The rapid development of scientific and technological progress in recent decades has determined the leading role of endoscopic studies, including FGDS, in the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The use of modern equipment with thin probes, the ability to insert them through the nose, and the use of various methods of local anesthesia and sedation makes the procedure less unpleasant and painless.
In some cases, patients are forced to abandon this diagnostic method for various reasons. Most often this is due to the presence of contraindications. It is also possible for the patient to categorically refuse to undergo the procedure, due, for example, to fear or psychological unpreparedness . Then, to make a diagnosis, the doctor recommends using other alternative methods. We will talk about this in our article and take a closer look:
- what are the contraindications to FGDS;
- when it is impossible to do without gastroscopy;
- Is it possible to perform FGDS under anesthesia;
- what alternative research methods exist;
- how informative they are and what diseases they detect;
- what is the cost of various methods for examining the upper gastrointestinal tract in the Russian Federation.
Contraindications for examination
Indications for gastroscopy are quite wide. It allows the doctor to obtain important information about the condition of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, identify pathological changes in them and take tissue sections for analysis . The study is recommended for any complaints that may be associated with dysfunction of the upper digestive tract. However, not all patients are prescribed this diagnostic procedure, even if it is needed.
Technique for fibrogastroduodenoscopy
Preparation for gastroduodenoscopy begins at home, on the eve of the procedure, usually scheduled for the morning.
The subject must ensure that there is no food in the stomach at the time of the study, so dinner before the procedure should be no later than 18 hours. It should not be dense, but quite nutritious and easily digestible.
In the following hours, you are only allowed to drink a little clean water. On the day of the FGDS, you should not drink, eat, or smoke in the morning. Nicotine can significantly increase gastric secretion, and the real picture of its condition during the study will be distorted. Dentures must be removed before probing.
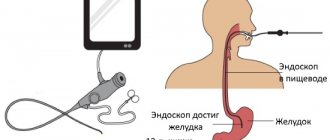
For the study, regardless of which area of the gastrointestinal tract will be observed, the same device is used - an endoscope. Endoscopes are equipped with thin probes that automatically “enter” the esophagus, so the patient does not even have to make any effort during the procedure.
The duration of a basic study does not exceed 5-7 minutes; when collecting contents or detecting complex pathologies, the procedure can last another 20 minutes. The examinee should not be afraid or embarrassed by such natural manifestations as belching or the urge to vomit, lacrimation or discharge from the nasal passages.
All these manifestations are normal, and all subjects undergo them easily. The main thing is that, despite the discomfort, the procedure does not cause pain, and the nearby medical staff will tell you how to breathe correctly and swallow the carefully advancing probe.
To collect gastric secretion, its appearance is first stimulated with various drugs - insulin, histamine, histagol.
In what cases are there no analogues?
Among the indications for gastroscopy, there are several particularly important ones, in the presence of which it cannot be avoided :
- gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting "coffee grounds" or black stools);
- bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus (bloody vomiting);
- foreign bodies in the esophagus or stomach.
This is due to the fact that in such cases FGDS is performed not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for therapeutic purposes. it is not possible to eliminate the problem using other methods , it is impossible to replace the procedure.
It is also important to perform gastroscopy in patients with suspected gastric cancer and the need for a biopsy . After all, the patient’s management tactics depend on the results of the study.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT)
To examine the stomach and esophagus, MRI and CT are used very rarely, but they are quite applicable as an alternative method. The principle of operation of modern computed tomographs is based on emitting a magnetic field on the body and receiving impulses from internal organs, which are recorded on a special film in the form of clear images. The step of obtaining sections (images) is set by the program or the doctor. Thanks to the MRI machine, you can thoroughly study every millimeter of any organ. CT also examines organs layer by layer, only using x-rays.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Today, this examination is considered the most accurate and safe, since doctors have a real opportunity to look inside the body without intervention and examine any structure. As you may have guessed, tomography also has contraindications and disadvantages. A relative contraindication is pregnancy. The disadvantages of MRI include the inability to examine the function of an organ, monitor its functioning, secretory and enzymatic activity. CT is used even less frequently.
You cannot examine a patient with any metal structures in the body (bone pins, screws, vascular clips), and especially with pacemakers. Failure to comply with this condition may cost a person his life.
Not long ago, 2 completely new methods of diagnosing the stomach without the use of a fiberscope and the associated discomfort appeared: gastropanel and capsule gastroscopy.
Anesthesia and sedation
If performing gastroscopy is difficult due to the psychological status of the patient or the presence of epilepsy or organic diseases of the central nervous system, then the study is best carried out under sedation or intravenous anesthesia.
For everyone else, this may be a good way to get through the procedure without unnecessary worry and stress. Sedation for EGD is widespread throughout the world. Read more about it in our article.
General anesthesia is often used in young children, which makes the procedure easier tolerable and easier.
Is gastroscopy possible without swallowing the probe?
In order to answer this question, you need to understand - what is gastroscopy? Translated from ancient Greek “γαστήρ” - stomach and “σκοπέω” - I look. Of course, classic gastroscopy without swallowing a probe is impossible , because it involves examining the stomach from the inside using an endoscope.
Currently, there are other methods for examining the stomach that allow visualization of the organ without penetrating into the cavities of the human body. They, of course, cannot completely replace FGDS, but with their help you can obtain useful information about the anatomy of an organ and its functional activity:
- assess the condition of the stomach wall , its inner surface;
- identify changes in the relief of the mucous membrane, the presence of neoplasms;
- characterize his motor activity and much more.
Help Using probeless methods, it is impossible to perform any diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, such as biopsy, analysis of gastric acidity, removal of polyps , etc.
Alternative methods without gastroscopy
The use of alternatives to gastroscopy of the stomach instead of classical FGDS and capsule gastroscopy is possible only in the presence of serious contraindications to the type of diagnosis: with an extensive fresh burn of the esophagus, its obstruction and the presence of esophageal varices in a progressive form. Any physical impact on the walls of the organ can lead to disastrous consequences, so the specialist selects methods that can replace gastroscopy of the stomach and its variations.
Experts call instrumental methods the closest analogues of FGD without swallowing a gastroscope in terms of effectiveness and efficiency:
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast;
- CT scan of the digestive organs;
- MRI of the stomach and intestines;
- Ultrasound of the stomach;
- electrogastrography;
In addition, a desmoid test and a set of laboratory tests can be used.
X-ray with contrast
Fluoroscopy, that is, a dynamic examination of the digestive tract using X-rays, is a painless alternative to FGDS without the need to swallow tubes. It is possible even for patients in serious condition.
Since hollow organs are poorly visualized in X-rays, fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach is performed with a contrast agent. Their choice depends on the existing violations:
- if the walls of the esophagus and stomach do not have through damage, fluoroscopy is performed with a barium solution;
- if there is a suspicion of perforation of the stomach, rupture of the esophagus and failure of the sutures after surgery on these organs, triiodinated water-soluble contrast agents are used;
- if detailed visualization of the mucous membranes is necessary, double contrast consisting of a barium solution and air is used.
The drugs are administered into the digestive tract immediately before the examination, after which the patient is placed on the X-ray table. The position is selected based on diagnostic purposes.
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography as an alternative to FGD without swallowing is not widely used due to the high cost of the procedure. The procedure is known as virtual gastroscopy, as it helps to identify changes in the structure of the mucous membranes and muscle layer of the gastrointestinal tract: polyps, ulcers, tumors, foreign bodies, perforations.
The study is carried out using a tomograph that emits X-rays. A significant drawback of the method: the inability to discern small pathological lesions on the mucous membranes. To improve the picture, the doctor may use a tube that is inserted into the esophagus and air is pumped through it.
Important! CT with air injection into the esophagus is similar in sensations to conventional gastroscopy with swallowing of the probe. During the procedure, the doctor does not have the opportunity to take a biopsy or stop the bleeding, so it cannot be called a worthy alternative to FGDS without swallowing the tube.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Another method of examining the stomach without gastroscopy is magnetic resonance imaging. It allows you to identify polyps, ulcers, inflammation, damage to the mucous membranes and muscle layer, tumors, diaphragmatic hernias without swallowing probes. MRI can detect helminthic infestations and congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The examination is absolutely painless and can be performed with or without contrast. MRI as a replacement for FGDS is not used in cases of severe kidney damage, the presence of a pacemaker, metal stents and staples (clips) on blood vessels and internal organs.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
Ultrasound examination is not considered as a full-fledged alternative to FGDS without the need to swallow probes: the method is not informative for diagnosing disorders in air-filled organs. However, ultrasound is used to identify the motor-evacuation functions of the stomach and intestines, pathologies of blood vessels and lymph nodes located next to them.
High-quality visualization is possible only by examining the duodenum, gallbladder and pancreas valves, as well as the pylorus. If serious changes are detected, a more in-depth study will be required, including a biopsy, which can only be done during gastroscopy.
Desmoid test
The method is an indirect way of detecting changes in the composition of gastric juice. To perform the test, the patient must swallow a rubber bag containing methylene blue dye. Under the influence of hydrochloric acid and pepsin, the catgut thread with which the pouch is tied dissolves, and its contents enter the digestive tract, and then into the kidneys and intestines, turning stool and urine blue. In the absence of digestive enzymes and HCl, coloring does not occur.
It is possible to replace FGDS with a desmoid test only to confirm achlorhydria - the absence of hydrochloric acid and pepsin in the gastric juice. If other pathologies are suspected, this method is impractical, so it cannot be called a full replacement for gastroscopy without swallowing the probe.
Electrogastrography
EGG or electrogastroenterography allows you to evaluate the motor functions of the stomach and esophagus without gastroscopy and the need to swallow a probe and capsules. The examination is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall using a special device. Unlike FGDS, the method does not require special preparation and does not cause discomfort.
During an EGG, the doctor records electrical fluctuations created by the walls of the stomach and, based on the electrogastrogram pattern, draws conclusions about existing pathologies. The method allows you to identify tachygastria (hypertonicity) or bradygastria (hypotonicity) of the stomach. The method is not suitable for diagnosing gastritis, ulcers, polyps and tumors.
What can be replaced?
If the patient has contraindications to FGDS, the doctor prescribes an examination using alternative methods. It is considered advisable to combine several diagnostic procedures to obtain more accurate data and prevent errors at the diagnostic search stage.
Sometimes patients themselves look for an alternative to gastroscopy, experiencing discomfort or fear of the study. In such cases, it is better to coordinate your actions with your doctor and choose a diagnostic method together . After all, to make a diagnosis in each case, a different amount of examination may be required. Below we list the main alternative studies and briefly discuss each of them.
Preparation
Before undergoing capsule endoscopy, the patient must perform a number of actions to facilitate the procedure:
- within two days, start eating only liquid or solid food;
- do not consume cabbage, legumes, alcohol, milk, fresh baked goods, carbonated drinks;
- take medications that reduce flatulence 24 hours before;
- on the evening before the study, to cleanse the intestines, take the medicine “Fortrans” - from 16.00 to 20.00, drink a liter of suspension (one sachet per liter);
- stop eating food altogether within 12 hours;
- the procedure lasts 6-8 hours, the capsule is washed down with plain water, taken on an empty stomach;
- During the procedure, you can play sports, but do not make sudden movements or lift weights;
- After a certain time, which is prescribed by the doctor, the patient comes to the hospital to remove the capsule; this must be done naturally.
How to check the esophagus without swallowing the intestine?
Transnasal route of administration
The principle of transnasal gastroscopy
In people with a pronounced gag reflex , as well as in children, the endoscope can be inserted through the nose. This method allows you to avoid irritation of the root of the tongue and all the unpleasant symptoms associated with it. This is written in detail in a separate article.
Using a thin probe
The diameter of modern endoscopes does not exceed 6-8 mm. But, if necessary, thinner probes - 3-5 mm - can be used for research. They are indispensable in pediatric practice; if necessary (for example, in case of difficulties when inserting an endoscope into the gastrointestinal tract), they can also be used in adults.
Video capsule
This is the first painless method of high-quality visualization of all parts of the digestive tube, which does not require additional sedation of patients and is characterized by a high level of safety.
Its essence lies in the introduction of a special video capsule into the body, which, moving through the gastrointestinal tract along with its contents, takes a series of pictures that are transmitted to a recording device.
Initially, it was used only for diagnosing intestinal diseases, but thanks to improvements in equipment, it is now successfully used to diagnose pathologies of the esophagus and stomach. Read about video capsule endoscopy here.
Is there an alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach?
Gastroscopy is one of the most reliable methods for diagnosing gastric pathologies. In patients, such an appointment usually causes only negative emotions: the procedure is not pleasant. Are there alternative research methods?
How is gastroscopy performed?
Gastroscopy refers to endoscopic examinations. It is carried out using a special device - a gastroscope. It is a long flexible probe, inside of which there is a fiber-optic system. In fact, the instrument is a soft, long tube with a camera.
During the procedure, a probe is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus, from where it enters the stomach. During the study, the surface of the organs is displayed on the monitor, and video and photographic recordings are made. If necessary, other procedures can be performed during gastroscopy:
- biopsy;
- pH-metry;
- removal of polyps;
- stopping bleeding;
- administration of necessary drugs.
In most cases, the patient does not need anesthesia, but some clinics offer temporary “freezing” of the throat. This is due to the unpleasant side effects of gastroscopy: unpleasant painful sensations occur in the throat, and the gag reflex is acute.
During the procedure, the patient lies on the right side and should be as relaxed as possible: tension in the esophagus and larynx can cause damage to the mucous membrane
If additional procedures are not performed during gastroscopy, the procedure takes 1-3 minutes. Discomfort in the throat goes away after a few hours, and at first there are problems with speech.
Other
Desmoid test
It is a simple way to tentatively diagnose pathological conditions associated with achlorhydria (lack of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice). For this purpose, the patient swallows a thin rubber bag with methyline blue, tightly tied with catgut. If there is free HCl in the stomach, catgut dissolves and the dye enters the body and is excreted in the urine, based on the color change of which a conclusion is made.
Gastropanel
a complex of laboratory tests to diagnose stomach diseases
To do this, blood is taken from a vein, in which the content of gastrin (a hormone produced in the stomach), pepsinogen types 1 and 2 (precursor of the gastric enzyme - pepsin), and antibodies to H. Pylory are determined.
Laboratory methods for examining the stomach
Laboratory assistants at work
How can you tell anything about the stomach based on blood results? It turns out that it is possible! Laboratory methods are of great importance in establishing a diagnosis and are actively used in gastroenterology. The material for the study is the patient’s blood, feces, gastric and duodenal juice.
Blood
A general and biochemical blood test is the first thing that any doctor prescribes to diagnose gastritis. Blood counts and their levels can tell a lot about your general condition, the presence of an inflammatory process, infection, and the functioning of digestive enzymes and hormones. Specifically, indicators of gastric function include hemoglobin, leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), pepsinogen and gastrin levels. Their fluctuation indirectly indicates the presence of gastritis, ulcer bleeding and other diseases.
The amount of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori (immunoglobulins M and G) is also examined in the blood. Helicobacter is a bacterium that causes inflammation of the gastric mucosa. If it is detected, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Feces
Stool analysis shows the presence of hidden bleeding, enzyme dysfunction (changes in coprogram), worm eggs, and signs of dysbacteriosis.
Container for collecting biomaterial
Gastric juice
This method will tell you how to determine the functional state of the gastric mucosa. The juice is collected through a thin probe. Each portion of the material is examined separately. pH-metry is also carried out - this is a determination of acidity. The obtained indicators play an important role in prescribing treatment.
All laboratory methods are used to diagnose functional indicators of the stomach, and therefore are not suitable for determining space-occupying formations, narrowing or obstruction of the esophagus, or detecting the source of bleeding.
What pathologies can be identified?
Various alternative diagnostic methods reveal signs of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but often cannot confirm the diagnosis due to the lack of biopsy and morphological examination.
Table 1. Diagnostic capabilities of each method.
| Gastritis | Peptic ulcer | Stomach cancer | |
| Ultrasound | Indirect signs, it is not possible to accurately diagnose | Determines the presence of an ulcerative defect, but does not have the ability to assess the benignity of the process | Assumes but does not confirm |
| X-ray | Same | Same | Same |
| Video capsule endoscopy | Same | Same | Same |
| CT, MRI | Same | Same | The same Evaluates the prevalence of the process |
| Gastropanel | Detects H. Pylory infection | Assess risk | Same |
| Electrogastroentnerography | Detects only disorders of motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. | ||
| Desmoid test | Determines the presence or absence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. | ||
| GERD | Foreign bodies | Benign tumors, polyps | |
| Ultrasound | Yes | Yes | Yes, but cannot reliably distinguish from a malignant process |
| X-ray | Yes, but the sensitivity is low | Yes | Same |
| Video capsule endoscopy | Yes (detects Barrett's esophagus) | Yes | Same |
| CT, MRI | — | Yes | Same |
| Gastropanel | Same | — | — |
| Electrogastroentnerography | Detects only disorders of motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. | ||
| Desmoid test | Determines the presence or absence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. | ||
Gastropanel
This blood test can check several indicators. Based on their level, an experienced and competent doctor will be able to draw conclusions regarding the pathology of the gastric mucosa.
So, the gastropanel explores:
- Antibodies to H. pylori (Helicobacter), the bacteria that causes stomach ulcers.
Antibodies to Helicobacter pylori of the IgG class are detected starting 3 weeks after infection
- Pepsinogen I and II (precursors of the gastric enzyme pepsin). By their meaning one can judge which part of the stomach is affected.
- Gastrin 17 (a hormone that regulates the production of hydrochloric acid).
Based on the totality of all indicators, a conclusion is drawn in which the doctor indicates the degree of dysfunction of the gastric mucosa and possible causes (atrophy, hypotrophy, hyperacidity and others). The examination is expensive and not informative enough, since it is impossible to visually see the condition of the organ from the inside, but sometimes it is an excellent diagnostic method stomach without gastroscopy.
Many diseases, including cancer of the stomach or esophagus, may not manifest themselves and are detected at the last stage.
That is why gastroscopy remains the leading examination for diagnosis.
Price
The cost of examining the stomach using the above methods in the Russian Federation varies depending on the region, the prestige of the clinic and the qualifications of the specialist and equipment.
The price for the same procedure can differ significantly in the center of the capital and on the outskirts. Therefore, if there is a need to undergo examination in private clinics, it is better to familiarize yourself with their capabilities and pricing policy in advance.
Table 2. Cost of FGDS and other studies in the Russian Federation (in rubles).
| Moscow | St. Petersburg | Voronezh | Ekaterinburg | Krasnoyarsk | Ufa | |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | 800-3300 | 800-2800 | 540-1500 | 500-1500 | 450-1200 | 150-3080 |
| X-ray of the stomach | 1000-13000 | 1450-4500 | 650-2400 | 200-2500 | 200-1900 | 400-4200 |
| FGDS | 1000-36000 | 200-12000 | 400-3000 | 730-6800 | 250-2000 | 500-3030 |
| Video capsule endoscopy | 6000-111000 | 10000-78000 | From 55000 | 37000-50000 | From 53000 | From 65000 |