Every year there is a tendency to expand and modernize innovative diagnostic methods. Just a few years ago, glandular tissue pathology could only be verified using a laboratory hormonal blood test. However, in our time, the arsenal of diagnosticians has been enriched with more modern and informative methods, one of which is computed tomography (thyroid, parathyroid glands), which allows a more accurate examination of the endocrine organs.
Indications for computed tomography (CT) of the thyroid gland
Computed tomography of the thyroid gland allows you to examine the tissues of the neck and determine any structural changes in them at the earliest stages of development. This procedure may be prescribed to confirm a preliminary diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment for various diseases.
A thyroid CT scan is recommended for the following disorders:
- sudden change in voice - the appearance of this symptom may signal the development of tumor formations and compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Computed tomography of the thyroid gland is performed to identify tumors in the throat, identify inflammatory processes and determine the cause of a sudden change in the patient’s voice;
- difficulty in swallowing liquid or solid food - discomfort, difficulty swallowing, or pain during swallowing can be observed in patients with thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland). This disease occurs when various infections enter the body or chronic viral diseases worsen. In addition, such a symptom may indicate the development of tumor processes;
- compression of the esophagus - patients have difficulty swallowing, a so-called “lump in the throat” occurs, and pain appears in the process of swallowing food. A thyroid CT scan is prescribed to determine the cause of such unpleasant sensations. Assessment of the thyroid gland is necessary to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment regimen;
- diseases of the trachea - timely CT scanning of the thyroid gland ensures the detection of all structural changes, incl. determination of inflammatory processes in the trachea, cysts, tumors, suppurations and chronic diseases in the early stages. The development of pathological processes in the trachea can be accompanied by pain, discomfort, difficulty breathing and many other symptoms;
- enlarged lymph nodes - this disorder can occur if infections and viruses enter the patient’s body, as well as if metastases from the thyroid gland enter the lymph nodes. If the presence of a malignant neoplasm is suspected, contrast is injected before starting a CT scan of the thyroid gland.
What can be seen with a thyroid CT scan?
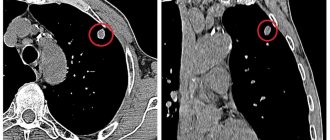
Computed tomography involves obtaining layer-by-layer sections, resulting in a three-dimensional image of the areas under study. The images visualize the location and type of tumor formations. In case of cancer, a CT scan of the thyroid gland shows metastases.
The study helps to accurately determine the size and location of the gland, the degree of compression of surrounding organs.
The images show blood vessels, bones, and lymph nodes.
In addition to assessing the condition of the thyroid gland, a CT examination also reveals:
- atherosclerotic changes;
- injuries to the cervical spine;
- A CT scan will show a parathyroid adenoma and other pathologies of neighboring organs;
- damage to neck tissue.
With abnormal localization of iron, in many cases it is recorded in the retrosternal region.
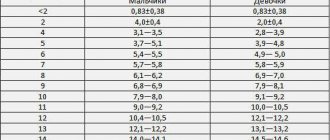
The gland in a healthy state has a homogeneous tissue structure. The volume of the adult thyroid gland is 18-25 cm³. For children, the indicator is calculated depending on age.
Computed tomography (CT) of the thyroid gland: advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of thyroid CT include the absence of the need for surgical intervention in the body, as well as the short duration of the procedure itself. Using this method, specialists have the opportunity to obtain clear images and visualize all tissues in the areas under study, thanks to which an experienced diagnostician can make the correct diagnosis and identify the causes of its development.
The only disadvantages of thyroid CT include limitations in the frequency of use of this method - the study cannot be performed more than twice a year. In case of emergency, three procedures are allowed, at intervals of no shorter than one month.
What can be detected: normal and pathological
Changes in position, size, shape
Normally, the thyroid gland is located in the lower third of the sublingual region of the neck, surrounding the trachea in front and on the sides. The gland consists of two lobes and an isthmus. Its structure is normally homogeneous, density 70-120 units. Hounsfield. After contrasting, the density increases to 150-200 units.
If there are positional anomalies, thyroid tissue can be found anywhere in the area of the thyroglossal duct - from the base of the tongue to the upper mediastinum. This disorder is called ectopia. An enlarged gland is usually associated with a goiter, tumor, or cyst.
- On CT without contrast, it is difficult to distinguish a hyperplastic node in the parenchyma from a tumor or cyst. An ultrasound-guided aspiration biopsy with cytological examination of the aspirate is required.
- The reduction and deformation of the gland is caused by a previously performed operation. Possible options: removal of a lobe or isthmus, total or subtotal resection.
Edge Characteristics
- The sides of the organ may be clear or blurred.
- Clear edges are characteristic of benign tumors, goiter, and low-grade neoplasms.
- Invasive margins are a specific sign of malignant tumors: carcinoma, lymphoma, metastases.
Goiter and benign tumors push neighboring structures to the side, but do not infiltrate them, unlike malignant ones.
Nodal changes
The thyroid nodule can be colloidal, hyperplastic, tumor, mixed. Nodules are distinguished between probably benign and potentially malignant.
- The former are monitored over time using ultrasound and Dopplerography; if the size of the node increases, a biopsy is performed under sonography control.
- Potentially malignant nodes require surgical intervention: excisional biopsy, lobectomy, total thyroidectomy.
In addition to assessing the primary tumor, the method makes it possible to visualize adjacent organs and lymph nodes of the neck and upper mediastinum. The apexes of the lungs, vertebrae, and airways can also be assessed. In addition, CT shows the degree of narrowing of the tracheal lumen, complications after surgical treatment, punctures, inflammatory changes (thyroiditis, abscess).
Features and Limitations
Thyroid CT is better than ultrasound for visualizing goiters hidden behind the sternum and for assessing deep lesions and looking for ectopic thyroid tissue. However, ultrasound makes it possible to more accurately assess the likely nature of the foci identified in the gland.
Doppler ultrasound is used to assess blood flow. Even contrast does not achieve the sensitivity and specificity similar to sonography.
Please note: Ultrasound is better suited for identifying and assessing superficial lesions; tomography provides a “broad view” of the neck organs.
X-ray computed tomography of the thyroid gland with contrast
Computed tomography of the thyroid gland with contrast is indicated for patients with suspected cancer. This type of examination allows you to detect changes in the thyroid nodes and glandular tissues.
Any contrast agent is based on iodine. The substance is administered intravenously. During the administration of contrast, patients may experience reactions such as nausea, local fever, and the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth. These sensations should not cause concern, since they are only confirmation of the entry of the contrast agent into the vessels. After 15-20 minutes, most of the substance is excreted by the kidneys.
The contrast agent should not be administered to patients with an allergy to iodine, as well as those suffering from a number of diseases: diabetes mellitus, renal failure, hyperthyroidism.
How is a thyroid CT scan performed?
An examination of the thyroid gland lasts, on average, from 5 to 15 minutes, depending on whether contrast was administered. Examinations using contrast agents take longer.
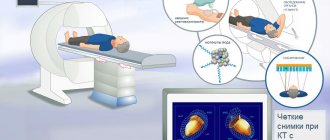
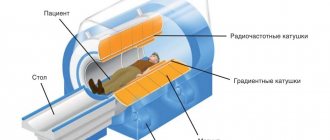
To carry out the procedure, the patient needs to lie down on a mobile couch, which is pushed into the ring of the tomograph machine.
If a CT scan of the thyroid gland must be performed with a contrast agent, it is sequentially injected into the cubital vein using the bolus method (automatic dispenser) just before the start of the study.
Then the specialists prepare the tomograph, determine the type of scanning, and select the optimal mode of operation of the device. During the diagnostic study, the table constantly moves, and the tomograph ring rotates around it.
The operation of the tomograph is indicated by the presence of slight noise. The patient has no painful sensations.
What to do before a CT scan
In order to exclude false results before undergoing a thyroid CT scan, it is important to follow the rules:
- 2-3 days before the examination, do not take medications or eat foods containing iodine.
- When examining with a contrast agent, do not eat food 6-8 hours before the scan.
- Come to the diagnosis in comfortable clothes that do not have metal elements. Remove metal jewelry, watches, belts, hair accessories, otherwise the products may cause erroneous results.
If the patient is not aware of the presence of an allergic reaction to iodine preparations, then an allergy test is performed.
Computed tomography (CT) of the thyroid gland: contraindications
Despite its relative safety, thyroid CT involves the use of ionizing radiation, so uncontrolled use of this procedure should be avoided. In order to reduce the level of radiation, the frequency of computed tomography must be strictly limited, and the benefits and harms of the procedure are assessed by a specialist.
CT scanning of the thyroid gland is contraindicated in the following categories of patients:
- pregnant women (at any stage);
- children under 14 years old
- patients with an allergy to contrast agent (iodine);
- overweight persons (more than 150 kilograms).
Computed tomography of the thyroid gland is not performed during pregnancy due to the high likelihood of harmful effects on the fetus caused by X-rays. If a nursing mother undergoes the procedure, breastfeeding must be stopped for at least two days after the examination.
Thyroid CT is usually not prescribed for pediatric patients. However, in situations where the benefits of the examination outweigh the possible risks, the procedure can be performed on children, having first carefully read the rules for preparing for tomography, which will be more stringent than for adults.
The procedure is also contraindicated for persons with an allergic reaction to the contrast agent that occurred during a previous scan, which should be reported to the doctor.
Due to the presence of weight restrictions for all tomographs, patients with excess weight (exceeding 150 kilograms) are selected other methods for diagnosing the thyroid gland, for example, Doppler ultrasound.
CT (computed tomography) is a modern diagnostic technique. It is used in a variety of medical fields, in particular in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid diseases. The reliability of the examination results, as well as the effectiveness and safety of tomography, largely depend on the professionalism of specialists and the quality of medical equipment.
The Yusupov Hospital in Moscow is equipped with modern computed tomographs that meet the highest safety and reliability criteria. Appropriate professional training and the highest qualifications of the clinic’s specialists ensure high quality of diagnostic procedures of any degree of complexity, including CT of the thyroid gland, CT of the parathyroid glands, CT of the pancreas with contrast. What the study shows, whether any pathologies were found - all this is deciphered in detail by the doctors of the Yusupov Hospital, who, based on the results of the examination, select an effective treatment regimen for the identified diseases.
Author
Vladimir Vladimirovich Kvasovka
Deputy General Director for Medical Affairs, therapist, gastroenterologist, Ph.D.
Possible contraindications for diagnosis
There are no strict contraindications to the procedure. CT scanning is only not recommended:
- pregnant women;
- children under 7 years old;
- breastfeeding.
But, if there is a certain risk, doctors can prescribe computed tomography even for these categories of patients. Thanks to modern equipment, it was possible to significantly reduce the radiation dose received by the body during this study. But the patient will still receive a certain portion of x-ray radiation. In some cases, radiation is a lesser evil than the pathology being studied.
It is also contraindicated to conduct a thyroid examination using a computed tomograph if the patient:
- claustrophobia;
- overweight (more than 150 kg).