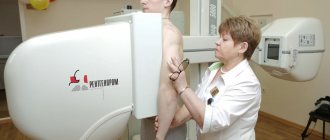
Modern medical practice cannot be imagined without the use of x-rays. With its help, simple X-rays of bones and internal organs are obtained, it is used for fluorography of the chest organs and mammary glands, and it forms the basis for CT studies and contrast studies of blood vessels.
Radiography is widely used in pediatric practice. The World Health Organization states that in the presence of serious indications and in the absence of alternative diagnostic methods, X-ray examination should be carried out in children of any age.
Despite such statements, many concerned parents are interested in whether it is harmful for their child to have an x-ray? And this is quite understandable, because the main responsibility of every parent is to take care of the health of their children. And while the benefits of many other procedures are obvious, radiography raises many questions.
The effect of X-rays on the child’s body
In children, internal organs are located close to each other. Often, when X-rays are performed, healthy parts of the body are also affected, which means that the amount of radiation received also increases.
During one x-ray session, a child will receive from 0.01 mSv to 0.6 mSv. This is considered minor exposure and does not adversely affect the child's body.
In a small child, the red bone marrow occupies a larger area than in an adult. It reacts to x-rays more than other organs. X-rays ionize blood cells. Some doctors believe that this leads to the formation of malignant tumors. Other groups of doctors see no harm in taking x-rays and no connection with the development of cancer cells. But research on this topic is still underway, and no group of doctors has an exact conclusion.
How is it harmful and dangerous?
X-rays are small doses of radiation. They affect the body and increase the chance of developing a tumor in the body by 0.001%.
As a result of long-term radiation, X-rays most strongly affect the hematopoietic organs:
- minor changes in blood structure;
- decreased immunity for a short period of time;
- changes in the structure of leukocytes and a decrease in their number - leukemia;
- decrease in platelet count - thrombocytopenia;
- decrease in the number of red blood cells - erythrocytopenia.
Hazardous effects of X-rays:
- development of malignant tumors;
- metabolic disease;
- dysfunction of the genital organs;
- blurred vision;
- skin aging.
Children are not given X-rays of the thyroid gland or genitals, and girls are not given X-rays of the ovaries. This can lead to impaired fertility.
Doctors prefer to perform less harmful procedures on children: ultrasound or computer fluorography. Such opportunities are not always available; complex diseases are diagnosed only with the help of X-rays.
Negative consequences of X-ray diagnostics and ways to avoid them
Modern X-ray machines are difficult to compare with those that were used 10-15 years ago - the intensity of the X-ray dosage has become significantly lower, especially in special medical equipment intended for small patients. In addition, the duration of radiation exposure during an image is extremely short - 1-2 seconds are enough to achieve the desired result. This feature allows you to minimize the risk of complications after an x-ray, even if it is performed several times - the amount of radiation will still be insufficient to cause changes in the cells of the child’s body.
No doctor will order an x-ray for a child without a reason; sometimes it just doesn’t seem obvious. However, if a specialist recommends this type of diagnostics, it means that there is simply no worthy alternative, and all that remains is to take measures to reduce the negative consequences of radiation.
Folk remedies for removing radiation from the body
If a child often has to undergo x-rays, it makes sense to additionally consult with a diagnostician regarding effective measures to reduce radiation exposure to a small body - this will minimize the already insignificant risks, reducing them to almost zero. Thus, as a comprehensive measure, many experts advise, after an X-ray examination, to slightly adjust the diet, focusing on healthy foods that help neutralize the effects of X-rays (of course, if the child is allowed such foods by age). What dishes are excellent at removing low doses of radiation typical of X-ray machines? Their list is not so small:
- a glass of warm milk immediately after visiting the clinic;
- grape juice with pulp;
- fish and seafood rich in iodine;
- fermented milk products with fiber and potassium;
- persimmons and other fruits containing a supply of vitamins in combination with iodine;
- natural olive oil, preferably cold pressed;
- dried apricots, prunes and dishes containing them;
- bee pollen or honey;
- quail eggs;
- beet.
In addition, you should actively feed your child compotes, fruit drinks or green tea, and focus on broths and first courses - abundant fluid intake will help you cope with the X-load faster. If your baby takes a complex of vitamins, make sure that they contain:
- Carotene (provitamin A) is a substance that has a positive effect on the processes of restoring cell structure. An additional dose of provitamin can be obtained from fresh carrots, tomatoes, sea buckthorn, and apricots.
- Selenium is one of the best natural antioxidants that protects the body from the negative effects of the environment. You can enrich your diet with selenium by focusing on rice, legumes and eggs.
- Methionine is a substance that promotes cell regeneration. Contained in quail eggs, green beans, and sea fish.
However, you should not feed the child too much after repeated x-rays - light, split meals help to quickly cleanse the body, and therefore it is not recommended to overload the gastrointestinal tract.
Indications for x-rays
Indications for radiography:
- fractures;
- diseases of the chest organs;
- foreign objects in the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract;
- dislocation of the hip joint;
- skull injury;
- suspicion of the formation of cancerous tumors;
- diagnosis of dental condition.
In newborns
A newborn is never given an x-ray for prevention. A doctor may prescribe this diagnostic method to children when the diagnosis needs to be made quickly and accurately.
Indications for x-ray of a newborn:
- injuries sustained during and after birth;
- pneumonia;
- ingestion of foreign objects into body organs;
- musculoskeletal pathologies;
- intestinal obstruction;
- preparation for surgery, if you need to find out more information.
Grudnichkov
X-rays are taken for infants under one year of age for the same reasons as for newborns. Complications after childbirth may not appear until several months later. Since X-rays are not taken just in case, after a difficult birth mothers need to closely monitor the health and behavior of the baby. If there are complaints about the child’s health, the doctor will send him for examination. Birth injuries are better visible on x-rays and may not appear externally.
Children from one year old
Children over one year of age undergo x-rays for the following indications:
- body injuries caused by falls;
- if the child has swallowed a foreign object or there is a suspicion that he has;
- diseases of the chest organs.
A child two years old and older may undergo a preventative X-ray of the head after a fall to rule out traumatic brain injury.
New X-ray machine on the channel "GTRK Mari El".
Types of X-ray examination
There are several types of radiographs depending on different criteria. Depending on the way the image is displayed, X-rays can be film or digital. It is preferable to do a digital x-ray; its dose is 0.1-0.3 mSV. Film apparatus 0.3-0.5 mSV.
It is important to understand that a lot depends on the manufacturer of the device, and these doses are not received by the child, but the radiation from the device. To determine this, a modified exposure meter is required, which calculates the received radiation exposure due to the organ being studied, its density, and the dose emitted by the device. Such equipment is not available everywhere, and it is not always possible to find out about the dose received.
A chest x-ray is done in two projections. Nothing depends on the wishes of others - the doctor will prescribe the study that will better illustrate the problem in the image.
Important! When prescribing an x-ray, parents should not refuse it, and choose a medical institution with a digital x-ray machine; this will be the key point in a harmless examination of the child. For information about x-ray equipment, ask your x-ray technician.
How often and how many times can x-rays be taken?
Children under one year of age are recommended to have x-rays no more than twice a year. If this is not possible, doctors try to wait 4 to 6 months between irradiations.
Children under 12 years of age, according to WHO recommendations, are allowed to have x-rays no more than 6 times a year. Several months should also pass between procedures.
But it happens that a child needs to have a series of x-rays taken. This increases the risk of radiation. Typically, young children are sent for x-rays twice: upon admission to the hospital, and upon discharge from it. This is considered the minimum dose, which in comparison with the danger of the disease is the least evil.
Children over 14 years of age are recommended to undergo fluorography of the lungs every year. A child suffering from tuberculosis and other dangerous diseases is given an x-ray every year.
How to do chest x-rays for young children
Whenever possible, an X-ray of the child’s lungs is done using a digital device, since it provides a minimal dose of radiation. If there is no diagnostic device at the doctor’s place of work, they try to conduct research in another institution. The doctor is provided with an image and its description, which is carried out by a radiologist. In preparation for a chest X-ray for children, clothing and metal objects are removed. Areas not to be irradiated are covered with a lead apron.
The youngest children are reliably captured because movement distorts the image results. In this case, you will have to do a repeat study, which increases the radiation dose.
A children's X-ray machine is different from an adult's. Therefore, parents should familiarize themselves with the procedure for research before undergoing the session. In order not to expose the baby to the risk of repeated examination, it is necessary to ensure temporary immobility during the examination. The devices are stands made of non-solid material. The clamps securely hold the torso and limbs. Such a device is not required for children over 5 years of age.
It doesn't take much time to develop pictures. However, the radiologist is required to make a description. Therefore, the results of the work are given to the patient’s parents the next day or at another time prescribed by the doctor.
Important! Postnatal injuries may not be clinically apparent, but a pediatric chest x-ray will clearly show this in newborns.
Calculation of the maximum permissible radiation dose for children
The doctor considers the amount of radiation exposure for each child individually. The radiation exposure rate for a child per year is equal to two x-ray procedures, which is from 0.01 to 1.2 mSv. If a child is prescribed a larger number of procedures, parents can find out which types of x-rays will cause the least harm. Often these procedures are paid, but are carried out on modern computer devices, with less radiation than from a microwave oven.
When calculating the permissible dose, 4 factors will be taken into account:
- physical characteristics of the child;
- duration of irradiation;
- radiation dose;
- number of procedures.
Features of the procedure in children
Young children over two years old are given x-rays in the presence of adults. Parents ensure the baby's immobility. In cases where the child cannot lie still, he is secured with special straps.
Stillness is an important part of the procedure. The photo will blur at the slightest movement.
The baby is protected as much as possible from unnecessary radiation by wearing a lead apron and pads. Anyone accompanying the child must also wear such an apron.
Children under two years of age are placed in a special flask that ensures immobility.
X-ray flask
What is the harm of x-rays?
It works on the following principle: ionizing radiation emitted by a special apparatus penetrates thin, low-density tissues and stops at denser layers, resulting in a familiar picture.
At first glance, everything seems safe. But the fact is that this radiation is radioactive. And radiation, as is known, is capable of changing the structure of cells, knocking particles out of atoms; this leads to changes in the DNA structure (sometimes there is a risk of cancer). And given the fact that in childhood the growth and development of cells is especially rapid, radioactive radiation is doubly dangerous.
However, don't be scared. The harm from X-ray radiation is low and the likelihood of any harmful consequences is extremely low. In addition, modern medicine uses completely safe digital equipment. Also remember that doctors prescribe x-rays only in the most extreme cases, when it is simply impossible to do without it (for dangerous diseases). In all other situations, doctors try to make do with other means (for example, ultrasound) so as not to further injure the child’s body.
How to reduce the negative impact of radiation on a child’s body?
There is no need to specifically remove radiation from the body; after turning off the X-ray machine, there is no radiation left in the body. But doctors recommend that to prevent the consequences of x-rays, children should drink milk and eat raw vegetables and fruits throughout the day.
Children's food should include foods that contain iodine:
- bananas;
- dill;
- parsley;
- fish;
- persimmon.
It is better to avoid heavy foods containing yeast for 1–2 days.
How is the examination carried out?
The progress of the procedure largely depends on the type of X-ray unit and the age of the child. Before the examination, jewelry and other objects that may distort the image are removed from the child. The doctor then places the child on a couch or in front of an x-ray machine in a position comfortable for viewing. After the small patient is in the required position, he is asked not to move or breathe. The picture is taken within a few seconds, and its quality directly depends on the child’s behavior. 5-7 minutes after the completion of the X-ray of the child’s nasopharynx, the parents will receive an image.
What is the price?
Prices in clinics vary greatly in cost. The cost may only include the x-ray procedure itself, or perhaps a doctor’s appointment. In clinics, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, you can get a free service or a service at a low price.
| Name | Price, rub |
| 1. Chest X-ray | 1 066 |
| 2. X-ray of the abdominal cavity | 1 179 |
| 3. X-ray of the skull | 1 086 |
| 4. X-ray of the pelvic bones | 1 415 |
| 5. X-ray of joints | 1 243 |
| Prices are relevant for three regions: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg | |
Is it possible to take x-rays at fever?
Anonymous comments are disabled in this journal. Your IP address will be recorded. Log in No account? Create an account. Remember me. Facebook Twitter Google. Previous Share Flag Next. My son is sick, today is the first day, the temperature is 39 and above, dropping to .4. The pediatrician listened, prescribed treatment, but said it was necessary to rule out pneumonia, that is, take an x-ray. I made an appointment for tomorrow, so I’m thinking about how to take it. In general, what are the precautions for transporting a child at the onset of illness with a high, albeit low, temperature?
Should you dress warmly so as not to get too windy or lightly so as not to sweat? Should I take a canister of fruit juice and Nurofen with me? We go by car to a paid clinic by appointment at an exact time, there should be no queues. In general, I’m a little at a loss, because usually I keep a person with a fever at home, stripped down to his underpants, but then there’s an x-ray, pneumonia, panic, I can’t figure out how best to handle all this. Tags: child illnesses, x-ray. Post a new comment Error Comments allowed for members only Anonymous comments are disabled in this journal.
We will log you in after post We will log you in after post We will log you in after post We will log you in after post We will log you in after post Anonymously. Your reply will be screened Your IP address will be recorded. Post a new comment. Preview comment. Post a new comment 13 comments.
Anonymous comments are disabled in this journal.
Video
About the pros and cons of the procedure, as well as how often you can do an x-ray for a child on the “Doctor Komarovsky” channel.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 1 vote(s), average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article: