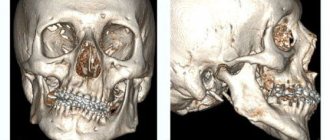
Before tooth extraction or dental surgery, the doctor sends the patient to take a panoramic photograph of the teeth or an orthopantomogram (OPTG). This is an image of the bone and soft tissue of the dental system, using it, the doctor can determine the condition of the dentition, periosteum, and identify the true cause of the disease. The method is very useful, since external examination provides only 50% information.
What does an orthopanoramic photo show?
An OPTG image of teeth gives a clear picture of the condition of the roots of the teeth and periosteum, which is convenient for carrying out a complete diagnosis and treatment.
Caries in a panoramic photo
Using a panoramic photo you can identify:
- carious lesions hidden from view;
- tumors, cysts, granulomas;
- pathologies of the root system;
- lesions of the peri-root space;
- condition of crowns and fillings;
- cracks, fractures, atrophic processes;
- horizontal and unerupted wisdom teeth;
- depth of gum pockets;
- congenital pathologies.
A panoramic photograph of the jaw is an image produced by a digital camera. It can be printed as a photograph, viewed on a monitor, and even sent to colleagues via the Internet.
Forensic (forensic) photography
Forensic photography is one of the branches of forensic technology. The development of forensic photography is based on the scientific foundations of general photography. In modern literature, the term “forensic photography” is used, emphasizing the forensic aspect of using this recording method. The name “Forensic Photography” remains traditional, which reflects the final result of its application: consideration, research, evaluation of photographic images by the court.
Thus, the subject of forensic photography is a scientifically developed system of types, methods and techniques of photography used during investigative actions, operational activities and forensic examinations for the purpose of investigating crimes and presenting visual evidence to the court.
Forensic photography consists of two parts: investigative photography (capturing) and expert photography (investigating).
Forensic significance of the use of photography
The forensic significance of using photography is that it allows:
- when conducting investigative actions, record (capture) objects, their details and circumstances related to the event under investigation;
- when carrying out operational investigative actions, obtain information about the criminal and the criminal actions he commits;
- when conducting examinations related to criminal cases, capture the general appearance of material evidence received for examination, identify invisible and low-visibility signs, obtain images of the objects under study to identify them and illustrate conclusions.
Types, methods and techniques of investigative (capturing) photography
For the subsequent classification of investigative photography, the following bases were chosen: by object (type) of shooting; by method (method) of shooting; according to the purpose of the forensic photograph (photography techniques).
The type of investigative photography includes objects that fall into the orbit of the investigation, and the investigative actions themselves.
Investigative photography methods are practical activities in the recording of investigative actions, objects and traces.
Shooting techniques are the recording of a certain amount of information in a photograph to solve investigative and tactical problems.
Thus, investigative photography is a scientifically developed system of types, techniques, and photographic methods used in the process of preliminary investigation to capture material data of evidentiary value and to examine material evidence for operational purposes.
Types of investigative photography:
- recording of individual investigative actions: inspection of the scene of an incident, investigative experiment, presentation of persons or objects for identification, photographing during a search, etc.
- photography of living persons and corpses;
- photography of individual objects, footprints (shoes), hands, vehicles, tools, tools, etc.;
- photographing documents and other objects that came into the orbit of the investigation.
Investigative Photography Techniques
When conducting forensic operational photography, the investigator captures objects from one, two or several points.
The main focus when photographing from one point is to ensure that there are no perspective distortions, and that the objects themselves look the way we usually perceive them in reality.
When photographing from two opposite points, the following rules must be observed: the object (area) being photographed must be located on the same imaginary line, the distance from the central object (or group) to the person photographing must be equal, when shooting on the ground, the angle of inclination to the photographed object must be the same.
Photography from four points involves almost the same rules as shooting from two opposite points. Only one more direction is added, and in fact the shooting is carried out along the diagonals of a square or rectangle. Therefore, such shooting is sometimes called “envelope shooting.”
Panoramic photography (photography) is a method of obtaining a photograph with a changed ratio between the sides of the photo frame by increasing its length (the panorama can be horizontal, vertical and oblique).
The panorama can be circular or linear. The first type will be a sector panorama. A circular and sector panorama is taken from one point by turning the camera (if necessary, capture objects and the surrounding area) (Fig. 11.1). Linear panorama - by moving the camera along the object being photographed, while the distance to the photographed object must be constant, and the optical axis must be perpendicular to the plane of the object (Fig. 11.2).
Rice. 11.1. Scheme of sectoral panoramic shooting
Rice. 11.2. Scheme of linear panoramic shooting
In order to avoid unfixed areas of the object in photographs, it is necessary to “overlap” one frame with another by approximately 10% when shooting. It is recommended to shoot a flat image using a linear panorama. A sector panorama is more convenient, for example, for shooting a road turn, when the camera is positioned at one point inside this turn. Stereoscopic photography makes it possible to capture a section of terrain with three-dimensional objects (or individual complex objects), i.e. the way we actually see them with both eyes.
Measuring photography makes it possible to determine the actual dimensions of objects and traces from a photograph.
Measuring photography with a scale bar (scale photography) (Fig. 11.3). The basis of this method is to obtain a scale in the form of a ruler in a photograph directly with the object. When shooting, it is necessary to set the scale in the plane of the object being photographed. The plane of the film in the camera must be parallel to the plane of the trace, and the optical axis is perpendicular to the plane of the trace and passes through its center. The scale bar is located in the frame “on the edge”, with millimeter divisions towards the object.
Identification photograph (signalistic). When photographing living faces, the photograph is taken at 1/7 life size. The right profile, full face and 3/4 from the left are photographed. If necessary, the person is photographed in full length in the clothes in which he was detained, etc. Signal photographs are made 6x9 cm in size and pasted onto one photo table side by side, with a “profile” photograph on the left, 3/4 on the right
During hygienic photography of a corpse , which is carried out for its subsequent identification or registration, in the event
if it was not possible to establish the identity, the photograph is taken on the table (since this, as a rule, happens in the morgue), and a half-length portrait is made in 1/7 life-size. The right profile, 3/4 from the right, full face, 3/4 from the left, left profile are photographed. If necessary, before photographing, the corpse is toileted (this does not exclude the obligatory shooting with damage, i.e. in the form in which the corpse was found). It is unacceptable (if it is not known what clothes the corpse was found in) to dress it in anything random. Lighting should not create deep shadows or distort the appearance of the corpse.
For all types of signal photography, it is necessary that hair does not cover the auricle and photography is carried out without a headdress. The exception is when photographing a detained person, when he is photographed in the clothes in which he was detained.
Macro photography is the photography of forensic objects in life size or with magnification (usually no more than 10-20 times). Macro photography can be done with stationary long-focus cameras, or with conventional cameras using extension attachment rings.
Extension rings are screwed onto the camera in place of the lens, and a standard lens is screwed into them. The set has three rings of different heights (8, 16, 25 mm), and thus in total you can get an additional focal length, i.e. convert a stock lens from 50mm to 100mm.
Rice. 11.3. Large-scale photograph of the cartridge case
Color photography is a method of capturing forensic objects in a color image. One of the main requirements when conducting color photography during the preliminary investigation and in expert practice is the use of a neutral gray scale (can be in the form of a ruler or circle), which is photographed next to a colored object, and taking into account the contrast of forensic objects, which are photographed using color photographic materials .
Digital photography (Fig. 11.4) is a method of recording forensic objects in which the photochemical processes of obtaining an image are replaced by electromagnetic ones. However, the quality of digital photography is still lower than conventional 35mm photography.
Rice. 11.4. Forensic Digital Photography Kit
Investigative photography techniques. Based on the amount of information captured in photographs, they can be classified into orientation, overview, focal and detailed.
Orienting photographs contain an image of the scene of the incident and the adjacent area (Fig. 11.5). These photographs make it possible to understand the position of the scene of the incident among the surrounding objects, as if to navigate the area.
Survey photographs are photographs that directly depict the scene of the incident (Fig. 11.6). The boundaries of the photograph should approximately coincide with the boundaries of the scene of the incident.
Rice. 11.5. Orientation photo
Nodal photography is the recording of a group of objects, individual objects or traces at the scene of an incident that are most important for the crime under investigation (Fig. 11.7).
Rice. 11.7. Knot photography
Rice. 11.8. Detail photo
Detailed photography is the recording of individual (usually small) objects or traces on these objects, i.e. This is a capture of the details of the situation at the scene of the incident (Fig. 11.8).
Rice. 11.6. Sightseeing photo
Types, methods and techniques of expert (research) photography
Expert photography as a scientifically developed system of types and photographic methods used in forensic examinations for the purpose of capturing objects, traces and individual signs for their comparison during the study, illustrating the expert’s conclusion, as well as for identifying invisible and weakly visible signs.
Many objects that appear in investigative photography, methods, and techniques are also used in expert photography. But there are also specific ones that are characteristic only of expert photography.
When conducting examinations, the following photographic methods may be used:
Microphotography is a method of obtaining a photograph using a microscope connected to a camera or using special microphoto installations.
Contrasting, color separation photography (increasing contrast). The main task is to separate objects that are very similar in color in order to identify objects, differentiate them and analyze them.
Color bleeding is a photographic separation from the background and transformation of a faintly visible (or invisible) difference in shades (colors) of the original into a brighter, visible one.
Colour contrast. Primary amplification is carried out by selecting light filters and lighting sources. To weaken the positive color of the image, a light filter of the same color that needs to be weakened is used, and to enhance it, a filter of an additional color is used. To weaken color contrast, materials that are sensitive to a given color are needed; to enhance it, on the contrary, materials that are insensitive to a given color are needed.
Shooting under special lighting conditions. Basically, this is the identification of a relief surface using shadow photography and the identification of colorless spots, traces, strokes, etc. due to specular or diffuse reflection (shooting reflective traces).
Photography in infrared and ultraviolet moons. Photography in ultraviolet rays using ultraviolet illuminators "OLD-41", "Tair-2" will allow you to identify and photograph with a conventional camera on ordinary black-and-white photographic materials traces of etching, inhomogeneous document materials and inhomogeneous dyes (which under ordinary lighting are perceived as homogeneous), foreign fibers, stains, etc.
Through the action of infrared rays, for example, their penetration through “flooded” texts, these texts can be captured when photographed through an electron-optical converter.
X-ray radiography. This is a method of obtaining an image by shining an object with X-ray, gamma and beta rays. This shooting method is used to study the internal structure and condition of the combat parts of firearms, parts of locks (hard short-wave x-rays); identifying texts written with invisible ink containing salts of heavy metals.
In spectrography, special (spectral) photographic plates with high resolution are used to photograph the results of spectral analysis.
Color photography when conducting expert research is used in cases where color is an illustration of the research process, identifying and recording an invisible color image, and an illustration of the results achieved by the expert.
Holographic shooting methods are currently used both for recording and studying forensic objects. If a laser beam is directed at the developed hologram, a three-dimensional image of the fixed object appears in space, containing complete information about it.
The most widely used holographic methods are now used in the forensic study of documents to distinguish the strokes of graphite pencils, blue carbon copies, black and blue ink through color separation photography, as well as to read filled-in, crossed-out, smeared notes and prints, restore etched, faded, washed-out texts, identify additions and other changes in documents through laser luminescence.
Thus, the purpose of expert photography can be determined by the tasks it solves: illustration of the comparative research being carried out, identification of the invisible and invisible, visual confirmation of the expert’s conclusion with photographs.
Procedural consolidation and registration of photographs during the investigation of crimes
The results of photography can be used in a criminal case only if they are properly documented.
The protocols of investigative actions during which photography was used must reflect the following information:
- the use of photographic means (type of device, type of lens, brand of filter, photographic material used, illuminants, etc.);
- photographic objects;
- conditions, procedure and methods of photographing, nature of lighting, time of shooting, indication on the plan or diagram of the scene of the incident, shooting points;
- about the results obtained (when required).
Photographs attached to the protocol should be presented in the form of photo tables. Under each photo you must put a number and give a brief explanatory note. Each photograph is sealed with the seal of the investigative agency (in this case, one part of the seal impression is located on the edge of the photograph, and the other on the table paper). Photo tables must have headings that indicate the protocol of which investigative action they are attached to and the date of its implementation. To confirm the authenticity of the photographs, they are certified by the signature of the investigator and the person who took the photograph (if possible, with the signatures of witnesses and participants in investigative actions).
Photo tables (and negatives in a bag with a similar explanatory inscription) as appendices to the protocol are filed in criminal cases along with the protocol of the investigative action. The use of photography in forensic examination is indicated in the research part of the expert’s report, which also indicates the type of photography and its main conditions.
Photographs attached to the expert’s report are also presented in the form of photo tables. A short explanatory caption is given under each photo.
Scientific Foundations of Photography
Photography (from the Greek photos - light, grapho - I draw, write, i.e. drawing with light, light painting) is a set of methods for obtaining time-stable images of objects on photosensitive layers, by fixing in them photochemical changes that occur under the influence of light radiation emitted or reflected by an object. The photographic process is based on the proposition that only those rays can chemically act on a substance that are absorbed by this substance, and this proposition has become the basic law of photochemistry. The first photographic method of obtaining a high-quality image on silver salts, which was of practical importance, was invented by the Frenchman L. Daguerre in 1837. The birthday of modern photography is January 7, 1839, when D. Arago reported at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences on a new method for recording light images on photosensitive material. In honor of the author of the invention, it was called “daguerreotype”. Modern photography is based on the classical method of obtaining a light image on a photosensitive layer, the basis of which is halogen silver (the most common is silver bromide), suspended in gelatin. It is this compound that has the ability to accumulate light radiation, and then, when developed, turn it into a visible image, increasing the sensitivity of perception tens of thousands of times. The principle of obtaining a photographic image can be schematically represented as follows: light reflected from an object and carrying information about it passes through the camera lens into a light-proof camera and is then projected and accumulated on a photosensitive layer of photographic material.
The photographic process goes through the following stages: exposure (photography); negative process; positive process.
In the negative process, the latent image that appears in the photosensitive layer of the photographic material during shooting turns into a visible image - a negative, in which the blackening is the opposite of the brightness of the details of the object. A positive process is a set of operations as a result of which a positive image is obtained from a negative, the brightness ratio of which corresponds to the brightness ratio of the subject being photographed.
0
Author of the publication
offline 51 minutes
Forensics.ru
1 004
Site administration
Comments: 1Publications: 9619Registration: 05/24/2020
When to refer for OPTG
An orthopantomogram or panoramic photograph of the teeth is done in the following cases:
- before root removal in order to prevent complications;
- in the treatment of periodontal disease to determine the disease group;
- when diagnosing jaw tumors;
- with flux;
- in orthopedic practice, for example, when you need to install braces;
- in case of traumatic injury to the jaw;
- with diagnoses of unknown etiology.
An x-ray helps the orthodontist assess the condition of the skeletal and muscular system of the oral cavity and carry out timely treatment if any abnormalities are detected. And also examine the maxillary sinuses for sinusitis and sinusitis.
X-rays are indicated before tooth extraction, since the roots and the condition of the gums behind the teeth can be seen on the film. Timely detection of pathology will help to avoid complications, so teeth should not be pulled out without a preliminary panoramic image, especially wisdom teeth.
Dental materials contain a composition that stands out in contrast when photographed. This is done so that the shape of the filling material can be tracked. A photograph of a tooth on film helps you choose the right treatment and allows you to get a complete picture of the condition of the mandibular canal, maxillary sinuses and nasal passages. The doctor has the opportunity to determine the position of the nasal septum. If it is curved, then there is a high probability of chronic or allergic rhinosinusitis.
OPG gives a clear picture of the condition of the patient’s dental system. Therefore, it is necessary for high-quality diagnosis of diseases. During long-term treatment, OPTG is done several times to monitor the healing process.
What is this procedure?
OPTG otherwise stands for “panoramic photograph of the dental system.” This is a type of radiography used during the diagnostic phase. In dentistry, diagnostic studies are given great importance, since only a high-quality photograph of the teeth will allow a correct diagnosis and treatment planning.
An orthopantomogram is performed using a beam source and its receiver. Focusing occurs on a limited part of the object that needs to be studied. By setting certain settings, the specialist receives a very clear picture of exactly the area that interests him at the moment.
Executing the procedure
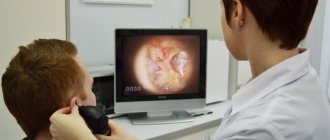
It is in vain that patients are frightened when they hear that they are being sent to take a panoramic photograph. This completely painless and quick procedure is much safer than x-rays. A digital orthopantomogram is performed within 30 seconds; after 5 minutes the image on film will be ready.
There are no problems with orthopantomograms in large cities, since modern dental clinics are equipped with the necessary equipment. However, its high cost makes the examination inaccessible in small settlements, so many patients are still unable to undergo an orthopantomogram to fully diagnose the disease.
To obtain a tomogram, the patient needs:
- free your head and neck from all metal objects and jewelry;
- position yourself inside the orthopantomograph;
- put on an apron;
- hold a plastic tube in your mouth with your lips closed;
- grasp the handles of the orthopantomograph;
- fix the pose for a while.
The device makes a circular revolution around the patient's head and displays the finished image on the screen. In just a few minutes you can receive a printed photo.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of OPTG compared to conventional x-ray:
- The radiation dose is reduced by 70-90% (no more than 0.02 mSv). When compared, for example, with fluorography, the latter puts ten times more stress on the body
- Obtaining information about the teeth of two jaws at once
- Undistorted, clear image
- Ability to enlarge the desired area on the computer screen
- This method can be used even during pregnancy in the second trimester and during breastfeeding
- X-ray examination is safe, therefore it can be prescribed to persons with developmental disorders and the elderly
- The accuracy of the study allows you to stop the development of the disease at the initial stage
- Complete absence of discomfort
- Diagnosis of pain with localization unknown to the patient
- Diagnosis of tumors, cysts, i.e. asymptomatic diseases
- Saving time for doctor and patient – the process is quick and uncomplicated
- Fixation of the patient's head in accordance with his anatomical features, which avoids human movements and blurring of the image
- OPTG can be performed in patients with disabilities and children
- A digital panoramic image can be sent via the Internet to any city or country as needed
- The resulting panoramic image can be stored in computer memory, on a flash drive, disk or other removable media
- Usually the laboratory assistant also prints out a picture of the jaws on paper
Disadvantages of an orthopantomogram:
- Risk of undergoing the procedure for women during pregnancy, especially in the 1st trimester
- The radiation dose, although small, is still not useful, and is equal to approximately a two-hour flight in an airplane
- The image is flat and therefore does not provide accurate information about the shape and size of various anatomical structures
- If there are “Soviet” type metal prostheses in the mouth, the OPTG procedure is contraindicated
Main advantages of the procedure
Dental orthopantomography has many advantages:
- High level of safety: the irradiation dose is much less than with radiography, which allows you to take pictures multiple times. The procedure is harmless for children and the elderly.
- Quickly obtain the final result.
- Possibility of transmitting images via the Internet.
- The quality of the image makes it possible to detect the disease in the early stages of development.
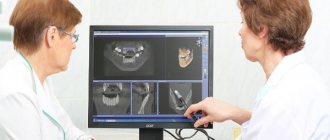
- Viewing on the monitor makes it easier for the doctor to diagnose and treat: the orthopanoramic image can be enlarged for a detailed examination of individual areas.
- The adjustable height of the emitter helps to adapt the device to any patient, be it a child or a disabled person in a wheelchair.
How does the procedure work?
To get a picture of the jaw, which is called “panoramic,” the patient needs to carefully listen to the doctor’s instructions: stand next to the device and tightly wrap your lips around a special tube. You need to stand still so that the data received is as informative as possible. This is not difficult to do, because it will take no more than 1-2 minutes to remain motionless and not move your head (during this time, a sensor producing X-ray rays will rotate around your head). Then the doctor will get down to business, who will need about 10 more minutes to process the data using a computer program.
The photo shows the OPTG procedure
Some disadvantages
Indications for orthopantomography have some limitations. Pregnant women are not recommended to undergo the procedure, like any other x-ray examination. Restrictions are also imposed on nursing mothers. In early infancy, only an orthodontist can send you for OPG.
The procedure is also contraindicated for people with severe diabetes, thyroid diseases, kidney failure, allergies to iodine, and epilepsy.
Usually the clinic doctor conducts a survey to determine the presence of any contraindications. If this does not happen, the patient must report health problems independently.
Indications for orthopantomogram
An orthopantomogram is almost always needed. Without it, it is impossible to carry out competent surgical, orthodontic, periodontal, endodontic treatment, implantation and prosthetics.
Important! You should not completely rely on the results of an x-ray examination. Due to the fact that three-dimensional objects are transferred to a two-dimensional plane, distortions are possible. It should be supplemented with other diagnostic methods.
The doctor prescribes a dental x-ray if:
- Supernumerary teeth.
- Full or partial edentia.
- Delay in eruption of milk or permanent units.
- Bite pathologies.
- Periodontal and periodontal diseases.
- Root canal treatment.
- Removal of teeth, especially complex and extreme ones - eights.
- Before prosthetics, implantation, sinus lift and other surgical interventions.
- Jaw injuries.
An orthopantomogram also allows you to assess the quality of treatment, both during therapy and at its end.
Interpretation of the orthopantomogram
OPTG in dentistry is an opportunity to diagnose areas of the oral cavity hidden from view: tooth roots, gum tissue. The doctor, looking at an overview image of the teeth, will immediately determine the condition of the roots and jaw of the patient, detect pathology and, based on the result, prescribe the correct treatment. Panoramic photography is invaluable for orthodontics, as it simplifies the diagnosis of many dental diseases.
For the average patient, a panoramic image is a complete mystery, but it can be deciphered. OPTG decoding is not that difficult. First you need to pay attention to the image on the film: the jaw should have a “laughing” appearance. If the dentition looks like a sad smile, this indicates a poor-quality image; looking at it, it is unlikely that it will be possible to correctly diagnose the disease.
An orthopantomogram shows an image of the jaw, but not in mirror image. It must be considered as belonging to another person. This means that the image of the left side will be on the right, and the right side will be on the left.
The classification of dentition is deciphered in the form of numbering, but not the usual one. The fact is that the dentition in the picture is divided into four segments. The upper right are tens, the upper left are twenties, the thirty are lower left, the forties are lower right. Numbering begins with the central incisors. The upper right central incisor is numbered 11. The wisdom tooth in the lower right row is numbered 48. Having mastered this wisdom, you can pleasantly surprise the doctor by mentioning numbering.
Safety and radiation exposure –
There are a lot of untruths written on the Internet regarding X-ray examinations in dentistry. You may find that such a picture can be taken only once a year; on other sites they say that it can be taken even once a day. All this happens because most “dental” sites on the Internet are written not by dentists, but by ordinary programmers for the purpose of placing advertising on their site.
Radiation exposure is measured in microsieverts (µSv) or millisieverts (mSv). According to the Ministry of Health of Russia dated December 21, 2012, the radiation dose when performing 1 orthopantomogram for a patient over 15 years old should be 55 μSv (=0.055 mSv), and for a patient under 15 years old – 24 μSv (=0.024 mSv). The indicated radiation doses are given only by digital orthopantomographs; the radiation exposure of film devices will be higher.
Conclusions: the maximum permissible radiation dose for the population (according to SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03) is a dose not exceeding 1000 μSv per year. Thus, you should not take such a picture more than once a month, because... You must take into account that the body is also affected by normal background radiation.
Risks when performing an orthopantomogram –
X-ray irradiation has a more negative effect on a weakened body, especially if such studies are repeated.
Even a small dose of radiation can stimulate genetic disorders and the appearance of malignant tumors. In children, the risks are always higher, because Children's bodies have increased radiosensitivity. Therefore, in no case should you exceed the permissible radiation dosages that we described above. When contacting a clinic, you should definitely ask what type of orthopantomograph is installed in this clinic, and what radiation exposure will be received for 1 image. The fact is that clinics often purchase equipment that is outdated in Europe, and the radiation exposure from outdated models can be 2-3 times higher - from the recommended radiation dose of 55 μSv, normally received for 1 panoramic image.
According to the medical literature, a rough estimate of the risk of malignant oncology after an orthopantomogram is 1 case in 20,000,000, for children aged 1 to 10 years - 1 case in 10,000,000. In general, these are very low rates (compared to many other types of X-rays), although they also seem dangerous.
Comparison of the radiation exposure of an orthopantomograph with targeted images - the radiation exposure from targeted images will be much less, and in 1 day of treatment you can safely take 4-5 such images, but no more than 100 images per year. The usual radiation dose for 1 digital intraoral dental x-ray will be (if modern rather than outdated equipment is used):
- lower jaw – 2.0 µSv (patients under 15 years old – 1.0 µSv),
- upper jaw – 5.0 µSv (patients under 15 years old – 3.0 µSv).
Postoperative OPTG
In modern dental clinics, a panoramic photograph of the jaw is taken both before and after surgery. In the first case, it is necessary to obtain information about the condition of the jaws and select the optimal treatment method, and in the postoperative period - to monitor the healing process.
Thanks to the overview image, the dentist monitors changes in the patient’s health, notes improvements, and prevents complications in the healing process.
The cost of an X-ray examination is low; for example, in Moscow it will cost about 1 thousand rubles.
Advantages of OPTG
A panoramic image not only makes the specialist’s work easier, but also increases the effectiveness of treatment. This type of diagnostics has many advantages, among which are the following.
- An image is taken very quickly using a digital camera, which reduces exposure time. The reduction in radiation exposure reaches almost 90%.
- Modern equipment allows you to instantly obtain an accurate image of your teeth, ensuring that you do not have to undergo repeated irradiation.
- The doctor can examine each area of interest in more detail, enlarging it using software.
- There are practically no contraindications.
- Improving the quality of treatment by obtaining the most accurate data.
- The procedure is completely painless, does not cause discomfort and is safe for the patient. The photo can be taken by anyone, except pregnant women.
- The doctor has the opportunity to store all received data in the form of an electronic archive, having constant access to the information that interests him. This simplifies control over the progress of treatment and allows you to compare the state of the bite “before and after” as it is corrected.
An orthopantomogram is one of the most advanced diagnostic methods, showing the most accurate data. This advantage allows you to more competently plan and carry out treatment, obtaining better results, while a regular dental photograph provides rather vague data. What seems like an incomprehensible image to us is a complete picture for a specialist, telling him about your characteristics, the condition of your teeth, their location, the passage of nerves and much more.
We have told you in sufficient detail about this procedure. But if you have been prescribed an orthopantomogram at the dentist, and you would like to learn even more about it, then we bring to your attention an interesting video. After looking at it, you will understand how diagnostics are made, what the specialist sees in the image, how he analyzes the information and based on what he draws conclusions.
Preparing for a panoramic dental photograph
The procedure does not require special preparation. You can consume drinks, food and medicine - this will not affect the x-ray in any way. Immediately before the procedure, metal jewelry must be removed from the body. It is not recommended to drink alcohol.
When visiting a dentist, you must take panoramic and x-ray photographs from the last few years, as well as a medical history. With their help, the doctor will be able to track visible changes in the patient’s health status or compare treatment results.
X-ray radiation poses a possible risk to pregnant women. According to some studies, it can negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fetus. Pregnant women should tell their dentist about their pregnancy. In this case, carrying out OPTG depends on the ratio of possible risks and benefits.
How to make a circular dental radiograph
The patient is invited to the diagnostic room, which is equipped with a special device - an orthopantomograph.
For safety, a lead apron is put on the body, which does not allow rays to pass through and protects the internal organs from ionizing effects.
The patient needs to remove all metal objects: earrings, chains, piercings, glasses, clothing items. This is necessary in order to eliminate the appearance of artifacts in the final picture. The procedure is performed in the following order:
- the person is located opposite the device on a special platform. You need to stand or sit in such a way as to ensure proper contact with the area being examined;
- a bite is made on the plastic part. To do this, you should close your lips around it and freeze in the position indicated by the radiologist;
- the patient waits for the scanner to pass through (20-40 seconds) in a fixed position. To ensure immobility, a plate is pressed to the chest of the subject, and he must hold on to the handles of the orthopantomograph. The speed of the procedure allows you to take even a children's panoramic photograph of the jaws without complications and restarting.
There are no painful sensations or discomfort during scanning, the state of health remains at the same level.
Analysis and decoding
The correct reading of an orthopantomogram largely depends on the quality of the image.
This:
- contrast;
- definition;
- size of the covered area;
- natural image distortion.
The technique for reading an image is based on:
- on studying the condition of bone tissue: interdental septa;
- internal structural changes;
- unerupted teeth;
- temporomandibular joint;
- mandibular sinuses and canal.
- crown position;
The effectiveness of orthopantomography increases with the complex use of the method, in difficult cases: when diagnosing deformations of the facial part of the skull, facial asymmetry, etc.
Performance
Upon completion of preparation, the radiologist will turn on the machine and take the required number of images
Orthopantomography is a technically simple procedure that takes up to 5 minutes.
Before starting X-ray diagnostics, get rid of metal objects that obscure the image: removable dentures, glasses, etc.
Further:
- Sit down and press your chest against the platform;
- Fix your head;
- Bite the detector;
- Close your lips and press your tongue to the roof of your mouth.
Once preparation is complete, the radiologist will turn on the machine and take the required number of images.
Features of orthopantomography
OPTG provides orthodontists with a number of additional options when diagnosing the disease:
- Orthopantomography allows you to examine in detail the location and structure of these difficult-to-treat teeth.
the ability to see the entire tooth with roots;
- determine the size and condition of the root canals and pulp chamber;
- condition of the bone tissue of both jaws;
- Presence (absence) of periosteum.
OPTG images also contain important information for maxillary dental surgeons about the condition of the paranasal sinuses.
general information
Basic research in dental practice provides a complete picture for therapeutic, orthopedic, and surgical procedures. Without a panoramic image, in many cases the dentist and otolaryngologist do not begin treatment.
In advanced cases, it is the circular dental radiograph that explains the cause of the severe inflammatory process and shows the volume and density of dilapidated bone tissue.
Orthopantomography or panoramic photography is recognized by experts as an effective method of radiographic examination . It allows you to see problems between teeth, under crowns, and also give the doctor information about the condition of the temporomandibular joints and maxillary sinuses. The bone tissue surrounding the tooth is also clearly visible. With the help of panoramic photograph of the teeth , the doctor detects problems that do not yet make themselves known by any symptoms, but the teeth or gums are already suffering from them.
As a result of orthopantomography, the patient will receive an overview panoramic image of all teeth, jaw area and joints. The attending physician will analyze the X-ray examination, not missing any details, and based on the panoramic image of the teeth, he will be able to make the right decision on the necessary treatment.
Panoramic photographs of teeth are recommended to be carried out annually as a preventive examination, and also if you plan to:
- surgical intervention;
- implantation;
- dental prosthetics;
- correction of bite;
- teeth extension;
- complex treatment of the oral cavity.
Peculiarities:
- one image shows the lower and upper jaw;
- the doctor sees the condition of hard/soft tissues, the structure of both jaws;
- The overview image completely covers the dentition up to the jaw joints.
Panoramic shooting process
The panoramic photograph is taken while standing. The patient must remove all metal objects (jewelry, earrings, piercings). To protect against excess radiation dose, the patient is wearing an X-ray protective lead apron. However, the radiation dose to patients with digital orthopantomographs is 20 times less compared to film ones and does not exceed the daily radiological dose received from natural radiation sources.
A dental image from digital devices can be immediately displayed on a computer monitor without processing films, which provides more convenient and durable storage: a dental image can be recorded on any digital media (CD, flash card), printed or viewed on a computer.
What can be seen in a panoramic photograph of the jaw?
A panoramic photograph provides a detailed, visual description of various areas of the jaw. An orthopantomogram even shows hidden inflammatory processes that cannot be recognized on a regular x-ray.
The technique allows you to establish:
- depth of periodontal pockets;
- granulomas, dental cysts;
- quality (density, volume) of periodontal tissue;
- the presence of hidden carious cavities;
- the position of impacted (unerupted) and dystopic (horizontally or obliquely growing inside the gums) “wisdom teeth”;
- quality of root canal filling, condition of fillings;
- chronic inflammation of the apex of the tooth root;
- development of inflammation of soft tissues at an early stage;
- condition of the maxillary sinuses, temporomandibular joint, all teeth;
- The otolaryngologist is interested in the penetration of dental roots into the maxillary sinus. Timely detection of the defect explains some of the causes of diseases of the ENT organs.
Note! When preparing for surgery of any degree of complexity, an orthopantomogram is required. A detailed, accurate picture of the condition of the dentofacial apparatus provides additional information to the jaw surgeon and prevents medical errors. Extraction of units with multiple roots, impacted or semi-retained “eights” also requires a panoramic image.
Advantages
Modern X-ray technology has many positive aspects:
- maximum accuracy of the study, detection of the smallest defects at an early stage;
- safety: the radiation dose during the procedure does not exceed 0.02 msv. A person receives a similar dose during long flights on aircraft;
- the use of digital equipment reduces the research time by several times;
- circular x-ray allows you to accurately diagnose dental diseases, even with a latent course;
- the doctor can examine the tooth germs;
- analysis of the location of the temporomandibular joints makes it possible to recognize arthritis: asymmetry is observed in the disease;
- the patient receives a transcript of the image on a photo or digital medium;
- Each image is archived. In a few minutes, the doctor can easily track the dynamics of changes and adjust the treatment plan;
- The dentist receives the test result in just 10 minutes. High-speed data processing using a computer program, saving images on digital media and in an archive provide the doctor with detailed material for prescribing and monitoring treatment.