The normal functioning of the body largely depends on the stability of sugar levels in our blood. When consuming carbohydrates and sweets, processes occur that convert them into glucose. It is used by our body as energy. Glucose enables a variety of functions, including processes that occur in the body at the cellular level. Knowing how sugar is indicated in a blood test, you will be able to control its level and promptly recognize problems that arise with an increase or decrease in this indicator.
Glucose level
First of all, it should be noted that from a medical point of view it is correct to say “glucose level”. Sugar consists of a whole group of substances, but glucose is determined in the blood. But the term “blood sugar” itself has so confidently entered into speech that it is used in this form not only in conversations, but also in medical literature. Sugar is indicated in a blood test by the Latin letters GLU, from the word “glucose”.
First of all, this indicator informs us about the state of carbohydrate metabolism in the body. Glucose comes with complex carbohydrates, which are broken down in the gastrointestinal tract and enter the bloodstream. Hence the conclusion that in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the absorption of glucose may be impaired. The glucose that enters the blood is only partially used by the body; most of it is deposited in the form of glycogen in the liver. Further, in emergency cases (emotional, physical stress), glycogen is broken down and glucose is released into the blood.
Conclusion - the liver is a storehouse of glucose, so when it is diseased, blood sugar levels may also change. The neuroendocrine system, adrenal glands, and pancreas are responsible for the exit from the liver, synthesis, and absorption of glucose. Therefore, the pathology of any of these organs causes a malfunction in blood sugar levels.
Latin notation in general analysis
A general blood test is the first test for which a competent doctor prescribes a referral to check the general condition of the patient’s body.
In the presence of inflammation or an oncological process, the composition of the blood according to the results of a general examination will have deviations from the norm. On the general analysis form you can see the following symbols in Latin:
- Hgb. This is hemoglobin. The norm for females is 120-140 g/l, for males – 130-160 g/l. Decreased with anemia, kidney problems, internal bleeding. Increases with dehydration, heart failure, pathologies of the blood system;
- Rbc. These are red blood cells. They contain hemoglobin. The standard for women is 3.7-4.7x1012/l, for men 4.0-5.1x1012/l. The concentration decreases with blood loss, anemia, chronic inflammation, and in late pregnancy. The level of red blood cells increases in diseases of the lungs, bronchi, kidneys, heart, liver, and when treated with hormone-containing drugs;
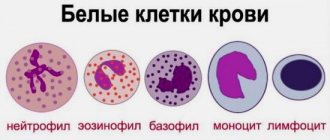
- Wbc. Denotes white blood cells. The norm for both sexes is 4.0-9.0x109/l. The rate decreases when there is a viral infection in the body, or when taking anticonvulsants and analgesics. The number of leukocytes increases during infections, inflammation, allergies, and neoplasms. Taking cardiac and hormonal medications also helps to increase this indicator;
- Plt. These are platelets. Their optimal value is 180-320x109/l. The concentration decreases in case of poisoning, hormonal imbalance, liver pathologies, spleen diseases, when taking diuretics, antibiotics, hormones, nitroglycerin. An increase is observed during inflammation, in the postoperative period;
- ESR. Stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Shows the course of the disease. The optimal value is 2-15 mm/h for women, 2-10 mm/h for men. The level decreases with poor blood circulation and anaphylactic shock. ESR increases in the presence of infection, inflammation, hormonal imbalance, anemia, and kidney problems. During pregnancy, this figure also increases.
Regulation in the body
It is very important that the sugar level in the body is always normal. Having figured out how sugar is indicated in a blood test, you can now control this indicator. If it becomes lower or higher, the following consequences may occur:
- Dizziness, possible loss of consciousness, resulting in coma.
- When sugar levels rise, severe fatigue occurs. It gets dark and the picture before my eyes blurs.
How blood sugar is regulated in the body, consider the principles of the mechanism:
- When sugar levels rise, the pancreas recognizes a signal to produce insulin. The liver begins to process excess glucose into the element glucagon. At the same time, the sugar level drops.
- When sugar is low, the pancreas receives a signal to stop insulin production, and glucose begins to be synthesized from glucagon. The liver temporarily stops processing glucose into glucagon. Blood sugar levels rise in the body.
- With normal sugar levels, when you eat food, the pancreas produces insulin, which helps glucose enter the cell and provide it with energy. The liver is at rest at this time.
Blood sugar and cholesterol: normal for women and men, tests, risk groups
Almost all people have heard about such an insidious disease as diabetes, but few people know that it is often asymptomatic and getting rid of this disease is very difficult. Tests that allow you to monitor the level of glucose in the body - a test using a glucometer or a laboratory test.
The blood sugar level in women and men differs depending on age, the presence of acute or chronic diseases, the time of meal and the method of testing (blood from a finger or a vein).
What is blood sugar
The name “blood sugar” is a purely popular designation for the medical term “blood glucose.” This substance plays a significant role in metabolism, because it is pure energy for all organs and tissues of the body.
Glucose is stored in the muscles and liver in the form of glycogen, and this reserve is enough for the body for 24 hours, even if sugar is not supplied from food. The hormone insulin is capable of converting glucose into glycogen, which, if necessary, returns to its original state, replenishing energy reserves, and controls sugar levels.
When conducting diagnostics to determine sugar levels, many patients wonder how sugar is indicated in a blood test?
Blood is a liquid tissue containing various cells and substances that perform important functions in the human body.
Qualitative and quantitative diagnostics of blood components make it possible to monitor physiological processes in the human body, promptly identify deviations from the physiological norm of the indicator and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
What types of diagnostics are there?
Blood tests are usually carried out to achieve certain goals.
One of the goals is prevention, which helps prevent the development of various diseases.
The second purpose of the examination is to confirm the diagnosis of the presence of a pathological process in the body.
Such information can be seen in a general blood test, which allows you to track:
- level of immunity in adults or children
- to what extent are the body's cells supplied with oxygen and essential nutrients?
- blood clotting level
- support of a process such as homeostasis.
In addition, tests such as biochemical analysis and diagnostics of blood sugar levels are often carried out.
Using biochemical analysis, the functioning of internal organs, their systems and metabolic processes is assessed. A distinctive property of blood sampling for biochemical analysis is that it evaluates the state of enzymes that are produced by liver tissue cells - aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyltransferase.
The amount of these enzymes in blood serum is normally small, since they are synthesized mainly in liver cells.
A blood test reveals changes in their quantity, which allows one to draw a conclusion about the development of pathological disorders in the liver such as cirrhosis and hepatitis; in addition, diseases of the heart, blood, and pancreas are detected.
If necessary, a medical specialist can prescribe a procedure for collecting test material for blood sugar levels. Such diagnostics allow you to see the level of glucose in the body and how well it is absorbed and used by cells.
Deviations from physiological norms may indicate the presence of disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism and the progression of diabetes mellitus.
Why is blood taken for sugar?
Enter your sugar or select your gender to receive recommendations Searching Not FoundShow Searching Not FoundShow Searching Not FoundShow
Blood in the human body is a liquid tissue.
This type of tissue performs certain physiological functions.
Blood contains a large number of highly specialized formed elements and liquid plasma with various chemical compounds dissolved in it.
The main functions that blood performs in the body are as follows:
- Nutrients, glucose, water, fats and amino acids are carried through the blood to the cells of all tissues of the body.
- Oxygen is transported to the cells of all tissues of the body due to the presence of the circulatory system.
- The body is cleansed of metabolic products.
- Thermoregulation and maintenance of optimal body temperature are carried out.
- Protecting the body from the invasion of various viral particles and bacteria.
- Ensuring the uninterrupted operation of all internal organs and systems.
If one of the processes is disrupted, the composition of the blood changes, which informs about possible diseases or the development of pathologies.
In addition, it is necessary to donate blood for analysis if you have the following symptoms:
- exhaustion of the body and sudden weight loss with a unchanged diet and lifestyleꓼ
- Feeling constantly tired, memory loss and inability to concentrate
- manifestation of dry mouth
- increased urination.
That is why carrying out such an examination as a blood test (including sugar) is quite important.
During the study, blood can be taken from a vein or a finger. As a rule, material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach to obtain more accurate results. Sometimes, after another blood sugar test, the doctor may change the current course of treatment, as a change in the situation during the course of the disease is indicated.
The data obtained from a blood sugar test shows the chemical level of changes in the human body. Thus, the specialist who performs the study determines the dynamics of the development of the pathological process.
Conducting laboratory diagnostics to check blood sugar levels makes it possible to diagnose a disease such as diabetes in the early stages of its progression.
This procedure is performed on all women during pregnancy, as gestational diabetes often develops, which can lead to negative consequences in the development of the fetus.
A normal sugar level in the analysis is a condition for the absence of deviations from accepted medical norms.
The table, which is a transcript, indicates how sugar is designated in the analyzes.
Interpretation of test results
What symbol indicates the level of glucose in the blood? What can the transcript of the laboratory results tell us?
The information obtained in the laboratory in a general blood test is indicated in a certain way.
To maintain good health, every person must eat properly and variedly. For the normal functioning of the body, it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, etc.
But due to an incorrect lifestyle, an unbalanced diet and a number of other features, the content of certain vital components may be overestimated or underestimated. This article will discuss the normal levels of blood sugar and cholesterol.
Sugar norm
How is sugar indicated in a blood test?
Most blood counts are read through tests performed on hematology analyzers. They allow you to immediately read 24 parameters, including “blood sugar,” which is designated here as GLU. Indicators are determined only by conducting a biochemical blood test or a special medication to determine glucose levels.
Many people try to find out how sugar is indicated in a general blood test. So, know that a general blood test deciphers only some parameters, such as hemoglobin, red blood cells, the number of blood cells and some others. You will not know your blood sugar level from a general analysis. A general analysis is carried out in order to determine the overall condition of the body. The only thing that can be said is that an indicator such as RBC or hematocrit can indicate the presence of diabetes; it indicates the ratio of plasma and red blood cells in the blood. For a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a biochemical detailed blood test for additional examinations. To the question of how sugar is indicated in a biochemical blood test, we give the answer - in Latin letters GLU.
What tests show sugar?
Glucose is a necessary component of energy metabolism. In the analysis it is designated in Latin as GLU. A special hormone, insulin, is involved in regulating its quantity and processing.
If there is a lack of it, the body's absorption of sugar is impaired. With such disorders, it is constantly present in the blood and urine. To determine existing abnormalities, laboratory testing is prescribed to the patient.
Reasons for appointment:
- dry mouth;
- itching and dry skin;
- constant thirst;
- long-term non-healing wounds;
- lethargy and weakness;
- frequent urination.
At the first stage, a main test is prescribed, which shows sugar. It includes a general urine test and blood glucose test. They are considered the most informative methods at the first stage of identifying pathology.
Testing is carried out in a medical facility. Capillary or venous blood is suitable for testing for sugar. An alternative is a rapid test, which is carried out using a special device - a glucometer.
A general urine test is included in the list of basic studies. It provides important information about the patient's health status. Normally, there should be no sugar in the urine. Its presence is a sign of diabetes or prediabetes.
In situations where sugar is detected in the main tests, additional testing is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Research is ordered in case of controversial issues:
- if sugar is not detected in the blood, but sugar is detected in the urine;
- if the indicators are slightly increased without crossing the diagnostic limit;
- if sugar in urine or blood was present in several cases (occasionally).
Note! Experts say changes in analysis can appear several years before clinical diagnosis. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo a preventive examination annually.
Video about sugar tests:
We measure glucose at home
Modern medical technology allows you to determine your sugar level yourself. You can purchase a glucometer for this purpose at any pharmacy. To do this, it is not necessary to understand how sugar levels are indicated in a blood test. The standard kit of any device includes a starter pack of special test strips and sterile lancets. The treated surface of the skin on the finger needs to be pierced with a lancet, and then a drop of blood is transferred to the test strip. By inserting it into the device itself, you can find out the result, which will be displayed in numbers on the screen.
Some types of glucometers are capable of reading information from capillary blood from any place on the body, be it the forearm, shoulder, or thigh. However, know that the fingertip has the highest blood circulation, so this is where you can get the best results at home. This is very important because sugar levels can change quickly with various emotional and physical stress, as well as after eating.
Conducting additional research
In some cases, a basic test for the amount of sugar in the blood is not enough; in such situations, the patient may be prescribed additional tests. There are three additional methods for diagnosing blood glucose concentrations:
- OGTT is a test to determine glucose tolerance, performed orally;
- Glucose load test;
- HbA1c – determination of the amount of glycated hemoglobin.
OGTT
An oral glucose tolerance test is also called a sugar curve; it requires several samples of material. The first time blood is taken on an empty stomach, then the patient drinks a certain amount of glucose solution. The second sampling of material is carried out an hour after consuming the solution. The third time blood is taken an hour and a half after drinking the solution. The fourth sampling is carried out two hours after drinking the drug. When comparing the information received, the test allows you to determine how quickly sugar is absorbed.
Glucose load test
A similar test is carried out twice. The first time blood is taken on an empty stomach, then the patient drinks 75 grams of glucose solution. The second time the material is collected two hours after consuming the glucose solution. Before carrying out this analysis, you should not eat, drink alcoholic beverages, smoke, move actively, or vice versa, just lie down or sleep, all these factors will affect the final result.
If the sugar level is no more than 7.8 mmol/liter, that is considered normal. If the readings range from 7.8 to 11 mmol/liter, the condition can be considered prediabetes. At levels above 11 mmol/liter, patients are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
HbA1c
Determining the level of glycated hemoglobin allows you to identify long-term excess blood sugar levels (up to three months). This analysis is carried out in laboratory conditions. The normal blood sugar level varies from 4.8 to 5.9% relative to the total amount of hemoglobin.
Carrying out tests to determine blood sugar levels plays an important role not only in the treatment, but also in the prevention of diabetes and other pathologies that develop against the background of a low or high dosage of glucose in the blood. It is necessary to follow the basic rules and take tests at the frequency established by doctors, this will allow you to respond in a timely manner to changes occurring in the body.
Kochetkova R.I.
Therapist of the first category, private medical, Moscow. Scientific consultant of the electronic journal "Diabet-sugar.rf".
Norm
Now that you know how sugar is indicated in a blood test, take a look at the test result and make sure that your levels are normal. What should they be? On an empty stomach in the morning from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. Numbers from 5.6 to 6.6 indicate impaired tolerance to blood sugar; this condition can be called borderline between pathology and normal.
An indicator of 6.7 mmol/l gives reason to suspect the presence of diabetes mellitus in the patient. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must prescribe a glucose tolerance test - an analysis two hours after the sugar load. With such a test, the normal value should increase to 7.7 mmol/l, impaired tolerance will be detected at 7.8 - 11.1 mmol/l. Confirmation of diabetes mellitus is 11.2 mmol/l.
The importance of testing
The most common procedure is a blood test. Prescribed before many more important medical procedures, appointments, or during the diagnosis of a disease. During this procedure, blood is taken from finger tufts and preferably on an empty stomach. Based on the results, the doctor is able to generate an overall picture of the patient’s health.
It happens that after the next blood sugar test, the doctor may make changes to the already prescribed course of treatment depending on the results. Indicators of a blood sugar test demonstrate the chemical level of changes in the human body, on the basis of which subsequent conclusions are made about the patient’s condition and the development of his disease.
A blood sugar test indicates many different indicators, thanks to which the disease is detected even at the earliest stage of development, which helps to react in time and prescribe treatment.
By testing a pregnant woman's blood for sugar, the doctor will be able to determine not only her condition, but also the condition of the fetus. In case of suspicion of the development of alleged deviations, promptly prescribe appropriate treatment.
| Diagnostics | Analyzes
Diabetics have to regularly test their blood for sugar. However, not everyone can decipher the information that is hidden under columns of numbers and symbols or Latin names.
Many people believe that they do not need this knowledge, because the attending physician will explain the results obtained. But sometimes you need to decipher the test data yourself.
This is why it is important to know how sugar is indicated in a blood test.
With Latin letters
Sugar in a blood test is designated by the Latin letters GLU. The amount of glucose (GLU) should not exceed 3.3–5.5 mmol/l. To track health status in biochemical tests, the indicators presented below are most often used.
- Hemoglobin HGB (Hb): the norm is 110–160 g/l. A smaller amount may indicate the development of anemia, iron deficiency or folic acid deficiency.
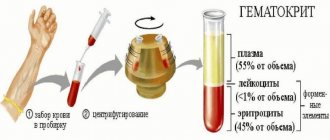
- Hemocrit HCT (Ht): the norm for men is 39–49%, for women – from 35 to 45%. In diabetes mellitus, the rates usually exceed these parameters and reach 60% or more.
- RBC red blood cells: the norm for men is from 4.3 to 6.2 × 1012 per liter, for women and children - from 3.8 to 5.5 × 1012 per liter. A decrease in the number of red blood cells indicates significant blood loss, lack of iron and B vitamins, dehydration, inflammation, or excessive exercise.
- WBC leukocytes: normal 4.0–9.0 × 109 per liter. A deviation upward or downward indicates the onset of inflammatory processes.
- Platelets PLT: the optimal amount is 180 – 320 × 109 per liter.
- Lymphocytes LYM: their percentage ranges from 25 to 40%. The absolute content should not exceed 1.2–3.0 x 109 per liter or 1.2–63.0 x 103 per mm2. Exceeding the indicators indicates the development of infection, tuberculosis or lymphocytic leukemia.
In diabetes, a significant role is played by the study of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), which indicates the amount of proteins in the blood plasma. The norm for men is up to 10 mm per hour, for women – up to 15 mm/hour.
It is equally important to monitor good and bad cholesterol (LDL and HDL). The normal value should not exceed 3.6–6.5 mmol/l. To monitor kidney and liver function, you should pay attention to the amount of creatine and bilirubin (BIL).
Their norm is 5–20 mmol/l.
General analysis
To determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, determine the amount of hemoglobin and blood cells, a general blood test is prescribed. The data obtained will help identify inflammatory processes, blood diseases and the general condition of the body.
Blood sugar levels cannot be determined using a general analysis. However, elevated hemocrit or red blood cell counts may indicate the development of diabetes. To confirm the diagnosis, you will need to donate blood for sugar or conduct a detailed study.
Detailed analysis
In a detailed analysis, you can track blood glucose levels for a period of up to 3 months.
If its amount exceeds the established norm (6.8 mmol/l), then a person may be diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
A complete blood test (GLU) can track blood sugar levels for up to three months.
Often, the results of the analysis are revealed by the percentage of the level of hemoglobin and glucose molecules. This interaction is called the Maillard reaction. With increased blood sugar, the level of glycated hemoglobin increases several times faster.
Special analysis
To detect diabetes mellitus, endocrine disorders, epilepsy and pancreatic diseases, a special blood sugar test will be required. It can be carried out in several ways.
- Standard laboratory analysis. Blood is taken from a finger between 8 and 10 am. The analysis is carried out on an empty stomach.
- Glucose tolerance test. The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. First, blood is taken from a finger. Then the patient drinks a solution of 75 g of glucose and 200 ml of water and donates blood from a vein for analysis every 30 minutes for 2 hours.
- Express research. Blood sugar testing is done using a glucometer.
- Analysis for glycated hemoglobin. The study is carried out regardless of food intake. It is considered the most reliable and accurate, as it allows you to detect diabetes at an early stage.
To understand the results of the data obtained, you need to know not only how sugar is indicated in a blood test, but also what its norm is.
In a healthy person, this figure does not exceed 5.5–5.7 mmol/l. If glucose tolerance is impaired, sugar levels can fluctuate from 7.8 to 11 mmol/l.
Diabetes is diagnosed if the numbers exceed 11.1 mmol/l.
Designation of glucose in foreign countries
The designation “mmol per liter” is most often used in the post-Soviet countries.
But sometimes it may happen that a blood sugar test needs to be done abroad, where different designations for glucose levels are accepted.
It is measured in milligram percentages, written as mg/dl and indicates the amount of sugar in 100 ml of blood.
The normal blood glucose level in foreign countries is 70–110 mg/dl. To convert these data into more familiar numbers, you should divide the results by 18.
For example, if the sugar level is 82 mg/dl, then when converted to the usual system, the result will be 82: 18 = 4.5 mmol/l, which corresponds to the norm.
The ability to make similar calculations may also be needed when purchasing a foreign glucometer, since the device is usually programmed for a specific unit of measurement.
Knowing how the level of glycemia is indicated in tests and what its acceptable norms are will allow you to identify a dangerous disease in the early stages and take timely measures. If there is a deviation upward or downward, you should immediately consult a doctor and reconsider your lifestyle and diet.
The normal functioning of the body largely depends on the stability of sugar levels in our blood. When consuming carbohydrates and sweets, processes occur that convert them into glucose. It is used by our body as energy.
Glucose enables a variety of functions, including processes that occur in the body at the cellular level.
The general condition of a person is characterized by various factors. The amount of sugar in the blood may exceed a certain norm.
Also, a blood test may reveal low glucose levels. Both lead to disruption of the functions of the entire body.
At the same time, the immune system suffers, and as a result, frequent inflammatory diseases - in the form of boils and fungal infections.
Other common symptoms of diabetes are dry mouth and increased urine output. Peeling appears on the skin and as a result everything itches. The person experiences constant fatigue and weakness.
If you notice at least one symptom, you need to check your sugar levels.
How glucose is indicated in a blood test - with the Latin letters Glu, just as sugar is indicated in tests.
Features of the analysis
It is imperative to regularly check your blood for glucose. Anyone can experience serious problems with the body if this indicator is not within normal limits.
Those patients whose parents or grandparents suffer from diabetes mellitus should especially pay attention to tests and take them regularly. This is a hereditary disease, it is transmitted genetically, and descendants need to monitor their health.
Blood sugar analysis is the most reliable and objective indicator of the health status of people with diabetes.
Deciphering a blood sugar test is necessary in order to understand how serious the situation is with such an insidious disease as diabetes, because often there are no symptoms at all.
What does a blood sugar test show?
Patients with diabetes undergo a blood test, regardless of the type of diabetes.
A blood test allows you to assess the state of the body's metabolic systems and make a decision on treatment tactics for diabetics.
The analysis evaluates indicators such as glucose in the blood plasma, as well as the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.
Thanks to sugar tests, the patient can find out the glucose level, because glucose plays an important role in the body - it supplies energy to all cells.
The norm in an adult patient is 3-5.5 mmol/l. According to the recommendation of doctors, you need to donate blood for sugar at least 2 times a year.
This material is devoted to the features of the blood sugar test (hereinafter referred to as ACS).
Medical term
The terminology “blood sugar, sugar test” has become part of the daily speech of citizens.
But among medical terminology there is no such concept as blood sugar, because sugar consists of a large number of elements.
So the correct name is blood glucose test.
There are 4 methods for determining blood glucose, namely:
- Laboratory - analysis is carried out in medical institutions. The main advantage is obtaining a 100% reliable result.
- Express - carried out using a home device called a glucometer. When using this device, blood from your finger should be applied to a special test strip. You can get the result in a couple of seconds. The disadvantage is the receipt of unreliable information (error up to 20%) due to non-compliance with the rules for caring for the device.
- Load analysis – blood testing is performed in 2 stages. Read more about this method in our article.
- Glycated hemoglobin - thanks to this technique, you can determine your sugar level over the past 3 months. This method is most often used in the treatment of diabetes.
Designation on the form
On the medical form, AKC is designated by letters such as “GLU.” This designation is associated with the word “glucose”. GLU informs the patient about how carbohydrate metabolism occurs in the body.
A similar combination is used in biochemical analysis, as well as in special studies.
Important! Glucose is measured in mmol/liter (hereinafter mm/l).
Cost of tests
Most people have a natural desire to control everything. With diabetes, this aspect becomes key in the life of a sick person. At home, almost all diabetics use a glucometer to monitor their blood sugar levels after meals.
What's in everyone's blood General blood test. For this test, blood is drawn from a finger prick. What do the letters that laboratory technicians mark on medical forms mean?
R.B.C. This is the designation for erythrocytes - red blood cells. One milliliter of blood from a healthy person should contain from 3.8 to 5.8 million red blood cells. If there are fewer of them, this is a sign of anemia. The following indicator will confirm the disease.
H.G.B. Hemoglobin (normal 110-165 g per liter of blood). If the hemoglobin level is below these figures, then we are really talking about iron deficiency anemia. Low hemoglobin levels also interfere with blood clotting. If the numbers are higher than normal, this is a hint of chronic leukemia - a benign blood disease.
NBTs are platelets that are involved in blood clotting. Normally, there should be from 350 to 500 thousand of them in one millimeter of blood. A reduced content indicates increased bleeding, a tendency to bruise and warns of blood diseases.
W.B.C. This is the designation for leukocytes - white blood cells. Their norm is 3.5 - 10 thousand in one milliliter. A decrease or increase in the number of leukocytes is a sign of inflammatory processes.
LIM. In this case we are talking about lymph nodes, which should be up to 30 percent of the total number of leukocytes. Exceeding the norm warns of possible tuberculosis or lymphocytic leukemia, but only a doctor can make final conclusions based on additional research.
EOD. If there are more than 5 percent of eozonophils, which are designated PVD, then the person has an allergy.
ESR. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The norm should not exceed 17 - 18 mm per hour. If red blood cells sediment at a rate above 20 mm per hour, this is a sign of inflammation.
Your biochemistry
If a general blood test shows deviations from the norm, biochemistry is prescribed. Blood is taken from a vein. Biochemistry tells how the kidneys and liver work, what is the water-salt metabolism and the balance of microelements in the body.
Glucose. Its norm is 3.50 - 5.80 mm per liter of blood. An elevated level indicates a risk of developing diabetes mellitus.
Glucose takes part in providing the body with oxygen and producing energy. Doctors attach special importance to monitoring this indicator, since any deviations can indicate serious violations.
It is necessary to test blood for sugar in the following cases:
- dramatic weight loss without changing your daily diet and lifestyle;
- decreased performance, constant fatigue;
- dry mouth, thirst;
- the volume of urine excreted increases.
It is recommended for all patients to periodically donate blood specifically for sugar, since a general analysis will not show the level of glucose in the blood.
This simple procedure will help monitor your health and begin treatment on time if you suspect the development of any disease.
Having received a form with test results from a doctor, it is not easy to understand at first glance what is hidden behind the names or columns of numbers and symbols.
Of course, the attending physician will be able to tell you everything about the tests, but it will not be superfluous to know how the tests indicate blood sugar, the presence of an inflammatory infection or other diseases.
How is blood sugar indicated in Latin letters?
Most of the blood test results are performed on hematology analyzers, which can automatically calculate up to 24 parameters simultaneously. Designations are written in Latin letters, followed by the obtained laboratory data.
To indicate blood sugar, the following combination of Latin letters is used - GLU (Glucose) or glucose. The concentration is indicated in mmol/l. Normally, this figure varies from 3.89 to 6.38 mmol/l.
These indicators are indicated only when conducting a biochemical or special medicinal blood test for glucose.
In detailed analysis
Finding out your sugar level when receiving a detailed blood test is quite simple. This data is indicated in a line designated in Latin letters GLU or Glucose.
As mentioned above, according to the norm, this figure should not be lower than 3.89 mmol/l and higher than 6.38 mmol/l.
An indicator that is too low or too high may indicate a danger to human health.
A decrease in sugar levels to 2 mmol/l can lead to critical disturbances in the functioning of the human central nervous system.
Detailed blood tests are also used to determine average sugar levels over a period of up to three months. This test is prescribed to detect diabetes mellitus.
The results are interpreted by determining the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that binds to glucose molecules. This reaction is called the Maillard reaction. This reaction occurs faster and the level of glycated hemoglobin in the blood increases if glucose levels are elevated.
In general analysis
In a general blood test, you can see only a few parameters, for example, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the amount of hemoglobin, the number of blood cells and others.
A general blood test is designed to determine blood diseases and detect inflammatory processes in the body.
This analysis is prescribed to determine the general condition of the body.
Blood sugar levels cannot be determined using a general blood test.
But, when deciphering an indicator such as hematocrit or RBC, one can judge the suspicion of diabetes, that is, a decrease in blood glucose levels. This indicator indicates the ratio of red blood cells and plasma in the blood. Normal levels range from 2 to 60%. If the indicator increases, a person may be diagnosed with diabetes.
Special blood test for sugar
A special blood sugar test is prescribed to detect diabetes mellitus, endocrine disorders in the body, epilepsy, and pancreatic diseases.
There are several types of blood sugar tests:
- laboratory;
- express analysis using a glucometer;
- glucose tolerance test or exercise test;
- analysis for glycated hemoglobin.
As in a detailed blood test, you can find out your glucose levels in the line with the same name. Normal values for a healthy person range from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. If the indicator is higher, the person most likely suffers from diabetes.
If the readings are below normal, we may be talking about hypoglycemia.
Sugar levels may have the following indicators:
- 5.5 -5.7 mmol/l (when a person is healthy);
- 7.8 mmol/l or 7.8-11 mmol/l two hours after eating (the person has impaired glucose tolerance);
- 7.8 mmol/l or more than 11.1 mmol/l two hours after eating (for diabetes).
Designation of blood glucose indicators
To determine the level of glucose in the blood, the calculation of data in millimoles per liter is most often used. This unit of measurement is used primarily in post-Soviet countries. Abroad, blood sugar levels are often measured in mg% or milligram percent.
These indicators can also be written as mg/dl. This data indicates the number of milligrams of glucose or sugar in 100 milliliters of blood. The norm for these data is from 70 to 110 mg%.
To convert this data into more familiar ones, you can use a special formula. It is necessary to divide the indicators in mg% by 18. Reverse calculations can be made in the same way.
Knowledge of this translation principle will be required for people who plan to undergo testing abroad or purchase a glucometer abroad. These devices can only be programmed for one unit of measurement.
Conclusion
After food enters the human body, that is, any amount of proteins, fats or carbohydrates, the level of glucose in the blood rises. Depending on the type of food, sugar levels can rise very quickly and fall just as quickly, or rise and fall gradually.
An organ such as the pancreas immediately responds to an increase in glucose by producing insulin.
Two to three hours after eating, blood glucose levels usually return to normal. That is, at different times of the day, the level of glucose in the blood may vary.
Signs of high sugar
Having explained what letters indicate sugar in a blood test, we will introduce you to the symptoms of high glucose levels:
- Feeling thirsty. This may indicate that your glucose levels are elevated. And this can serve as a sign of diabetes. When the body loses its ability to maintain normal sugar levels, the kidneys work more actively, they take additional moisture from the body. Frequent urges and dehydration occur. A signal is received to replenish water supplies.
- Fatigue. If sugar is not converted into energy, it simply sits in the blood, fatigue sets in, and sometimes you even want to lie down and take a nap.
- Dizziness. Frequent dizziness is a signal to consult a doctor. Possible increase in blood sugar.
- Legs and arms swell. Blood pressure and diabetes lead to kidney problems, followed by improper filtration of fluid, resulting in swelling.
- Tingling, numbness. When the temperature changes, a tingling sensation is felt in the limbs.
- Loss of vision. The sensitive nerve endings in the eyes are damaged as a result of high sugar and blood pressure. The function of the blood vessels in the eyes deteriorates and diabetic retinopathy occurs.
Interpretation of indicators and their meanings
A blood test has a lot of symbols, and finding sugar among them is not difficult if you know how it is formulated.
Biochemical analysis and its interpretation:
- Total protein is the amount of protein in the donor’s blood, which is directly involved in its coagulation and transportation of various substances throughout the body.
The norm depends on age - 64/8p g/l for an adult.
Excess - various infectious diseases, arthritis or even oncology.
Glucose (Glu) is the blood sugar that is most important for diabetics. Responsible for the entire carbohydrate metabolic process in the body. Norm – 3.30-5.50 mmol/l
The norm is 3.30-5.50 mmol/l.
Increase – diabetes mellitus.
- Urea is formed as a consequence of the breakdown of proteins in the body.
The norm is 2.5-8.3 mmol/l.
Increased – diseases of the kidneys, intestines and urinary system.
- Cholesterol (LDL, HDL), involved in the metabolic processes of fat cells and the body's production of vitamin D. It directly affects sex hormones.
The norm is 3.5-6.5 mmol/l.
Excess – atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases.
- Bilirubin (BIL) is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin and is itself an orange pigment.
The norm is 5-20 mmol/l.
Increased – B12 deficiency, jaundice, oncology.
- Creatinine is an indicator of kidney function. Participates in the energy exchange of tissues.
The norm is 53-115 µmol/l, the range is large due to the direct relationship of the patient’s weight, which affects the indicators.
Increased – renal failure.
- α-amylase is involved in the process of breakdown and absorption of carbohydrates.
Norm –28-100 units/l; pancreatic – 0-50 units/l.
Increased – peritonitis, diabetes mellitus, etc.
- Lipase is one of the enzymes produced by the pancreas. Promotes the breakdown of fat cells.
The norm is 190 units/l.
Excess – pancreatic disease.
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALAT, ALT) is a special-purpose enzyme. Used to diagnose liver conditions. Occurs in the blood due to the destruction of liver, heart or kidney cells.
The norm is 41 units/l in males and 31 units/l in females.
Exceeding symbolizes the rapid death of organ cells.
In brackets there is a designation in Latin letters or abbreviations, which are used mainly when testing blood for sugar.
Biochemical is considered a special subtype of general analysis. It is carried out only if the doctor has identified deviations from the norm in the general analysis report indicating a certain disease. Thus, it is clarified what specific disease arose in the patient, and only after a biochemical analysis is a more targeted diagnosis carried out.
In biochemical analysis, sugar is designated as glucose or its Latin abbreviation - Glu. The limited limits of the norm are ready to accurately indicate to the physician whether the patient has diabetes. Depending on how much the actual data differ from the norm, appropriate conclusions are drawn regarding the type of disease.
Since glucose is additionally responsible for the process of carbohydrate metabolism in the body and is produced by the pancreas, it can be concluded that diabetes occurs due to a violation of the digestive system in some cases. Concomitant diseases are also determined by the same biochemical analysis, the data of which can be easily deciphered after familiarization with the indicators and their meanings.
Ways to lower blood sugar
If you are familiar with the decoding of the symbols in a blood test, then you can easily determine whether your blood glucose level is elevated. What ways are there to lower your sugar levels and keep them under control?
- Maintain an optimal weight.
- Stick to a diet that includes a variety of vegetables, fiber, fruits, and few calories. Avoid alcohol completely.
- Spend more time relaxing. Get enough sleep. Go to sleep and wake up at the same time.
- Don't drink coffee at night.
- Exercise for at least half an hour a day.
Designation of glucose in foreign countries
The designation “mmol per liter” is most often used in the post-Soviet countries. But sometimes it may happen that a blood sugar test needs to be done abroad, where different designations for glucose levels are accepted. It is measured in milligram percentages, written as mg/dl and indicates the amount of sugar in 100 ml of blood.
The normal blood glucose level in foreign countries is 70–110 mg/dl. To convert these data into more familiar numbers, you should divide the results by 18. For example, if the sugar level is 82 mg/dl, then when converted to the usual system you will get 82: 18 = 4.5 mmol/l, which corresponds to the norm. The ability to make similar calculations may also be needed when purchasing a foreign glucometer, since the device is usually programmed for a specific unit of measurement.
Is it possible to cure diabetes?
It is impossible to completely recover from diabetes. Modern science has not yet come up with such methods. By controlling glucose levels and knowing how sugar is indicated in a blood test, it is quite possible to alleviate the course of the disease.
In type 1 diabetes, the cells responsible for producing insulin are completely destroyed. Patients constantly need to inject insulin into their body. In the second type, insulin resistance occurs. This is when the body does not know how to use insulin.
With infrequent surges in blood sugar, a proper diet and exercise allow you to control glucose and live a normal life.
The importance of blood sugar for the body
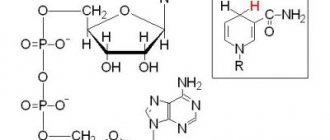
Sugar or sucrose is a special chemical substance from the class of carbohydrates, a natural compound necessary for the life of all living cells, both plant and animal origin.
There are different opinions about sugar. Some consider it “white death” or “sweet death”, while others cannot imagine their existence without sweets and consider it a source of energy and strength. In order not to go to such extremes, you should know about its composition, role in the body, beneficial and harmful properties.
Sucrose is a complex carbohydrate whose molecules stick together to form crystals . Each sugar molecule consists of 2 components: glucose and fructose. Once in the digestive tract, this molecule is split and both of its components are absorbed into the blood from the intestines and distributed throughout the body. Glucose immediately takes part in all metabolic processes, and fructose goes through a certain cycle and eventually also turns into glucose.
The benefits of sugar
Glucose, released from sugar molecules, plays the main role in the energy exchange of all cells, supplying the body with 80% of the total energy required for life processes.
Sugar plays a special role in maintaining liver and muscle cells, and also promotes the production of serotonin in the body - the “joy hormone”, necessary for the normal functioning of the neuropsychic sphere.
Excess glucose is converted into glucagon in the liver, creating a reserve that is released into the blood when there is a lack of sugar. Excess fructose promotes its transformation into fats, which are also an energy “depot”.
Sugar is very important for the proper functioning of the digestive system, so a study of its level is most often prescribed if there are suspicions of diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
The harm of sugar
Sugar itself, as such, when consumed wisely, does not cause harm to the body. A negative effect occurs when there is excessive consumption or insufficient energy consumption due to physical inactivity.
Consequences of excess or lack of glucose:
- Calcium binding and its deficiency in the body, resulting in diseases of the teeth and skeletal system;
- Excessive formation and deposition of adipose tissue (obesity);
- Predisposition to the development of atherosclerosis.
Low indicator level
In what cases can a decrease in blood glucose levels occur? In the following:
- Malabsorption syndrome, when the absorption of glucose into the blood is difficult.
- Severe toxic liver damage, fulminant necrosis. When glucagon release cannot occur.
- Endocrine pathologies: with a decrease in the synthesis of contravascular hormones; with Addison's disease (the adrenal cortex does not produce enough hormones); with insulinoma - increased insulin synthesis.
Who needs to donate blood
A sugar test is necessary for patients who have already been diagnosed with diabetes; they must constantly, ideally daily, measure the indicators, and if they deviate from the norm, take measures to stabilize the value. Not only the quality of life of people with diabetes, but also their very existence depends on such procedures.
People who have relatives with diabetes, as well as patients who are obese, should undergo an annual examination. People who do not have a predisposition to pathology are recommended to take a blood sugar test once every 3 years after reaching the age of 40 years. The frequency of testing for blood glucose concentrations for pregnant women is prescribed by the doctor; ideally, patients awaiting replenishment of their offspring should be tested for sugar once a month, as well as every time other blood tests are performed.
Factors affecting blood sugar levels
The table shows conditions that affect the concentration of glucose in the blood, increasing or decreasing it.
| Excess sugar | Sugar deficiency |
| Eating before taking material | Starvation |
| Physical or psychological stress | Drinking alcoholic beverages |
| Diseases of the endocrine system | Metabolic disorders |
| Epilepsy | Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (enteritis, pancreatitis), gastric surgery |
| Malignant tumors of the pancreas | Liver diseases |
| Carbon monoxide poisoning | Pancreatic neoplasms |
| Taking corticosteroids | Disorders of the vascular system |
| Taking diuretics | Chloroform intoxication |
| Increased nicotine content | Insulin overdose |
| Thyroxine | Sarcoidosis |
| Indomethacin | Arsenic exposure |
| Estrogens | Stroke |
The dangers of low glucose levels
What are the signs of low sugar and why is a decrease in blood glucose levels dangerous?
- When there is a lack of glucose, cells feel energy starvation. The brain is most sensitive to this. The predominant signs of energy starvation are damage to the central nervous system.
- Signs in the early stages: trembling, hunger, nausea, sweating, rapid heartbeat, peeling skin around the lips, anxiety.
- Late signs include: impaired attention, confusion, difficulties in communication, drowsiness, headaches, blurred vision, inadequate perception of what is happening, disorientation.
- If there are early signs, the patient must help himself, consult a doctor in time, and find out the cause. In later stages, loved ones should get involved, since it is difficult for the patient to cope with the situation on his own. Without treatment, irreversible processes can occur, including hypoglycemic coma and irreversible brain damage.
The consequences of low blood sugar can be quite dire. Inappropriate behavior of the patient can lead to various incidents - domestic or road traffic. In this case, you simply need to seek medical help.
Causes and symptoms of hyperglycemia
Increased blood glucose concentrations lead to a syndrome called hyperglycemia. Its causes may be either insufficient insulin production or its relative insufficiency due to excess sugar entering the body, as well as decreased sensitivity to insulin.
Hyperglycemia is considered a condition in which fasting blood sugar exceeds 6.1 mmol/l, and 2 hours after a meal exceeds 8 mmol/l.
Hyperglycemia is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- Increased thirst;
- Increased urine output;
- General weakness;
- Headache;
- Dry and itchy skin.
Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to disruption of tissue microcirculation, the development of hypoxia, fragility of blood vessels, and damage to nerve fibers.
Hypoxia entails many complications: dystrophic changes in organs (heart, liver, kidneys), the development of vascular atherosclerosis, tissue circulatory disorders, trophic disorders, disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system. Immunity also decreases, and complications of an inflammatory and infectious nature develop.
In severe cases, when the blood glucose level is above 30 mmol/l, hyperglycemic (diabetic) coma develops.
Hyperglycemic coma is manifested by lethargy, loss of consciousness, shallow breathing, decreased blood pressure, weakened pulse, and the characteristic smell of acetone from the mouth. This condition is completely reversible if treatment measures are taken in time.
Ways to lower blood sugar
Hyperglycemia requires constant correction and control.
Lowering blood sugar levels is carried out using a combination of the following methods:
- Diet therapy;
- Medications;
- Traditional medicine.
Diet to lower blood sugar
Compliance with a diet is a necessary condition for the treatment of hyperglycemia, that is, diabetes mellitus.
The basic principles of nutrition for diabetics are:
- Reduced carbohydrate content;
- Increased protein content;
- Sufficient amount of fiber and vitamins;
- Calculation of the calorie content of food so that it corresponds to the patient’s energy consumption, taking into account his activity and type of occupation;
- Eat small, frequent meals to avoid sudden changes in glucose levels.
Among foods with a low glycemic index, the “champions” are seafood: mussels, shrimp, squid, oysters. They not only contain virtually no carbohydrates, but are also rich in easily digestible protein, minerals and biologically active substances.
Legumes are very useful, especially soybeans. Tofu soy cheese is well known, which is rich in vegetable protein and B vitamins and calcium. Low-fat sea fish, boiled beef, and turkey meat are very useful. Recommended cereals include oatmeal and buckwheat; they are rich in iron, vitamins, and contain fewer carbohydrates.
Half of the diet of diabetics should be vegetables - fresh and stewed. Moreover, you should choose green vegetables: cabbage of any kind, cucumbers, lettuce, spinach, leeks, greens, asparagus, artichokes, green beans.
A special place is occupied by the earthen pear - Jerusalem artichoke, it contains inulin - an analogue of insulin. Suitable fruits include citrus fruits - lemon, orange, grapefruit, as well as green varieties of apples and nuts. Recommended seasonings are bay leaf, pepper, garlic, they increase metabolism and cell sensitivity to insulin.
Drug reduction of sugar
To normalize high glucose levels, glucose-lowering tablets and insulin replacement therapy are used.
Drugs for normalizing blood sugar are divided into 2 groups:
- Stimulating the production of insulin by the pancreas;
- Increasing tissue sensitivity to insulin and muscle glucose consumption.
Group 1 includes glibenclamide (Maninil), chlorpropamide and their analogues, as well as new generation long-acting drugs - gliquidone, diabeton, minidiab and others.
Representatives of the 2nd group - pioglitazone, rosiglitazone, metformin, new generation - acarbose, sitagliptin, liraglutide, Forxiga and others. There are many such drugs, their selection is carried out individually depending on the type of diabetes.
Insulin treatment is prescribed as replacement therapy for type 1 diabetes; the doctor determines the dose and frequency of use individually.
Many types of insulin are used - by duration of action, by components and created by genetic engineering. According to the method of application, injections are distinguished with a syringe, a special “pen”, or an insulin pump with programmed automatic administration of the drug.
Folk remedies
The effectiveness of the main treatment of diabetes is increased by proven folk remedies: tincture of horseradish, garlic, onions, oats, bean pods, decoction of lilac buds, currant leaves, ginger tea.
Before using any traditional medicine, you should definitely consult your doctor.
Measuring blood sugar at home
Modern medical technologies allow diabetic patients to regularly monitor their sugar levels without time-consuming visits to the doctor and laboratory, that is, at home. For this purpose, portable glucometers are used, for which just a small drop of blood from a finger prick is sufficient.
The frequency of sugar monitoring in type 2 diabetes is usually once a month, and in insulin-dependent diabetes, more frequent analysis may be needed, depending on the severity of the disease and methods of correcting blood sugar.
Among the variety of glucometers, you need to choose the most suitable and convenient one. For example, for young people with an active lifestyle, you need to choose unpretentious devices with quick analysis calculations, for example, the One Touch device. For older people, devices with a larger screen and fewer functions, for example, Satellite, Diakont, Accu-Chek, will be more convenient.
All devices for home express glucose monitoring are divided into 3 types:
- Photometric, which uses a light sensor that records light passing through the strip;
- Electrochemical, recording the electric current passing through the strip;
- Non-invasive, do not require a puncture and determine the level of glucose in the blood flow in the capillaries of the earlobe.
There are devices that, along with glucose, determine other biochemical blood parameters (cholesterol and other lipids), which is very important, for example, in type 2 diabetes with a tendency to obesity and atherosclerosis.
In any case, in order for the choice of the device to be optimal and the interpretation of the result of a blood glucose test to be as reliable as possible, you should consult a doctor.
The video demonstrates the general rules for using a glucometer.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is understood as a condition when the level of glucose in the blood drops to 3 mmol/l or below. This condition is even more dangerous than hyperglycemia, because vital processes in all organs and tissues are disrupted, and if assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the patient can be lost in a fairly short time.
The causes of hypoglycemia can be fasting, all kinds of diets for weight loss, dysfunction of the digestive tract, excessive exercise, as well as an overdose of insulin or glucose-lowering drugs in patients with diabetes.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia:
- Nervous excitement, anxiety;
- A strong desire to eat something, especially sweets;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Palpitations;
- Trembling in the body;
- Disorientation in space;
- Numbness of body parts.
When assistance is provided, the symptoms of hypoglycemia quickly disappear; otherwise, convulsions, loss of consciousness, respiratory and heart failure develop, coma quickly develops, and death may occur.