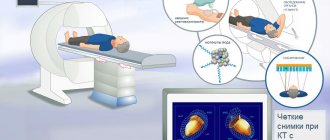
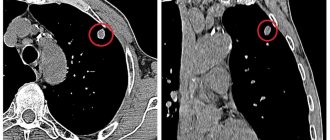
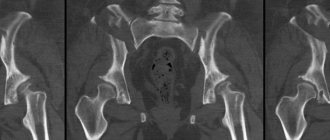
Computed tomography of the temporal bones is performed for adults and children to identify pathological changes and structural anomalies. CT does not require special preparation, and contraindications are minimal.
The temporal bones perform a number of important functions. Arteries, nerve fibers, and a movable upper jaw are attached to them. They serve as a natural protection for the inner ear and the complex vestibular system. Any damage to the temporal bones is fraught with serious consequences, for example, problems with hearing, vision, brain function, and the functioning of blood vessels. For a quick and accurate diagnosis of this area, a CT scan of the temporal bones is prescribed.
The procedure is painless and takes a minimum of time - 5-10 minutes without the use of contrast and up to 30 minutes with the introduction of contrast.
During the examination, a minimal level of x-ray exposure is used, however, repeat tomography can be done at least after 3 weeks.
When is a temporal bone diagnosis prescribed?
Using computed tomography, layer-by-layer images of organs and tissues are obtained with sections less than 1 mm. The objective of the study is to assess the integrity of bone structures and identify the pathological substrate. The method is also important for preoperative assessment.
Neurologists, neurosurgeons and otolaryngologists refer for tomography. Damage to the temporal bones is dangerous for hearing problems, impaired coordination of movements, and internal bleeding. Diagnostics reveals inflammatory, tumor and traumatic pathologies. Indications for CT of the temporal bones:
- headaches, hearing loss without causes identified by other methods;
- purulent discharge, inflammation of the middle ear;
- mastoiditis;
- proliferation of bone tissue in the auditory system;
- dysplasia;
- tumor neoplasms;
- vestibular disorders;
- injuries, fractures;
- liquorrhea;
- examination before implantation of the hearing electrode;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- suspicion of infections that could get from the paranasal sinuses into the inner, middle ear;
- destruction of the temporal bones;
- developmental anomalies.
CT is done in emergency cases or at the final stage of the examination, when other methods have not been effective enough.
Computed tomography is indispensable when examining the part of the temporal bone - the pyramid, where the inner and middle ear are located. Examination of this area involves contrast enhancement.
Indications and contraindications for CT of the temporal bones
Computed tomography is an extremely effective research method that can help identify many diseases. Indications for its implementation are:
- pain symptoms in the temple area of unknown etiology;
- frequent dizziness;
- discharge from the ear;
- a sharp decrease in vision or hearing;
- the presence of neoplasms and metastases;
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
- mechanical damage to bone;
- soft tissue hemorrhage;
- otosclerosis, etc.
Often, CT is used in preparation for an upcoming operation or to evaluate the results after it.
Important! The method has no age restrictions; a CT scan of the temporal bones can be performed on a child or an elderly person if there is a referral from the attending physician.
Contraindications to CT of the temporal bones are:
- pregnancy (undesirable at any stage);
- allergy to the composition of the contrast agent;
- excessive weight of the patient (the maximum permissible weight of the patient when performing CT scans on closed-type equipment is 120-130 kg).
If the patient suffers from mental illness associated with uncontrolled physical activity or fear of confined spaces, a sedative may be used.
Not every clinic has the ability to perform a CT scan of the temporal bones in Moscow. There are even fewer places where the examination and interpretation of the results will be performed professionally. By contacting the Stolitsa network of clinics, you can be confident in the highly qualified doctors and the accuracy of the examination. Take a step towards effective treatment right now!
Pros and cons of the method
CT is an effective examination method for hidden cracks and fractures, as well as for hearing diseases of unknown origin.
Benefits of diagnostics:
- painlessness;
- scanning speed and quick results;
- obtaining three-dimensional images;
- non-invasive;
- informative for injuries of the skull base, temporal bones, paranasal sinuses;
- the radiation dose is lower than with an X-ray machine;
- unlike MRI, it is possible to examine patients with ferromagnetic, electronic implants;
- does not require lengthy preparation;
- minimum contraindications.
Disadvantages of computed tomography include exposure to x-rays.
Technique
During a CT scan, the patient is positioned on a special table, which moves to the main part of the device during the examination. While the tomograph is operating, the medical staff goes into the next room and monitors the work from there.
During the examination, the tomograph will rotate around the patient's head with a slight noise. To accurately focus the radiation on the temporal region, the head should be kept motionless. This will ensure high image accuracy. The patient's head is sometimes secured to the pillow with straps.
The provider may ask you to hold your breath or change your head position.
This should only be done if instructed to do so. Images of the temporal region are performed in at least two projections, sometimes in three:
- frontal - lying on your back or stomach (with holding your breath and no swallowing movements);
- transverse - on the back;
- lateral – rarely performed for ENT diseases.
The contrast agent helps to better visualize soft tissues; its use is indicated for inflammation and abscesses, and suspected vascular problems. It is administered immediately or after plain images without contrast are obtained.
The tomograph has the ability to communicate with personnel. Any discomfort may be reported during the procedure. Upon completion, the doctor checks the quality of the resulting images and their information content. If they allow diagnosis, the procedure is completed.
Contraindications
CT scanning is not performed if the patient’s body weight is more than 120-150 kg (depending on the capabilities of the device).
The use of the method for children under 5 years of age is limited due to the child’s inability to remain still during the procedure and greater sensitivity to radiation. However, it is permissible if there are compelling reasons, there is a risk to life, or it is impossible to make a diagnosis using other methods (ultrasound, MRI).
Computed tomography is contraindicated in pregnant women, as X-rays have a negative effect on the fetus.
Tomography with contrast is contraindicated for:
- intolerance to iodine-containing drugs;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- renal failure;
- multiple myeloma;
- severe diabetes mellitus.
During lactation, a woman should not breastfeed for 3 days after a CT scan.
CT scan of the temporal bones
CT scan of the temporal bones is carried out to study such anatomical structures as the temporal bone, arteries, large nerves and soft tissues of organs responsible for the normal functionality of the auditory, masticatory, and vestibular apparatus. X-ray and ultrasound of this area are not informative methods and diagnosing pathologies can be difficult. Computed tomography will allow you to take layer-by-layer images that are combined by a computer into three-dimensional objects. A layer thickness of several millimeters allows one to obtain accurate, detailed images of even minor pathological changes, and therefore is a highly informative study.
The 32-layer Toshiba Aquilion RXL tomograph, used in the Miracle Doctor clinic, allows for high-quality diagnostic examination, and the level of qualification and experience of radiologists to prepare an objective conclusion, which is included in the price of a CT scan of the temporal bones. Pictures can be recorded on electronic media or sent by e-mail.
When a patient is looking for where to get a CT scan of the temporal bone, as a rule, he is referred by a specialist - a neurologist, otolaryngologist, neurosurgeon, in order to obtain an accurate image of the following structures to clarify the diagnosis after previously performed other examination methods, for inflammation, injuries, tumors according to indications:
- temporal bone injuries;
- inflammatory diseases of the ear;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- progressive hearing loss;
- pathology of the facial nerve;
- identified malignant neoplasms.
Thus, a detailed, ultra-clear 3D image makes it possible to obtain an accurate picture of the anatomy and morphology of the patient’s organs for such conditions and diseases as:
- Hematomas and traumatic injuries of soft tissues and bones;
- Purulent contents between the meninges;
- Signs of arachnoiditis, encephalitis, abscess;
- Developmental anomalies and pathologies of bones and organs of the inner ear;
- Neoplasms.
All these manifestations are helped to identify by the so-called tomography of the temporal bone, in which in fact not only the temporal part of the skull itself, but also such organs and systems as:
- pyramids of the temporal bone;
- cells and antrum of the mastoid process;
- cochlea, vestibule, anterior and posterior semicircular canal;
- auditory ossicles of the middle ear;
- walls of the external auditory canal;
- jugular fossa.
A CT scan of the temporal bones at an adequate price in Moscow can also be performed with the introduction of a contrast agent in order to increase clarity in viewing the soft tissues and vessels of this area. The contrast is carried through the bloodstream throughout the body so that the contours of the smallest pathological changes are very well visualized. A contrast study is prescribed by a specialist after identifying the patient’s possible contraindications to the introduction of an iodine-containing agent into the blood - renal and liver failure, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, individual reaction to iodine preparations. There are also a number of contraindications for CT without contrast - pregnancy, breastfeeding, childhood.
Conducting a CT scan of the temporal bones
The study is carried out by appointment by calling the clinic. The operator helps you choose the optimal time, explains the details of the procedure, preparatory aspects depending on whether the procedure is planned with contrast or not, and guides you by cost.
Before a study with intravenous contrast, you should limit your food intake for 6 hours before the procedure. You can drink clean water without restrictions.
The remaining restrictions relate to foreign bodies on the patient’s body that may affect the reliability of the images - metal jewelry, hearing aids, dentures. They will definitely be asked to remove them.
To avoid involuntary movements during scanning, the head will be secured with a special pillow and straps. The patient lies down on a couch, which slides into the central opening of the scanner while the images are being taken. The scanning progress is monitored by an operator who communicates with the patient via speakerphone. The scanning lasts several minutes and does not bring any sensations to the patient - painless, without discomfort.
CT scanning of the temporal bones with contrast takes more time, as it is performed in 3 stages: without contrast, then the drug is injected and the scan is repeated with a contrast agent.
Conclusion after CT scan of the temporal bones
Taking a CT scan of the temporal bones means not only obtaining images of the required area using a multi-slice tomograph. An experienced radiodiagnostic specialist analyzes the images and describes them, making a conclusion about the identified pathologies, their nature and extent of distribution. Thus, the patient receives a disk with images and a radiologist’s report to provide to the attending physician. Based on the clinical picture and the results of all examinations performed, the attending physician has the right to make a diagnosis.
Despite the fact that CT is a modern type of examination, it is based on the use of X-rays. So CT of the temporal bones is not recommended to be performed more than once a year.
ATTENTION!
CT scans are temporarily not performed for children under 5 years of age. CT scans can be performed in children if the child can lie calm and motionless for 15 minutes.
CT examinations under sedation are temporarily not performed.
Sign up for diagnostics
Preparation for the procedure
For tomography without contrast, no preparatory measures are required. The iodine-containing drug is administered on an empty stomach, with the last meal no later than 6 hours before the examination.
CT with contrast requires a fresh blood test for creatine and urea, reflecting the state of renal filtration. In case of functional disorders, the method is contraindicated.
Two days before the examination, stop taking the diabetes medication - metformin. Using the drug together with the administration of a contrast agent can cause biochemical blood disorders.
Applying Contrast
Sometimes, during a CT scan, an iodinated contrast agent is injected into the patient's cubital vein. The substance makes images clearer and improves visualization of cerebral arteries and veins. It is used in the study of soft tissues, to detect tumors, assess their size and configuration.
CT scan of the temporal bones with contrast
The condition of the bones can be fully assessed without the injection of a contrast agent. It is used to more accurately visualize the structure of soft tissues and blood vessels and determine the location and size of tumors. The substance is administered intravenously, does not harm the patient’s health and leaves the body on its own over the next couple of days. The time of administration of the contrast agent is determined individually: shortly before or during the procedure, after a series of photographs have already been taken.
How to diagnose
During the CT scan, all metal jewelry, removable dentures, and hearing aids are removed. The patient lies on his back on the tomograph table, his head is fixed with a pillow or straps. The surface moves smoothly inside the device.
Medical staff watch from an adjacent room, interacting using a built-in audio communication system. The patient may be required to hold their breath for a short time.
Contrast-enhanced tomography uses an iodinated substance. There are two types of its use: orally, intravenously through a catheter. First, a study without contrast is performed. Then, after the dose of the substance is administered, a second scan is performed.
After obtaining images of the area being examined, the doctor checks the quality of the images. When clear results are obtained, the diagnosis is completed and the patient is allowed to stand up.
Examination time
CT scan lasts no more than 5-10 minutes. With contrast enhancement, the diagnostic time increases to 30 minutes. Formulation of the conclusion takes 30-60 minutes; in complex cases, the period may be extended to 2 days.
Advantages and disadvantages of CT of the temporal bones
The advantages, undoubtedly, include the high accuracy and information content of the method. If necessary, based on the obtained images, you can create a 3D model of the area under study. Carrying out a CT scan of the temporal bones involves the use of X-ray radiation, but its dose is so small that it does not harm the patient’s body. Important positive aspects are also the short duration of the procedure (if contrast is not used, diagnostics can last no more than 5 minutes) and its affordability (the cost of CT is significantly lower than MRI).
As for the disadvantages, the main risks in performing a CT scan are related to the body’s possible reaction to the contrast agent. However, this issue can be resolved by conducting preliminary tests and analyses. In addition, it is not advisable to be exposed to X-ray radiation too often. The exposure dose is small, however, the shortest recommended interval between CT scans should be at least 3 weeks.
CT scan of the temporal bones is often the final diagnostic method, so it should be treated with special attention. Our clinics use only the most modern equipment, and the examination is performed by highly qualified specialists. If you want diagnostics to be truly high-quality, contact Stolitsa!
Decoding the results
The interpretation includes a description of the images obtained during diagnosis and a conclusion regarding the identified pathology.
A CT scan of the temporal bone shows in detail the anatomy of the pyramid, mastoid process, middle and inner ear, and jugular cavity. The data is deciphered by a radiology doctor.
Based on the images obtained, the following is revealed:
- chronic, acute otitis;
- hemorrhages;
- purulent accumulations;
- hidden fractures and cracks;
- mastoiditis, otosclerosis;
- soft tissue injuries;
- development of tumors and infections.
The diagnostic results are given to the patient in the form of a sheet with images and a conclusion. Data can be recorded on external electronic media (disk or flash drive).
Norm
It is important to remember that a CT scan is not a definitive diagnosis. Only a comprehensive examination using instrumental and laboratory methods, taking into account the clinical picture, will allow the attending physician to establish the disease and choose the tactics for managing the patient.
What can a CT scan of the temporal lobes show?
When a computed tomography scan of the temporal region is performed, the image specialist analyzes the appearance of the skull bones, the condition of the middle and inner ear, the pyramids and mastoid process, and the auditory canal. Based on the footage, the doctor can identify:
- Chronic or acute otitis media.
- Abscess.
- Development of infection.
- Otosclerosis and mastoiditis, as well as other modifications of the temporal bones.
- Presence of tumors.
- Fractures, bone cracks.
- Soft tissue injuries.
- Hemorrhages.
The structure of the pyramids of the temporal bones, the presence of neuromas and tumors, the causes of discharge from the ears, the abnormal structure - this is what tomography shows when studying this area. If there are internal injuries, the procedure will reveal areas of fresh bleeding.
Depending on the contrast or non-contrast method, CT diagnostics takes 10-30 minutes. Transcription lasts less than 1 hour.
Risk assessment
With contrast-enhanced tomography, allergic reactions, side symptoms from the kidneys, dizziness, and nausea are possible. One of the possible complications is thyrotoxic crisis, which occurs 5-6 weeks after diagnosis. Occurs with latent hyperthyroidism.
Frequent use of CT scans increases the likelihood of developing cancer. The risk can be reduced by limiting the radiation dose.
How often can CT scans be done?
This examination uses x-rays. This imposes restrictions on the permissible frequency of diagnostics. It is recommended to use CT no more than once a year. If there are strong indications, the procedure can be repeated after 6 months.
Regimen after CT
After tomography with contrast, it is recommended to drink 2-3 liters of liquid per day to quickly eliminate iodine-containing substances. When taking metformin, therapy is resumed two days after the procedure.
When is the examination scheduled?
CT in the treatment of ear diseases is required in complex cases when it is not possible to establish a diagnosis in any other way. It is prescribed in the following cases:
- suspicion of tumors and abscesses;
- injuries to the ear and temporal region;
- dizziness;
- restrictions on the mobility of the upper jaw;
- chronic otitis;
- pain of unknown etiology;
- purulent discharge from the ear canal;
- before surgery;
- with long-term infectious diseases of the ear;
- deterioration, hearing loss - sensorineural, conductive or mixed type;
- suspicion of structural anomalies;
- degenerative changes in bone tissue.
See also
Symptoms of ear otosclerosis, treatment with and without surgery, folk remedies, prognosis
Read
The study is also prescribed when a diagnosis is made, when treatment does not have an effect, and clarification of the state of internal structures and their response to therapy is required.
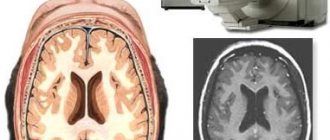
Comparison of CT and MRI
An alternative method for diagnosing the temporal bones is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Externally, the devices are similar, but unlike computed tomography, MRI does not use X-rays and does not irradiate the patient. Therefore, the method is used during pregnancy.
In both cases, a three-dimensional image is created with the ability to examine layer-by-layer sections of the organ. The differences lie in the identification of specific pathologies.
CT is more informative for bone injuries, brain damage, and fresh hemorrhages. Bone tissue is capable of absorbing X-rays well, resulting in clear images.
Computed tomography is useful in diagnosing hidden fractures and cracks. MRI provides a more complete picture when identifying tumors and soft tissue pathologies. Therefore, CT is often used in emergency diagnostics, and MRI is often used in outpatient treatment.
MRI is based on the influence of a magnetic field; examination is impossible if there are metal structures in the body: hearing implants, cardiac neurostimulators, clipped vessels, prostheses. There are no such restrictions for computed tomography.
MRI image
The time of the procedure also differs: 5 minutes for CT, 40-60 for MRI.
The difference between MSCT and conventional CT
Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) is a type of CT performed on high-speed tomographs with multiple detectors. Thanks to the method, more accurate two-dimensional and three-dimensional images are obtained.
MSCT reduces examination time and reduces radiation exposure by 30-40%.
The latest generation equipment allows you to obtain images and show physiological processes in real time.
HOW DO YOU DO IT?
The patient is placed on a couch, which is then placed in the cylindrical tunnel of the tomograph so that the patient's head is inside the tunnel. The examination lasts about 25 minutes. If contrast is performed, this time increases to 45 minutes.
During the entire procedure, the patient must remain motionless, since the clarity of the images depends on this. If necessary, the patient's head can also be fixed with special soft rollers. Due to the complexity of the study, the results of the examination with a transcript from the doctor are usually given to the patient the next day, and for emergency indications - within an hour. In conclusion, the doctor describes in detail the detected pathologies and makes recommendations. With the results, the patient can subsequently contact his attending physician, who referred him for an MRI, or a specialist recommended by the doctor.
The MRI scan images are recorded on a CD and given to the patient.
Temporal bone MRI price
depends on the reputation of the clinic and the equipment used during the examination.
CT or MRI, which is better?
It is not entirely correct to compare these methods with each other, since they are based on different principles of image acquisition. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. The doctor decides whether to send the patient for a CT or MRI based on the purpose of the examination.
If we consider the difference between CT and MRI, then for comparison it is necessary to take the following factors:
Device capabilities
. MRI scans best soft tissue, ideal for assessing the condition of the muscles, ligaments, and tendons around the shoulder joint. CT most accurately demonstrates bone tissue. If a fracture, arthritis or bone tumor is suspected, it is better to entrust the diagnosis to a computed tomography scan. The device is capable of constructing a 3D projection of the joint based on the data obtained during scanning.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you may need to use both methods.
Duration of the procedure
. For a computed tomography scan, it only takes 1-2 minutes. Scanning using magnetic waves will require the patient to remain motionless for 15 to 30 minutes.
Harmfulness
. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner has no restrictions on the number of examinations, since it emits impulses that are less harmful to the body than X-rays. A CT scan, on the other hand, is based on X-rays and cannot be performed on a single patient more than twice a year.
A visual demonstration of the capabilities of CT and MRI devices:
| CT | MRI of temporal bones |
CT allows you to build 3D models:
| 3D model |
Advantages of the method and possible risks
This diagnostic method has several advantages:
- obtaining 3D images and volumetric reconstruction (allows you to enlarge images without losing quality);
- high information content;
- small dose of radiation;
- speed (the procedure can take only a few minutes);
- low cost.
Despite the positive aspects of computed tomography, this technique carries certain risks:
• cumulative effect of radiation (if you are often subjected to such diagnostics);
• allergic reaction (occurs in 2-4 patients out of 100).
How much does the procedure cost?
- On average, the price of a CT scan of the temporal bones in Moscow is 3500-5000 rubles.
- The cost of a less informative x-ray examination is 1500-2000 rubles.
- MSCT will cost an average of 5-6 thousand rubles, and MRI 4000-5000 rubles.
Computed tomography of the temporal bones is a very informative examination, and in comparison with other alternative methods it is also attractive in price (not counting x-rays, which provide less information). Pathologies of the temporal bones can negatively affect the organs of hearing, vision, and brain, so if alarming symptoms appear, it is necessary to carefully check their cause.