A periodic or constant increase in blood sugar, which is a sign of insufficient absorption by tissues or insulin deficiency, negatively affects the functioning of internal organs, blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Until a certain time, elevated blood sugar does not manifest itself with specific symptoms, although irreversible destructive processes in the most vulnerable organs - the heart, blood vessels, and visual organs - may already begin in the body. Controlling sugar levels and preventing them from rising to dangerous levels is the most accessible measure to prevent diabetes.
Symptoms
Sometimes an impending disease is nevertheless “declassified”, and when blood sugar is elevated, it is signaled by quite distinct symptoms (signs). These manifestations are almost the same among representatives of the opposite sexes.
Among women
It is believed that diabetes mellitus has more dangerous consequences for women than for men, since the former quickly lose their vision, lose emotional balance, and turn into “hysterical individuals.” They are much more likely to experience complications from the genitourinary system. Strong thirst (polydipsia), increased appetite against the background of rapid weight loss, increased diuresis, dry mucous membranes - these are the symptoms that occur in a woman with high sugar.
In men
The first sign of high blood sugar in men is usually an increase in the volume of urine produced (polyuria). The consequence of frequent urination is gradual dehydration of the body, leading to irresistible thirst. These are the most characteristic signs of increased blood sugar, which are symptoms in men. In addition, obesity or, conversely, weight loss, irritability or apathy, prolonged festering of wounds and increased fatigue may occur.
Main symptoms of diabetes
Signs of High Glucose Levels
In general, the symptoms of diabetes are similar for most patients, although they may differ depending on age and duration of the disease. As a rule, the first signs of high sugar are as follows:
- Dry mouth is one of the classic manifestations of diabetes.
- Polydipsia and polyuria. Extreme thirst and passing a large volume of urine are the most typical symptoms of high sugar levels. Thirst is the body's signal to replenish lost water to avoid dehydration. The kidneys, in turn, filter the excess glucose, releasing an increased amount of urine.
- Fatigue and weakness. Sugar does not reach the cells, remaining in the blood, so muscle tissue lacks energy to be active.
- Poor healing of scratches, wounds, abrasions, cuts. It is important to avoid breaks in the skin as they are prone to infection, which creates further problems.
- Increase or decrease in body weight.
- Characteristic signs of diabetes are skin diseases and genital infections that cause itching. This may be furunculosis, candidiasis, colpitis, inflammation of the urinary tract and urethra.
- Body odor of acetone. This manifestation is typical for very high sugar levels. This is a signal of diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition.
One of the most characteristic signs of high sugar is constant extreme thirst.
Later, the patient develops the following symptoms of high sugar:
- Maculopathy and diabetic retinopathy are eye diseases characterized by blurred vision. Retinopathy, which affects the blood vessels in the eyes, is the leading cause of blindness in adults with diabetes.
- Bleeding gums, loose teeth.
- Decreased sensitivity in the extremities: tingling, numbness, goosebumps, changes in pain and temperature sensitivity on the hands and feet.
- Digestive problems: diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, fecal incontinence, difficulty swallowing.
- Swelling of the extremities as a result of retention and accumulation of fluid in the body. Such signs more often appear when diabetes is combined with arterial hypertension.
- Manifestations of high sugar include chronic renal failure, protein in the urine and other kidney disorders.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Erectile dysfunction, frequent urinary tract infections.
- Decreased intelligence and memory.
With a slight increase in sugar, signs may be mild or absent. Often, patients suffering from type 2 diabetes have no complaints and are not aware of their condition. The diagnosis may be made accidentally, during examination or treatment for another reason.
Signs of a sharp increase
When a sudden and sharp increase in blood sugar, usually occurring as an initial symptom of type I diabetes, the patient's condition is life-threatening. It is accompanied by:
- sudden fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- drop in blood pressure;
- often - epigastric pain;
- blurred vision;
- dry skin, tongue and mucous membranes;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- skin itching;
- drowsiness, slow reflexes, fainting.
Both the sick person and the people around him should know what to do in circumstances when sugar is elevated, especially if this happens suddenly.
Why does it increase?
An elevated blood sugar level that is significantly higher than normal, manifested by characteristic symptoms, is called hyperglycemia. To understand how to treat this condition, it is necessary to find the cause of hyperglycemia. A high sugar level does not always indicate the onset of diabetes, but this factor is at the top of the list of reasons for an increase in this indicator. Several other factors that cause blood sugar to rise:
- vitamin deficiency due to deficiency of biotin, vitamin B7;
- eating disorders, gluttony (often with bulimia nervosa, manifested by an uncontrollable passion for satiety);
- drug therapy with corticosteroids, protease inhibitors, fentamidine, niacin, thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, some antidepressants, antitumor drugs from the group of monoclonal bodies;
- non-diabetic hyperglycemia due to stress after a stroke or myocardial infarction;
- inflammatory, infectious or organ diseases accompanied by a decrease in tissue insulin resistance (atherosclerosis, hypertension, coronary artery disease, etc.);
- chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex.
It is possible to determine exactly why sugar increases only through careful differential diagnosis, medical history, and testing.
Folk remedies
When treating hyperglycemia, you should not look for methods that will reduce the level of sugar in the bloodstream in just one day, bringing it to normal. Similar methods do not exist in alternative medicine. All the remedies and medications recommended by her help to slowly reduce glucose levels. Let's look at the most popular of them:
- Oat decoction. This recipe is quite simple. To prepare the healing remedy, you will need to take oatmeal in the volume of one glass, to which add 600 ml of boiling water. Boil the resulting mixture for 15 minutes over low heat. Next, the decoction should infuse. All it takes is 20 minutes. Take the finished product three times a day, 1/3 cup. It is worth noting that this mixture is very useful for the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chicory root decoction. This remedy has a beneficial effect on the pancreas and helps lower blood sugar. To prepare the drug you will need 1 tsp. chicory roots, which should be pre-chopped. Raw materials are poured 1 tbsp. boiling water Boil the mixture over low heat for 10 minutes. The cooled decoction is considered ready for use. The recommended dosage is 5 ml up to five times a day.
- Bird cherry decoction. This remedy in alternative medicine is considered one of the most effective. Bird cherry berries are used in its preparation. They will need to take 1 tbsp. l. then pour a glass of boiling water. This mixture should be placed on low heat and brought to a boil. After 3 minutes, the product can be used for treatment. They drink it for a month, ½ tbsp. three times a day. After a break, the course can be repeated.
- Healing teas. When preparing these healing potions, those herbs are used that, due to their composition, are capable of lowering blood sugar. Among them are St. John's wort and clover, linden blossom, as well as currant and lingonberry leaves. All these components are taken in equal proportions. They are thoroughly crushed, and after 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of raw materials into a glass of boiling water. After this, the tea is left to infuse the mixture for 15 minutes. This medicine is taken twice a day.
So, we have looked at the answer to the question of why blood sugar has risen. The reasons for this problem can be very different. To eliminate it, it is important to consult a doctor.
What does a high level mean and why is it dangerous?
Let's take a closer look at the issue of high blood sugar. As noted above, when this indicator becomes sharply elevated, it means that hyperglycemia has developed and the question arises of how to treat it.
Normally, 2 groups of hormones regulate blood sugar levels:
- insulin is the only hormone that has hypoglycemic (sugar-lowering) properties;
- hyperglycemic (increasing sugar) - growth and adrenal hormones (glucocorticosteroids), glucagon.
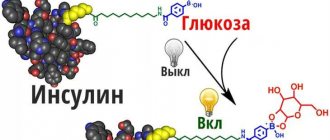
Insulin, to a greater or lesser extent, affects all parts of metabolic processes in the body, the first of which is carbohydrate. This process provides the body with energy to carry out all other functions - blood circulation, breathing, movement, etc. Activation of insulin production by the endocrine cells of the pancreas occurs when the sugar content rises, from which the tissues acquire the ability to absorb this carbohydrate.
Mechanism of action of insulin
At what indicators is the level considered high? To answer this question, let’s remember the normal ranges: 3.5–5.5. Indicators that are above the upper limit of the reference range are considered elevated.
Most patients understand that if blood sugar is elevated in the results of a blood test, something needs to be done to stabilize it, but few understand why an elevated level is dangerous. Persistently elevated plasma sugar potentiates disruption of all types of metabolism:
- protein;
- fat;
- carbohydrate;
- water-salt and mineral.
Having acquired a chronic course, hyperglycemia progresses to diabetes mellitus, which threatens such multiple organ disorders as:
- diabetic angiopathy, including increased fragility and permeability of blood vessels, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, coronary disease, encephalopathy;
- diabetic foot syndrome - trophic ulcers, pain in the calf muscles, destruction of the joints and bones of the feet due to poor circulation in the lower extremities;
- nephropathy – damage to the vessels of the kidneys, with disruption of their functions up to failure (observed in 40-45% of patients 15-20 years after diagnosis);
- retinopathy - damage to the blood vessels of the eyes, destruction of the retina and its detachment, leading to loss of vision, is found in 80-95% of patients
- polyneuropathy – damage to peripheral nerve endings, leading to impaired sensitivity, chilliness and swelling of the extremities, paresthesia (a feeling of “crawling goosebumps”, tingling or burning on the skin), occurs in 75% of patients.
Of all these unpleasant consequences of diabetes, a pathological condition called “diabetic foot” stands out. As a result of progressive damage to the vessels of the extremities and the formation of trophic ulcers, patients develop infection of soft tissues and purulent-necrotic processes (gangrene), in severe cases leading to amputation of the limb.
Loss of limbs, loss of vision, kidney failure – the list of consequences of diabetes is daunting, but it doesn’t end there.
If glucose concentrations suddenly increase to dangerous levels, a person may fall into a hyperglycemic coma. In some cases this ends in death. That's why if you have high sugar levels, you should do everything necessary to regulate its concentration in the blood.
High blood sugar: causes, symptoms and treatment at home
Normally, the blood glucose level (glycemia) in an adult ranges from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. This indicator depends on many factors (gender, age, mental and physical state, and others), and indicates the occurrence of physiological processes.
An increase in glucose levels is called hyperglycemia, which is accompanied by a number of specific symptoms and can be life-threatening.
Why does blood sugar rise?
The following causes of hyperglycemia are distinguished:
- infectious diseases;
- systemic diseases;
- use of steroid drugs;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- stress;
- predominance of easily digestible carbohydrates in the diet.
A short-term increase in sugar can provoke an attack of angina, epilepsy or myocardial infarction. The level of glucose in the blood will also increase if severe pain or burns occur.
The best endocrinologists
How does high sugar manifest itself?
High blood sugar levels usually present with several symptoms. If an acute form of hyperglycemia develops, then they are expressed most intensely. The following signs may indicate increased blood glucose levels:
- dryness of the oral mucosa, thirst;
- disturbance of urination (frequent, copious, including at night);
- itchy skin;
- changes in body weight in both directions;
- increased drowsiness;
- weakness, fatigue;
- dizziness, headache;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- long-term healing of skin lesions;
- visual impairment;
- increased susceptibility to infections;
- impaired potency in men.
If you notice similar symptoms (not necessarily all), you need to take blood glucose tests.
How symptoms develop
The mechanism of development of each of the symptoms listed above is somehow related to glucose. Thus, a frequent desire to drink (polydipsia) occurs due to the binding of water molecules by sugar. Liquid migrates from the intercellular space into the lumen of blood vessels. As a result, the tissues become dehydrated.
At the same time, the increase in blood volume due to the incoming water provokes an increase in blood pressure and increased blood circulation in the kidneys. The body seeks to get rid of excess fluid through urination, and polyuria develops.
Without insulin, glucose molecules cannot enter cells. Therefore, when it is insufficiently produced by the pancreas, as happens in type 1 diabetes, the tissues experience an energy deficit. The body is forced to use other ways of energy supply (proteins, fats), as a result of which body weight decreases.
Obesity occurs when the functional activity of insulin-dependent receptors is impaired - type 2 diabetes. In this case, insulin is produced in sufficient quantities, stimulates fat synthesis, and glucose also does not enter the cells, leading to energy starvation.
Energy deficiency in brain tissue is associated with feelings of weakness, dizziness, and rapid onset of fatigue. Experiencing a lack of glucose, the body intensively oxidizes fats. This causes an increase in the content of ketone bodies in the bloodstream, and leads to the appearance of acetone odor from the mouth.
The inability of glucose to penetrate tissue also affects the immune system - leukocytes become functionally inferior and cannot fully fight infection.
Any damage to the skin becomes an “entry” for pathogenic microorganisms. Slow healing is also facilitated by excess sugar in the wound tissue, which becomes a favorable breeding ground for microbes.
Diagnosis of hyperglycemia
The basis of diagnosis is testing for glucose tolerance (tolerance). To do this, blood is drawn on an empty stomach in the morning and the sugar content is determined. After which the patient takes a glucose solution orally. Two hours later, blood is taken again for analysis.
The reliability of the indicators depends on a number of conditions:
- the analysis is carried out against the background of emotional and physical calm;
- 10 hours before the procedure you should not eat anything;
- the day before the test, you need to avoid excessive physical activity;
- The period of time (2 hours) after taking the glucose solution must be spent in a calm state, sitting or lying down.
Results in which the first glucose measurement shows 7 mmol/l, and the second more than 11, give grounds to diagnose diabetes mellitus.
In addition to glucose, the content of other compounds in the blood is detected, such as:
- glycated hemoglobin (shows the average blood glucose value over the last three months);
- incretins (hormones that activate the release of insulin);
- amylin (regulates the volume and rate of glucose entering the blood after eating);
- glucagon (activates liver cells to produce and release glucose).
Methods for reducing hyperglycemia
The basis for lowering sugar levels is the elimination of the factor that caused hyperglycemia. So, if taking medications leads to an increase in blood glucose levels, you should consult with your doctor about their possible replacement.
If you have thyroid or other diseases, you need to cure them. In the case of gestational diabetes (during pregnancy), a review of the diet is sufficient.
In case of primary development of diabetes mellitus or if the cause cannot be eliminated, therapeutic treatment is indicated. To do this, for a disease developing in the first type, insulin injections are prescribed, and for the second type, drugs that lower glucose levels are prescribed.
Despite the fact that in each individual case the therapeutic regimen is drawn up individually, there are rules common to all patients. You should strictly follow your doctor’s instructions, monitor your diet, lead a healthy lifestyle, and regularly test your blood for sugar levels.
Nutrition for hyperglycemia
A careful review of your diet is the first thing to do if you have high blood glucose levels. There are a lot of dietary recommendations based on reducing the amount of simple carbohydrates in food.
Reducing the calorie content of dishes should be combined with the simultaneous preservation of the required amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
Carbohydrates should be predominantly of the slow type, with a low glycemic index. Daily caloric intake is calculated based on individual characteristics. In this case, the daily amount of food should be divided into several (up to 6) meals, with intervals of no more than three hours.
The menu should include foods that help lower blood glucose. This:
- sour fruits;
- citrus;
- berries (lingonberries, rowan);
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- fresh greens.
Buckwheat has priority among cereals. When boiled, it has low calorie content and high nutritional value. Buckwheat contains minerals, vitamins and active substances that help not only reduce sugar, but also body weight, as well as cleanse the body of toxins and waste.
The following recipe will help significantly lower your glucose levels. You need to mix a tablespoon of cereal crushed to a powder with a glass of kefir, let it brew for 7-9 hours. You need to drink the mixture 60 minutes before meals for a week.
What are the dangers of high blood sugar?
Complications resulting from elevated blood glucose levels can be either acute, quickly manifested, or long-term. In the first case, hyperglycemia can cause conditions such as:
- damage to the central nervous system, coma, precomatose state (manifested by impaired nerve conduction, disorder of reflex connections, partial or complete loss of consciousness);
- ketoacidosis;
- dehydration of the body;
- lactic acid coma.
Such conditions have previous symptoms. These are: severe weakness, thirst and a large volume of urine excreted (up to 4 liters). If such signs appear, you should urgently seek medical help.
Long-term consequences of high sugar levels in the body:
- damage to the blood and nerve vessels of the lower extremities, followed by necrosis and gangrene;
- kidney damage, consisting in the complete loss of the renal structures of their functions, followed by the development of failure (represents a threat to life);
- destruction of the retina of the eyes, leading to loss of vision.
Elevated blood sugar levels do not always indicate the presence of pathology in the body. If symptoms appear more and more often, and others join them, then you must definitely donate blood for glucose levels and consult with a specialist.
Traditional medicine recipes
Traditional medicine has accumulated many recipes designed to reduce blood glucose levels. Below are the most effective ones.
- Take oats, about a glass or half a half-liter jar. Pour boiling water over it (6 cups). Cook over low heat for an hour. Alternatively: keep in a water bath or put in the oven for the same time. When the broth has cooled, it should be strained. You can take it in any quantity throughout the day for an unlimited time.
- Take 40 grams of walnut partitions. Place them in half a liter of water and cook over low heat for an hour. After the broth has cooled completely, it needs to be strained. The product should be used before meals. The dosage is one tablespoon. You can store the decoction in the refrigerator.
- In spring, you need to collect lilac buds before they bloom. Steam two tablespoons of raw material with 0.4 liters of hot water and leave to brew for 6 hours (it is best to do this in a thermos). After the infusion is ready, it should be strained. Drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Wash and grate the horseradish (root). Dilute the resulting slurry with a fermented milk product (kefir, yogurt, sour milk, natural yogurt) in a ratio of 1:10. The product should be used before meals, three times a day. Dosage – one tablespoon.
- Prepare an infusion of bay leaves: 10 crushed leaves will require 200 ml of boiling water. Pour the raw materials into a thermos and leave for a day. Strain. The infusion should be taken warm, about 4 times a day (no more). Dosage – a quarter glass before meals.
Decoding glucose content
When we talk about blood glucose, it means the same as sugar content, since glucose is the end product of the breakdown of carbohydrates, which serves as the most convenient source of energy for the body. To give an idea of dangerous blood glucose levels, let's compare different blood sugar test results.
5 mmol/l
Those with this result of a blood sugar test need not worry - the value of 5 mmol/l is within the reference values and does not require correction. In the units of measurement adopted in many countries of the world - milligrams per deciliter - this figure corresponds to 90 mg/dl.
Test strips for glucometer
6 mmol/l
A reading of 6 mmol/l is also normal, but is a borderline value. This means there is a risk of having high blood sugar in the future. In international units of measurement, the figure corresponds to 108 mg/dl. If such a value is detected, in-depth blood tests may be required.
7 mmol/l
If the sugar result is 7 mmol/l, this is increased glucose, which, as a rule, means diabetic onset in an adult. In milligrams per deciliter, this is 126 mg/dL. The condition refers to mild hyperglycemia. Confirmation of diabetes mellitus requires mandatory additional studies:
- blood stress test for glucose tolerance;
- for glucose and ketone bodies in urine;
- on insulin and C-peptide in the blood.
The most complete diagnostic picture of diabetes mellitus is provided by the analysis of glycated hemoglobin - the average value of blood sugar determined over 3-4 months.
8 mmol/l
A value of 8 mmol/l (or 144 mg/dl) indicates moderate hyperglycemia and requires immediate action. An endocrinologist, neurologist or therapist will explain what a person should do with such results, depending on what caused the high sugar.
Diet
The main way to normalize blood glucose levels is diet. The number of calories consumed is calculated depending on your body type and physical activity. Fractional nutrition is indicated - eating 5-6 times a day in small portions at regular intervals. In addition to lowering sugar levels, the goal of diet therapy is to normalize weight. With increased body weight, the daily calorie intake should be reduced by 250-300 kcal from the daily value recommended for a given age and lifestyle.
The basis of the diet is vegetable protein; foods containing carbohydrates are allowed only those that have a low glycemic index. Recommended:
- vegetables in raw and thermally processed form (fresh vegetables should be eaten daily, their share should be at least 20% of all vegetables);
- lean meat, offal, fish, seafood;
- eggs (no more than two per day);
- natural dairy and fermented milk products;
- cereals (buckwheat, millet, barley, pearl barley, oat flakes);
- bakery products from unleavened dough, whole grain, rye;
- legumes;
- berries, fruits, as well as fresh juices from them;
- black natural coffee, black, green, white, herbal tea, unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks;
- some sweets (marshmallows, marshmallows, marmalade, small amounts of honey, dark chocolate);
- vegetable oils.
In case of hyperglycemia, it is necessary to adhere to a plant-protein diet, excluding high-carbohydrate foods
For hyperglycemia, it is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
Even half an hour of physical therapy exercises a day helps normalize blood sugar levels. Among other things, regular physical activity is one of the measures to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Exclude from the diet are confectionery products except those permitted, baked goods made from butter and puff pastry, rice, semolina, sausages, bacon, ham, rich meat broths, fatty, smoked and pickled foods, pasta, fatty and hot sauces, fast food. , snacks. You should give up sugar, if it is difficult to do this right away, leave a small amount of it, gradually reducing it until it is completely removed from the diet. Alcohol is also prohibited, with the exception of a small amount (1-2 glasses) of natural dry red wine 1-3 times a week.
What to do?
If test results show high blood sugar, this does not necessarily mean that a person needs drug treatment. Making a decision on prescribing hypoglycemic drugs or insulin is the prerogative of a specialist, so the first thing to do when characteristic symptoms and increased sugar concentrations are detected is to consult a doctor. All further actions should be agreed with a medical specialist.
If a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus has already been made, drug therapy is being carried out, but the sugar level still has jumped, all the more so you should seek the help of your doctor in order to avoid life-threatening situations. Such patients should adhere to the following rules before visiting a doctor:
- keep glucose levels under control at all times;
- drink more water;
- review your diet and reduce the amount of high-calorie foods to a minimum;
- if glucose is not higher than 14-15 mmol/l, engage in feasible physical activity;
- if the glucose level is above 15 mmol/l, you should refrain from physical activity.
When blood sugar is very high (20-33 mmol/l), and it rises spontaneously, the first thing to do is call an ambulance.
What is the normal blood sugar level?
The tests indicate the glucose level; this parameter has a certain framework within which it may fluctuate slightly during the day. The lowest value is observed in the morning, and the highest is after a meal, which lasts for a short period of time. High blood sugar is noted if it is beyond the following normal levels. This meaning differs among different groups of people. Normal indicators include the following numbers:
- Adults (women and men) – 3.9-5 mmol, after meals no higher than 5.5 mmol;
- During pregnancy – 3.3-5.5 mmol;
- Children under 1 year old - 2.8-4.4 mmol; in children over 1 year old, the norm corresponds to an adult;
- Patients with diabetes – 5-7 mmol.
To check glucose concentrations, blood can be taken from a finger or a vein. There is a difference between sugar levels, so results will vary. The normal indicator may differ according to this factor:
- capillary blood – 3.3-5.5 mmol;
- venous – 4-6.8 mmol.
How to treat?
Treatment of hyperglycemia, as a rule, consists of a set of comprehensive measures to reduce blood glucose levels, improve metabolism or eliminate the causes of high sugar:
- if it was provoked by taking medications, find an adequate replacement for these drugs that does not have such side effects;
- when the cause lies in somatic or other diseases, treat them;
- if the impetus for the increase was overeating, involve mechanisms for regulating the diet (diet);
- To improve metabolism and normalize body weight, individually selected physical therapy is recommended.
Hormone replacement therapy with insulin is prescribed only when type I diabetes is diagnosed.
The issue of prescribing medications should not be decided by the sick person on their own - the types of medications, as well as their dosage, can only be selected by a doctor.
Increase in sugar in the morning
There are several reasons for high blood sugar in the morning. This can be fixed, you just need to determine which of them caused the problem:
- Dawn syndrome. Every morning from four to six o'clock there may be a rise in sugar. At this time, hormones are activated that stimulate the synthesis of glucose in the liver, which enters the blood and leads to an increase in sugar. Healthy people cope with this situation by producing enough insulin to compensate for glucose.
- Somogyi syndrome. At night, there is a sharp drop in sugar associated with an overdose of insulin. After such stress, the body takes glucose from its reserves and morning levels increase.
High blood sugar in the morning is not necessarily associated with diabetes. This can also occur in completely healthy people in the following situations:
- heavy physical activity;
- intense long-term mental activity;
- threat to life, severe fright and fear;
- serious stressful condition.
The blood sugar concentration in all these cases normalizes after eliminating the exposure factor without medical assistance. In addition, there are a number of serious diseases that increase sugar levels. These include burns, myocardial infarction, stroke, liver disease, and brain injury. In these cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor to receive appropriate treatment and solve the problem of morning high blood sugar.
How to reduce?
Since glucose is absorbed by the body only through the hormone (insulin), it is impossible to lower blood sugar levels with any food or folk remedies. Therefore, if intensive glycemic control is necessary, one should rely solely on the tenets of evidence-based medicine. To effectively control blood sugar, medicine uses a number of antidiabetic, or hypoglycemic, agents:
- insulin preparations intended for intramuscular administration;
- meglitinides – active ingredients nateglinide, repaglinide;
- alpha-glucosidase inhibitors – miglitol, acarbose;
- thiazolidinediones – pioglitazone, rosiglitazone, diaglitazone, etc.;
- biguanides – metformin, buformin;
- sulfonylurea derivatives - glipizide, gliquidone, chlorpropamide, etc.
The drugs listed below insulin are intended for oral administration in type II diabetes.
Hyperglycemia during pregnancy
Due to a hormonal imbalance, pregnant women may develop a special type of hyperglycemia - gestational diabetes. In this case, glycemia remains normal on an empty stomach, but increases sharply after eating. Such changes in blood sugar are unsafe for the intrauterine development of the fetus, since they can be complicated by abnormalities of the brain and cardiovascular system in the child. In order to identify pathology in advance, pregnant women are shown a glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks.
Possible reasons
Most often, the cause of the symptom is:
- Diabetes. In the vast majority of cases, the chronic manifestation of hyperglycemia is the main characteristic of this disease.
- Poor nutrition. Severe disturbances in the normal diet, as well as the predominance of high-calorie foods in food, can lead to acute forms of hyperglycemia and are not associated with its diabetic form.
- Stress. Post-stress hyperglycemia is typical for patients with weak immunity, most often against the background of the development of a local inflammatory process.
- Severe wide-spectrum infectious diseases.
- Taking a number of medications - rituximab, corticosteroids, niacin, free form asperaginase, beta blockers, 1st-2nd generation antidepressants, protease inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, fentymidine.
- Chronic lack of B vitamins in the body.
Causes of high sugar levels in adults and pregnant women
As medical practice shows, in 90 percent of cases, persistent chronic hyperglycemia in adults is a manifestation of diabetes mellitus, mainly type 2. Additional negative factors are usually poorly developed circadian rhythms of sleep and wakefulness, stress at work, as well as a sedentary lifestyle accompanied by obesity.
The increased blood sugar level in pregnant women deserves special attention - hyperglycemia here can be temporary, associated with the restructuring of the body as a whole and hormonal changes in particular (physiological manifestation), or be a special type of diabetes mellitus - the so-called gestational diabetes, which occurs during during pregnancy and often disappears after childbirth. If in the first case, ordinary medical monitoring of the patient’s condition is sufficient, in the second, the disease, detected in 4-5 percent of women in an interesting position, can harm both the fetus and the health of the expectant mother, so experts prescribe complex therapy taking into account the current physiology sick.
Causes of high blood sugar in newborns and children
In children of primary school age and adolescence, hyperglycemia is usually associated with a number of factors - poor nutrition, stress and the development of infectious and inflammatory processes against the background of activation of endogenous counter-insulin hormones, which are produced in large quantities with the active growth of the body. Only in some cases, after excluding all the above reasons, are children diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, mainly type 1.
Hyperglycemia in newborns deserves special attention - it is caused by a number of factors that are usually not related to the classical causes of symptoms in children and adults. In the vast majority of cases, an increase in blood sugar levels occurs due to active intravenous administration of glucose in newborns with low body weight. In premature babies in the first days of life, hyperglycemia is a manifestation of a lack of the hormone that breaks down proinsulin, often against the background of incomplete resistance to insulin itself.
The transient type of hyperglycemia can also be caused by the administration of glucocorticosteroids, fungal sepsis, respiratory distress syndrome, and hypoxia. As modern medical statistics show, more than half of newborns admitted to the intensive care unit for one reason or another have elevated blood sugar levels. Although high glucose levels are less common than classic hypoglycemia, the likelihood of complications and the risk of death is greater.
How to get tested?
No special preparations should be made for the procedure of collecting a blood sample for sugar. The test is taken on an empty stomach; you cannot have breakfast on the day of blood donation. A few days before the procedure, follow your usual diet, normal lifestyle, and preferably, do not fast, so as not to provoke a false increase in glucose due to its compensatory production by the liver. Restrictions apply only to actions on the eve of taking blood samples:
- do not eat or drink sugary drinks 8-10 hours before donating blood;
- limit physical and emotional stress 2-3 hours before the procedure;
- On the day of taking the test, do not eat, you can drink, but only clean water.
Any other drinks (tea, coffee, juice) drunk before visiting the laboratory can distort the results of the analysis.
How to avoid diabetes if your sugar is a little high?
If your blood sugar is slightly elevated, go in for sports.
The human body, like all living things in the world, is subject to change. Each person has their own sugar threshold. How to avoid diabetes if your sugar is a little high? There is no need to worry if you have such a problem, but you need to act correctly.
- As mentioned above, the cause of increased sugar can be various conditions of the body or life situations.
- This may be due to the improper functioning of some organs in the body. You need to undergo an examination, which the doctor will additionally prescribe for you.
- We can also talk about chronic or one-time stress. Try to calm down or take a sedative such as Valerian or Corvalol .
- Eating too many sugar-containing foods before testing can also have an effect. If, for example, you ate cake the day before the sample was taken, this may distort the test result. In this case, repeat the analysis in a couple of days.
But it is worth noting that sometimes when we are talking about an increase in sugar, we are talking about something else:
- Blood sugar levels in men and women depend on age.
- In older people, sugar levels also increase. On average, in people 50–60 years old it should be up to 6 mmol/l .
- In women, sugar levels depend on hormonal levels. For example, pregnant women during the perinatal period showed that their blood sugars would be higher than when they were not pregnant.
Important: The lowest glucose level in a person is observed at 3 – 6 o’clock in the morning. Of course, it is difficult to measure sugar at this time. This can be done if you have your own blood glucose meter at home. There is no need to go to the laboratory, but you can check your glucose level at home.
All doctors say that you should eat normally before the test, but it is still advisable to eat less sugar before the day of blood donation. This will show a more complete and correct picture.
Tip: If you have high blood sugar, you need to pay attention to the liver and pancreas. Contact a good doctor, he will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
More important tips:
- Play sports
- Eat right
- Get rid of excess weight
- Eliminate sugar-containing foods from your diet
- Avoid fatty and fried foods
- Avoid foods with a high glycemic index.
High glycemic index foods
Remember: You need to live this lifestyle all the time! As soon as you break your diet or routine, your sugar may rise.
You can also use recipes from traditional medicine to stabilize blood sugar:
- Drink decoctions and infusions from blueberry, clover, and nettle leaves. Pour one tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of water, strain after 20 minutes and drink 3 times a day, 1/3 cup .
- You can use bean pods, calamus root, corn silk, or regular chamomile flowers. Decoctions from these plants will relieve inflammation and improve the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
- Chamomile tea improves the general condition of the body and usually does not harm a person in any way. But be careful: if you are allergic to chamomile, you should not drink this tea.
Of course, at the first discomfort you should consult a doctor. But you can try to improve blood sugar and the state of the digestive system as a whole, and eliminate mild infections at the initial stage on your own. Traditional medicine recipes are a great help. However, if the condition worsens, do not put off visiting a doctor, otherwise all this can lead to complications that are difficult to treat.
A device for measuring at home
A home blood sugar monitor is helpful for monitoring blood sugar. Today, portable glucometers for private use are popular. These devices are equipped with a glucose oxidase biosensor that can calculate blood glucose levels (glycemia) within seconds. There are several types of glucometers from the first to the latest generations. Included with the measuring device, as a rule, there are additional means of manipulation - scarifiers for pricking a finger, semi-automatic syringe pens for dosed administration of insulin, replaceable cartridges with the active substance. There are devices that measure blood sugar levels without puncture.
Symptoms of high sugar
The classic list of external symptoms of high blood glucose includes:
- Constant strong thirst.
- Sudden non-dynamic weight gain or loss.
- Frequent urination.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Dry skin and mucous membranes.
- Vision problems, spasms of accommodative muscles.
- Arrhythmias.
- Weak immune response to infections, poor wound healing.
- Deep noisy breathing, moderate form of hyperventilation.
- In acute forms of hyperglycemia, severe dehydration, ketoacidosis, disturbances of consciousness, and in some cases coma are observed.
It should be understood that the above signs can be indicators of the symptoms of various diseases, therefore, if you detect at least a few negative manifestations, you should consult a doctor and get tested to determine an accurate diagnosis.