Is it possible to do an MRI of the head with metal crowns on the teeth?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a highly informative examination method. It allows you to identify defects in tissues and organs as small as 0.2 mm - such pathologies are not detected by other diagnostic devices. But doctors warn that MRI and metal are a dangerous combination.
A stalemate is developing - most adults have metal structures in their mouths: dentures, pins, braces, etc. And they still undergo MRI. So are metal products really contraindications for examination?
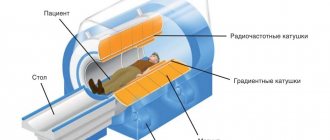
To give an answer, you need to explain the principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. It sends out radio waves and magnetizes the nuclei of hydrogen atoms located throughout the body. The latter “respond” to a powerful magnet or, in other words, enter into resonance. Based on the arrangement of hydrogen atoms, the program creates a picture and displays it on the monitor.
But not only the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, but also metals can “respond” to the magnet of the device. However, not all: there are materials that cannot be affected. These are paramagnetic materials:
- titanium; (titanium crowns for teeth and their characteristics)
- platinum;
- aluminum;
- tantalum.
Cases of displacement of metal products are very rare
In addition to paramagnets, there are 2 more groups of metals:
- Ferromagnets. These include iron, chromium, nickel, cobalt, and steel. They react strongly to the magnet: they heat up, move and can even “break out” of the body. There were cases when a part of the body with an installed ferromagnetic structure (arm, leg) “stuck” to the tomograph and the device had to be completely demagnetized - there was no other way to free the patient.
- Diamagnets. These are hydrogen, copper, silver, gold (gold crowns on teeth, frills). They are not significantly magnetized and do not heat up or move during MRI. However, they create interference and distort the picture.
Braces and MRI
Some patients wearing braces mistakenly believe that when examined on a tomograph, the orthodontic structure in the mouth heats up, produces an electric shock, or may even explode. All this is nothing more than a myth spread by ignorant people. In fact, the interaction of braces with magnetic radiation does not cause any harm to health and nothing terrible happens during the examination.
But, despite this, it is not worth undergoing an MRI in braces, especially those containing metal. They can significantly spoil the quality of the images, and you will simply waste your money on an expensive procedure. The fact is that braces are a fairly large structure, and it can greatly distort the study data.
Removing braces before the MRI procedure and installing them after is a fairly simple operation performed by a dentist
If you really need to undergo a tomography examination, then come to your orthodontist, explain the current situation and ask him to remove the braces for the duration of the procedure. The next day he will put it back, fixing it in the same position.
Should you tell your doctor that you have dental implants?
Dental replacement implants are made primarily from titanium. This is a paramagnetic material that does not resonate with a magnetic tomograph. But this does not mean that there are no restrictions on the examination.
To avoid having to undergo an MRI twice, notify your doctor about the implant so that he can change the machine settings
The diagnostician must be informed about artificial teeth for two reasons:
- Titanium is capable of distorting the picture. Yes, the metal does not heat up and does not move. But it can create minor interference. In order not to undergo an expensive procedure twice, it is better to immediately notify the doctor about the implant - he will change the settings of the device.
- The titanium pin is not the only element of the implant. In addition to the rod itself, there is also an abutment (gum former) and a crown. They are made from ceramics or various types of metal and then lined with porcelain.
Therefore, patients are always asked about the presence of implants at least twice: when giving a referral and immediately before diagnosis.
Risks of MRI diagnostics with titanium dentures
Due to the fact that prostheses implanted into the jaw bone are mostly made of paramagnetic titanium, magnetic resonance imaging with dental implants is a completely feasible and completely safe procedure. Titanium is a biologically inert material, i.e. it is not able to oxidize and release harmful substances during contact with bones, muscles and blood vessels of the human body. Of course, in medicine it is not pure titanium that is used, but its alloys with a small amount of other elements. This is done to make the material durable and light. But they also do not have any negative impact when undergoing an MRI.
By the way, titanium is comparable in strength to steel, and in lightness - to aluminum. Therefore, this metal has received recognition not only from dentists, but also from traumatologists and orthopedic surgeons.
Titanium is also used to produce abutments, gum formers, and metal arches (bases) for dentures.
How can MRI affect iron crowns?
Prostheses made of iron, steel, cobalt alloys and other ferromagnetic materials are still most often installed. Yes, there is titanium, porcelain and zirconium dioxide - but they are expensive, so not everyone can afford them.
Iron orthopedic structures are durable and cheap. But they become a problem if you need to do an MRI for 4 reasons:
- They distort the picture. The results will not be accurate. This is especially critical when diagnosing oncological pathologies: MRI is the best method for identifying tumors at the initial stage, when recovery success is high.
- They get very hot. This leads to a burn of the mucous membrane.
- They move from their place. After displacement, the crowns will have to be adjusted, re-attached, or new ones made.
- Possible loss. The magnetic field attracts metal crowns - it literally rips them out of your mouth.
Iron crowns get very hot and distort MRI results
Patients with metal prostheses are recommended to remove the structures before MRI or undergo another study - CT, PET. The above applies to closed-type tomographs or when examining the head, cervical or thoracic region. There is no risk when diagnosing other parts of the body.
Impact of implants on the quality of results
Before carrying out the procedure, warn the specialist about the presence of a dental structure.
The MRI device will not have a negative effect on dental structures, but the presence of metal may negatively affect the quality of the image. It will become fuzzy, blurry, and the doctor will not be able to determine the condition of the structures.
Distortion is observed during examination:
- thoracic region;
- brain, skull;
- shoulder joints.
Not long ago, improved devices with PET/MRI technology began to be introduced. The new model eliminates the influence of noise from metal objects on the image. Before carrying out the procedure, you need to clarify which tomograph is used in the office . If an old-style device is installed, the doctor will adjust it taking into account the foreign body in the body, which will help improve the image of the area being examined
Myths for patients with implants
Before undergoing an MRI, people with artificial teeth are frightened by their acquaintances with stories: they say that the implants are torn out, tearing the gums and breaking the jaws. But these are just rumors with little truth.
There are 3 misconceptions about undergoing MRI with implants:
- The implants will be pulled out of the jaw. 90% of the rods are made of titanium, which does not react to magnetic fields. In addition, the metal pins are embedded in the bone, so they physically cannot move.
- The implant will distort the picture. The rod itself is made of paramagnetic material and does not affect the data. But the crown on the implant can be made of di- or ferromagnetic alloys. And it already affects the results of the examination.
- The implant will heat up, causing tissue burns. Again, titanium does not resonate with a magnetic field. Only a crown with a cobalt-nickel or chromium frame can heat up.
Implants are not an absolute contraindication to examination. There are limitations, but they are related to the capabilities of the device - some models cannot be configured so that they do not react to metal parts. In this case, they simply select another medical center with more powerful and modern equipment.
Implants are not an absolute contraindication to MRI if it is possible to change the device settings
How it works
Magnetic resonance and electromagnetic response measurements provide a clear three-dimensional image of the organ. This is a completely safe and painless test, however, due to the use of magnetic fields, it has its limitations. They relate to various metal devices and structures that may be in the human body and interfere with the procedure.
Referred patients often ask if an MRI can be done with a post in the tooth. In short, yes, it is possible, but you need to remember some of the nuances of the examination.
Other problems with crowns
In addition to affecting MRI results, metal crowns cause other problems: they break, chip, and the root canals and gums underneath may become inflamed, or the tooth stump may collapse. But most often, fixed dentures become loose or fly off.
What to do if the crown of a tooth is loose or has fallen off?
Crowns or bridges made of diamagnetic or ferromagnetic metals may begin to wobble after MRI. This is due to the displacement of the prostheses during the examination and subsequent decementation. In the future, the structures will fall out.
The presence of metal structures does not affect the results of a CT examination
However, the causes of poor fixation are not always related to magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes dentures become loose and fly off due to:
- washing out the cement from under the crown - if its edge does not fit tightly to the neck of the tooth, the bond (adhesive composition) is gradually destroyed under the influence of saliva and drinks;
- poorly made design - it will not fit tightly if it does not follow the shape of the tooth in the smallest detail;
- small volume of the stump or its destruction - the remains do not hold the prosthesis, and it flies off.
Regardless of the reason, contact an orthopedic dentist. He will correct a loose or fallen crown and re-fix it. If the prosthesis cannot be repaired, a new one will be made and installed.
Swallowed a crown...
When a crown falls out, it is often swallowed along with saliva, food or drinks. There is no reason to worry - it will come out on its own along with the feces in a few hours or 1-2 days.
The only dangerous situation is when the prosthesis splits. In this case, an x-ray is taken, the location of the bridge or crown is determined, and then the stomach is washed out or an enema is given.
If you swallow a crown, it will be passed out in your stool within a maximum of 2 days.
But, in any case, the swallowed crown is reported to a gastroenterologist, surgeon or traumatologist. Magnetic resonance imaging is postponed until the structure is removed from the body.
How long does a crown stay on a tooth?
The service life of entire crowns primarily depends on the material. So:
- metal ones last an average of 5 years;
- metal-ceramic – 8-10 years;
- ceramic and zirconium dioxide - 10-15 years and above.
The duration of wearing dentures is also affected by: how well the supporting tooth was treated and ground, the skill of the dental technician and the quality of oral care. The dentist is visited every six months to remove plaque from products and adjust them. And after 7-10 years, most crowns become unusable and are replaced with new ones.
But loose and broken dentures will not last long: from several days to a couple of weeks. Therefore, people contact the clinic immediately: the faster the doctor adjusts or replaces the bridge or crown, the greater the chance of saving the abutment tooth.
This is how a crown is sawed
MRI of the brain
The most complex procedure that requires maximum attention is the study of the brain, heart, and coronary vessels. MRI remains practically the only way to diagnose tumors of any size, oncology at the first stage. If you have iron crowns, complications are possible:
- heating the oral tissues above the pin;
- metallic taste;
- absence of entire areas in the photographs.
In such a situation, doctors have to make an important decision: if MRI cannot be replaced by another method, and the disease develops rapidly and is fatal, it is better to remove dental braces and crowns. After treatment, re-implantation can be performed.
How are crowns removed from teeth, indications?
In cases where the crown or bridge has moved during the MRI, they are removed and installed again or replaced with new prostheses. They do this in the following ways:
- sawing - the prosthesis is drilled out using drills with a cooling system; after removal, the structure is unsuitable for further use;
- ultrasound – ultrasonic waves destroy the cement, and the crown is easily removed from the stump;
- Koch apparatus - a special drill breaks the bond with gentle pushes, then the structure is lifted and removed;
- Coronaflex apparatus - compressed air is supplied under the edge of the prosthesis, this is the only method that eliminates damage to the structure and supporting teeth;
- special tools or sliding crown removers - used after destruction of the adhesive base using one of the above methods.
Orthopedic structures are also removed in case of resorption of cement, chips of ceramic lining, damage to the frame, inflammatory processes in the root canals, or the patient’s desire to replace the prosthesis with a better one.
It doesn't hurt to remove crowns
Is it possible to shoot on your own?
Sometimes the bridge or crown is so loose that the patient can tear it off himself. However, this should not be done, because... possible:
- damage to the prosthesis;
- fracture of the stump or root system of the tooth;
- traumatization of the mucous membrane or adjacent units.