The article is under development.
Normally, the interhemispheric fissure has a strictly median position; the width in a newborn of 30-34 weeks of gestation is 2.8 ± 0.2 mm, in older infants it is 2.0 ± 0.1 mm. Separate assessment of the interhemispheric fissure and the falciform process is possible only in cases of fluid accumulation along the fissure and in cases of atrophy of the brain substance.
An arched deformity usually indicates a space-occupying process or fluid accumulation in the intrathecal space on one side. Displacement of the interhemispheric fissure and falciform process without deformation usually indicates hypoplasia of the cerebral hemisphere, which is often combined with changes in the facial skull.
Assessing the size of the various parts of the ventricular system is necessary to exclude ventricular enlargement (ventriculomegaly). The most stable dimensions are the body (depth no more than 4 mm) and its anterior horn (depth 1-2 mm); the occipital horn is often asymmetrical, variable in depth and size; the dimensions of the 3rd ventricle are 2-4 mm. Assessing the 4th ventricle is difficult, so attention is paid to its shape and structure, which can change significantly with abnormalities in brain development.
Using NSG, you can identify the level of occlusion (aqueduct - 60%, foramen of Monroe - 25%, foramina of Luschka and Magendie 10%, subarachnoid space - 5%).
There are:
- Initial signs of expansion of the ventricular system, manifested by an increase in the depth of the bodies of the lateral ventricles to 5-8 mm, the disappearance of lateral curvatures and the appearance of a rounded shape of the lateral ventricles; The 3rd and 4th ventricles are not dilated;
- Moderate ventriculomegaly - body depth up to 9 mm, slight uniform expansion of all parts of the lateral ventricles; The 3rd ventricle is enlarged to 4-6 mm, the 4th ventricle is usually normal;
- Severe ventriculomegaly - the depth of the bodies is more than 9 mm, the 3rd ventricle is dilated - interthalamic fusion in its cavity is visible, the 4th ventricle and the brain cisterns are dilated.
The average size of the cistern magna in a full-term newborn is 4-5 mm; In premature babies, the size of the cistern magna varies depending on the gestational age and can reach 10 mm or more.
The quadrigeminal cistern is usually represented by a hyperechoic line between the 3rd ventricle and the cerebellar vermis, its thickness is no more than 3 mm. It can increase with subarachnoid hemorrhages and with cysts of this cistern, which are difficult to differentiate from an arachnoid cyst in this area.
The dimensions of the cavity of the transparent septum can vary from 2 to 10 mm.
Neurosonography is normal - Protocol
The interhemispheric gap is 1 mm (the norm is up to 4 mm).
Subarachnoid spaces - 2 mm (normal is up to 3 mm).
The cavity of the transparent septum: not expanded.
Anterior horns of the lateral ventricles: on the right - 3 mm; on the left - 3 mm (norm up to 5 mm). Body of the lateral ventricle – on the right – 3 mm; on the left - 3 mm (norm up to 5 mm). Temporal horns are not detectable (normal). Atrium - filled with choroid plexuses (normal up to 12-16 mm). Occipital horns are not detected (normal).
The third ventricle is 2 mm (normal is up to 4 mm).
The fourth ventricle is triangular in shape in the sagittal plane, not dilated (normal is up to 8 mm).
Choroid plexus - 10 mm, with smooth and clear contours.
The brain parenchyma is of medium echogenicity. The pattern of convolutions and grooves is distinct. The echogenicity of the subcortical zones is not changed. Caudothalamic notches are not changed. Periventricular areas have normal echogenicity.
The structures of the posterior cranial fossa are differentiated. Large tank 5 mm (norm up to 12 mm).
Stem structures are of normal echogenicity.
In the CD mode, the arteries of the circle of Willis are determined up to branches of the 4th-5th order, zones of hypo- and hypervascularization are not identified, the course of the vessels is not changed. Indicators of velocities and peripheral resistance in the arteries of the brain are not changed: ACA IR - 0.72 (normal up to 0.72). Venous blood flow is not changed, the maximum speed in the vein of Galen is 7 cm/s (the norm is up to 10 cm/s).
CONCLUSION: The brain parenchyma is not changed. The intrathecal spaces and ventricles are not dilated. Cerebral blood flow parameters are normal.
About the gap between the hemispheres
A gap between the hemispheres must be present, but its dimensions cannot exceed 3 mm. If it is slightly enlarged, then we can talk about the anatomical features of the child’s development.
The disease is indicated by a condition when the interhemispheric fissure is widened and filled with fluid. Often, the baby is diagnosed with diseases such as rickets, hydrocephalus or intracranial pressure. But doctors do not make a diagnosis based on neurosonography; the clinical picture is also important. This condition is also called dilatation. Sometimes the anomaly is detected immediately in the maternity hospital; it also happens that parents detect suspicious symptoms by the 5-6th month of the child’s life.
During the examination of the newborn, the doctor will ask the parents questions such as:
- What is the baby's sleep like, how many hours a day, what are the wakefulness intervals, etc.
- Regurgitation frequency.
- Is the child calm, does he have hysterics that last more than 5 minutes.
- Questions regarding the baby’s reflexes, how he reacts to changes in temperature, flashes of light, loud sounds.
- When a doctor examines a child for the presence of rickets, the disease may be indicated by an enlarged fontanel, a wide forehead and a smooth nape with worn-out hairs.
Neurosonography can reveal abnormalities in brain function, but the results of this study must be correctly deciphered.
The doctor also measures the circumference of the head, which makes it possible to suspect hydrocephalus, the color of the skin, the presence of a marbled pattern, checks the fontanel and eyes for the absence of strabismus or Graefe's syndrome (in which the child's eyes roll up so much that the whites are visible).
NSG cyst - Protocol
The brain structures are formed correctly and asymmetrically. The furrows and convolutions are pronounced. In the projection of the lobe, an anechoic formation is visualized - mm, communicating with the cavity of the lateral ventricle.
The lateral ventricles are asymmetrically dilated. Anterior horns of the lateral ventricles: on the right - 3 mm; on the left - 3 mm (norm up to 5 mm). Body of the lateral ventricle – on the right – 3 mm; on the left - 3 mm (norm up to 5 mm). Temporal horns are not detectable (normal). Atrium - filled with choroid plexuses (normal up to 12-16 mm). Occipital horns are not detected (normal).
Periventricular tissues and areas of the basal ganglia have increased echogenicity.
CONCLUSION: cyst in projection
When to treat?
But often the expansion of the interhemispheric fissure is accompanied by concomitant diseases, in which case medications are prescribed to eliminate this pathology.
So, if there is rickets and the child lives in an area with little sunlight, medications containing vitamin D will be prescribed.
If intracranial pressure is detected, then weak diuretics are prescribed, which promotes the rapid outflow of fluid from the hemispheres. You will also need drugs like Asparkam or Diacarb, which contain potassium, to prevent hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. An indicator of the baby's health will be his good health.
If neurological disorders are present, then you will need to take vascular medications to improve cerebral circulation (Actovegin, Cerakson) and sedatives at night (Bayu-Bai, Sleep Formula, Dormikind).
NSG agenesis of the corpus callosum - Protocol
The structures are not formed correctly. The corpus callosum is absent. The interhemispheric fissure is not widened. The lateral ventricles are dilated: The grooves and convolutions extend fan-shaped from the bodies of the lateral ventricles.
The third ventricle is flask-shaped dilated (mm), pulled upward.
The fourth ventricle is elongated.
Periventricular tissues have normal echogenicity.
The choroid plexuses are deformed and not dilated.
CONCLUSION: agenesis of the corpus callosum. Dilatation of the lateral and 3rd ventricles.
In what cases is urgent consultation with a doctor necessary?
You will need to contact a neurologist soon if your baby has the following symptoms:
- poor sleep;
- if the child is often very excited;
- he is frightened by sharp sounds, which leads to crying or screaming;
- severe fountain vomiting;
- squint or different pupil sizes appeared;
- head circumference increased more than normal;
- protrusion and slow overgrowth of the fontanel;
- eyes bulge or roll back in such a way that only the whites are visible;
- convulsive condition, or regular twitching in the chin, arms or legs;
- the nose often bleeds;
- skin marble pattern;
- with changes in atmospheric pressure the child becomes restless.
In this case, an enlarged interhemispheric fissure in children requires specific treatment.
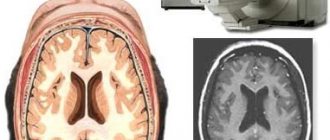
What does an MRI of the brain look like?
A classic example of an MRI scan of the brain is shown in the pictures below. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed in the transverse (or axial - figure below) and longitudinal (or sagittal - figure above) planes.
The study is performed in several modes. The main ones are T1 and T2. Images obtained in these modes are often also called T1-weighted or T2-weighted images. The images shown above were taken in T1 mode.
The main difference between these modes is how liquid and air are displayed in the pictures. In T1 mode, tissues containing a large amount of water have a darker color, while in T2 mode they are bright, light. This is easy to understand by looking at the pictures above - the eyeballs are visualized in the form of light paired rounded formations; on one side they are bright and light, on the other - dark. Therefore, the picture on the right was taken in T1 mode, the picture on the left in T2. There is also a difference in how the gray matter of the brain is displayed in these modes. In T2 mode it is lighter than white matter.
In fact, there are many more modes - FLAIR, DWI, STIR and so on. One mode is used to suppress the signal from fat-rich tissues, another is used to study the distribution density of protons in tissues, and a third is used to evaluate the Brownian motion of water molecules. That is why a full course of MRI diagnostics for doctors lasts more than one month.
What to Expect
According to statistics, 80% of newborns experience neurological disorders, which do not pose a particular threat to health and disappear over time without consequences. But there are incompetent doctors who, without understanding the situation, rush to make a terrible diagnosis.
For example, when the interhemispheric fissure widens, some doctors assure the child’s parents that he has increased intracranial pressure. But these two diagnoses are not always present simultaneously. It is worth understanding that intracranial hypertension is a serious disease that requires special treatment. Therefore, it is impossible to make such a serious diagnosis as ICP based on the detection of expansion of the cerebral hemispheres.
Neurosonography can answer many questions, but not all, and therefore, if the doctor makes a serious diagnosis based on this study, parents should request additional examination of the baby.
Preparation and method of performing neurosonography
This method does not require special preparation. During the procedure, the baby should be well-fed and not thirsty. If the child falls asleep at this time, then this is even welcome, since it is necessary for the head to be motionless.
After an ultrasound of the baby's head is performed, the result will be ready within 2 minutes.
When going for neurosonography, do not forget to take a diaper to put under your baby, as well as a bottle in case the procedure is prolonged. Before going to the NSG, do not lubricate the fontanel site with any creams or ointments, even if there are indications for this. Otherwise, the sensor will have poor contact with the skin and the visualization of the internal image of the brain will deteriorate.
The procedure itself generally resembles a regular ultrasound. First, the baby needs to be placed on the couch, after which the sensor should be lubricated with gel and the neurosonography session should begin.
Ultrasound examination of the brain of newborn children (normal anatomy)
Moscow Compiled by: A. Gurevich, E. Zubareva. Reviewers: Mikhail Ivanovich Pykov - head. Kotlyarov Petr Mikhailovich - head. Purpose: methodological recommendations are intended for ultrasound diagnostic doctors of medical organizations subordinate to the Moscow Department of Health. This document is the property of the Moscow Department of Health and may not be reproduced or distributed without appropriate permission. Ultrasound of the brain neurosonography in children of the first year of life.
.
What do deviations from normal ultrasound readings mean?
Prenatal screening is carried out to assess the anatomical features of the fetus by measuring the main dimensions of the head, abdomen, and limbs. Based on these parameters, the correspondence of the gestational age to the date of the last monthly bleeding is established - this is done to exclude intrauterine growth retardation. Most often, this syndrome occurs in the third trimester and can be caused by:
- harmful habits of the expectant mother;
- diseases of the urinary and respiratory organs;
- arterial hypertension;
- infectious diseases;
- anomalies in the structure of the organs of the reproductive system;
- violations of the monthly bleeding cycle;
- multiple pregnancy;
- low or polyhydramnios;
- gestosis;
- primary infertility;
- complicated course of previous pregnancies;
- premature placental abruption;
- intrauterine infection;
- abnormalities of fetal formation.
If the parameters of the fetal size differ slightly from the norm, this is most likely evidence of the developmental characteristics of a particular baby
When performing an ultrasound scan at a later stage, the doctor examines the structure of the baby’s organs and diagnoses possible congenital developmental pathologies. The reasons contributing to their occurrence are considered to be heredity - defects are transmitted from parents through gene mutations, the teratogenic effects of certain medications, harmful working conditions of parents, previous infectious diseases, ionizing rays, toxic substances, mechanical factors - incorrect position of the child or the presence of tumor-like formations in the mother uterus), maternal injury in the first trimester.
If the head circumference parameters exceed normal values, the doctor evaluates the size of the tummy circumference and the length of the bones of the limbs - not all babies develop proportionally and the head may be larger than the rest of the body. A significant increase in biparietal (distance between the temporal bones) and fronto-occipital dimensions indicates the presence of tumor-like neoplasms in the brain or on the bones of the skull, encephalocele - cranial hernia, hydrocephalus - hydrocephalus.
These anomalies are considered very severe and incompatible with life - premature termination of pregnancy is required. A decrease in BPD and LZR indicates intrauterine growth retardation syndrome and requires corrective measures - the use of drugs that improve uteroplacental circulation and ensure timely delivery of nutrients to the fetus. Otherwise, such defects will lead to the death of the baby.
With a significant decrease in the size of the fetal head, underdevelopment or absence of the cerebral hemispheres (paired formations united by the corpus callosum into the brain) or the cerebellum (the small brain responsible for motor function) may be observed. In this situation, it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy.
Interpretation of fetal ultrasound
During each study, the doctor takes certain measurements, their interpretation allows you to determine the size of the unborn child during its development. To make it more convenient for our readers to understand the examination protocol, we provide a table with the norms of ultrasound indicators:
| Gestation period (by weeks) | Weight (g) | Height (cm) | Heart rate (beats) | LZR (mm) 50th Ave. | BPR (mm) 50 | Coolant (mm) 50 | Exhaust gas (mm) 50 | KTE (mm) 50 | DKG (mm) 50 | DBC (mm) 50 | WPC (mm) 50 | DCP (mm) 50 | TVP (mm) 50 | |
| 10 | 4 | 3,1 | 165 | — | — | — | — | 31 | — | — | — | — | 1,5 | |
| 11 | 7 | 4.1 | 160 | — | 17 | 51 | 63 | 42 | — | 5,6 | — | — | 1,6 | |
| 12 | 14 | 5,4 | 155 | — | 21 | 61 | 71 | 53 | — | 7,3 | — | — | 1,6 | |
| 13 | 23 | 7,4 | 150 | — | 24 | 69 | 84 | 63 | — | 9,4 | — | — | 1,7 | |
| 14 | 43 | 8,7 | 165 | — | 27 | 78 | 97 | 76 | — | 12,4 | — | — | 1,7 | |
| 15 | 70 | 10,1 | — | — | 31 | 90 | 110 | — | — | 16,2 | — | — | — | |
| 16 | 100 | 11,6 | — | 45 | 34 | 102 | 124 | — | 18 | 20 | 18 | 15 | — | |
| 17 | 140 | 13 | — | 50 | 38 | 112 | 135 | — | 21 | 24 | 24 | 18 | — | |
| 18 | 190 | 14,2 | — | 54 | 42 | 124 | 146 | — | 24 | 27 | 27 | 20 | — | |
| 19 | 240 | 15,3 | — | 58 | 45 | 134 | 158 | — | 27 | 30 | 30 | 23 | — | |
| 20 | 300 | 16,4 | — | 62 | 48 | 144 | 170 | — | 30 | 33 | 33 | 26 | — | |
| 21 | 360 | 26,7 | — | 66 | 51 | 157 | 183 | — | 33 | 36 | 35 | 28 | — | |
| 22 | 430 | 27,8 | — | 70 | 54 | 169 | 195 | — | 35 | 39 | 38 | 30 | — | |
| 23 | 500 | 28,9 | — | 74 | 58 | 181 | 207 | — | 38 | 41 | 40 | 33 | — | |
| 24 | 600 | 30 | — | 78 | 61 | 193 | 219 | — | 40 | 44 | 43 | 35 | — | |
| 25 | 660 | 34,6 | — | 81 | 64 | 206 | 232 | — | 42 | 46 | 45 | 37 | — | |
| 26 | 700 | 35,6 | — | 85 | 67 | 217 | 243 | — | 45 | 49 | 47 | 39 | — | |
| 27 | 875 | 36,6 | — | 89 | 70 | 229 | 254 | — | 47 | 51 | 49 | 41 | — | |
| 28 | 1000 | 37,6 | — | 91 | 73 | 241 | 265 | — | 49 | 53 | 51 | 43 | — | |
| 29 | 1105 | 38,6 | — | 94 | 76 | 253 | 275 | — | 51 | 55 | 53 | 44 | — | |
| 30 | 1320 | 39,9 | — | 97 | 78 | 264 | 285 | — | 53 | 57 | 55 | 46 | — | |
| 31 | 1500 | 41,1 | — | 101 | 80 | 274 | 294 | — | 55 | 59 | 55 | 48 | — | |
| 32 | 1700 | 42,4 | — | 104 | 82 | 286 | 304 | — | 56 | 61 | 58 | 49 | — | |
| 33 | 1920 | 43,7 | — | 107 | 84 | 296 | 311 | — | 58 | 63 | 59 | 50 | — | |
| 34 | 2140 | 45 | — | 110 | 86 | 306 | 317 | — | 60 | 65 | 61 | 52 | — | |
| 35 | 2380 | 46,5 | — | 112 | 88 | 315 | 322 | — | 61 | 67 | 62 | 53 | — | |
| 36 | 2620 | 47,4 | — | 114 | 90 | 323 | 326 | — | 62 | 69 | 63 | 54 | — | |
| 37 | 2850 | 48,6 | — | 116 | 92 | 330 | 330 | — | 64 | 71 | 64 | 55 | — | |
| 38 | 3080 | 49,7 | — | 118 | 94 | 336 | 333 | — | 65 | 73 | 65 | 56 | — | |
| 39 | 3290 | 50,7 | — | 119 | 95 | 342 | 335 | — | 66 | 74 | 66 | 57 | — | |
| 40 | 3460 | 51,2 | — | 120 | 96 | 347 | 337 | — | 67 | 75 | 67 | 58 | — | |
Interpretation of abbreviated terms:
- HR – fetal heart rate;
- LZR (fronto-occipital size), BPR (bi-parietal) – dimensions of the head;
- Coolant and exhaust gas – circumference of the head and abdomen;
- KTP – coccygeal-parietal size;
- DC and DB - length of the tibia and femur bones;
- KDP and DKP - the length of the humerus and forearm bones;
- TVP—thickness of the collar space;
- 50th Ave (percentile) – the average value typical for a certain stage of pregnancy.
The table shows average parameters and you need to take into account that your baby may differ from them! Now let's take a closer look at the final data of each of the three mandatory prenatal (antenatal) screenings, which are aimed at identifying the risk of developing pathological processes.
Features of diagnostics of the fetus and uterus
Ultrasound scanning is considered a universal, non-invasive, convenient and safe technique for examining patients. Its essence lies in the analysis of the transformation of mechanical vibrations of structures of various densities above the audible frequency. Ultrasound equipment uses the acoustic impedance of sound waves with a frequency of 2–10 MHz. During pregnancy, the examination does not cause discomfort or pain to either the mother or the baby - it is performed using a special sensor.
Subject to diagnosis:
- anatomical features of the developing baby;
- placenta – “child’s place”;
- umbilical cord - umbilical cord;
- amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus;
- the uterine cavity, its ligamentous apparatus and appendages.
The purpose of ultrasound is to assess the condition of the pregnant woman and the unborn baby, and to diagnose possible congenital and genetic syndromes. This is especially important in cases where there is a special indication - a hereditary predisposition to such anomalies.
Expectant mothers can be completely confident in the safety of ultrasound - ultrasonic waves do not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and cannot provoke a disruption in its development
Interpretation of ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to determine the size of the fetus, the amount of amniotic fluid, the degree of premature aging of the placenta, its integrity and the place of attachment to the uterine wall. Practitioners use the indicators of this examination to choose tactics for managing the gestation period and preparing for the process of expulsion of the fetus.