The luteal gland, located in the ovary, whose main task is to produce the female hormone (progesterone) is called yellow body.
Its distinctive feature is the temporary cycle of life. It begins to develop after ovulation and disappears with the onset of menstruation. If the result is positive, the corpus luteum remains.
What is the corpus luteum
An important stage on the path to pregnancy is ovulation and the corpus luteum. Many people know about the first process that this is the release of a formed egg from the follicle. But what does the second designation mean? What function does it perform?
The temporary rudimentary gland that appears instead of the follicle after the female cell leaves it is called the corpus luteum. Its role is the production of the hormone progesterone, which promotes:
- a decrease in the level of FLH (follicle-stimulating hormone), which does not allow other follicles to mature;
- stimulating the growth of the functional wall of the uterus, preparing it for embryo implantation;
- relaxation of the smooth muscles of the uterus, which prevents the premature expulsion of the fetus from the uterus.
Lack of progesterone makes it difficult for the embryo to implant into the uterus and leads to spontaneous miscarriage, even if the embryo is successfully implanted.
The amount of hormone production depends on the size of the gland - the larger it grows, the more secretion it produces. It reaches its apogee 2 weeks after the cell leaves the ovary. All this time, the egg is in the stage of readiness for fertilization or, already fertilized, is moving towards the uterus. If there was ovulation, but fertilization did not occur, the glandular structure dissolves, and menstruation begins. Once conception occurs, it continues to function and secrete the hormone.
CT scan for ovarian cyst
CT and MRI are fairly accurate methods that allow you to determine the presence of a cyst, suggest whether it is benign or malignant, clarify its size and exact location, etc. In addition, in the case of a malignant cyst, diagnosis using contrast makes it possible to determine whether the tumor has metastasized to other organs and to accurately determine their location.
CT is performed using X-rays, which makes it possible to obtain sections of the organ in increments of approximately 2 mm. The collected and computer-processed sections are assembled into an accurate three-dimensional image. The procedure is absolutely painless, does not require complex preparation (all you need is to adhere to a certain diet for a couple of days before the procedure and, in case of constipation, take a laxative) and lasts no more than 20 minutes.
Given that the slice step is 2 mm, CT can detect formations of 2 mm in cross section or more. These are fairly small cysts and tumors that are at an early stage of development. Such accuracy of CT diagnostics allows you to begin timely treatment and avoid more serious consequences.
Contraindications to the method are pregnancy (due to exposure of the body to X-ray radiation) and allergic reactions to the contrast agent (in the case of CT with contrast). Such allergic reactions are not very common.
How to determine that the corpus luteum has developed
There are two ways to find out about the formation of a temporary gland:
- Laboratory testing - the amount of progesterone in the blood.
- Ultrasound examination - on a small formation on the ovary, which has a heterogeneous structure.
The accuracy of the diagnosis will depend on the experience of the doctor, the sensitivity of the research method, and the location of the gland itself.
What does the absence of a gland mean during an ultrasound examination if ovulation presumably occurred:
- there is no ovulation at all in this cycle or it has not yet occurred;
- a follicular cyst has developed when the grown follicle does not burst, but fills with fluid;
- problems with the development of follicles, there is a risk of impossibility of conception.
When menstruation is delayed, short-term gland can say a lot:
- If there is a corpus luteum, it means that the woman is pregnant, even when the fetus is not yet visible.
- The absence of such formation indicates a pathology of the reproductive system.
- If there is a fetus, there is no temporary gland - there is a risk of miscarriage. In this case, pregnancy can be maintained by taking medications containing progesterone.
What are the luteal phases?
The VT cycle begins during the ovulation period. The luteal gland quickly grows from the walls of the follicle from the moment the mature egg is released. Pregnancy cannot be determined by its presence. In the early stages, conception is confirmed only by hCG analysis; the fertilized egg is not visible on an ultrasound of the ovary.
There are 3 phases of the temporary gland:
- formation + development of vessels for blood supply to VT;
- secretory stage;
- regression (extinction, rebirth into a white body).
Initially, the membrane of the ruptured follicle closes, and the growth of the remaining granulosa cells accelerates. They form a loose tissue. Blood vessels grow abundantly inside the gland. These two phases last 3–4 days.
If an ultrasound does not show the corpus luteum in the right and/or left ovary, this means that the woman has a disrupted ovarian cycle due to gynecological or endocrine diseases.
After reaching a size of 1.5–2.5 cm, progesterone is actively produced within 1.5–2 weeks. The cycle ends on the last day before menstruation. If the egg is fertilized, the secretory stage continues until the 2nd trimester.
Folliculometry
Sometimes a more accurate diagnosis of ovarian activity is required in order to record the moment of ovulation or the growth of the glandular structure. For this purpose, ultrasound monitoring is used, starting from the beginning of the menstrual cycle until the appearance of the formed body. This is called folliculometry.
Repeated ultrasound examinations are necessary in several cases:
- if there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- to determine the exact day of ovulation;
- when stimulating ovulation.
The first ultrasound is usually prescribed on the 10th day of the cycle, and is repeated once a week or every 2-3 days, depending on the tasks. After finding the dominant follicle, the day of ovulation is calculated, then a confirmatory ultrasound is performed in phase 2.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Today, ovarian cysts are quite well diagnosed using a number of tools:
- An examination by a gynecologist, during which the patient’s complaints are clarified, and it is also determined whether the appendages are enlarged and whether there is pain in the lower abdomen.
- Pregnancy test. It is necessary not only to exclude ectopic pregnancy, but also to determine the possibility of performing a computed tomography scan.
- Ultrasound examination, which allows you to quickly and accurately determine the presence of a cyst and monitor the dynamics of its development.
- Laparoscopic examination. Its advantage is that it gives absolutely accurate results and, if necessary, precise and minimally invasive surgery can be performed during the procedure.
- Computed and magnetic resonance tomography.
What size should the corpus luteum be after ovulation?
Normally, the rudimentary gland should be within 1.4–2 cm. At different periods of the cycle, it has different sizes, which indicates the correct functioning of the female body, pathology or pregnancy.
The ratio of size and period is calculated by day:
- 12–15 mm – this is the size of the iron after ovulation (day 14–15 of the cycle) or at the end of the cycle (signals the absence of fertilization);
- 18–24 mm – normal development of the glandular structure 7 days after ovulation (days 21–22 of the cycle). Based on these sizes, it can be judged that ovulation was successful and the body is ready to assume the responsibilities of growing the fetus during fertilization;
- 24–30 mm – the woman is pregnant and the process is proceeding successfully;
- 31–40 mm or more – the presence of a cyst.
Increase in size
If there is a slight increase in the yellow-like structure (up to 3 cm), this does not always indicate pregnancy. To confirm conception, the presence of a fetus and other diagnostic indicators are necessary.
The gland can enlarge up to 6–7 cm, which is an indicator of the presence of a cyst. This does not affect pregnancy, but requires careful monitoring. Sometimes urgent therapy is required, but in most cases it disappears on its own by the end of the term or after the birth of the baby.
Downsizing
The insufficient size of the gland at a certain stage of the cycle means that it will not be able to provide the body with a sufficient amount of progesterone at the right time. This threatens pregnancy failure or fetal death. The formation of the placenta may be disrupted. Then the woman is prescribed hormonal therapy.
A decrease in size towards the end of the cycle is considered normal for a failed pregnancy, since the gland dissolves and then disappears completely.
Ovaries after menopause
Entering the postmenopausal period is defined as the absence of menstruation for one year or more. In Western countries, the average age of menopause is 51–53 years. In postmenopause, the ovaries gradually decrease in size and Graafian follicles stop forming in them; however, follicular cysts may persist for several years after menopause.
On a T2-weighted MR image (left) of a postmenopausal woman, the ovaries appear as dark “clumps” located near the proximal end of the round ligament. On the right, the tomogram also visualizes a hypointense left ovary, devoid of follicles. Although it is slightly larger than expected, overall the ovary appears completely normal. And, only if it is possible to detect an increase in the size of the ovaries compared to the initial study, the differential diagnostic series should first of all include a benign neoplasm, for example, fibroma or fibrothecoma.
Is the corpus luteum always formed?
The presence of this gland often indicates the successful completion of ovulation. But there are situations when a corpus luteum forms in place of the follicle without ovulation. This condition is called luteinization of the follicle. That is, on an ultrasound, the gland is clearly visible, but no egg or free fluid released from the follicle at the time of its rupture is observed.
If there is no corpus luteum after ovulation, this may indicate some kind of disorder in the reproductive organs. Then additional diagnostics are carried out and appropriate treatment for the detected pathology is prescribed. If the disease is not treated, there is a risk of losing the opportunity to bear and give birth to a healthy baby.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst (endometrioma)
Cystic endometriosis (endometrioma) is a type of cyst formed by endometrial tissue growing into the ovary. Endometriomas are found in women of reproductive age and can cause long-term bothersome pain in the pelvic area associated with menstruation. Approximately 75% of patients suffering from endometriosis have ovarian damage. On ultrasound, signs of endometrioma can vary, but in most cases (95%) endometrioma appears as a “classic” homogeneous, hypoechoic cystic formation with the presence of diffuse low-level echogenic areas. Rarely, endometrioma is anechoic, resembling a functional ovarian cyst. In addition, endometriomas can be multilocular and contain septa of varying thickness. In approximately one third of patients, careful examination reveals small echogenic lesions adjacent to the wall, which may be due to the presence of cholesterol accumulations, but may also represent blood clots or debris. It is important to distinguish these lesions from true wall nodules; if they are present, the diagnosis of endometrioma becomes extremely likely.
A transvaginal sonogram visualizes a typical endometrioma with hyperechoic foci in the wall. Doppler ultrasound (not shown) failed to detect blood vessels in these lesions.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst: MRI (right) and CT (left). Computed tomography is used primarily to confirm the cystic nature of the formation. MRI can usually be used to better visualize cysts that are poorly differentiated by ultrasound.
On MRI, hemorrhagic contents within the endometrioma lead to increased signal intensity on T1 WI. On T1WI with fat suppression, endometrioma remains hyperintense in contrast to teratomas, which are also hyperintense on T1WI but hypointense on T1FS. This sequence (T1 FS) should always complement MR imaging because it detects small lesions that are T1 hyperintense.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Radiation diagnostic methods suggest polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also called Stein-Leventhal syndrome, or are used to confirm the diagnosis.
Radiation criteria for PCOS:
- Presence of 10 (or more) simple peripheral cysts
- The characteristic appearance of a “string of pearls”
- Enlarged ovaries (at the same time, in 30% of patients they are not changed in size)
Clinical signs of polycystic ovary syndrome:
- Hirsutism (increased hair growth)
- Obesity
- Fertility disorders
- Acne
- Male pattern hair growth (baldness)
- Or increased androgen levels
What does PCOS look like? On the left, the MRI scan shows a typical “string of pearls” pattern. On the right, in a patient with an increased level of androgens in the blood, an enlarged ovary is visualized, as well as multiple small simple cysts located along the periphery. Obvious is the accompanying obesity. In this patient, MRI can confirm the diagnosis of PCOS.
Corpus luteum cyst
A glandular cyst is a body enlarged several times, which continues to reproduce hormones. The exact causes of this process are unknown, but, according to preliminary data, it can be judged that the ovaries are malfunctioning.
In fact, a cyst is the same benign tumor formed in the place of an unreduced gland. It can persist for 3-4 menstrual cycles or the entire pregnancy. Then, as a rule, it resolves on its own without harming the woman or the fetus.
If a corpus luteum cyst has formed and conception has not occurred, the next ovulation may proceed normally. But observation is still required to avoid complications.
In some cases, twisting, rupture or suppuration of the body occurs. This complication requires surgical intervention.
Appearance of two yellow bodies
It is not normal for two eggs to be released at once. This situation rarely occurs if ovulation has not been artificially stimulated using drugs. Accordingly, if two eggs are released at once, then two glands are formed.
It is quite possible for two corpora lutea to appear in both ovaries at once. If conception does not occur, then both of these formations will decrease in size and turn into scar tissue. If fertilization has occurred (in this case, two eggs), then a multiple pregnancy is diagnosed.
The corpus luteum in the left or right ovary is a temporary gland with hormonal activity. It is formed at the site of the egg, ready for fertilization. Its role is extremely important in the formation of pregnancy, so the absence of the gland does not allow conception to occur. For various pathologies, correction is carried out with medications.
To make an appointment with a specialist and get any clarification regarding the work of the center, you can call + 7 (495) 120-66-43.
Lines are open from 9 am to 9 pm every day, seven days a week. Remember, timely visit to the dentist is the key to a healthy smile and self-confidence. * Date and time will be agreed with you by phone
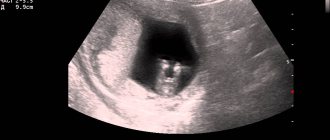
VT on ultrasound
On ultrasound, the corpus luteum is defined as a round, heterogeneous formation. It can also be seen with the research method through the abdominal wall (transabdominal ultrasound technique), but more reliable diagnostic results are obtained with the transvaginal method using an intravaginal sensor. This procedure is painless and may only cause psychological discomfort. What is the result of these gynecological examinations?
If VT is visualized in the ovary on ultrasound, this confirms that ovulation has occurred, but does not mean that pregnancy has occurred. The gland only provides favorable conditions for conception and makes its occurrence possible: progesterone triggers the preparation of the uterine epithelium for the attachment of the embryo. It occurs even in virgins.
You can find a corpus luteum in the right ovary, and this indicates that it was on the right side that the ovary was active in this cycle, and if a corpus luteum formed in the left ovary, this means that the dominant follicle has matured on the left side. The order of ovarian activity is not always sequential; normally, both ovulate, each through a cycle. But it may also be that for several cycles in a row, or even constantly, only one of these paired organs is responsible for ovulation, and then the corpus luteum is formed either on the right or on the left. The location of the active ovary does not affect conception.
If no VT was detected, then most likely there was no ovulation this month. Such an “empty” cycle is called anovulatory. This can be considered the norm during transitional stages of development for the female body: during the period of establishing a cycle in adolescence, after childbirth during lactation, during menopause. In reproductive age, anovulation indicates hormonal disorders and pathologies of the reproductive system.
It also happens that it was not possible to track when the corpus luteum appears, but pregnancy has occurred. This is only possible if the specialist who carried out the diagnostics was inattentive or the device was outdated. Without VT, pregnancy cannot progress: in the absence of hormonal supply, the fetus will die.