Platelet aggregation - what is it?
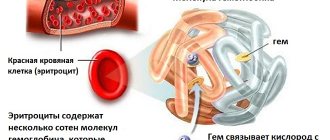
Platelet aggregation is a process in which cells stick together. This forms a plug that closes the wound. At the initial stage, blood cells stick together and later adhere to the walls of the vessel. The result is a blood clot called a thrombus.
Platelets are colorless blood cells involved in the clotting process.
In a healthy body, aggregation is protective: platelets clog the wound and bleeding stops. In some cases, the formation of blood clots is undesirable because they block blood vessels in vital organs and tissues.
- Increased activity of colorless blood cells can lead to stroke and heart attack.
- Decreased platelet production often leads to large blood loss. Frequent bleeding that does not stop for a long time leads to exhaustion and anemia (anemia).
According to statistics, one in 250 people die from thrombosis every year.
In order to prevent the disease, it is necessary to control the level of platelets and their ability to aggregate.
Doctors recommend conducting research when:
- frequent bleeding - uterine, from the nose;
- the appearance of bruises from the slightest injury;
- poorly healing wounds;
- swelling.
Normal indicators
Normally, aggregation is 25–75%. Such indicators indicate good hematopoiesis and sufficient oxygen supply to tissues and organs.
Platelet aggregation - platelets rush to the site of injury, stick together, close the wound and stop bleeding
Platelet norm - table
| Age | Indicator, x 10^9/l |
| Newborn | 100–420 |
| Child under one year old | 160–320 |
| 1–4 years | 150–300 |
| 15–18 years old | 180–340 |
| Men over 18 years old | 180–400 |
| Women over 18 years old | 150–380 |
Aggregation, which is also the body’s independent stopping of bleeding
How does everything happen?
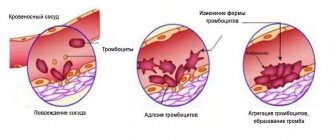
The vessel is clogged in several stages:
- the damaged vessel spasms, slightly reducing blood loss;
- adhesion begins - platelets rush to the damaged area, further reducing the flow of blood from the vessel, as they replace the damaged area of its wall;
- platelets all accumulate and conglomerates are created from them. This is what the aggregation looks like, with which a blood clot begins to form;
- the aggregation process forms a plug of platelets, colloquially called a scar or scab. It is still weakly held, and therefore it should be handled carefully, avoiding mechanical impact, in order to prevent new bleeding;
- thromboplastin fibrin threads makes the plug denser and stronger, compresses it, and then the scab holds better, and blood loss completely stops.
Platelet aggregation is one of the most important stages of stopping bleeding
Stopping bleeding does not end with aggregation, but this is one of its very important stages. However, there is another side to this coin. If aggregation is too high, the presence or absence of damage to the vessels does not matter: platelets will still stick together, creating blood clots. These clots begin to move along with the blood, preventing it from circulating. Soon the vessels become clogged, and the nutrition of the organs is disrupted.
Important! Even the most seemingly small, insignificant spontaneous reaction of this kind can completely clog very important arteries, which sometimes leads to death.
What is the norm?
Normally, aggregation in humans is 25-75%. That is, in his body, blood is produced “as it should”, and each of the tissues receives its own norm of iron and oxygen.
The platelet concentration in a healthy person is around 200-400 cells x 109 per microliter. Also, when examining blood, they use a stopwatch to check how long it takes for large platelet aggregates to form. In healthy blood, this process takes 10-60 seconds.
Platelet aggregation
Platelet Aggregation Test
A blood test allows you to identify deviations from the norm and diagnose pathologies of the hematopoietic and cardiovascular systems. In addition, the procedure is prescribed to monitor the dynamics of a number of diseases and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The analysis is carried out in laboratory conditions. To do this, blood is taken from a vein. Before the study, the patient is recommended:
- follow a diet prepared by a specialist for 1–3 days;
- 8 hours before the procedure, avoid foods high in fat, as well as take medications, including Voltaren gel (if possible);
- 24 hours in advance, avoid the use of immunostimulants, including coffee, alcohol, garlic, and stop smoking.
Only if the recommendations are followed, the analysis is considered reliable. Otherwise, there will be substances in the blood that affect the result.
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Before the procedure, you are allowed to drink only clean, still water.
After collecting venous blood, special substances are added to it - inducers, which in their composition are similar to the cells of the human body, promoting thrombus formation. For this purpose use:
- ADP - adenosine diphosphate;
- ristomycin;
- adrenalin;
- arachidonic acid;
- collagen;
- serotonin.
After collecting venous blood, special substances are added to it - inducers.
The method for determining aggregation is based on transmitting light waves through blood plasma before and after clotting. The nature, shape and speed of the light wave are also taken into account.
It should be noted that the study is not carried out if there is an inflammatory process in the body.
The indicator depends on the substance that was added to the blood and its concentration.
Aggregation rate depending on the inductor - table
| Substance is an inductor | Aggregation level, % |
| ADF | 30,7–77,7 |
| Adrenalin | 35–92,5 |
| Collagen | 46,4–93,1 |
| Ristomycin | 30–60 |
How to determine normality and pathology?
Can a blood test show the platelet aggregation ability of a particular person? After all, to conduct the study, blood is taken from a vein, and from that moment on, the body’s “orders” do not act on the blood cells. This type of analysis is called “in vitro”, a literal translation from Latin “on glass, in a test tube”. Scientists always try to study the reaction in conditions close to the human body. Only data obtained in this way can be considered reliable and used in diagnostics.
The most powerful means for penis enlargement
The guy went a little overboard with the product...
Gain weight
Find out details
dominator.ru
Platelet abilities are determined by induced aggregation. This means that substances that are not foreign to the body in chemical composition and that can cause blood clots are used as an inductor substance. Components of the vascular wall are used as inducers: adenosine diphosphate (ADP), ristocetin (ristomycin), collagen, serotonin, arachidonic acid, adrenaline.
Spontaneous aggregation is determined without inducers.
Quantification techniques are based on passing light waves through platelet-rich blood plasma. The degree of aggregation activity is studied by the difference in the light density of the plasma before the start of coagulation and after obtaining the maximum result. The rate of aggregation in the first minute, the nature and shape of the waves are also determined.
The rate depends on the inductor substance and its concentration.
Platelet aggregation with ADP is usually prescribed and assessed in combination with collagen, ristomycin and adrenaline.
The norm for analysis with ADP is from 30.7 to 77.7%. The amount of platelet aggregation with adrenaline varies from 35 to 92.5%. In a study with collagen, normal values are considered to be from 46.4 to 93.1%.
Types of aggregation
Doctors distinguish several types of aggregation:
- spontaneous - determined without an inductor substance. To determine the aggregation activity of platelets, blood taken from a vein is placed in a test tube, which is placed in a special device, where it is heated to a temperature of 37°C;
- induced - the study is carried out with the addition of inducers to the plasma. Typically, four substances are used: ADP, collagen, epinephrine and ristomycin. The method is used to determine a number of blood diseases;
- moderate - observed during pregnancy. Caused by placental circulation;
- low - occurs in pathologies of the circulatory system. A decrease in platelet levels can lead to various types of bleeding. Observed in women during menstruation;
- increased - leads to increased thrombus formation. This manifests itself in the form of swelling and a feeling of numbness.
Description and role in the human body
After tissue injury, platelets attach to the walls of the damaged vessel. As a result, cells stick together. Over time, fibrin threads, new glued cells and other elements are added to the resulting mass.
Against this background, a blood clot grows, which reaches large sizes, which can lead to blocking of the vessel and stopping the bleeding. The speed of such a process is very important, since the preservation of human life sometimes depends on it.
Blood clotting is influenced by a large number of factors. One of them is aggregation. In the absence of pathological conditions, it performs a protective adaptive function.
Aggregation features consist in the gluing of cells only in the damaged vessel. In this case, the process is considered positive.
However, there are situations where thrombosis is undesirable. For example, if a stroke or myocardial infarction is diagnosed.
This is explained by the fact that the formation of blood clots prevents the normal flow of necessary substances to vital organs.
Platelet hyperaggregation
If the level of aggregation (hyperaggregation) increases, increased thrombus formation occurs. In this condition, the blood moves slowly through the vessels and clots quickly (the norm is up to two minutes).
An increase in aggregation capacity leads to increased blood viscosity and thrombus formation
Herbs for thinning thick blood and strengthening the walls of blood vessels:
Hyperaggregation occurs when:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension - high blood pressure;
- cancer of the kidneys, stomach, blood;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- thrombocytopathy.
Increased levels of aggregation can lead to the following conditions:
- Myocardial infarction is an acute disease of the heart muscle that develops due to insufficient blood supply;
- stroke - cerebrovascular accident;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities.
Ignoring the problem can be fatal.
Treatment methods depend on the complexity of the disease.
Drug therapy
At the initial stage, it is recommended to take medications whose action is aimed at thinning the blood. Regular aspirin is suitable for this purpose. To prevent bleeding, the drug in a protective shell is taken after meals.
The use of special medications will help prevent the formation of new blood clots. All medications are taken only after consultation with the attending physician.
After additional studies, the patient is prescribed:
- anticoagulants - medications that prevent rapid blood clotting;
- novocaine blockade, painkillers;
- drugs that promote vasodilation.
Diet
Patients are recommended to replace protein foods with dairy-vegetable ones. The diet should contain:
- seafood;
- greenery;
- citrus;
- garlic;
- green and red vegetables;
- ginger.
It is very important to maintain a drinking regime, since an insufficient amount of fluid causes vasoconstriction, as a result of which the blood thickens even more. You should consume at least 2–2.5 liters of water per day.
Avoid foods that promote hematopoiesis:
- buckwheat;
- pomegranate;
- chokeberry.
Prohibited products - gallery
Chokeberry Pomegranate Buckwheat
ethnoscience
To treat increased platelet aggregation, non-traditional treatment methods are used. Before using decoctions and infusions, you should consult your doctor, since many medicinal herbs are prohibited for thrombocytosis.
- Sweet clover. Pour 1 tbsp boiling water over a glass. l. ground herbs, leave for 30 minutes. Divide the liquid into 3-4 equal parts and drink throughout the day. The course of therapy is a month. If necessary, repeat treatment.
- Peony. Grind the root and pour 70% alcohol in a proportion of 1 tbsp. l. for 250 ml. Leave in a dark place for 21 days. Take 30 drops before meals 3 times a day for two weeks. Then you need to take a break for a week and repeat the course.
- Green tea. Mix 1 tsp. ginger root and green tea, pour 500 ml of boiling water, add cinnamon on the tip of a knife. Infuse tea for about 15 minutes. You can add lemon for taste. Drink during the day.
- Oranges. It is recommended to drink 100 ml of freshly squeezed orange juice daily. Can be mixed with pumpkin juice in a 1:1 ratio.
Analysis results
In deciphering the test for platelet aggregation, each laboratory must indicate the reference values accepted for this diagnostic method. These are the average indicators that were found during a mass examination of healthy people. They are considered the norm.
Normal for children and adults
If there are age-related differences in the number of platelets in the blood (children have fewer of them), then for the ability to aggregate, uniform standards have been established:
- in seconds – from zero to 50 (the result may vary with different blood temperatures and research methods in a particular laboratory);
- as a percentage for spontaneous – 25 – 75;
- stimulated by ADP at a concentration of 5 µmol/ml - 60 - 89%, and at 0.5 µmol/ml - 1.4 - 4.2%.
Increased platelet aggregation
A tendency to accelerated platelet aggregation is observed in the following diseases:
- coronary heart disease (angina, heart attack);
- circulatory disorders in the peripheral arteries of the lower extremities (obliterating atherosclerosis);
- thromboangiitis;
- venous thrombosis;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- diabetes;
- congenital disorders of platelet structure;
- excessive cell formation;
- autoimmune diseases;
- DIC syndrome in shock, severe toxicosis of pregnancy, placental abruption, amniotic fluid embolism, cesarean section;
- tumor processes in the body.
Smoking, high cholesterol and blood sugar levels, hypertension, and stress factors can stimulate platelet aggregation. Antiplatelet agents are prescribed for treatment - Cardiomagnil, Clopidogrel, Curantil, Ipaton, Ilomedin, Agrenox, Brilinta.
Reasons for decreased
Weak spontaneous and stimulated aggregation is observed when:
- anemia;
- acute leukemia;
- renal failure;
- overdose of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents;
- liver cirrhosis;
- diffuse glomerulonephritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- angiomas;
- radiation sickness.
Congenital thrombocytopathies are accompanied by a change in the ability to aggregate (Glanzman, Pearson, May), release of cell “gluing” factors (aspirin-like syndrome), lack of storage of granules (“gray platelets”, Herzmansky syndrome), as well as various defects in heart defects, Marfan syndrome, Viskotta.
These conditions are characterized by increased bleeding, and radical elimination is not possible. Therefore, with reduced aggregation, the following diet is prescribed:
- lifelong ban on drinking alcohol, using vinegar (including canned vinegar);
- inclusion in the daily menu of products with vitamins A (beef or chicken liver, fish, sweet peppers), C (rose hips, black currants), P (cherries, chokeberries), peanuts;
- limiting seasonings, especially ginger, turmeric, fenugreek.
For drug therapy of congenital and acquired thrombocytopathies, Dicinone, Aminocaproic acid, and Calcium gluconate are used. A course of ATP, Riboxin and folic acid is prescribed 2 - 4 times a year. During breaks, herbal teas with hemostatic herbs are recommended - nettle, raspberry leaves, shepherd's purse, knotweed, yarrow.
And here is more about hereditary thrombophilia.
The platelet aggregation test shows their ability to join together to form blood clots. Prescribed to patients before surgery, during pregnancy, as well as when prescribing treatment for thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Spontaneous and stimulated aggregation is studied. This helps to correctly diagnose and carry out therapy.
If the result is elevated, then antiplatelet agents are prescribed; if aggregation is reduced, hemostatic agents are indicated.
Increased aggregation is a marker of hyperaggregation syndrome and thrombophilia. The most commonly used are the Born turbidimetric method, based on recording changes in the light transmission of platelet-rich plasma, and the method for studying platelet aggregation, based on the analysis of light transmission fluctuations caused by a random change in the number of particles in the optical channel.
Material for research.
Citrate platelet rich plasma
Research method
is determined by the operating procedure on a particular type of aggregometer.
Solutions of ADP, ristocetin, collagen, adrenaline, and arachidonic acid are most often used as inducers. Solutions of thrombin, serotonin, etc. can also be used.
Platelet hypoaggregation
A reduced level of aggregation is no less dangerous for the health and life of the patient. Insufficient platelet aggregation (hypoaggregation) causes poor blood clotting (thrombocytopenia). As a result, the formation of clots (thrombi) does not occur, which leads to severe bleeding.
Doctors distinguish between hereditary and acquired platelet hypoaggregation.
According to WHO, the disease affects about 10% of the world's population.
Low aggregation ability is activated by a viral or bacterial infection, physiotherapy, or taking medications.
Hypoaggregation occurs when:
- renal failure;
- chronic leukemia - a malignant disease of the circulatory system;
- decreased thyroid function;
- anemia (anemia).
Diet
Nutrition is an important factor in normalizing platelet levels. The diet should contain foods that promote hematopoiesis:
- buckwheat;
- fish;
- red meat - prepared in any way;
- beef liver;
- cheese;
- eggs;
- greenery;
- salads with carrots, nettles, bell peppers, beets;
- pomegranates, bananas, rowan berries, rosehip juice.
In this case, you should reduce or completely eliminate the consumption of ginger, citrus fruits, and garlic.
Traditional treatment
In advanced cases, treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting. The patient is prescribed:
- Aminocaproic acid solution 5% intravenously.
- Sodium adenosine triphosphate intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
- Preparations: Emosint, Dicynone, Tranexamic acid.
In case of severe bleeding, a transfusion of donor platelet mass is performed.
Patients should avoid taking medications that thin the blood:
- Troxevasin;
- Aspirin;
- Paracetamol;
- Ibuprofen;
- Eufillin;
- Antidepressants.
Drugs for the treatment of hypoaggregation - gallery
Tranexamic acid Dicynone Adenosine triphosphate Aminocaproic acid solution 5%
Unconventional treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are used as an adjuvant, since it is impossible to raise the platelet count only with the help of medicinal herbs.
- Nettle. Grind 1 tbsp. l. plants, pour a glass of boiling water and put on low heat for 10 minutes. Cool the liquid and filter. Take before every meal. The course is one month.
- Beetroot juice. Grate raw beets, add 1 tbsp. l. granulated sugar. Leave the paste overnight. In the morning, squeeze the juice and drink before breakfast. Duration of treatment: 2–3 weeks.
- Sesame oil. Used for both treatment and prevention. Take 3-4 times a day after meals.
What research is being conducted?
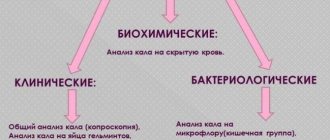
The platelet aggregation analyzer is a complete blood count. However, there are other studies that provide more accurate results. The main methods include the following tests:
- according to Sukharev;
- according to Lee-White;
- coagulogram.
Their essence lies in the fact that special substances are added to the blood that inhibit aggregation.
These components are similar to substances contained in the human body, which provoke blood clots. Such components are called inductors.
Preparing for analysis
Before performing the analysis, it is necessary to undergo certain preparation. For the results to be as accurate as possible, the blood fluid should not contain substances that could have a negative effect on it.
- A week before the analysis, some aspirin medications are excluded, since their use suppresses thrombus formation. If it is not possible to cancel these medications, the laboratory technician conducting the study should be notified.
- You must stop eating food for 12 hours. Products, especially those with high fat content, also negatively affect the results.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress.
- During the day, do not take alcoholic drinks, coffee, garlic, or smoke.
The analysis is postponed if there is an active inflammatory process.
Carrying out
Blood sampling is carried out in the morning, between 7 and 10 o'clock. The study can only be carried out on an empty stomach. It is allowed to drink still water.
Features during pregnancy
The level of aggregation during pregnancy is of great importance. The fact is that disruption of this process leads to serious consequences.
The norm during pregnancy is considered to be 150–380 x 10^9/l.
A slight increase in the indicator is associated with placental blood circulation and is considered normal. The upper threshold should not exceed 400 x 10^9/l.
The normal level of aggregation with the addition of any inductor is 30–60%.
Hyperaggregation
Platelet hyperaggregation is dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the baby, as it can cause miscarriage or spontaneous abortion in the early stages. Doctors name the main reasons for increased platelet aggregation during pregnancy:
- dehydration of the body as a result of vomiting, frequent bowel movements, insufficient drinking regimen;
- diseases that can provoke a secondary increase in platelet levels.
Pregnant women must undergo a medical examination and undergo regular tests. Only in this way can a deviation from the norm be noticed in time and appropriate measures taken.
With a moderate increase in the level of coagulation, it is recommended to adjust the diet. You should consume foods that thin your blood plasma. These are flaxseed and olive oils, onions, tomato juice. The diet should include magnesium-containing foods:
- chicken eggs;
- milk;
- legumes;
- cereals: oatmeal, buckwheat, barley.
If the diet does not bring results, drug treatment is prescribed.
Platelet standards in blood tests at different stages of pregnancy:
Hypoaggregation
A decrease in aggregation capacity is no less dangerous for the health of a pregnant woman and the fetus than hyperaggregation. In this condition, the vessels become fragile, bruises appear on the body, and the gums begin to bleed. This occurs due to a violation of the qualitative composition of blood cells or their insufficient production. Hypoaggregation can cause uterine bleeding during and after childbirth.
A decrease in platelet levels is provoked by the following factors:
- taking medications - diuretics, antibacterials;
- autoimmune and endocrine diseases;
- allergy;
- severe toxicosis;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of vitamins B12 and C.
To improve the synthesis of blood cells, a woman is recommended to consume foods rich in vitamins B and C:
- black currant;
- apples;
- Bell pepper;
- cabbage;
- lemons;
- rosehip tincture.
The doctor prescribes special medications that have a beneficial effect on the hematopoietic system without having a negative effect on the baby.
To avoid the negative consequences and risks associated with hyper- or hypoaggregation, doctors recommend conducting a study on platelet aggregation ability even when planning pregnancy.
How to understand the results?
An assay using three common inducers and adding new ones if required is done if one clotting factor predominates over the others. For diagnosis, the detected altered norm with one inductor in the absence of movement with the others is important. And the results are assessed by a specialist.
Here are the factors that can trigger a drop in aggregation:
- success of antiplatelet treatment;
- thrombocytopathy.
What can thrombocytopathy do?
This type of disease can be inherited from parents or acquired after suffering from certain diseases. According to statistics, every tenth person has this. What is common to such diseases is the presence of a connection with the ability of platelets to accumulate certain substances.
Because of this, the bleeding does not stop and blood clots do not form. This is fraught with the fact that the slightest scratch can cause severe external bleeding, and a bruise can lead to internal bleeding.
Thrombocytopathy is a serious disease characterized by decreased platelet aggregation
This is already noticeable in a child: such children often have bleeding gums, bleeding from the nose, bruises appear on the body from the slightest slap, and as soon as the child hits something with his knee or elbow, the place swells. Teenage girls suffering from this pathology have protracted periods, and a lot of blood is lost during them. As a result, anemia develops.
Important! All this may not appear until a person becomes ill with an infection caused by microorganisms, takes certain medications, or attends certain physical procedures.
Secondary thrombocytopathies
Symptomatic, or secondary, thrombocytopathies are formed due to the following pathologies:
- chronic leukemia;
- multiple myeloma;
- pernicious anemia;
- the last stage of development of uremia;
- thyroid dysfunction.
If a patient's bleeding is too severe during surgery, the surgeon can be sure that he has thrombocytopathy.
With thrombocytopathy, it is extremely difficult to stop bleeding
Aggregation also becomes higher in the following cases:
- widespread vascular atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- rupture of internal organs;
- thrombosis of arteries in the abdominal cavity;
- stroke;
- diabetes.
Features in children
Despite the fact that increased aggregation capacity is usually found in the adult population, recently there has been an increase in cases of the disease in children.
Hyperaggregation can be either hereditary or acquired. The causes of elevated platelet levels are not much different in adults. Mainly:
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- infectious and viral diseases;
- surgical intervention.
- In children under one year of age, hyperaggregation can be caused by dehydration and anemia. In adolescence, stressful situations and physiological growth of the body play an important role.
- Hypoaggregation in children manifests itself in the form of nosebleeds and bruises. Girls in adolescence may experience heavy periods. In 100% of cases, pinpoint rashes are observed on the skin, and 20% of children experience bleeding gums.
Treatment begins with finding out the cause of the deviation from the norm in platelet aggregation ability. Sometimes adjusting your diet and drinking regime is enough. In some cases, treatment of the disease that caused the abnormality is required.
Platelets in child tests:
If necessary, a hematologist will conduct an additional examination and prescribe medication according to the patient’s age and severity of the disease.
Indications for testing
A platelet aggregation test is not considered mandatory during a preventive examination in a medical facility. Such laboratory examination is recommended in the following cases:
- problems with blood clotting;
- predisposition to the appearance of blood clots;
- complaints of severe swelling, which is present on an ongoing basis;
- bleeding gums;
- thrombocytopenia or thrombophilia;
- high risks of hemorrhage;
- long wound healing process;
- complicated pregnancy;
- 1st trimester of gestation;
- IHD;
- presence in the medical history of autoimmune diseases;
- taking antiplatelet agents for therapeutic purposes - the indication is to monitor the effectiveness of therapy;
- phlebeurysm;
- pathological situations in which RFMC is increased;
- preparation for surgery;
- inability to conceive a child for a long time;
- previous unsuccessful artificial insemination procedures;
- prescription of hormonal contraceptives;
- von Willebrand disease;
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome;
- Glanzmann's thrombasthenia;
- the appearance of bruises even with minor impact on the skin.