal);
- bleeding in the postmenopausal period;
- differential diagnosis of adenomyosis, endometrial cancer, uterine developmental anomalies, intrauterine adhesions, submucosal (submucosal) uterine fibroids;
- infertility;
- the presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity;
- not carrying a pregnancy;
- control examination of the uterine cavity after surgical interventions;
- assessing the effectiveness of hormonal treatment;
- complicated period after childbirth.
Most often, contraindications are the same reasons for refusal for any surgical intervention, these are the presence of:
- infectious diseases - influenza, sore throat, pneumonia, acute pyelonephritis, thrombophlebitis;
- acute inflammatory processes of female genitalia;
- cardiac and vascular pathologies;
- chronic kidney and liver diseases;
- advanced cervical cancer;
- profuse bleeding from the uterine cavity.
Types of hysteroscopy
Today, several types of this procedure are widespread: therapeutic, diagnostic and planned hysteroscopy.
- A diagnostic test is prescribed for a woman with uterine bleeding. Remember, such a procedure is prescribed only after a series of examinations as prescribed by the attending physician.
- Planned is a control examination to identify problems with the uterine mucosa. It is also prescribed after termination of pregnancy, uterine anomalies and other pathologies associated with reproductive function.
- Therapeutic is carried out during the removal of uncharacteristic tumors on the uterine mucosa. There are also quite a few cases where therapeutic hysteroscopy is prescribed to remove intrauterine devices or their remaining parts. In this case, some violations and consequences may be observed. In particular, we are talking about bleeding after the procedure.
It is important to know: in addition to all of the above, there is gas hysteroscopy, which is performed in case of cervical rupture, since such a pathology is quite large and there is no possibility of creating other conditions to solve it.
During diagnostic and surgical hysteroscopy, complications may develop; they are divided into several types:
- Anesthetic type - due to the anesthetic drugs used, anaphylactic shock is possible.
- A group of complications caused by means for expanding the uterine cavity - most often occur when using carbon dioxide and liquids. Possible heart rhythm disturbances, metabolic acidosis and gas embolism.
- Surgical group of complications – perforation (perforation) of the uterus, bleeding.
It is important to know: immediately after completing the procedure, a woman may feel severe and sharp pain that does not stop for a long time. Do not rush to panic, this is not a sign of any violation. The pain is due to the fact that hysteroscopy is a serious surgical procedure.
How do you feel after the procedure?
Hysteroscopy is a fairly simple and completely painless procedure, but each woman has her own threshold of sensitivity and it is quite difficult to guess what the patient feels during the procedure.
- First of all, the patient is placed on a permanent basis in the inpatient department of the hospital, where the procedure itself will take place.
- Before undergoing the prescribed examination, she must pass all the tests prescribed by the attending physician. This includes: a vaginal smear, as well as a general blood and urine test.
- Next, you will need to see a therapist to identify possible inflammatory processes or diseases of other organs.
After passing all the above points, the patient can be allowed to undergo hysteroscopy (of course, if all indicators are normal).
It is important to know: before starting the procedure, you will definitely need to do an enema and completely empty the bladder of its contents in order to avoid unpleasant surprises during the hysteroscopy process.
So, if all the tests are within normal limits, and the procedure itself was quite useless and successful, then no surprises or consequences should happen. But what to do if something goes wrong? – remember, of course, there is a chance that even if the study is successfully conducted, there may be deviations from the established norm. So, let's take a closer look.
Most often, the cobweb is bothered by indistinct vaginal discharge. There may also be blood, but this will be discussed below. What could be causing the discharge? - you ask. Almost all medical devices can disrupt the integrity of the vagina and cause minor mechanical damage, which can result in various discharges.
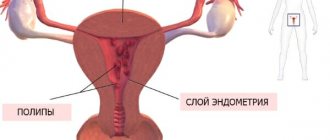
Female genital polyps
Formations of glandular or fibrous epithelial tissue, which, under the influence of disorders, grow on the mucous membranes of organs. They affect the digestive tract, ducts, nasal cavity, ears, and genitourinary system. In the genital area, women distinguish between polyps of the endometrium of the uterus, cervical canal, cervix and vagina. The most common are the first 2 types. Based on the structure and tissue of which the formations are composed, they are divided into several types:
- Glandular - soft, jelly-like is often found in patients of childbearing age.
- Fibrous - dense, on ultrasound it looks lighter than the surrounding elements, consists of connective tissue fibers. Occurs before and during menopause.
- Mixed - contains approximately equal amounts of glandular and fibrous biomaterial.
- Adenomatous - in structure it resembles the first type, but its cells are in an altered state, which may portend degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
- Placental - a growth of pieces of the placenta that has not completely separated. Occurs as a complication after childbirth, abortion, miscarriage.
- A decidual polyp is an excessive growth of the uterine lining during pregnancy.
The pathology is very dangerous, because the first 4 types are prone to malignancy to one degree or another. They also get damaged and bleed. Each formation has its own blood supply. Moreover, it can feed a fairly large vessel or a dense plexus of small ones. As a result of trauma to the growth, blood loss leads to iron deficiency anemia. Polyps often become infected and inflamed.
Attention! One of the negative effects is a mechanical obstacle to conception.
Symptoms of pathology
The clinical picture of polyps of the uterus or cervical canal is of a general nature, similar to other diseases of the female genital area:
- The duration of menstruation increases;
- Menstruation becomes heavy;
- Spotting and spotting occurs on any day of the cycle, after sex;
- With inflammation, purulent leucorrhoea is observed;
- Pain is felt in the lower abdomen and lower back.
Causes of female polyps
The formation of formations is caused by hormonal disorders, which can occur due to endocrine disease, taking corticosteroids or birth control pills, during changes during pregnancy, menopause. But there are other prerequisites:
- Excess weight;
- Childbirth with complications;
- Abortion;
- Immunity problems;
- Infections;
- Heredity.
Are other types of sex possible?
Often, women who have undergone hysteroscopy undergo long courses of treatment before and after it for any disease, or in the fight against infertility. And against this background, recommendations can be given for a long time to abstain from sexual activity. This is where the social question of the precariousness of family life comes into play.
It happens that the spouses of patients are unable to abstain from intimacy for a long period, as a result of which the family idyll begins to shake. Based on considerations of preserving the unit of society, women ask the question: Is not quite traditional sex possible? Hysteroscopy of the uterus is a vaginal operation and does not affect other organs and systems.
Therefore, oral sex after hysteroscopy is not prohibited at all. Reviews from patients who have gone through this claim that attempts at anal sex are also possible. This statement is incorrect. In the first four weeks, any stress on the pelvic organs should be excluded, since an increase in intra-abdominal pressure can be a provoking factor in the development of complications.
Just like any surgical intervention carries a risk of postoperative complications, complications of hysteroscopy can also arise. Of course, in the case of complex and time-consuming hysteroresectoscopy, complications will arise due to difficulties that arose intraoperatively.
Due to the fact that hysteroscopy is an operation, with the penetration of the instrument into the uterine cavity and the impact on the uterine mucosa and the vessels located in it, expanding the cavity of liquid or gas, complications associated with these moments may arise. And also the use of narcotic pain relief can also provoke a deterioration in a woman’s condition, threatening her life and health. Complications can be roughly divided into:
- Surgical;
- Anesthesia;
- Provoked by the environment to expand the uterine cavity;
- Long-term consequences.
Hysteroscopy is dangerous due to perforation of the uterus. This condition can occur when the hysteroscope, already in the uterine cavity, injures the wall of the uterus, partially or completely compromising the integrity of the organ. In cases where the integrity of the uterine wall is compromised, nearby organs to the uterus may also be damaged.
This condition threatens primarily with bleeding from the uterine vessels of the damaged area of the myometrium. And also, possibly, in the presence of a through hole in contact with the abdominal cavity, intestinal trauma, development of intra-abdominal bleeding, and, subsequently, peritonitis.
If the uterus is perforated, the operation is immediately stopped. In this case, the instrument that damaged the uterine wall is not removed, and, most often, a laparotomy is performed (entry into the abdominal cavity through a median approach) in order to inspect all abdominal organs, check the integrity of the organs, eliminate bleeding surgically, by sealing or ligating blood vessels, suturing perforation hole.
There are rare cases when the wall of the uterus is extensively damaged, or bleeding from the formed hole cannot be stopped. In this case, the uterus is removed after hysteroscopy. But these situations are more casuistry, since in any condition there is always a doctor’s struggle for the reproductive organ and full women’s health.
As you know, hysteroscopy is impossible without dilating the uterine cavity with liquid or gas for a better view of all structures. But, the introduction of gas into the uterine cavity can provoke a very serious condition such as a gas embolism. It occurs as a result of gas bubbles entering the lumen of damaged vessels, which, through the blood flow, can enter the vessels of the lungs or heart, thereby disrupting the process of hemodynamics (blood circulation).
This condition is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, shortness of breath, cyanosis (bluish color of the skin). This condition occurs abruptly during surgery and is treated only by anesthesiologists. This is why any operating room contains everything necessary to provide emergency assistance in the event of any complications.
Also, a sharp deterioration in the condition is possible when using liquid during hysteroscopy of the uterus. Complications, in this case, manifest themselves as a result of the absorption of fluid into the bloodstream, the development of pulmonary edema or hypervolemia - overload of the vascular bed. In this situation, diuretics are used to remove excess fluid from the body and resume the functioning of the cardiovascular system. And in case of pulmonary edema, oxygen therapy (oxygen inhalation) is performed.
This type of complication occurs very rarely and the most common cause is individual intolerance to medications, which the patient herself did not know about, since they had not been used by her before. Any other complications are practically excluded from the anesthesiological side.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
When the operation of hysteroscopy or hysteroresectoscopy has taken place, and the rehabilitation period has begun, long-term consequences of its implementation may appear. Synechia may occur after hysteroscopy - the appearance of peculiar adhesions in the uterine cavity, which depend on the individual characteristics of the body, and more often appear in women who have often undergone interventions on the uterus (abortion, curettage).
Inflammation after hysteroscopy is not typical only for this type of operation. Inflammation of the uterine mucosa is possible with any surgical intervention on the uterine cavity, especially when the patient does not take antibiotics properly. This type of complication may have a smell after hysteroscopy (unpleasant-smelling discharge), itching after hysteroscopy, bloating - all those symptoms that can accompany the inflammatory process.
Abstaining from sex as a result of different polyp removal methods
The duration of sexual rest after surgery will depend on the location of the formation, the method of elimination, associated problems and the severity of the case. Therefore, the timing is individual. Below we provide estimated times for different surgical methods.
Curettage or vacuum aspiration
Clinics in small towns do not have modern equipment, so polyps are removed using accessible methods. Both involve complete elimination of the endometrium:
- Scraping. The inner layer of the uterus is removed in stages using a surgical instrument called a curette. Everything happens blindly. There is a high risk of damage to the wall itself and bleeding. In this case, the polyp bed in most cases remains, which leads to relapse after a few months.
- An aspirator is a device that functions like a vacuum cleaner. Under the influence of a vacuum, the endometrium itself separates and comes out along with the polyps. The foundation of education may also remain. There is no risk of bleeding.
Sex after curettage is possible only after complete healing has been achieved. This usually takes about 8 weeks. In any case, a check with a gynecologist is necessary. If, as a result of intimacy, bleeding or pain occurs, then you need to wait another week.
Based on the results of aspiration, they focus on restoring menstruation. At the end of the first, the ban on sex is lifted. Usually your period comes in 3-4 weeks.
Attention! Vacuum and curettage provide a curative effect only in 30% of cases, the remaining 70% result in relapse.
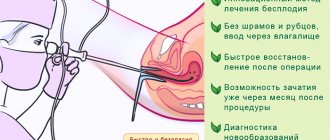
Hysteroscopy
A modern surgical method for manipulations in the uterus, which allows you to act locally and under visual supervision through a video camera. The polyp is eliminated by unscrewing and cauterizing the bed with an electric current. The procedure does not require a hospital stay; everything is done on an outpatient basis under mild general anesthesia. According to patients, they felt almost no discomfort after the procedure. Recovery occurs in a couple of weeks, but sex is allowed after the end of the first menstruation.
The best is laser and radiosurgical removal. The equipment is very rare and expensive, available in large medical institutions and private clinics in metropolitan areas. The advantage is tissue healing in a short time without scarring. The downside is the high cost of the procedure, which amounts to tens of thousands of rubles. Recovery occurs within 7-10 days. After 3-4 weeks, sexual rest may be canceled.
Resection and amputation of organs
Unfortunately, sometimes polyps become an indication for removal of the uterus and cervix. This is practiced for recurrent formations in women whose reproductive period has already ended. After 40, the risk of cancer increases, so removing an organ with polyps is a method of cancer prevention. In rare cases, extensive growths with purulent inflammation occur, in which case hysterectomy is performed at any age.
These are major surgeries that require you to stay in the hospital for some time. Despite the severity of the situation, the recovery period ranges from 1.5 to 2 months, if no complications arise.
Removal of a polyp of the cervical canal
Such an operation involves the surgeon working in a very limited space, there is a high risk of damaging the walls of the cervix. If everything went well, the recovery time is about 6 weeks.
Attention! This area is more exposed to impact during sex than the uterus, so even after rehabilitation, intimacy must be approached with caution.
Polyp removal during pregnancy
If the expectant mother has had the apex of the decidua removed by applying a tourniquet, no healing is required. After 2 weeks, when there are no other contraindications, intimacy is possible.
If uterine polyps of other types are removed during pregnancy, then in most cases sexual rest will be prescribed before childbirth. This is done to reduce all kinds of risks. After the operation, the cervix becomes weak, sometimes it is even necessary to install a pessary. There is still a possibility of recurrence of polyps, premature birth, and infection of the fetus.
Discharge after hysteroscopy
Even despite the fact that hysteroscopy is considered a minimally invasive and less traumatic method of diagnosis and treatment, used in the fight against infertility, uterine polyps, myomatous nodes of submucosal localization, and so on, there is still an intervention in the woman’s body, albeit with partial, but traumatization of genital tissues.
Nature of the discharge
After diagnostic hysteroscopy has already been performed, the discharge after surgery will be bloody in nature. This is due to separate curettage of the uterine cavity, completing the hysteroscopy procedure, in order to obtain histological material. During the process of curettage, a sharp surgical instrument seems to “cut off” the mucous membrane of the uterus, as a result of which the vessels feeding it are also damaged.
As a rule, on the first and second days after surgery, hysteroscopy or hysteroresectoscopy, the discharge is bloody, can be quite abundant, and dark in color. Pink discharge after hysteroscopy of the uterus is typical for the third or fourth day, but it is most likely not completely pink, but streaked with mucus. Further, the discharge from the genital tract becomes lighter and lighter, and, with rare exceptions, contains scanty streaks of the ichor component.
The duration of the discharge depends on its characteristics. If this is bloody discharge after hysteroresectoscopy of an endometrial polyp, for example, then its duration will be about two to three days. Then the bloody discharge is replaced by bloody discharge, which contains blood to a lesser extent, but contains its veins, a component of coagulated blood (but not a clot!).
The presence of discharge in women after an operation such as hysteroscopy, how long the discharge lasts and the nature of its manifestations as described above is the norm. But if the clinical picture does not fit into the norm. There is always a risk of complications during the postoperative period. The postoperative period after hysteroscopy can proceed differently.
In the case when bloody discharge acquires a bright scarlet color, or has the appearance of dark clots, and its intensity and volume increase so that not only personal hygiene products are saturated with the discharge, but also bloody spots appear on the bed, this indicates uterine bleeding, which, urgently needs to be addressed. postoperative period after hysteroscopy
It is also possible that there may be a slight, but long-lasting, bloody discharge - this is also a reason to seek urgent medical help.
There are parameters of discharge that may also indicate a woman’s urgent state. This is a yellow, greenish discharge with an unpleasant odor, but, as a rule, this condition is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen. Such symptoms may suggest the development of endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa and the addition of a secondary infection.
If there is spotting after hysteroscopy. How long does this type of discharge last? This is a frequently asked question. Spotting is typical on the third day after surgery and continues until approximately the seventh day. But if the period of spotting is prolonged, then you should consult your doctor.
It happens that questions are asked: what is the discharge after hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp? Or: how long should the discharge after hysteroscopy with curettage last? The fact is that regardless of the pathological focus that was removed (endometrial polyp, cervical canal polyp, or myomatous node), the nature and period of the discharge does not change.
It’s a different matter when it comes to diagnostic hysteroscopy without curettage. When, during examination with a hysteroscope, a normal endometrium is detected and without pathological structures in other organs of the reproductive system, curettage is not performed. And then, accordingly, there will be fewer discharges, their duration will be reduced. Bloody discharge may also occur after hysteroscopy.
In the case when a diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed without subsequent curettage, the next menstruation will begin on the day planned by the calendar. If separate curettage of the uterine cavity was performed, then the date of menstruation may shift by several days from the date previously calculated by the patient according to the regularity of her menstrual cycle.
In this article, we examined some aspects of the hysteroscopy operation, how long the discharge lasts, its nature, normality and pathology. Discharge is one of the stages of recovery of the body (endometrium to a greater extent) after the intervention. We will look at how exactly endometrial regeneration occurs after hysteroscopy, and what stages it is divided into, in the next article.
Sexual life in the presence of pathology
Is it possible to have sex with polyps in the cervical canal or uterus? There is no direct ban on intimate life. Let's consider the risks associated with sex:
- The formation, which is located partially or completely in the vagina, is mechanically damaged during intercourse, which leads to bleeding.
- The polyp emanating from the body of the uterus through the cervical canal becomes a bridge for bacteria from the outside. If in a normal situation most infections occur only in the vagina, then in such a situation the risk of infection of the upper parts of the reproductive system increases.
- Damaged polyps are easily infected, which is why complications arise. Bacteria multiply not only on mucous membranes, but also enter tissues and the bloodstream.
- A woman feels pain during deep penetration.
Therefore, having sex is not prohibited, but condoms should be used to avoid introducing not only STD pathogens, but also foreign flora. Avoid rough intercourse and positions with deep penetration.
Attention! If blood appears after each sexual intercourse, then it is better to stop intimate life for a while and consult a doctor.
Sex with a polyp during pregnancy
When carrying a child, the decidua protrudes from the opening of the cervix. During sexual intercourse, it is constantly injured, which leads to bleeding. The risk of fetal infection increases. Therefore, measures are taken:
- Sexual rest in case of severe bleeding, followed by application of a tourniquet to the tip of the polyp. The contracted part dries out, and the problem is solved before delivery;
- Condom use;
- Washing the genitals of men and women before sex.
During pregnancy, to be on the safe side, doctors often ban intimate life. But solving the problem in the described way helps to get rid of restrictions.
Time frame for the study
An endometrial biopsy is performed at certain times. Determining the day of the cycle on which material for research is taken depends on the purpose of the biopsy:
- 2-3 days before the onset of menstruation - in case of infertility as a result of insufficiency of the corpus luteum;
- for 8-10 days of menstruation - with heavy and prolonged bleeding;
- 1-2 days after the onset of acyclic bleeding - to determine the cause of the bleeding;
- immediately after the end of menstruation - with uterine polyposis;
- in the period from 17 to 24 days of the menstrual cycle, a study is carried out to determine the sensitivity of this layer to hormones.