Home » Laparoscopy » Sex after laparoscopy: when is sexual activity allowed?
April 12, 2020 Laparoscopy
Not only women who have undergone laparoscopic surgery, but also men who are sexual partners are concerned about the very important question of when can you have sex after laparoscopy? Despite the fact that laparoscopy is one of the safest and most gentle techniques, after its implementation there are some limitations. These restrictions include not only sexual activity, but also compliance with diet, hygiene and physical activity.
General restrictions
Sexual activity after laparoscopy is prohibited for at least 2 weeks. It applies to both women and men. On average, sex is allowed after a month.
This is due to the fact that the operation damages tissues and organs and they need recovery after laparoscopy. It also takes time for wounds to heal and stitches to be removed. If you do not meet the deadlines, complications are possible:
- seam divergence;
- bleeding;
- rupture of blood vessels;
- formation of infiltrate;
- introduction of infection.
In this case, intimacy will be unpleasant for the patient himself. At first, the wounds hurt, you feel severe weakness, discomfort during sexual intercourse, nausea and pain in the abdomen and peritoneum are possible. Therefore, it is unlikely that the patient will want to begin sexual activity at least in the first week.
How many days later you can have sex again after surgery is determined individually. Some patients return to intimate life after a few days, others have to abstain for a couple of months.
To determine how long sexual rest will last, observation by a doctor is necessary. Based on a visual examination, questioning and diagnostics (including ultrasound), he will determine whether the patient can return to intimate life. If restrictions continue to apply, the specialist must explain the reason why sexual activity cannot be resumed.
After approximately 4 weeks, you are allowed to return to having sex. However, please remember that:
- the first times should be as gentle as possible - passionate caresses can lead to bleeding, opening of wounds, and damage to blood vessels;
- it is necessary to protect yourself - preferably using barrier contraception.
Pregnancy immediately after laparoscopy is extremely undesirable and risks serious complications. Although women are prescribed hormone therapy, including oral contraceptives, condoms are the best option for protection. They will protect against premature pregnancy and prevent infection.
Important! You need to use condoms both for irregular sex and with a regular partner. Even a healthy man can carry germs and bacteria.
General recommendations
After surgery, women who spare themselves too much take longer to recover. Of course, there is no need to run a marathon immediately after the operation. But you need to get up as early as possible, sit down and walk slowly. This time is different for every woman, and it is impossible to say exactly how long it will take to lead an active lifestyle. Everyone's pain threshold is different, and it largely determines the pace of recovery.
Nutrition should be gentle only on the first day after laparoscopy. In the future, you are allowed to return to your normal lifestyle. The only thing you should give up is serious physical activity. It is necessary to wait time for the postoperative wounds to heal, and there is no danger of sutures coming apart and bleeding.
Sex after organ removal
If laparoscopy was performed for diagnostic purposes, then the negative consequences are minimal, and the period of abstinence does not last long - a week or a little more. It’s another matter when the operation was performed to remove organs: appendix, bladder, ovary, fallopian tube.
In each case, the limitation periods will be different:
- after removal of the ovarian cyst, sexual activity can be resumed no earlier than after 2 - 3 weeks;
- appendectomy (cutting out the appendix) does not impose restrictions on sex - you can make love after about a week, but not earlier than 5 days, otherwise the stitches may come apart;
- after removal of the gallbladder, intimate life is prohibited for at least 2 weeks, but usually the period is extended by 1 to 2 months;
- if an inguinal hernia has been removed, you can carefully resume sex after 14 days, while avoiding excessive tension in the abdominal muscles;
- When extirpating the uterus and appendages, you need to abstain for at least a month.
Additional Information! If stitches have been placed, you must wait until they are removed and only then resume sex.
Forecast
Sexual activity after removal of the uterus is quite possible, and is practiced by most women. Conception for physiological reasons is impossible in this case. For many, this factor, paradoxically, is a positive phenomenon: the absence of the need to use protection has a positive effect on sexual activity. The issue of having children is considered in the areas of adoption, surrogacy (with preserved ovaries) or adoption.
In general, sex after a hysterectomy is normal. It is possible if there is desire and an object of love. But the lack of sex life should not become a factor provoking depression: sex issues are relevant for all generations, healthy and sick, married and single, temperamental and calm, young and old. This is life and it goes on.
Sex after infertility treatment
Laparoscopy, which was performed to treat infertility, is considered a simple surgical procedure. Rehabilitation takes place quickly - within 1 - 2 weeks. After this period, you can resume your intimate life.
Also, having sex in such cases has a positive effect on the recovery of the body. Frictions and orgasm improve muscle tone, trophism, and accelerate healing.
Moreover, the sooner a woman resumes intimate life, the greater her chances of becoming pregnant after laparoscopy. Especially if obstruction of the fallopian tubes or polycystic disease was eliminated. As a rule, the fallopian tubes become obstructed again after a couple of months, and with the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), ovulation is restored for no more than 1 year.
Therefore, the doctor will allow you to have sex as soon as possible. However, after how many days sexual rest will be cancelled, it is decided individually in each case. So, when exfoliating cysts, extracting ovaries, fallopian tubes, the period is extended by a month. The most serious consequences of hysterectomy - in this case, restrictions may be imposed for 2 - 3 months.
Note! Before the first menstruation occurs after laparoscopy, it is necessary to protect yourself with condoms. Damaged organs can easily become infected during sex, and a weakened body cannot withstand pregnancy.
The situation is somewhat different when treating infertility in men, such as varicocele or hydrocele, using laparoscopy. After such surgical interventions, reproductive function will fully resume, so there is no need to rush into sex. It is necessary to understand that intimate caresses are equated to physical activity and should be limited for 3 to 4 weeks.
Laparoscopy: surgery or diagnosis
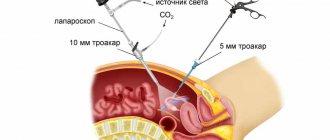
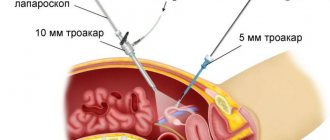
Laparoscopy is a technique by which surgical intervention is performed. The main difference between laparoscopy and traditional surgery is that there is no need to make an incision on the body. Instead of an incision, the doctor makes 3-4 punctures, through which a laparoscope and special instruments are inserted to perform manipulations.
Laparoscopy is the best diagnostic method through which it is possible to examine internal organs and detect pathological abnormalities. Thanks to laparoscopy, once pathologies are detected, it is possible to treat them or correct them surgically. It follows that laparoscopy includes both diagnosis and surgical intervention with the aim of carrying out manipulations to cure pathologies.
Laparoscopy has many advantages over classical surgery, but the main one is the high speed of postoperative recovery. After the operation, the woman can get out of bed and even walk around the room on the same day.
It is important to know! You can get up and walk after laparoscopy only with the permission of the doctor, because during complex operations you are allowed to get up on the second day.
Laparoscopic intervention lasts up to two hours, but no more. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. At the beginning of the operation, carbon dioxide is pumped into the patient’s abdominal cavity, the need for which lies in the fact that with its help it is possible to straighten the walls of this area. Initially, the first puncture is made through which the laparoscope is inserted. If deviations or pathologies are detected, a special instrument is introduced, with the help of which various actions are performed.
Bypassing restrictions in sex without harm to health
Long-term abstinence after laparoscopy is not easy for both women and men. But the restrictions apply only to traditional sex. You can satisfy your needs in another way.
It should be understood that all prohibitions are related to:
- risk of early pregnancy;
- possible infection;
- excessive tension in the abdominal muscles;
- the likelihood of damage to organs, tissues and suture dehiscence.
You can get around the restrictions by practicing oral sex or masturbating after laparoscopy.
Engaging in oral sex or self-pleasure is even beneficial. Orgasm after laparoscopy increases muscle elasticity, normalizes their blood supply, and accelerates healing.
Additional Information! However, even non-traditional types of sex are subject to restrictions for several days after laparoscopy. Therefore, any question of interest must be discussed with the attending physician: only he has a complete clinical picture and will tell you whether it is possible to engage in this or that sexual activity.
When is sexual activity allowed after laparoscopy?
Typically, outpatient surgery does not require much time for damaged tissue to heal, so most patients can have sex within a few days. On the other hand, if the operation was performed on the organs of the genitourinary system, you will have to wait several weeks before resuming sexual life.
You will have to use protection for another 2-3 months after resuming sexual activity. So laparoscopy and sex are quite compatible concepts, but in some cases you have to wait a little.
Men who have undergone surgery affecting the reproductive organs (for example, repair of an inguinal hernia) will have to give up sex for a long time (at least three weeks, or until the stitches have completely healed). Oral sex after laparoscopy is also prohibited. Doctors are concerned about saliva and bacteria getting into the unhealed area.
What to pay attention to during sex
Returning to sexual activity should be done carefully to avoid possible complications. During your first sex sessions, you need to listen to how you feel. It is advisable to turn on the light - this way the pathological discharge will be visible. You should stop petting and consult a doctor if:
- blood or brown discharge - these are most likely after surgery on the uterus and ovaries;
- pain;
- discomfort - any discomfort indicates incomplete tissue healing or the development of complications.
It is recommended to resume sex after laparoscopy no earlier than a month later. This is the average period required for tissue healing, restoration of organ functions and complete healing of wounds. If sexual intercourse occurred earlier, it must be remembered that the load on the abdominal cavity should be minimal. And if any unpleasant sensations occur, you should consult a doctor.
Sexual sensations in the postoperative period
Many sexually active women fear losing interest in sex after a hysterectomy. But doctors are unanimous: when health is restored after intervention, desire remains, and sex is permitted and can be enjoyable. Moreover, including this side of the relationship is very beneficial not only from a physiological point of view, but also for psychological health.
Loss of sensation is, first of all, a psychological problem that arises as a result of a woman’s incorrect self-perception or a change in attitude on the part of her sexual partner. In this case, consultation with a psychologist, psychotherapist or psychiatrist is necessary. In the vast majority of cases, the problem of complexes acquired during illness and treatment is successfully resolved.
Many women who have experienced sex after removal of the uterus note that their intimate life becomes richer and the sensations are brighter. And this is understandable: surgery is performed only after ineffective conservative therapy or after a long illness, when there is no other option. This means that in the preoperative period, sexual life was accompanied by difficulties and sometimes pain. Often, for these reasons, intimacy was completely excluded from life.
Progress of radical prostatectomy – surgery to remove the prostate gland
Have you been struggling with PROSTATITIS and POTENTITY for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Prostate cancer is a common male disease. The incidence of carcinoma increases progressively with age in men. It is believed that every seventh to eighth man over 75 years of age develops prostate cancer. Urologists recommend annual prostate monitoring after age 50. Men at risk should begin visiting a urologist annually at age 40.
Only preventive studies (monitoring PSA dynamics, digital examination, TRUS, and, if necessary, biopsy) help to suspect and verify carcinoma in the early stages. Subjective symptoms appear in men at stages III-IV, when prostatectomy is difficult or completely impractical due to the spread of tumor foci throughout the body.
Radical prostatectomy is a surgical procedure during which an organ, the prostate gland, is removed. Most often, this operation is resorted to when a malignant neoplasm of the prostate is detected in the early stages. If indicated, the surgeon removes not only the prostate gland, but also regional lymph nodes. In exceptional cases (if organ-saving techniques are ineffective), radical prostatectomy may be required for patients with benign hyperplasia. The procedure is similar to that for carcinoma, but there is no need to remove lymph nodes.
Indications
Prostate carcinoma located within the organ capsule, which corresponds to stages I-II. Severe compression of the urethral walls by tumor tissue in stage III cancer. Lack of effect from the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The intervention is carried out subject to the following conditions:
- serum prostate-specific antigen concentration does not exceed 20 ng/ml;
- After successful prostate removal, the patient is expected to live for at least 10 years.
Contraindications
- the presence of metastatic screenings of the primary prostate tumor;
- old age;
- severe background pathologies of various organs and systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine) that are in the stage of decompensation;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system that cannot be treated.
The operation is not advisable when the potential harm of the intervention significantly outweighs its potential benefit. Older men for whom anesthesia and surgery may be fatal are usually offered other cancer treatments.
Types of operation
The course of the intervention directly depends on the technique chosen by the doctor.
In clinical practice, radical prostatectomy is performed in accordance with the following methods:
| Open manipulation | Accesses used:
|
| Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy | A type of laparoscopic surgery is manipulation using a high-tech robot assistant “Da Vinci” (USA). |
Features of blood supply and innervation of the organ
The course of the operation is always planned taking into account the anatomical features of the organ, its blood supply and innervation: disruption of the nerve structure entails the impossibility of restoring sexual function, and injury to the blood vessels leads to massive bleeding that develops during the operation or in the early postoperative period.
Branches of the internal iliac artery (including the inferior cystic artery) supply blood to the seminal vesicles, the base of the prostate and its surface, and the base of the bladder.
Venous drainage occurs in the prostatic veins. These veins, together with the veins of the fundus of the bladder and seminal vesicles, drain into the Santorini plexus. As part of the neurovascular bundles, the nerves originating from the pelvic plexus are located on the sides of the organ (between the prostate gland and the wall of the rectum).
Preparatory activities
The attending physician prescribes laboratory and instrumental tests of the patient in advance in order to analyze the condition of the main organs and systems (liver, kidneys, heart). Based on these tests, a conclusion is made about the possibility of removing the prostate gland. The PSA level, a marker of prostate disease, is assessed. The urologist conducts a digital rectal examination and prescribes an ultrasound. The course of the operation is much easier to plan after performing a tomography and creating a three-dimensional model of the organ on a computer.
The patient must tell the doctor about all medications used. Some of them that affect the blood coagulation system will need to be interrupted. These drugs include anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, as well as some anti-inflammatory drugs (acetylsalicylic acid) and drugs from other pharmacological groups.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
The evening before the operation, the patient eats, after which he should abstain from food and any drinks (including water). Before the intervention, you will need to shave your pubic hair and cleanse your lower intestine with an enema. Leg binding is often performed to prevent complications from the veins of the lower extremities (thrombosis).
Anesthesia
Radical prostatectomy is performed under general anesthesia.
Patient position on the operating table
The man lies on his back, Tredelenburg position. At the level of the navel there is a small break in the table. This position allows you to increase the gap between the navel and the pubic symphysis. A Foley catheter is inserted.
Key points of retropubic surgery
Laparotomy (dissection of the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall) is carried out along the midline. The length of the incision is from the navel to the pubic symphysis. No peritoneal incision is made. The surgeon mobilizes the peritoneum and displaces it. Lymph node dissection is performed (excision of lymph nodes performed for the purpose of diagnosing metastatic lesions). The advisability of removing lymph nodes and the urgency of their histological examination is a controversial issue.
Using a tamper, the surgeon removes fatty tissue from the surface of the prostate gland. The endopelvic fascia is incised on both sides of the organ. Violation of the integrity of the fascia should be done extremely carefully due to the fact that the vessels of the Santorini plexus are located directly under it. Incisions made with a scalpel can be continued using scissors.
The doctor mobilizes the prostate gland with his fingers. The puboprostatic ligaments are dissected and the gland is displaced posteriorly, providing access to the dorsal veins. A ligature is applied to the superficial vein. Its intersection or coagulation is acceptable. Using a dissector or Dishan needle, the venous plexus is ligated. To facilitate the application of a ligature, the prostate is shifted posteriorly using a retractor or tuffer. Crossing the vessels of the venous complex and stopping bleeding. The course of the nerve-sparing operation involves holding the dissector closer to the midline in relation to the neurovascular bundle. Dissection of the anterior wall of the urethra, application of a provisional ligature to the wall for the purpose of subsequent identification. Removing the urethral catheter and crossing the urethra. The doctor mobilizes the posterior surface of the prostate.
Ligation of small vessels going to the prostate from the bundle lying between the layers of the lateral fascia of the pelvis. The bundle is retracted from the surface of the gland, the surgeon crosses the legs of the prostate. Isolation, ligation, dissection of the vas deferens. Excision of the seminal vesicles after applying ligatures to the vessels supplying the vesicles. Dissection of the bladder wall in the area of its fusion with the prostate gland. Removal of the prostate and seminal vesicles.
Stop bleeding
Suture material (catgut) is applied in two rows to form the bladder neck. The course of the operation with preservation of the proximal urethra is indicated under the following conditions: no TUR was performed, the tumor tissue did not have time to affect the base of the gland and the transition zone, the PSA level does not exceed 10 ng/ml. Formation of urethrovesical anastomosis. Material: chrome-plated catgut. Installation of a catheter and drainage, checking the tightness of the anastomosis. Suturing the surgical wound.
Postoperative period
Physical activity is indicated on the second day after surgery. To reduce pain, medications are prescribed: first opioids and then NSAIDs. If the course of the postoperative period is not associated with complications, on the third day the patient goes to the general table.
A balanced diet should be aimed at preventing constipation. A patient undergoing surgery should take antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor. It is necessary to avoid physical activity and drink plenty of fluids. The drains are removed.
The man is discharged with a Foley catheter in place on days 6-7. The catheter is removed 3 weeks after surgery. The patient then begins to perform Kegel exercises. You should be regularly examined by a urologist, monitor PSA levels, and report to your doctor about all possible alarming symptoms. Resuming sexual contacts is possible after consulting a doctor.
Complications
- venous bleeding;
- violation of the integrity of the rectal wall;
- damage to the ureters;
- anastomotic stricture;
- addition of infection;
- pulmonary embolism;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities;
- urinary incontinence;
- erectile disfunction
- lymphocele.
Perineal access
Radical prostatectomy, in which an incision is made into the skin and underlying tissue in the perineal area. The course of the intervention is associated with injury to the neurovascular bundle due to insufficient visibility. In addition, it is not possible to remove the lymph nodes. This manipulation is low-traumatic, but it is gradually being replaced by endoscopic interventions.
Laparoscopy
The procedure involves making several small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. Gas and instruments are introduced into the cavity. Radical prostatectomy is carried out under visual control: the laparoscope is equipped with a camera that transmits a color image to the display.
Robotic laparoscopy
The course of the prostatectomy operation resembles that of conventional laparoscopy, however, robotic assistant manipulators are inserted through the incisions. The doctor controls the actions of the Da Vinci system robot, focusing on video data.
The picture on the monitor is a three-dimensional enlarged image, allowing the operation to be performed with high precision. If necessary, not only the prostate is removed, but also the lymph nodes.
Benefits of laparoscopy
- the amount of blood loss is minimal;
- the risk of complications is significantly reduced;
- good tolerance;
- greater likelihood of restoration of sexual function and urinary control;
- short rehabilitation period.
Disadvantages of robotic intervention
- lack of qualified doctors who have studied the progress of robotic prostatectomy operations;
- high cost (explained by expensive equipment).
Consequences of early onset of intimate life
If a woman violates the doctor’s recommendations regarding the initiation of intimacy, then such an incorrect attitude can lead to serious complications. So, the consequences of an early start to sexual life:
- Bleeding may occur when the stitches come apart. A woman may lose a lot of blood. In this case, the problem can be solved surgically.
- The development of the inflammatory process can be localized in one area, or it can cover all reproductive organs.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system, in particular cystitis.
If a woman has had her uterus and other organs of the reproductive system removed, then we must not forget about contraceptive methods. Although there is no risk of unwanted pregnancy, there is still a risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases from a partner.
When can I return to sexual activity?
Many patients are embarrassed to ask their doctor if they can have sex and how long abstinence should be. Most often, it is allowed to resume intimate life 2-3 weeks after laparoscopic surgery. The main rule is that a woman should not experience any unpleasant sensations or discomfort during sexual intercourse. The doctor decides when you can have sex after laparoscopy based on the patient's individual situation.
If surgery was performed on the fallopian tubes, then it is possible to return to sexual life quite soon. Some patients say that they were allowed to return to normal life literally immediately after the operation. Moreover, in this case, women who had sex a week or two after laparoscopy recovered faster than those ladies who waited a month or more.
During sexual intercourse you should not experience discomfort or pain!
If stitches were placed during the operation, especially on the genitals, then it is better not to risk it and wait until they are removed. Those patients who have had sex up to this point can themselves provoke bleeding from postoperative wounds or sutures coming apart.
Why in some cases are women recommended to begin sexual activity earlier than after 2 weeks? The fact is that the orgasm obtained during sexual intercourse has a positive effect on the normalization of muscle tone, improves their functioning, helping to recover after surgery without loss of quality of life. Frictions performed by a man improve tissue elasticity and blood circulation in the genital organs, accelerating healing.
Many people are concerned about the need for protection. This is decided individually with each patient. For example, after uterine surgery, you cannot plan a pregnancy right away. Sufficient time must pass for the organ to recover and final scars to form.
In general, we can say that there is no single and precise recommendation on when you can have sex after laparoscopy. Some doctors insist that you need to wait about a month, some advise not to put it off for too long. A woman should focus primarily on her feelings. If nothing bothers you, then why give up pleasure? Moreover, sex helps speed up the recovery of the genital organs after surgery.
Doctors' opinion
Surgeons agree on the issue of resuming sexual activity after surgery to remove an inflamed appendix.
Surgeon of the highest category Avakumov I.V., Tver : “I recommend moderate intensity of sex to my patients after appendectomy only after the sutures are removed.”
Urological surgeon Nikiforov I.Z., Obninsk : “Moderate physical activity is always beneficial in the early and late periods of rehabilitation, improves lymph flow and blood circulation. I recommend sex only with a trusted partner, without any special research, with traditional positions.”
Surgeon E.E. Maykova, Omsk : “If a woman of childbearing age has undergone surgery to remove the appendix, you should return to sexual life only after 21 days, provided there are no complications. I recommend pregnancy six months after successful recovery.”
Indications and contraindications for laparoscopy
The main diseases for which surgery is indicated:
- Infertility.
- Identifying the cause of fallopian tube obstruction.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Uterine fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian and uterine cysts.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
- Dysmenorrhea.
- Appendicitis.
Often, indications for laparoscopy are acute situations in which there is a danger to life and health.
Sometimes these conditions can be caused by surgical pathology that cannot be cured in any other way. For example, obstruction of the fallopian tubes can be caused by adhesions in the pelvis. Appendicitis and ectopic pregnancy are acute conditions that require immediate surgical intervention.
Absolute contraindications include:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the blood coagulation system.
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases.
- Severe exhaustion.
- Diaphragm hernia.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Hypertensive crisis.